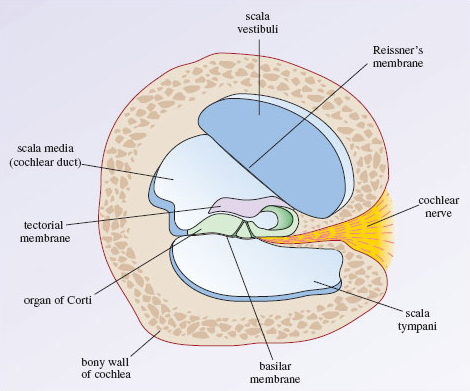
osseous and membranous cochlea
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
parts of the inner ear
cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals
subdivisions of the inner ear
osseous labyrinth and membranous labyrinth
cochlea is more posterior/anterior than the other inner ear parts
anterior
are the semicircular canals anterior/posterior to inner ear structures
posterior
shape of cochlea, length, # of turns, # of chambers
cone shape, 35 mm long, 2.5-2.75 turns, 3 chambers
what are the 3 chambers of the cochlea
scala vestibuli, scala tympani and scala media
the base of the cochlea is ___ and the apex is ___
base is wide, apex is narrow
osseous labyrinth houses what
scala tympani and scala vestibuli
what fluid fills the osseous labyrinth
perilymph (similar to CSF)
how do the scala tympani and vestibuli communicate?
helicotrema
core of the cochlea
modiolus
what combines in the modiolus?
the auditory nerve fibers from the organ of corti
what surrounds the modiolus
osseous spiral lamina
what is the osseous spiral lamina?
bony shelf-like structure wrapping around modiolus, BM attached to it
which end of cochlea is better for high frequency sounds
base, wider
which end of the cochlea is better for low frequency?
apex, narrow
diagram of bony and membranous labyrinth
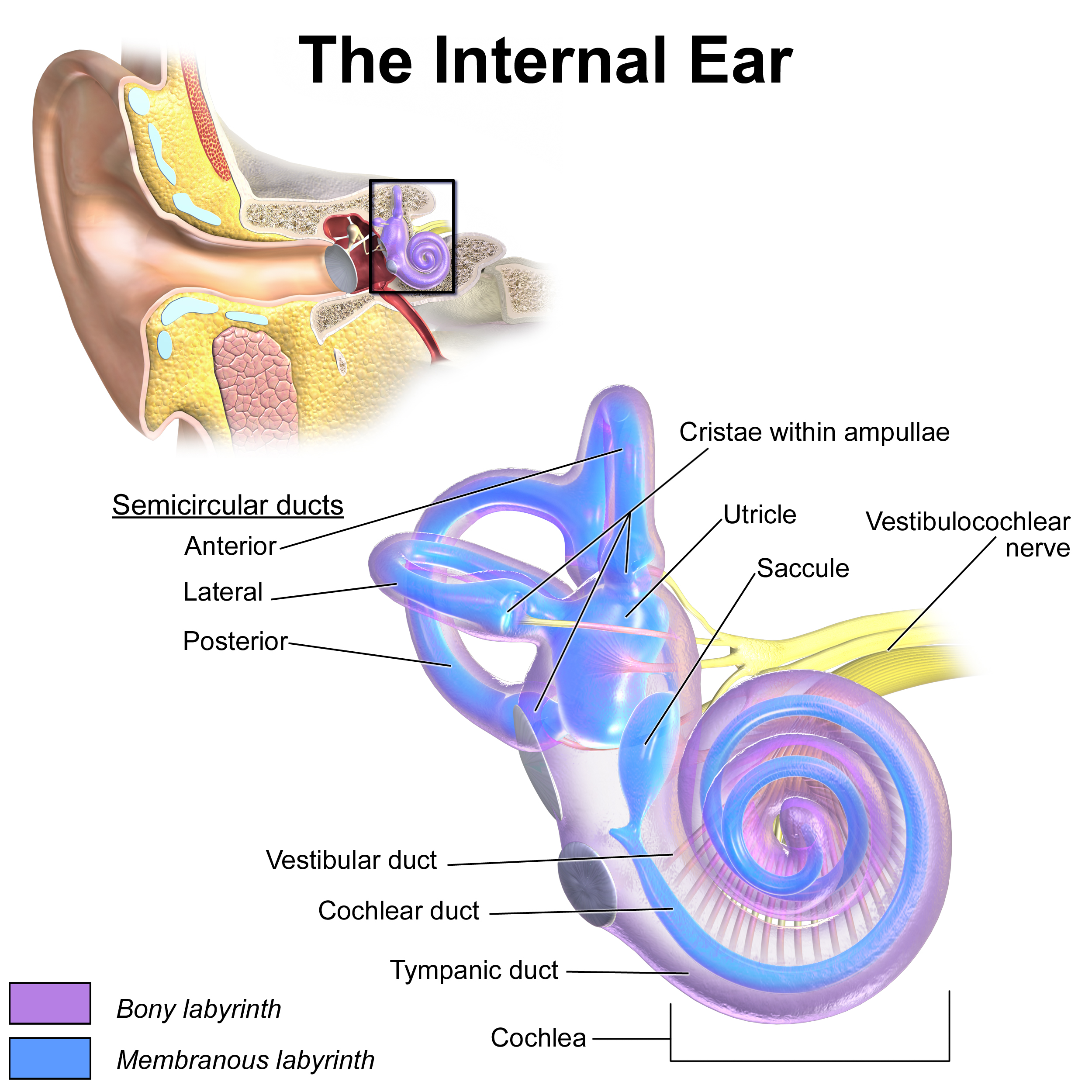
purple = perilymph
blue = endolymph
what does the membranous labyrinth house?
scala media
what does the scala media house?
organ of corti, inner and outer hair cells, supporting cells and tectorial membrane
what are the walls of the scala media
reissner’s membrance (roof), basilar membrane (floor), spiral ligament (lateral), stria vascularis
reissner’s membrane
roof of scala media, connects to the spiral limbus and spiral ligament
basilar membrane
floor of scala media, connects to osseous spiral lamina and spiral ligament
spiral ligament
lateral wall of scala media
stria vascularis
attaches to spiral ligament and produced endolymph
three chambers of cochlea and fluids within
scala vestibuli = perilymph
scala media = endolymph
organ of corti = cortilymph
scala tympani = perilymph
describe perilymph
low potassium (K+), high sodium (Na+), neutral at 0 mV
similar to CSF
describe endolymph
high potassium (K+), low sodium (Na+), positive at 80 mV
describe cortilymph
Organi of corti. low potassium (K+), high sodium (Na+), similar to perilymph
meniere’s disease
inner ear disorder with no known cause, but overproduction of endolymph is common - causes balance issues and damage to structures
perilymph fistula
abnormal communication between fluids - inner ear fluid leaking to middle ear at oval window
diagram of cochlea