Physiology - L2 - Cells & Transport
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Paramedic specific content Physiology Lecture 2 (including cell worksheet answers from Lecture 1)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Molecules can be made up of
The same atoms (elements) or different atoms (compounds)
List the following in order of size: Water, sodium ion, respiratory system, red blood cell, protein fibre, mitochondria, tendon, heart
sodium ion, water, protein fibre, red blood cell, tendon, heart, respiratory system
Organic Compounds
Molecules that exist only in living systems
Carbon atoms
what organic compounds are made around
Three main organic compounds
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
Cells are involved in
growth, repair, reproduction
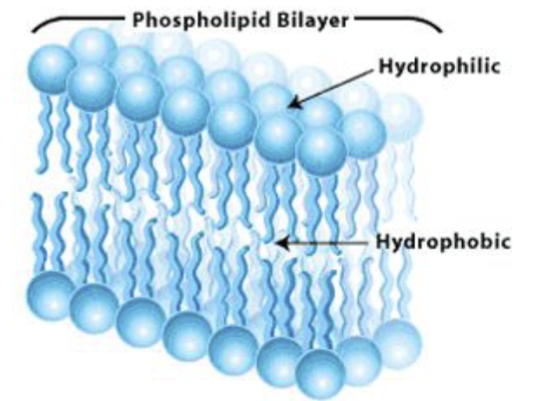
Phospholipid bilayer
