Neuromuscular disorders - lec 4
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
A sense of heaviness or “deadness” is known as _____
numbness
An abnormal sensation of burning, tingling, pins and needles is known as ______
paresthesia
A disturbance in the function of a nerve is known as _____
neuropathy
Pain/paresthesia/numbness along the distribution of a dermatome (referred pain) is known as _____
radiculopathy
A disturbance in the distribution of a nerve plexus, either distal to the spinal roots or proximal to the formation of the peripheral nerves, is known as ______
plexopathy
Primary muscle disorder is known as ______
myopathy
What ways do nerves respond to injury?
damage at axon, disruption of axon and/or myelin sheath (trauma), degeneration of axon and breakdown of myelin sheath (metabolic/toxic)
A complete absence of strength / total paralysis is called _____
-plegia
total paralysis in both limbs, one side of the body is known as ____
hemiplegia
total paralysis in both legs is known as ______
paraplegia
total paralysis in all four limbs is known as _____
quadriplegia
A less severe weakness / incomplete paralysis is known as _____
paresis
What would an abrupt onset of sx suggest?
vascular dz like stroke, toxic or metabolic disturbances
What would a subacute onset of sx over days to weeks suggest?
neoplastic, infectious or inflammatory causes
What would a slow onset of sx over mos-yrs suggest?
hereditary, degenerative, endocrine, or neoplastic
An episodic progression of sx may suggest _____
vascular or inflammatory origin
Steadily progressive sx suggests ____
neoplastic disorder or motor degenerative conditions
A rapid fluctuation of sx over short periods of time is characteristic of what condition?
myasthenia gravis
What should be ruled out if spinal cord pain is worse at night?
malignancy; order urgent CT or MRI
What should be ruled out w/ a hx of trauma?
fracture; start w/ plain films
what should be ruled out w/ bowel or bladder incontinence?
cauda equina syndrome; order urgent MRI
What are the most common causes of total spinal cord transection?
MVA (MC), falls, violence, sports accidents
What condition?
immediate flaccid paralysis & loss of sensation below the level of injury
spinal shock → loss of reflex activity; hypotension d/t unopposed vagal tone
flaccid areflexia, hrs-wks, eventually recover as hyperreflexia
priapism may be present
total spinal cord transection (spinal cord cut)
What imaging should be ordered for total spinal cord transection?
CT & MRI
How are total spinal cord transections managed?
ICU
immediate immobilization and surgical fixation
methylprednisolone → don’t use if penetrating or multi system trauma, or mod-severe TBI
painful spasms → Baclofen, benzodiazepine
What are possible complications w/ total spinal cord transections?
CV → neurogenic shock
Resp → resp failure, pulm edema, PNA
DVT/PE → all pts should get prophylactic tx
other → pressure sores, stress ulcer, paralytic ileus, temp control, inadequate nutrition
What is neurogenic shock?
part of spinal shock; distributive shock resulting in low BP occasionally w/ slow HR, attributed to disruption of autonomic pathways in spinal cord causing dec vascular resistance
What condition?
partial cord transection (hemisection), usually from penetrating trauma
diminished motor strength and fine touch, position, and vibration sensation on side of injury (ipsilateral)
loss of pain and temperature sensation on side opposite the injury (contralateral)
bladder function may be spared
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Decussates at medulla; proprioception and vibration
dorsal column
Decussate at spinal cord; pain & temp, light tough & pressure
spinothalamic
In Brown Sequard syndrome with injury to T10 on the L side, what would be lost BELOW the injury?
R (C/L): pain & temp, pressure & light touch
L (I/L): vibration, proprioception, D/T, UMN lesion
in Brown Sequard syndrome with injury to T10 on the L side, what would be lost AT THE LEVEL of the injury?
R (C/L): nothing
L (I/L): pain & temp, pressure & light touch, vibration, proprioception, D/T, LMN lesion
in Brown Sequard syndrome with injury to T10 on the L side, what would be lost ABOVE the injury?
nothing
Which lesion?
flaccid paralysis
areflexia/hypo
fasciculations
weakness
dec tone
atrophy
LMN
Which lesion?
spastic paralysis
hyperreflexia
inc tone
babinski
UMN
What is the treatment for brown-sequard syndrome?
early high dose steroids → methylprednisolone
neurosurgical consult to realign spinal cord via traction
What condition?
