Hypnosis in Sports Performance and Rehabilitation
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Hypnosis
Procedure involving focused attention and relaxation.
Franz Mesmer
Pioneer of hypnosis in the 1770s.

James Braid
Coined the term 'hypnosis' in 1840.
Clark Hull
Conducted first systematic hypnosis research in 1930s.
Hypnotizability
Measurable susceptibility to hypnosis effects.
Stanford Scale
Measures hypnotizability with a score up to 70.
Harvard Scale
Another method to assess hypnotizability.
Post-hypnotic amnesia
Inability to recall events after hypnosis.
Post-hypnotic suggestions
Instructions given during hypnosis affecting future behavior.
Illusions
Altered perception of reality during hypnosis.
Hallucinations
Perception without external stimuli during hypnosis.
Anxiety reduction
Moderate effect size (0.79) in reducing anxiety.
Medical procedures
Hypnosis aids in anesthesia and recovery post-surgery.
Pain relief
Strong evidence supporting hypnosis for pain management.
Effect size
Quantitative measure of hypnosis effectiveness.
Meta-analysis
Statistical analysis combining results from multiple studies.
Complementary medicine
Hypnosis categorized under alternative health practices.
Role playing
Hypothesis for why hypnosis may work.
Special state
Hypothesis suggesting hypnosis induces a unique mental state.
Kosslyn study
PET scan research on brain activity during hypnosis.
Cyna et al. study
Research on hypnosis in pregnancy and anesthesia.
Palsson et al. study
Investigated hypnosis effectiveness in clinical settings.
Honda et al. study
Survey on complementary medicine usage in the US.
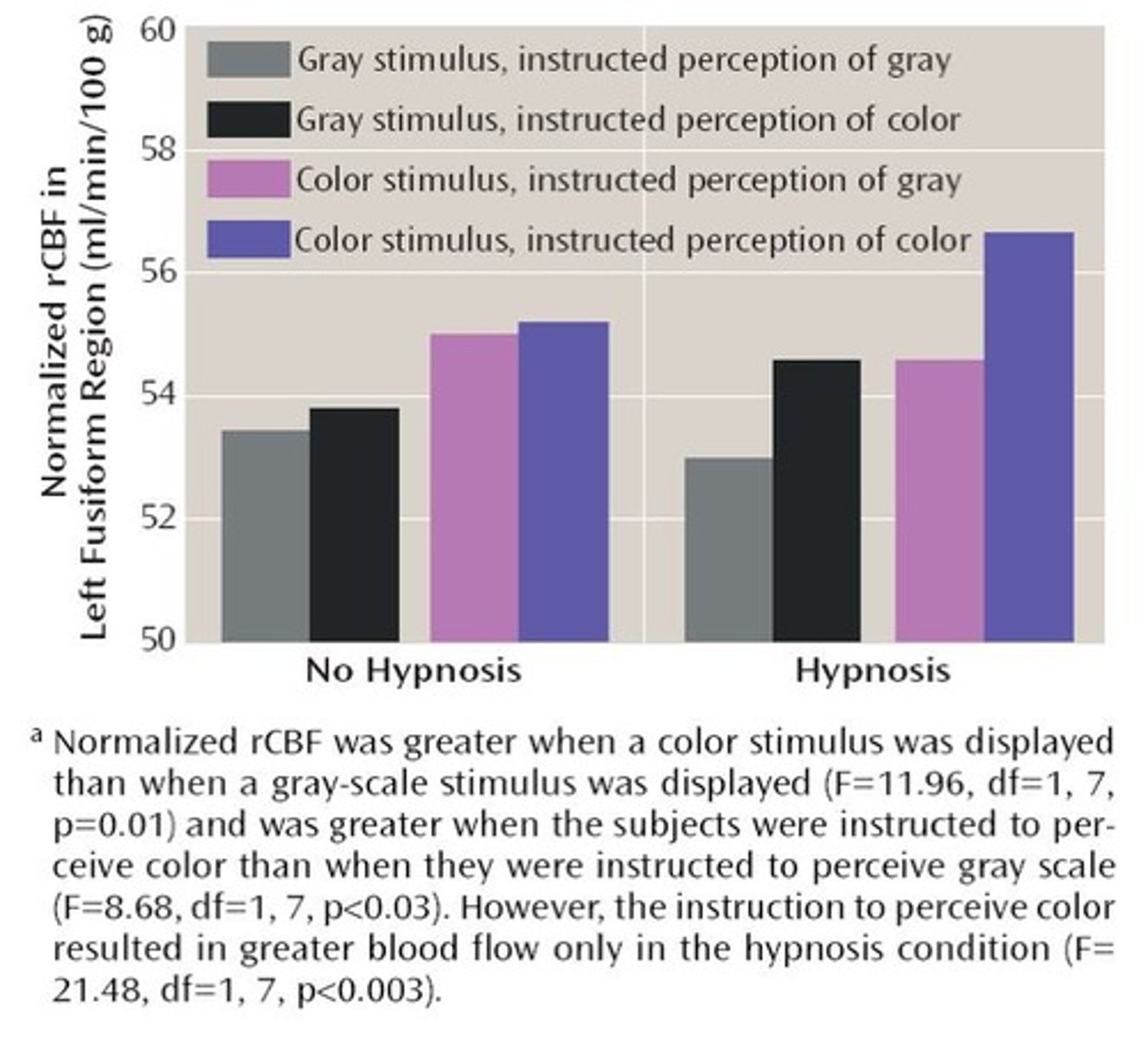
Left Fusiform Cortex
Region involved in color perception.
Hypnosis
Altered state of consciousness affecting perception.
Cerebral Blood Flow
Blood flow changes during hypnosis affecting perception.
Higher-Order Cognition
Complex mental processes influenced by hypnosis.
Pain Perception
Hypnosis can reduce pain sensitivity.
Anxiety Reduction
Hypnosis helps alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Imagery Ability
Enhanced visualization skills through hypnosis.
Self-Confidence
Increased belief in one's abilities via hypnosis.
Exercise Motivation
Hypnosis boosts motivation for physical activity.
Physiological Responses
Hypnosis alters body's reactions to exercise.
Autogenic Training (AT)
Self-hypnosis technique focusing on relaxation.
Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Neurological disorder affecting movement and coordination.
RCT
Randomized Controlled Trial for research validity.
Physical Therapy (PT)
Rehabilitation method improving movement and function.
Tremor Reduction
Hypnosis may decrease tremors in PD patients.
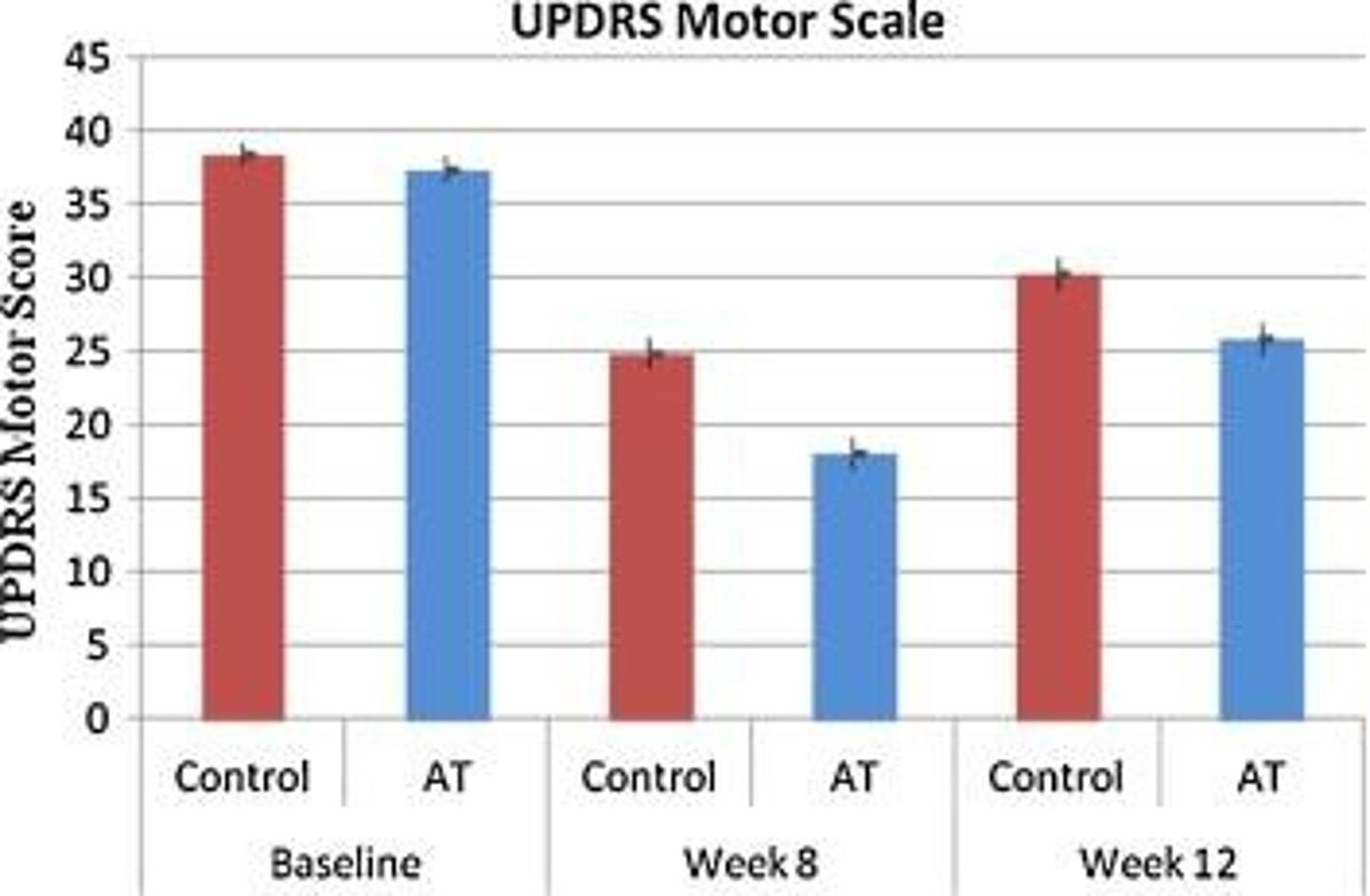
Clinical Improvements
Significant enhancements in movement and rigidity.
Ego Strengthening
Hypnotic suggestion enhancing self-esteem and resilience.
Soccer Skill Performance
Hypnosis improves accuracy in soccer volleys.
Controlled Studies
Research with strict protocols for reliable results.
Chipping and Putting
Golf skills positively affected by hypnosis.
Shooting Accuracy
Improvement in basketball and soccer shooting through hypnosis.
Experimental Evidence
Research supporting hypnosis effects on performance.
A-B-A-B Design
Research method alternating conditions to assess effects.
Hypnosis
A state of focused attention and heightened suggestibility.
Hypnotizability
Individual's susceptibility to hypnosis effects.
Verbal encouragement
Positive reinforcement to enhance performance.
Jump height improvement
0.58 cm increase from verbal encouragement.
Motor cortex activation
Increased brain activity during hypnosis imagery.