Makes up the structure of the cell membrane with a hydrophobic lipid tail and a hydrophilic phosphorus water loving head it acts as a barrier to water allowing the cell to function while helping to create a relatively stable environment within the cell
Head of phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophilic phosphorous
Tail of Phospholipid bilayer
hydrophobic lipid
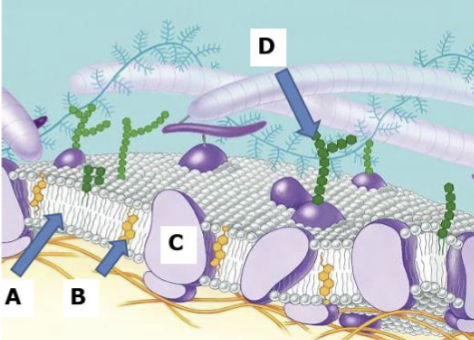
A
Phospholipid bilayer
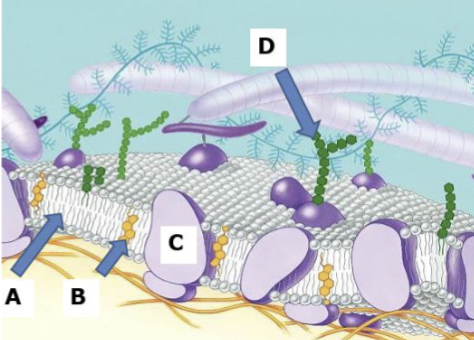