tumor pressing on dural sac; often metastatic
T spine MC affected; tender at tumor site
presents w/ pain, worse at night when pt recumbent
can cause permanent neuro impairment,
possible weakness + radicular sensory defects
epidural spinal cord compression
New back pain that worsens when lying down should raise suspicion for ______
tumor
What is the management of epidural spinal cord compression?
emergent CT/MRI & referral to neuro/onc
immediate radiation
rapid tx of tumor required to avoid permanent nerve impairment
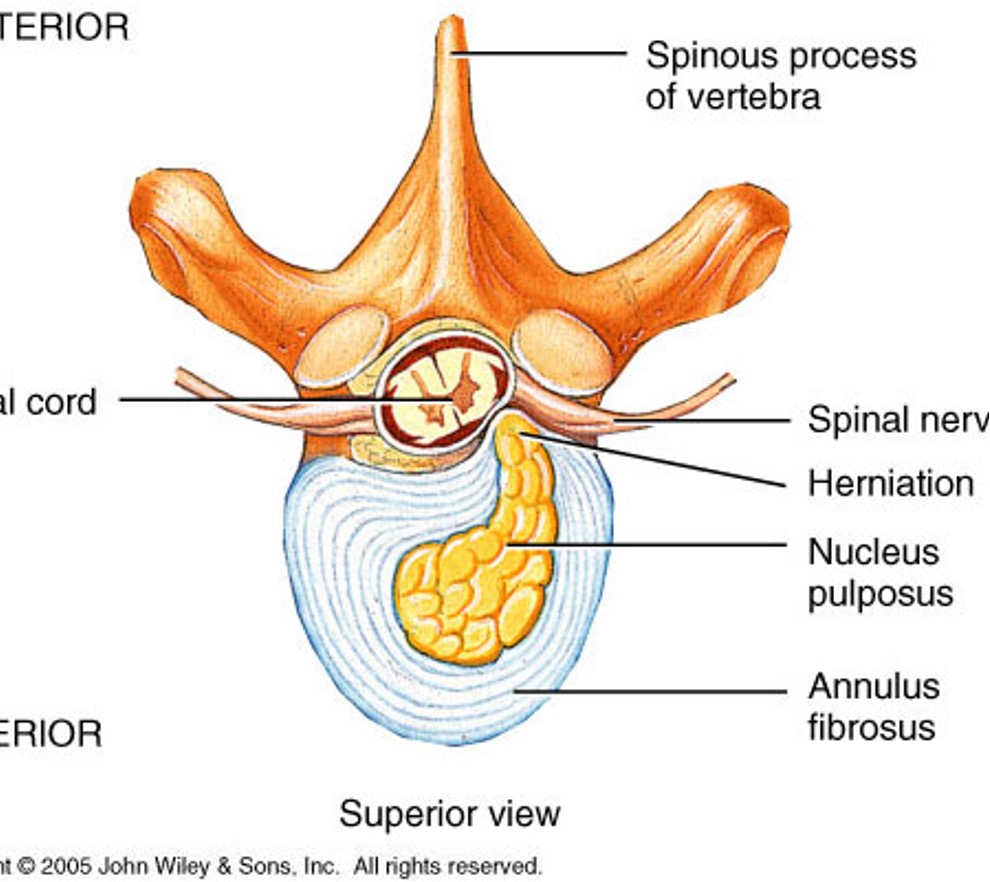
A “herniated” disc is also known as _____
intervertebral disc prolapse
What condition?