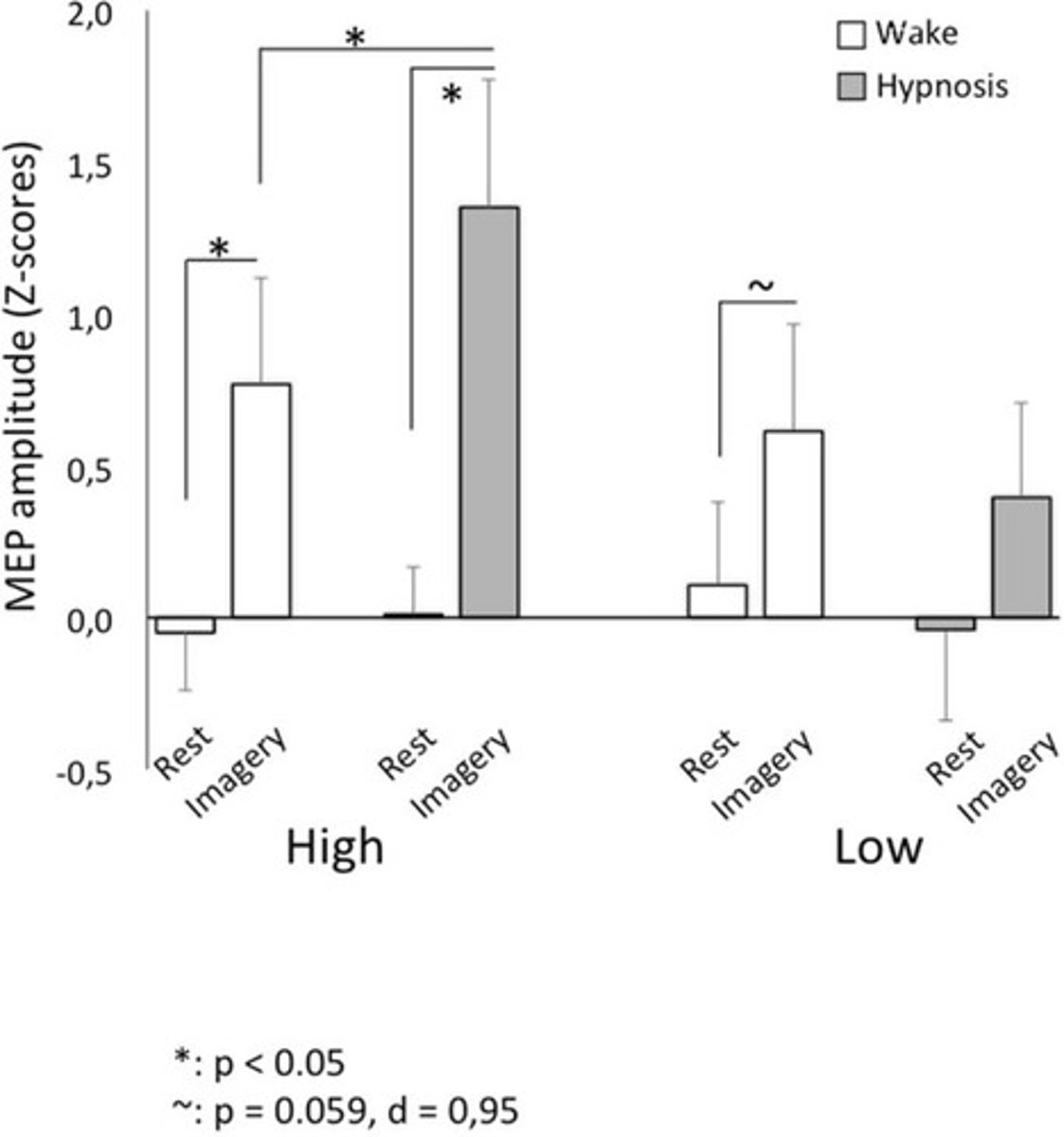
Transcranial stimulation
Technique to measure motor cortex activation.
Exercise-induced asthma (EIA)
Asthma triggered by physical activity.
Forced expiratory volume (FEV1)
Measurement of lung function during breathing.
Cortisol
Hormone released in response to stress.
Heart rate increase
Physiological response to hypnosis and suggestion.
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
Imaging technique to measure brain blood flow.
Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
Brain region activated during increased exercise suggestion.
Insular cortex
Brain area involved in emotional and physiological responses.
Thalamus
Brain region relaying sensory information.
Ergogenic effects
Performance-enhancing effects from hypnosis.
Physiological responses
Body's reactions to hypnosis and exercise suggestions.
Small significant improvement
Consistent minor enhancements in performance metrics.
Hypnosis in sports medicine
Underutilized technique by professionals in sports.
Hypnosis and anxiety reduction
Hypnosis can significantly lower anxiety levels.
Hypnosis for pain management
Effective in providing large pain reductions.
Clear, intense suggestions
More effective for performance improvement in hypnosis.
Beginner performance enhancement
Larger effects of hypnosis for less experienced individuals.
Independent replication
Necessary to confirm hypnosis effectiveness in studies.