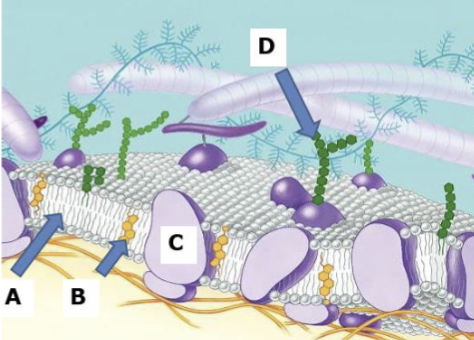
B
Cholesterol
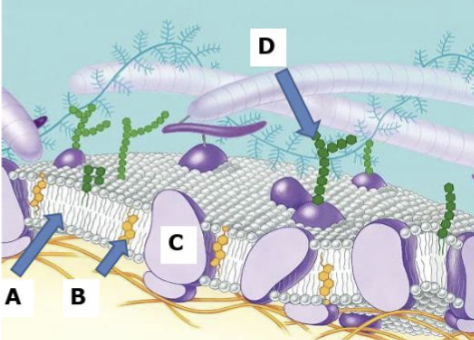
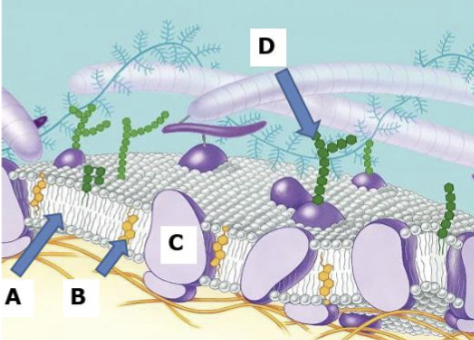
C
Proteins
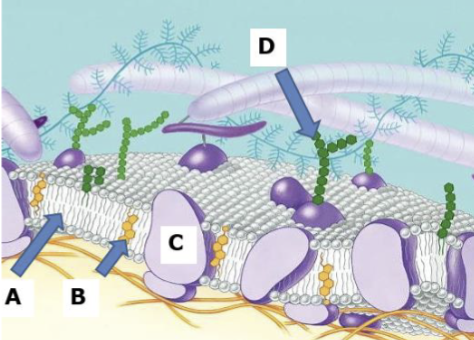
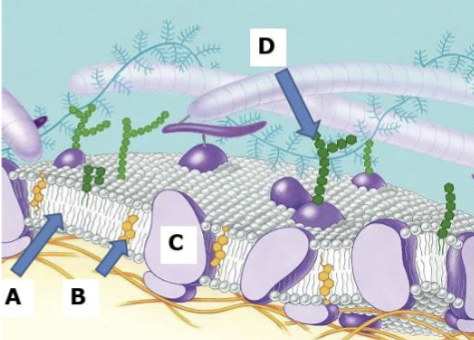
D
Carbohydrates
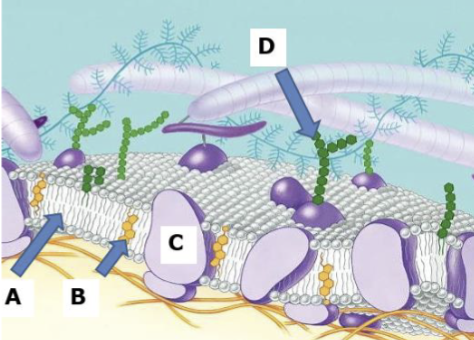
Proteins in the cell
allow the cell to interact with their environment such as transport and enzymatic activity
Transport
moving substances in and out of cells
Enzymatic activity