nucleus pulposus herniates and presses on nerve root (pinching 1 side of cord)
radicular sx along nerve distribution on one side
can be caused by heavy lifting
intervertebral disc prolapse
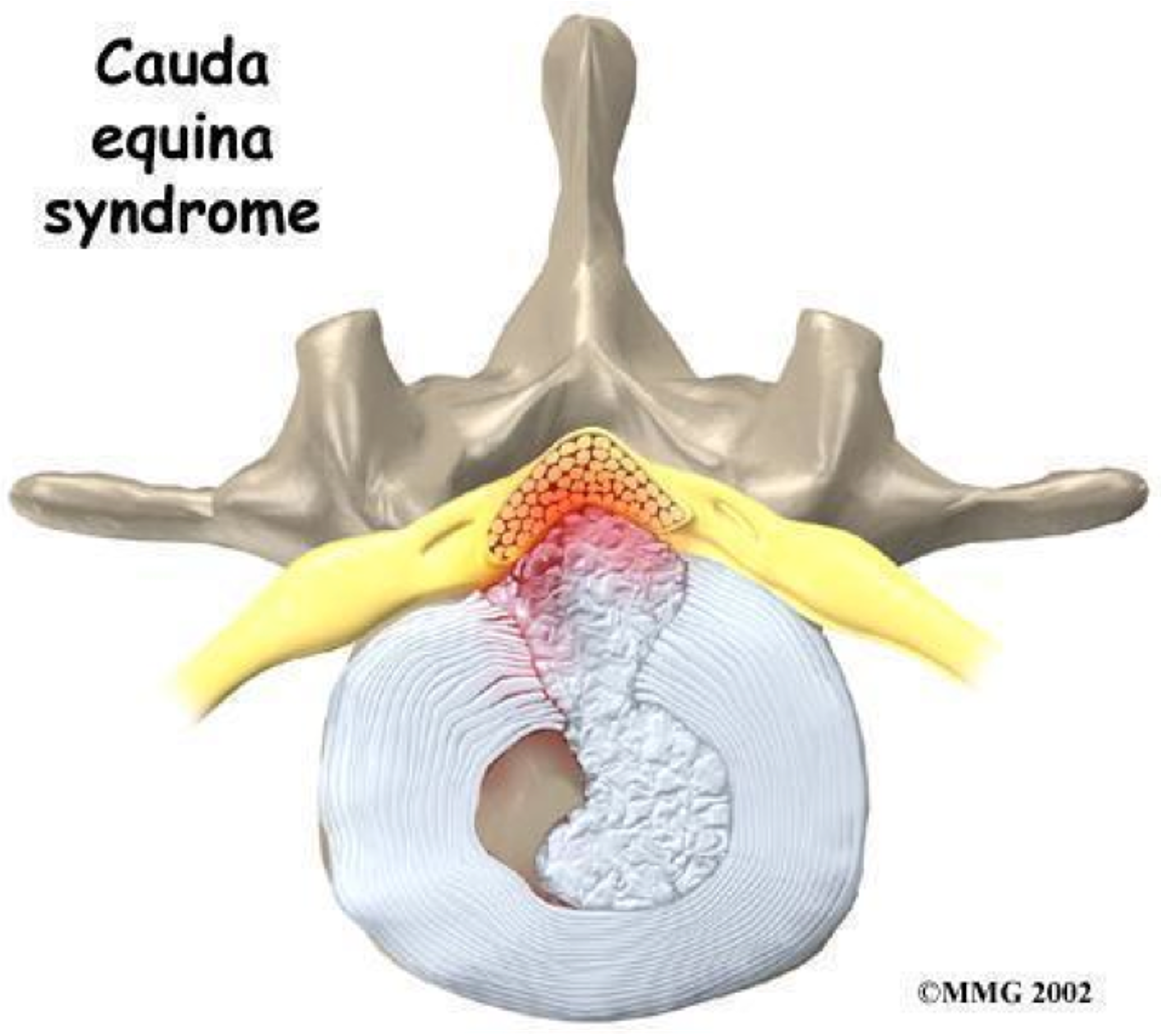
What condition?
centrally prolapsed disc that causes bilateral sx (compress both sides of cord)
variable motor and sensory loss in LEs
saddle anesthesia, bladder and/or bowel dysfunction
urgent MRI and neurosurgeon consult
cauda equina syndrome
what is the management for acute disc prolapse?
plain xrays, CT or MRI depending on presentation
urgent neuro/surgeon referral if significant radicular S&S (3/5 muscle strength)
bed rest vs activity vs PT
pain control → simple analgesics, muscle relaxants, epidural steroid injection
surgery
What is another name for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
lou gehrig’s disease
what condition?
degeneration of corticospinal pathways down to anterior horn cells
nerve cells gradually die
progressive disorder; fatal in ~3 yrs
mixed UMN and LMN deficit in limbs → weakness, easy fatiguability, normal sensation
presents b/t ages 30-60
normal intellect, no sensory/occulomotor defect (just motor issues)
ALS
What are sx of ALS?
tongue fasciculation → classic finding
+difficulty swallowing, chewing, coughing, breathing, speaking
Evaluation of ALS?
nerve bx, muscle bx (may reveal denervation atrophy);
EMG → fasciculations + fibrillations in both UE + LE, normal motor conduction velocity & sensory conduction
what is the treatment for ALS?
