Project managment strategies and product life cycle
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Critical path analysis (CPA)
product management method used to schedule efficient completion of process stages.
CPA - analysis of the stages in a project to ensure time-efficient completion
CPA ADV, DISADV
ADV
unecessary waiting time is identified
parallel processing opportunities can then be exploited for max efficiency
resource planning efficiency is improved
DIS ADV
impossible to accurately to represent highly complex activities
External factors may change and require management
it relies on possibly inaccurate estimates of activity durations
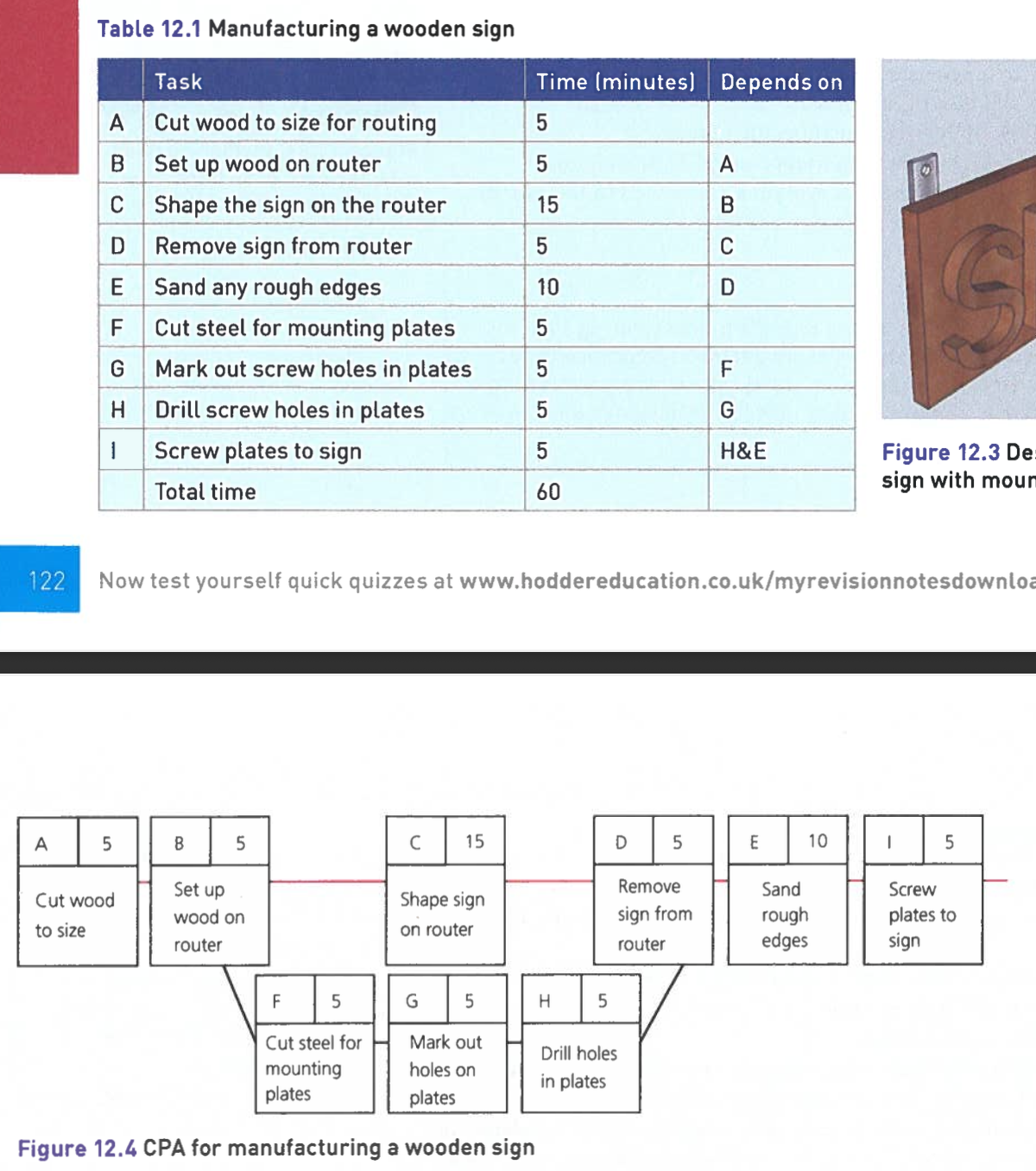
CPA for manufacturing a wooden sign
Scrum (agile manufacturing)
Scrum is a teamwork based flexible, holistic product development stage where you tackle a big project in short bursts (sprints), meet daily to adapt quickly, and constantly improve based on feedback.
Scrum Setup
product owner → scrum master/project leader/project manager → developers/development team/designers
scrum ADV, DISADV

Six Sigma system
main goal - To improve the output quality of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects. (short time scale)
five key value targets of Six Sigma
Reduction of defects
Reduction of process cycle time by removal of unnecessary stages and minimisation of errors
Reduction of pollution.
Reduction of costs by redesigning, simplifying and standarising components
Increased profit.
DMAIC
The five phases of a Six Sigma project:
Define
Measure
Analyze
Improve
Control
DEFINE Phase
To define the issue, set the project's scope and key goals, and dictate the skills needed for the team.
MEASURE Phase
The extent of the issue is measured. Decision points are identified, and customer-focused factors (quality, cost, schedule) are assessed.
ANALYZE Phase
It concentrates on analyzing where the measured issues occur and how value can be added for the customer.
IMPROVE Phase
Rectification procedures are introduced. This can include Poka-yoke (error-proofing) or conducting pilot runs to optimize the process.
CONTROL Phase
To control the new procedures by embedding them, monitoring quality, checking financial returns, and keeping records for future cycles.
Poka-yoke
A method for making it impossible to carry out a process incorrectly (error-proofing).
What three things are needed for a Six Sigma project to succeed?
Fully committed management support.
Provision of sufficient resources.
Access to detailed statistics and data.
Six Sigma ADV, DISADV

Product life cycle (PLC)
The introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and replacement cycle of products.
main goal of planning and monitoring a Product Life Cycle (PLC)?
To maximize sales from a product's introduction to its withdrawal.
"Introduction" stage of the PLC?
product first enters the market
Low sales and small profits.
Large investment.
Large expenditure on marketing.
"Growth" stage of the PLC?
development stage of a product becoming more popular
Market share grows.
Profitability improves.
"Maturity" stage?
the stage where sales of a product are at their greatest
Most potential customers already own the product.
It is the point of maximum profitability.
Companies must plan ahead for a replacement.
"Decline/Removal" stage?
when a product becomes less popular, no longer viable to sell
Profits fall with reduced sales.
Further production is no longer viable (profitable).
purpose of the "Extension/Replacement" stage?
To introduce upgrades or new models to extend the product's life and boost sales again.
What is "Demand Pull"?
When product designers respond to consumer demand for new features (e.g., consumers wanting a better phone camera).
What is "Technology Push"?
When a company's research and development (R&D) leads to new ideas that they must then convince consumers to buy (e.g., the failed launch of Google Glass).
What is the common confusion around the term "Product Life Cycle"?
It is often confused with a product's environmental life cycle (sustainability and recycling), but in business, it refers to its sales cycle in the market.