converting inactive substances to active ones or vice versa
Receptors
allow communication with cells and their surrounding areas
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
The fluid surrounding the cell that creates the external environment of the cell and includes every substance contained within it
Controlling composition of ECF
by creating relatively stable state e.g. homeostasis

Red Blood Cells
Disc shaped cells used to transport oxygen around the body in the form of oxyhaemoglobin - shape allows flexibility which aids in preventing blood clots

Skeletal Muscle Cells
Elongated cells with a very elastic and resistant plasma membrane, containing contractile proteins for movement
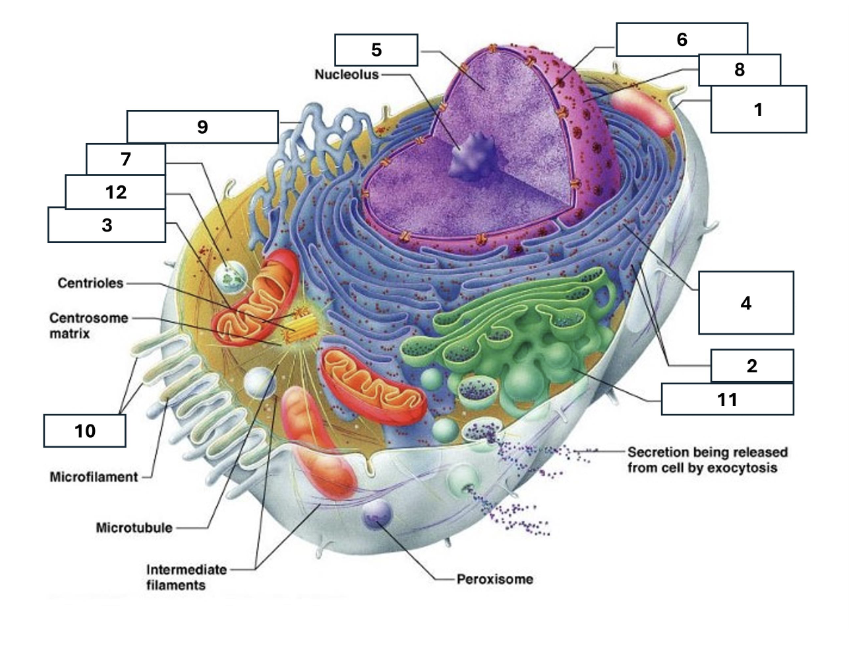
1
Plasma/cell membrane
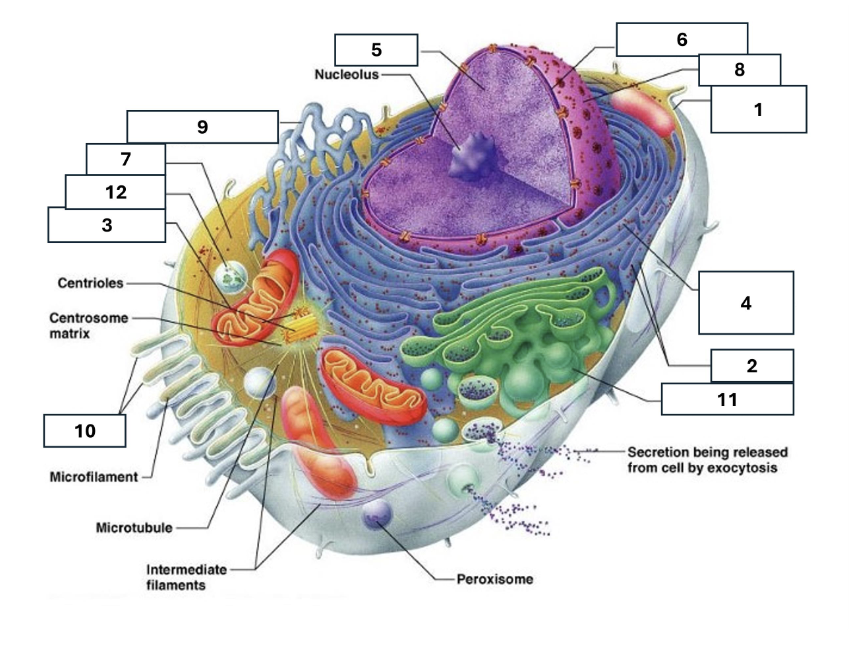
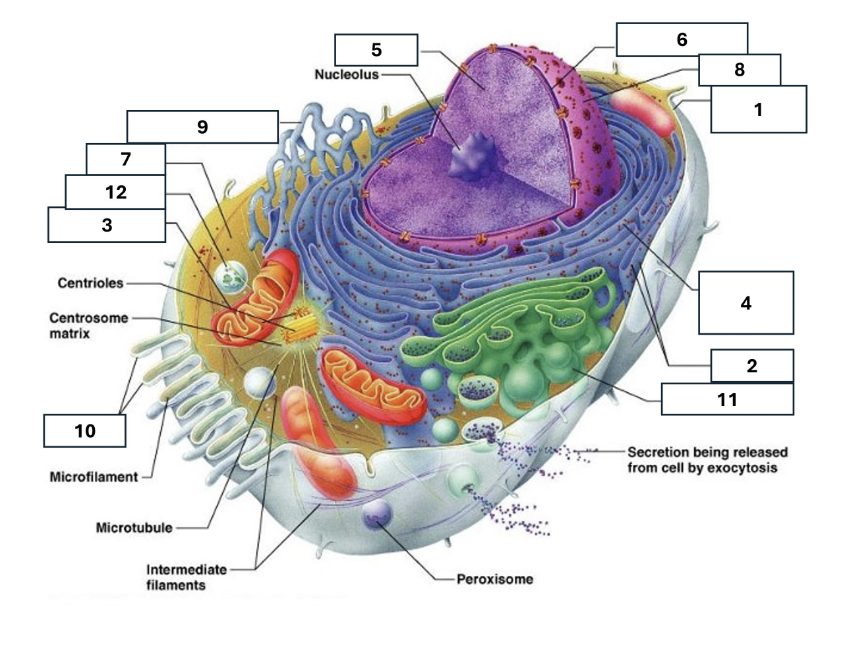
2
Ribosomes
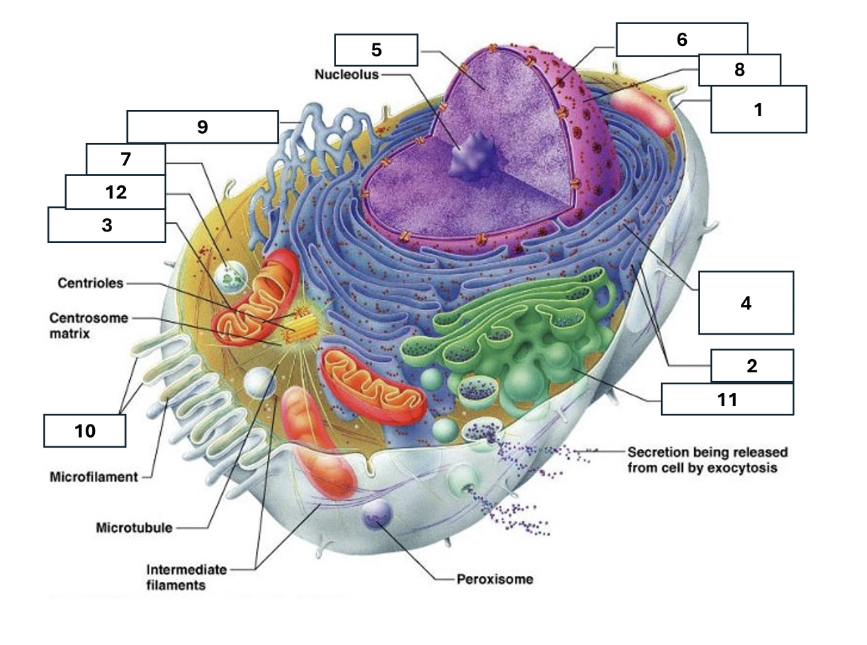