Riluzole→ inhibits presynaptic glutamate release, slows progression & prolongs survival (no cure)
other: baclofen, wheelchair, PEG tube, amitriptyline, communicative devices, etc
Which nerve is associated with Bell’s palsy?
facial
which nerve is associated with Saturday Night Palsy?
radial
which nerve is associated with carpal tunnel syndrome?
median
which nerve is associated with funny bone tingling?
ulnar
which nerve is associated with Meralgia Paresthetica?
lateral femoral cutaneous
which nerve is associated with compartment syndrome (surgical emergency)?
deep peroneal
what nerve is associated with Tarsal tunnel syndrome?
posterior tibial
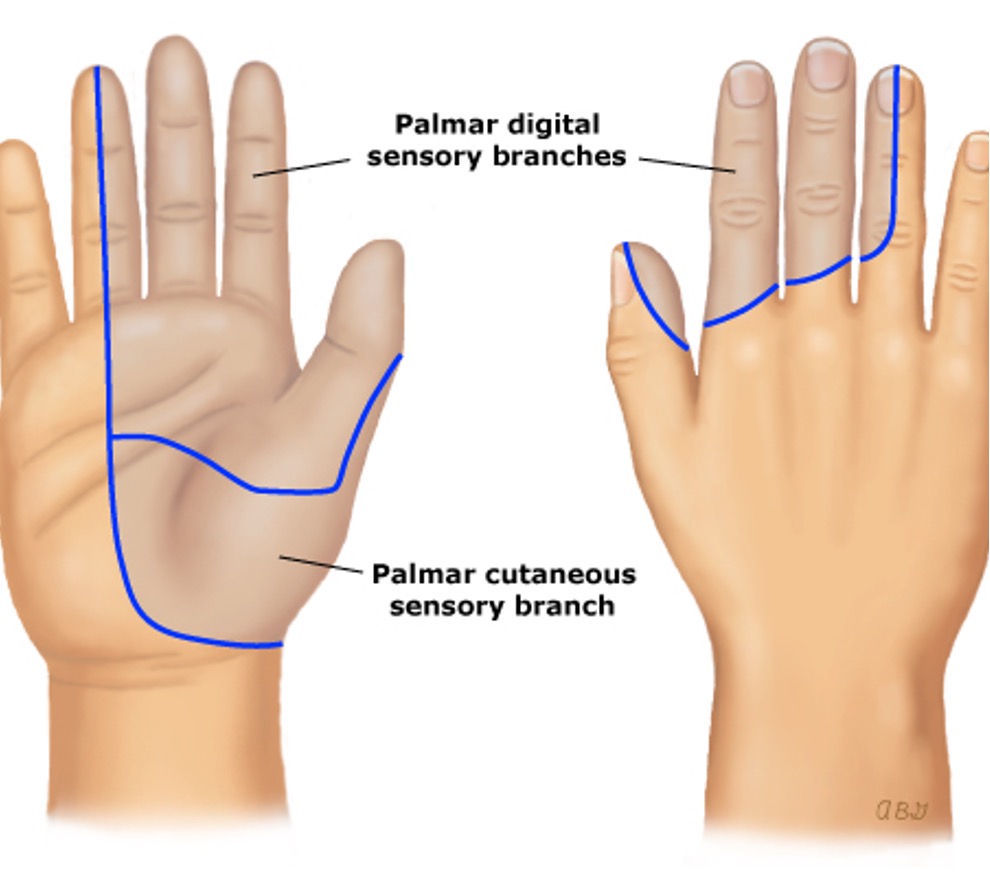
what condition?
compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel
pain or paresthesia - first 3 digits and radial half of 4th
worse at night; provoked by flexing/extending wrist or raising arms
alternating remission and exacerbation
F > M
carpal tunnel syndrome
What provocative maneuvers are used to examine carpal tunnel syndrome?
Phalen maneuver → pt fully flexes palms at wrist w/ elbow in full extension (positive = pain/paresthesia in median innervated fingers w/ 1 min wrist flexion)
Tinel test → firm percussion over course of median nerve (positive = pain/paresthesia of median innervated fingers that occurs w/ percussion over median n.)
what is the treatment for carpal tunnel?
surgical decompression for most; splinting w/ glucocorticoid injections or oral tx
What systemic / metabolic disorders can cause multifocal peripheral neuropathies?
vit B12 deficiency, alcoholism, leprosy, DM
what condition?
autoimmune inflammatory process
multifocal demyelination of white matter of brain and spinal cord (mostly cervical); asymmetric lesions
relapsing remitting pattern w/ chronic progressive course
intention tremors, scanning speech, ataxia, + babinski, clonus, loss of position & vibration sense, emotional decline vision complaints in single eye (triggered by retrobulbar neuritis), etc
F > M, mid 30s (20-50), caucasian/northern european
multiple sclerosis (MS)
Evaluation of MS?
MRI > CT → plaques / Dawson’s fingers
evoked potential test → time for nerves to respond to full stimuli (VER or VEP MC)
CSF → oligoclonal bands, myelin basic protein inc, etc
McDonald criteria

What CSF abnormalities are seen in MS?
inc Ig levels, lymphocytes
oligoclonal bands (pathognomic)
myelin basic protein may be elevated
glucose usually normal
What is the criteria called that is used for diagnosing MS that evaluates # attacks, lesions, and CSF findings?
Mcdonald Criteria
What is the treatment for MS?
directed toward relieving sx
corticosteroids → main tx for acute attacks
alt - plasmapheresis
disease modifying drugs for relapsing (interferon)
IVIG
regular exercise; avoid overwork, fatigue, excessive heat
spasticity→ baclofen, tizanidine
neuropathic pain → gabapentin, amitriptyline, etc
chronic fatigue → amantadine, modafinil
Who has the best prognosis for MS?
females, onset before 40, visual or somatosensory dysfunction (touch or tactile perception) rather than pyramidal or cerebellar
what condition?
disorder of a body region, usually distal limbs
pain (out of proportion), swelling, limited ROM, vasomotor instability, skin changes, patchy bone demineralization
usually follows fracture, soft tissue injury, or surgery
lasts median 7 mos
complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
which subtype of CRPS is WITHOUT peripheral nerve injury and most common?
type I
Which CRPS subtype is WITH peripheral nerve injury?
type II
What is the management for CRPS?
PT/OT
pain→ NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen), anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin), TCA (amitriptyline, nortiptyline), opioids
treatment most effective early in dz
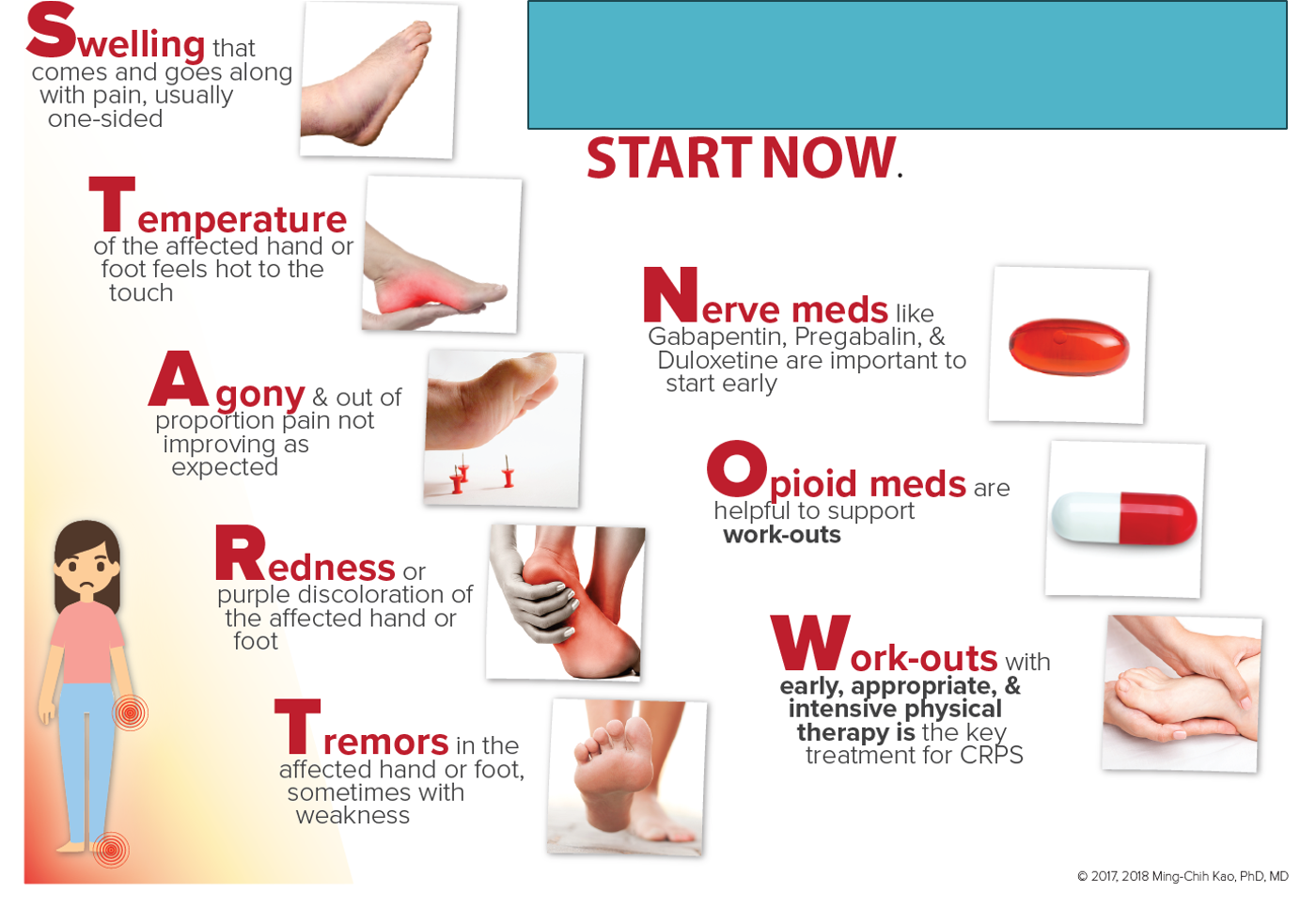
what is the mnemonic for CRPS dx and tx?
Swelling
Temperature
Agony
Redness
Tremors
Nerve meds
Opioid meds
Work outs
what condition?
viral infx → destruction of anterior horn cells in spinal cord → LMN sx
fecal oral transmission; dx from stool / nasopharyngeal secretions
prodrome- fever, myalgia, URI or GI sx
weakness or paralysis, can affect resp muscles
no specific tx
poliomyelitis
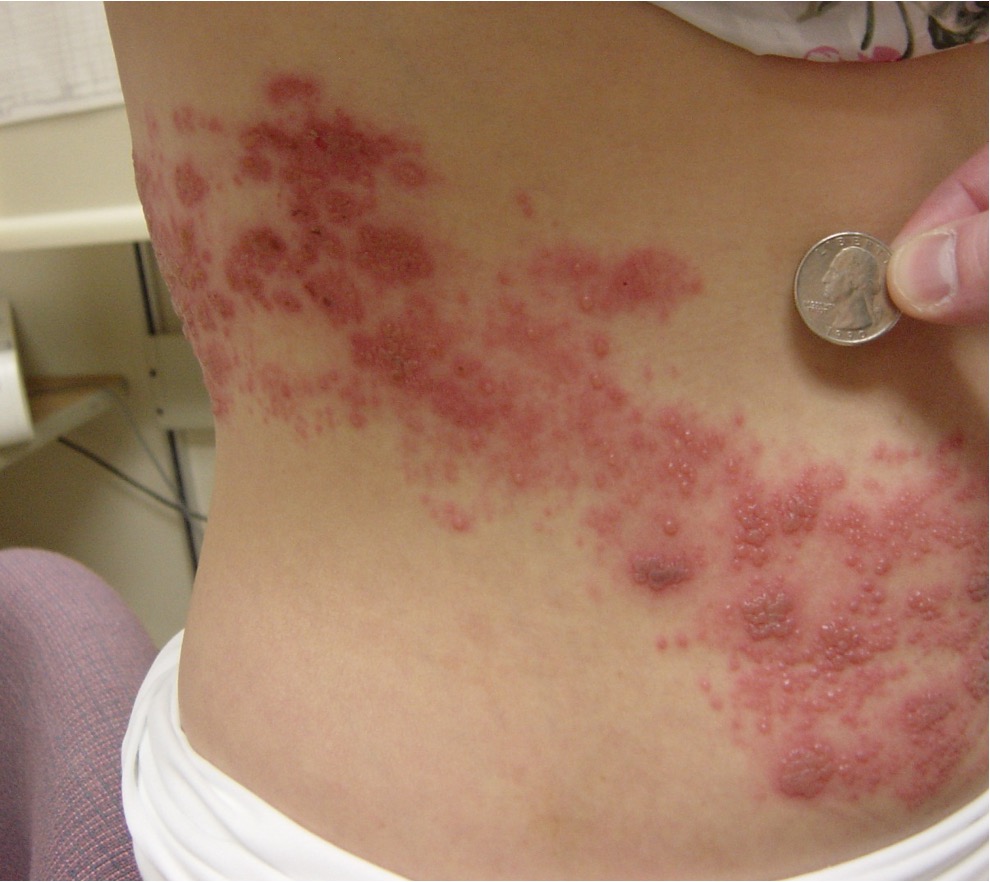
What condition?