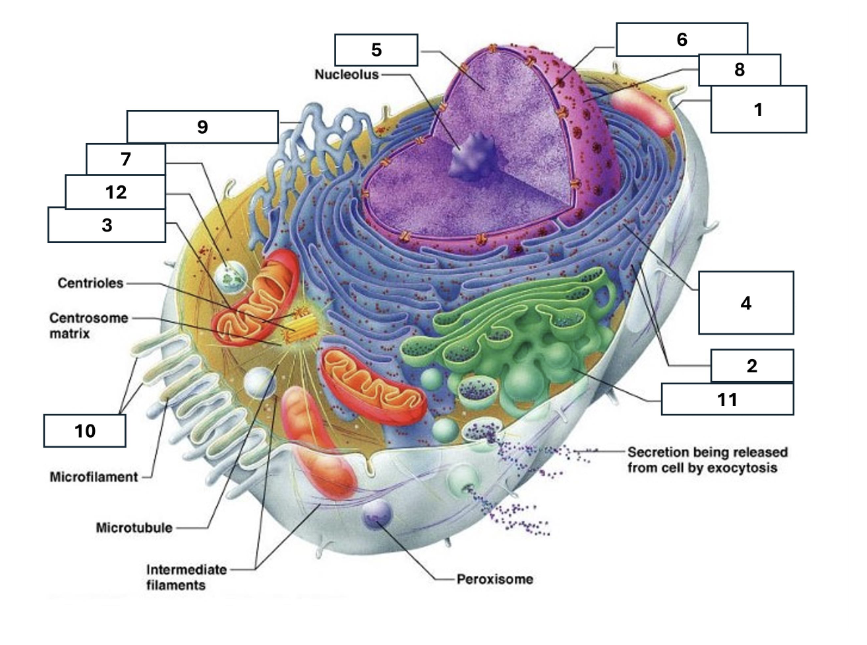
3
Mitochondria
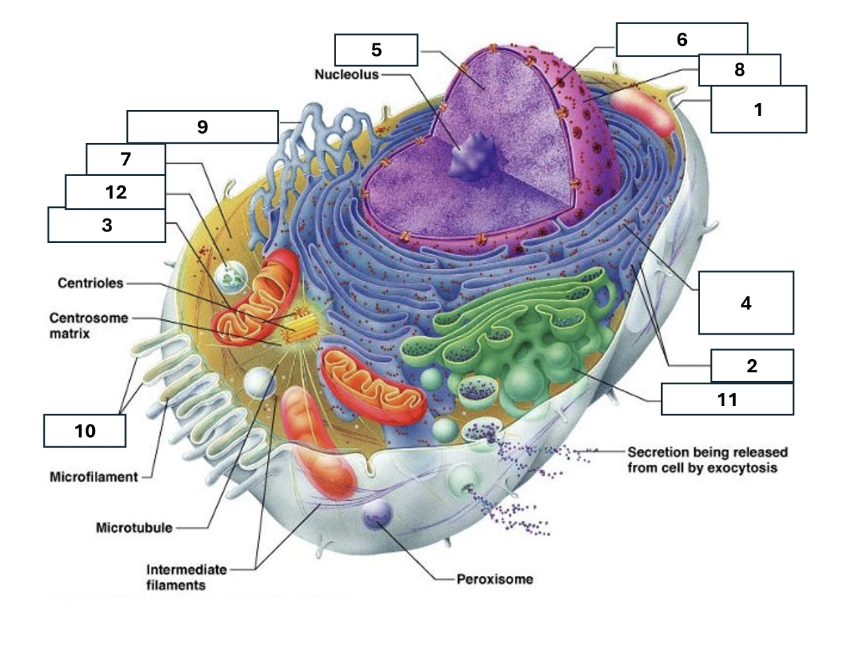
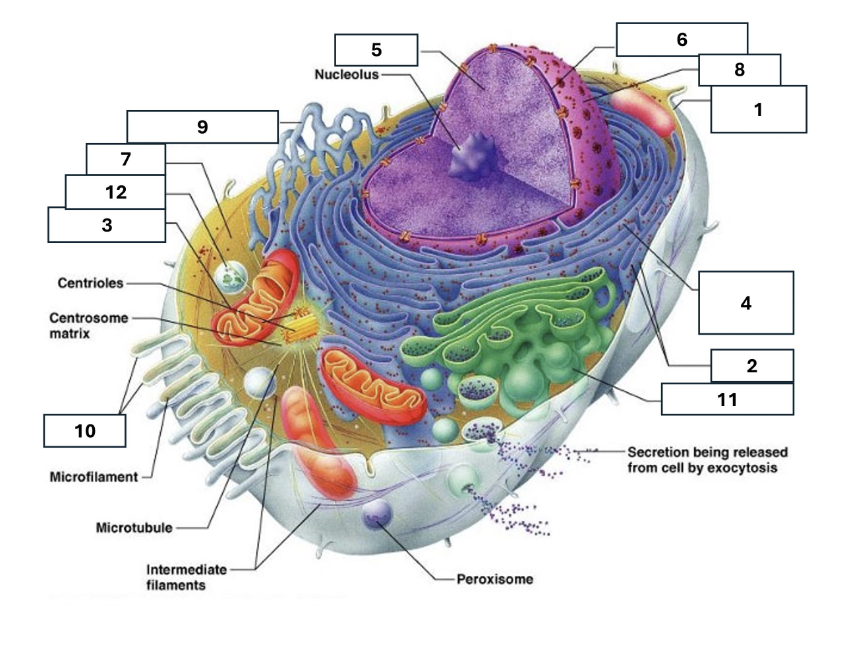
4
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
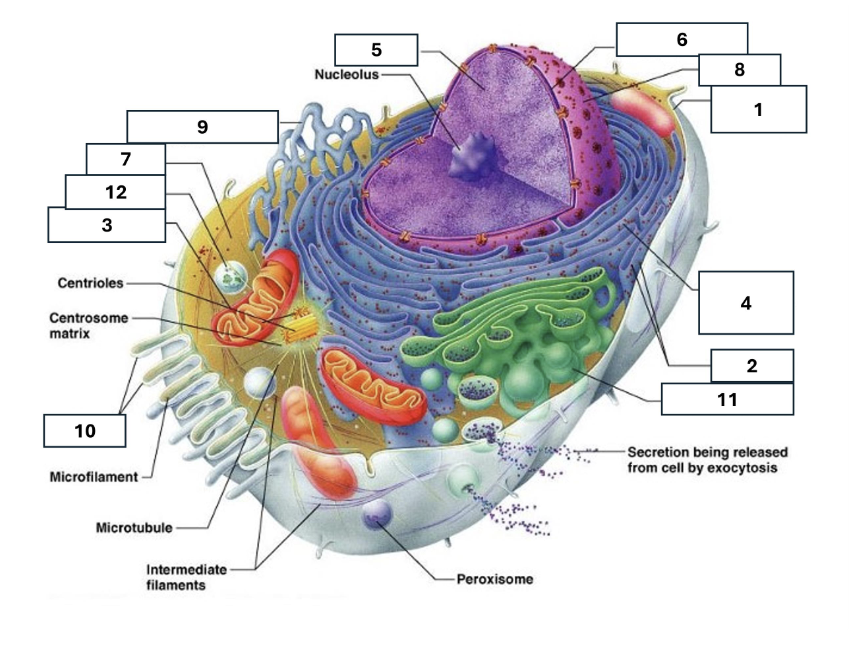
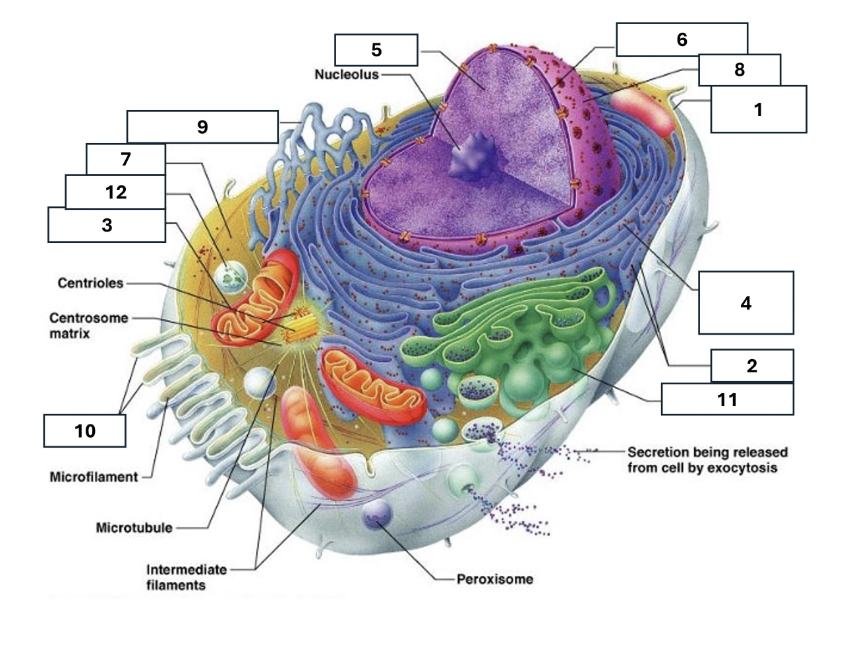
5
Chromatin/chromosomes
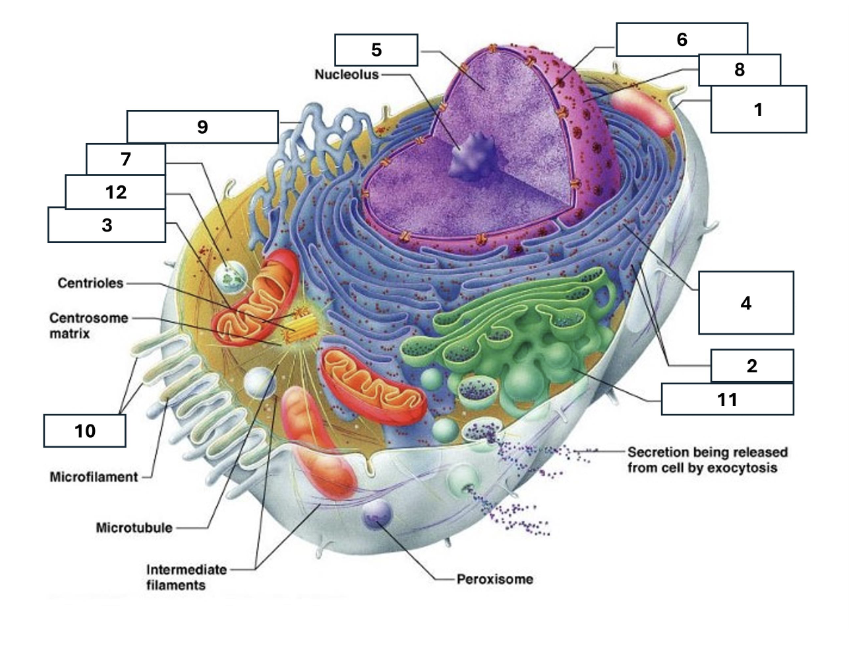
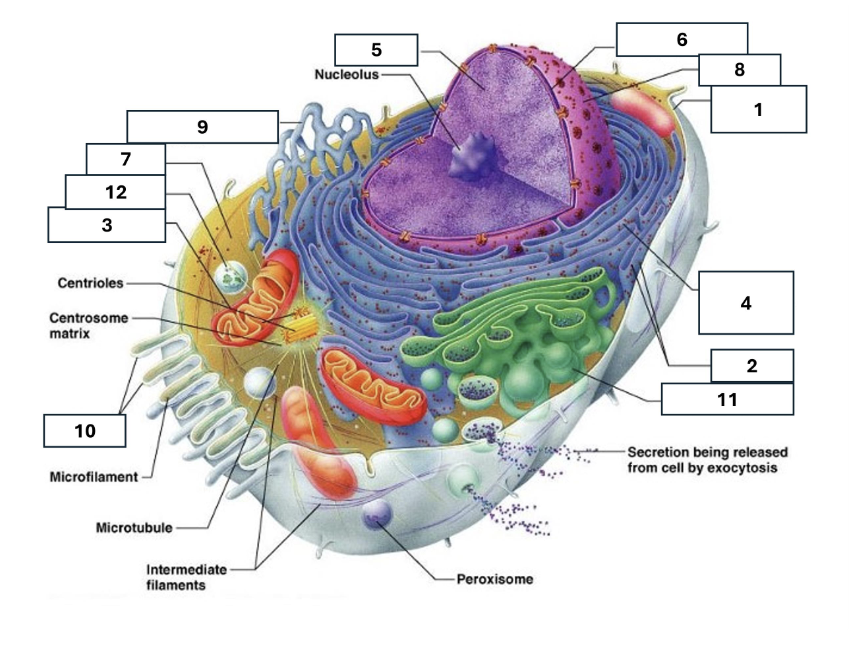
6
Nuclear envelope
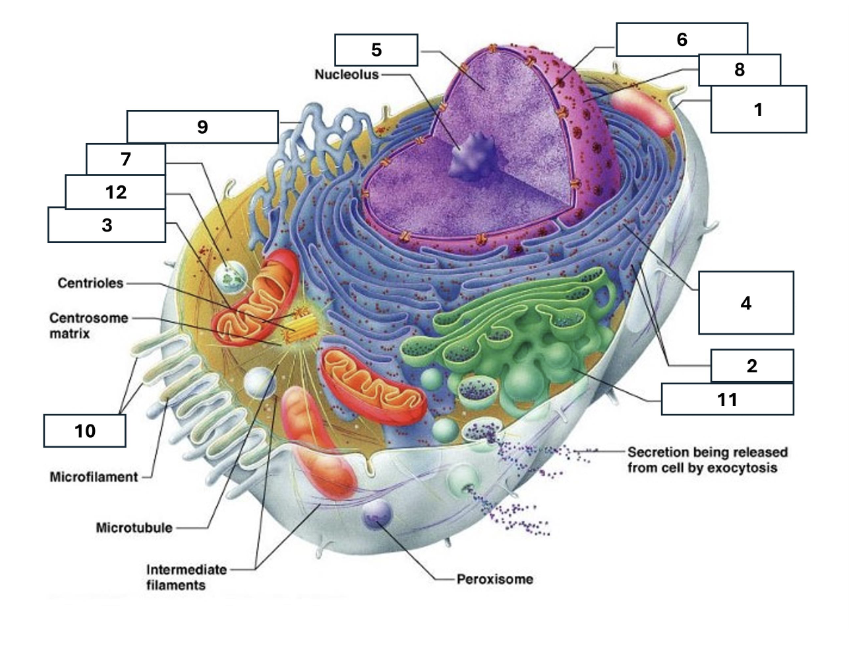
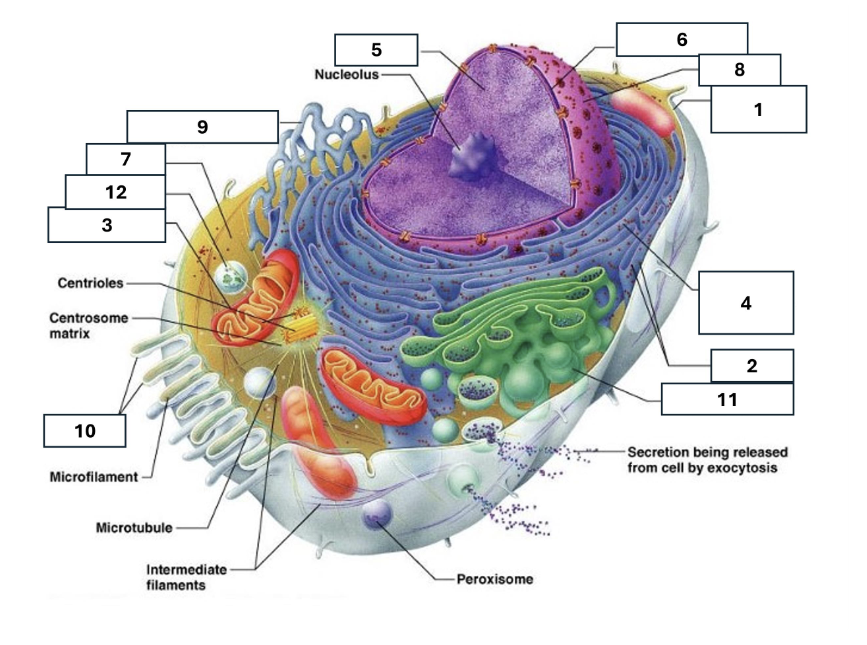