reactivation of VZV
severe pain, may precede rash
skin lesions similar to chicken pox that follow nerve root distribution (T & L roots MC) → maculopapules evolve into vesicles/pustules
hutchinson’s sign → lesions on tip of nose, indicates ophthalmic division dz
herpes zoster
what is the tx for herpes zoster?
antivirals → acyclovir, valcyclovir
steroids → reserve for severe
pain relief
postherpetic neuralgia tx → gabapentin or amitriptyline
What is another name for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS)?
acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy
What condition?
autoimmune disorder → destruction of myelin and/or axon by ganglioside antibodies
demyelination dz of peripheral nerves; usually an ascending paralysis; moves distal to central
follows an infx, immunization, or surgery; assoc w/ c. jejuni enteritis
M > F
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
What are ssx of GBS?
paresthesias of hands and feet → earliest sx
acute, symmetric ascending weakness of limbs
gait disorder
pain common, especially back and legs
resp muscle paralysis & CN involvement possible
How do you dx GBS?
LP (CSF) → albuminocytologic dissociation (inc CSF protein w/o inc WBC)
electrophysiology → marked slowing of conduction
What is the treatment for GBS?
hospitalization- cardiopulmonary support
plasmapheresis
IVIG
analgesics
What is the prognosis of GBS?
self limiting; 75% make full recovery w/in few mos-yr
What is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy?
DM
What is the most common peripheral neuropathic syndrome associated with DM that is insidiously progressive & can affect any peripheral nerve (including CN)?
diabetic polyneuropathy
What are ssx of diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
MC in toes and distal feet
tingling, burning, abnormal pain and temp sensation
reduced achilles tendon reflexes & vibratory sense in toes
hand numbness and sensory loss
stocking/glove distribution
How is a diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy made?
serial nerve conduction studies and labs to r/o other causes
How is diabetic peripheral neuropathy treated?
tight control of serum glucose
TCA → amitriptyline, nortriptyline
anticonvulsants → carbamazepine, gabapentin
lidocaine patch, tramadol
How is autonomic dysfunction treated in diabetic neuropathy?
orthostatic hypotension → fludrocortisone (volume expander, works like aldosterone)
gastroparesis → metoclopramide, erythromycin
diarrhea → loperamide
urinary incontinence → bethanechol
ED → sildenafil
CV risk factors → tight control BP and cholesterol, daily ASA, stop tobacco
What condition?
toxin exposure from contaminated wounds → transported along motor nerves into spinal cord → binds irreversibly to receptors in brain & spinal column → blocks release of GABA → unchecked excitatory impulses, inc muscle tone, spasms, rigidity
Tetanus / clostridium tetani
What is the treatment for tetanus?
tetanus immune globulin; hospitalization for resp/CV support
What condition?
toxin binds presynaptic sides of peripheral cholinergic synapses at NMJ → irreversibly disrupts Ach release → motor weakness or paralysis
(MC after ingestion of home canned food, rarely from wounds)
Botulism / clostridium botulinum
Who is at risk for botulism?
infants
_______ is an ascending paralysis; _______ is a descending paralysis
GBS; Botulism
What condition?
fulminating weakness 12-72 hrs after toxin ingestion
symmetric descending paralysis
diplopia, ptosis, blurred vision, facial weakness, dry mouth, dysphagia or nasal speech, paralytic ileus
difficulty w/ respiration, postural hypotension
no sensory deficits
normal DTRs unless involved muscles are weak
Botulism
What is the treatment for botulism?
antitoxin; supportive care
what condition?
autoimmune disorder; pure motor syndrome
blockage of neuromuscular transmission at the ACh post synaptic receptors
MC in young females
typically 20-40 yrs but can occur at any age
F 3rd decade
M 5th-6th decades
myasthenia gravis (MG)
What condition?
mild and intermittent onset over many years
crisis lasts hours or days
characteristic muscular weakness; worse in evening
extraocular, pharyngeal & facial, cervical, proximal limbs, resp muscles
ptosis & diplopia MC sx
MG
What condition?
defective ACh release from pre synaptic
abs against VGCC; SCLC
increased power with muscle contraction (improved power w/ repeated hand grip) → lambert’s sign
Lambert eaton (myasthenic) syndrome
How is MG evaluated?
Tensilon test = diagnosis
edrophonium 4mg IV improves grip strength w/in 30s
EP → EMG or single fiber, repetitive stimulation
IP assay → ACh receptor on antigen
What is the treatment for MG?
anticholinesterase→ mestinon, prostigmin (neostigmine)
immunosuppressants→ prednisone, azathioprine, etc
plasmapheresis
IVIG
thymectomy rec for all pts w/ generalized
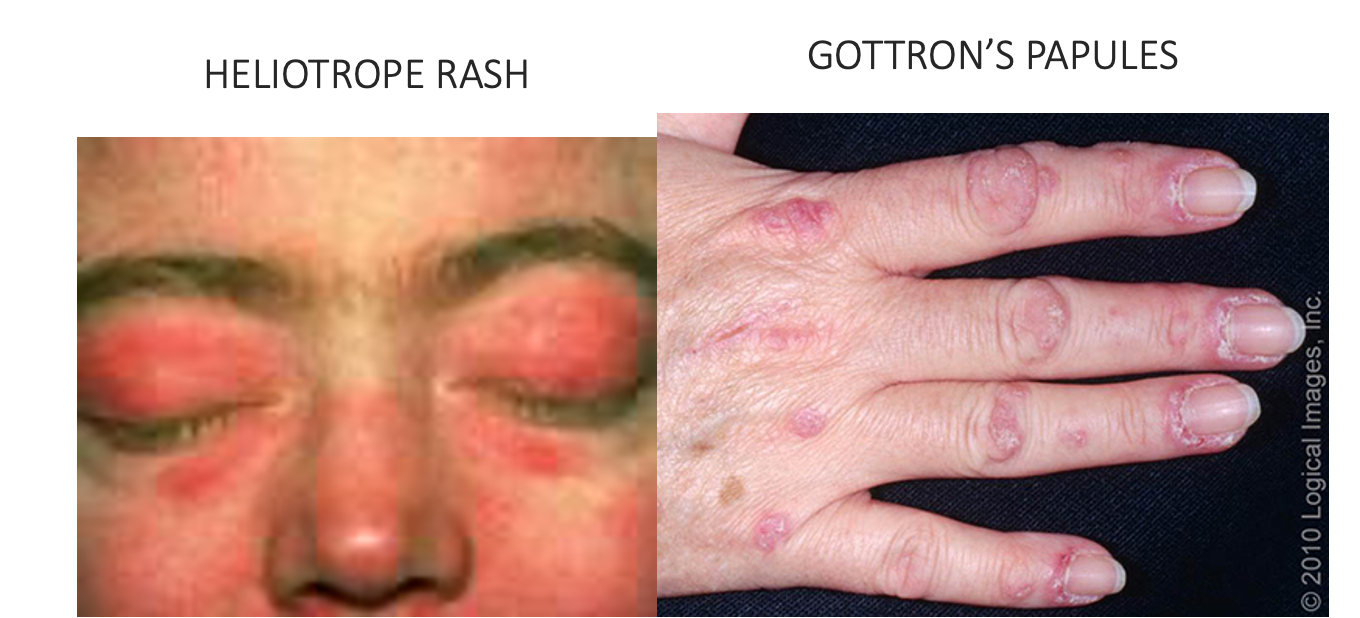
what condition?
autoimmune disorder causing inflammatory infiltration of muscles, destruction of muscle fibers
muscle pain, weakness, and wasting (proximal muscles)
heliotrope rash
gattron’s papules
polymyositis / dermatomyositis
What condition?
set of inherited myopathic disorders
progressive muscle weakness and wasting
no specific tx, encourage activity and avoid prolonged bedrest
PT for contractures and mobility
Eteplirsen slows progression
muscular dystrophy
what condition?
permanent non progressive central motor dysfunction that affects muscle tone, posture and movement
most prenatal & during development
manage w/ multidisciplinary team; PT/OT
tx w/ botox for spasticity & hyperreflexia
cerebral palsy