7
Cytosol
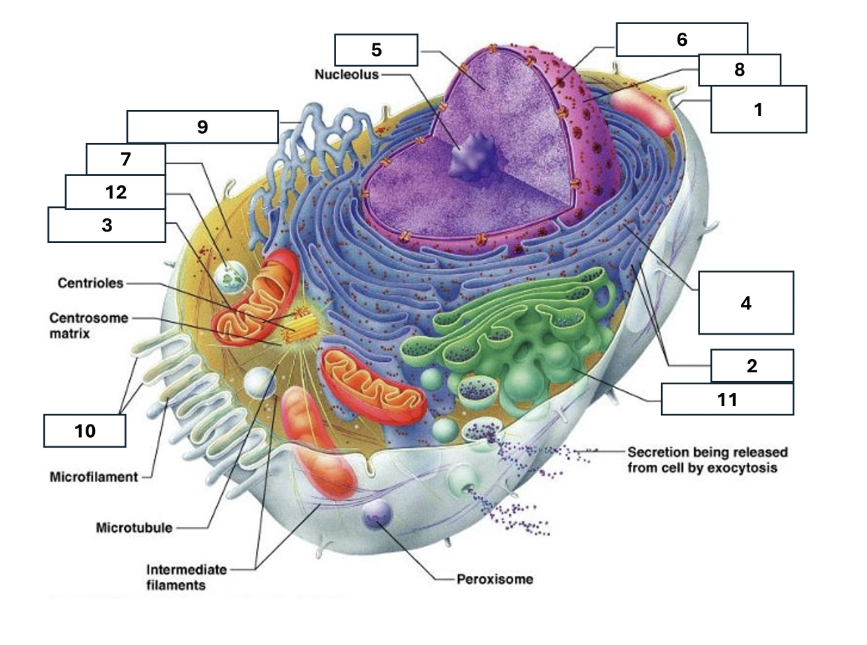
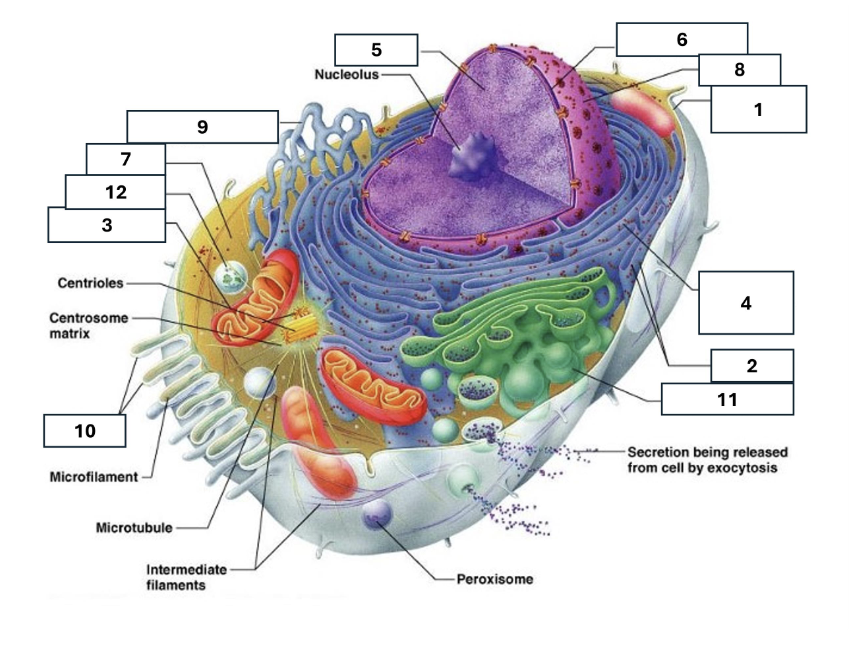
8
Nucleus
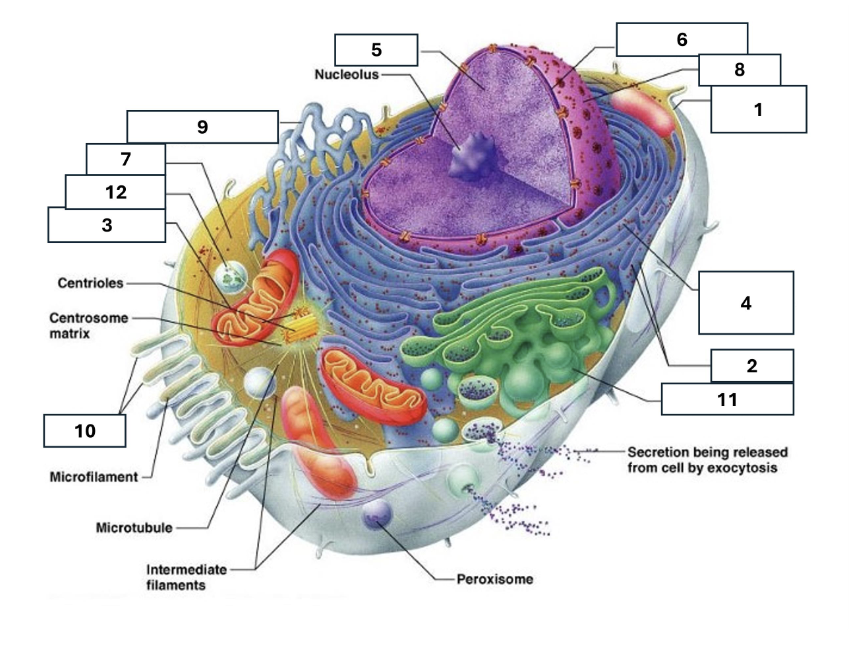
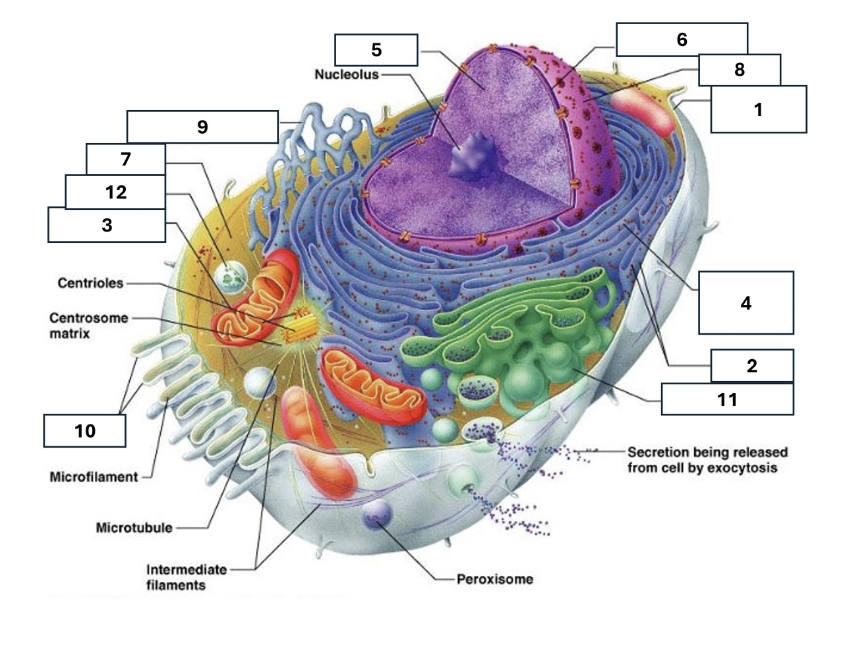
9
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
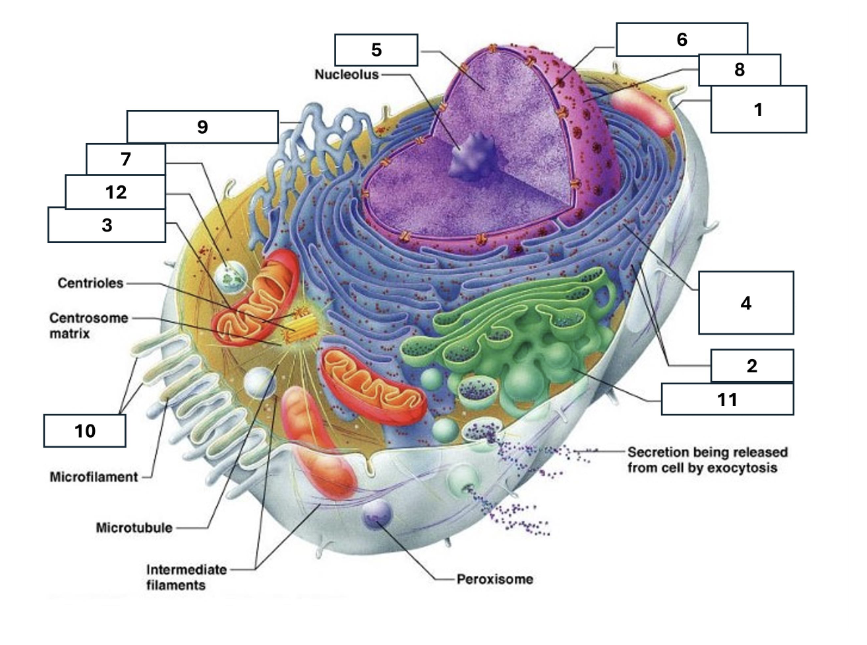
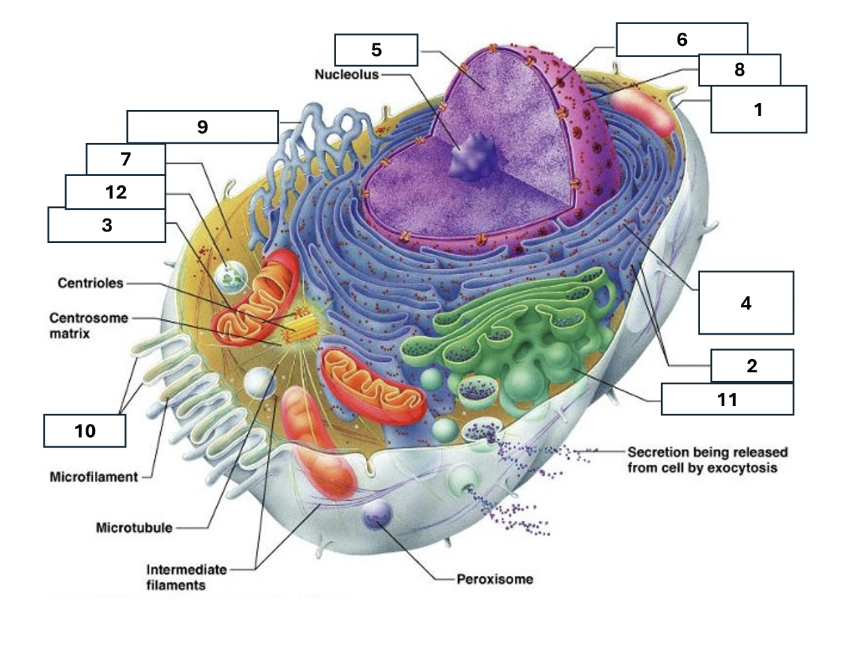
10
Microvilli
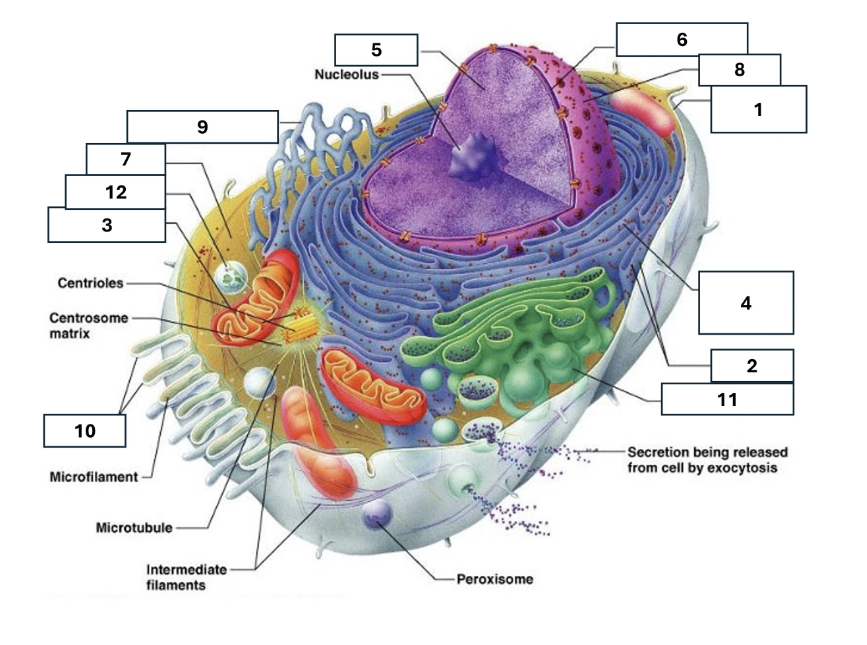
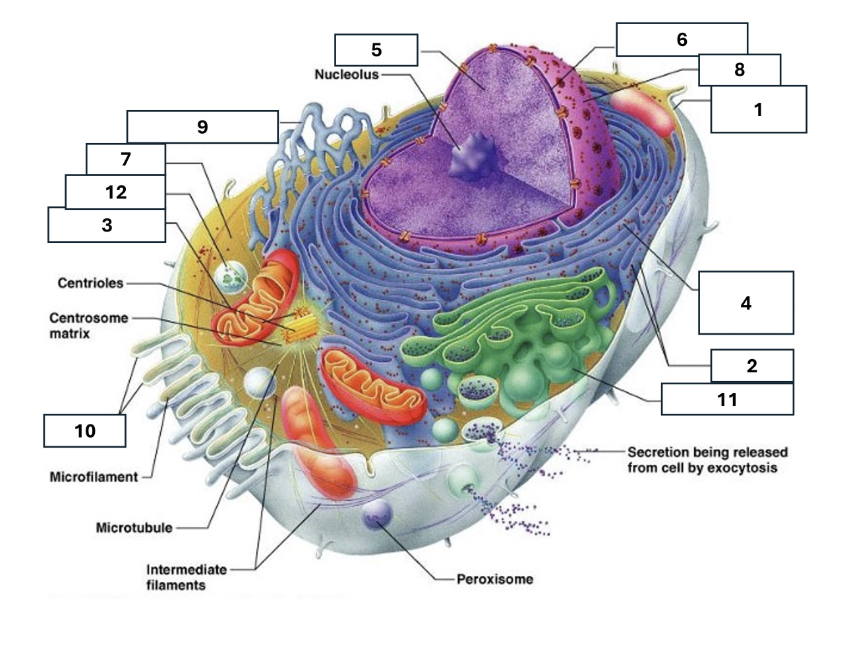
11
Golgi complex
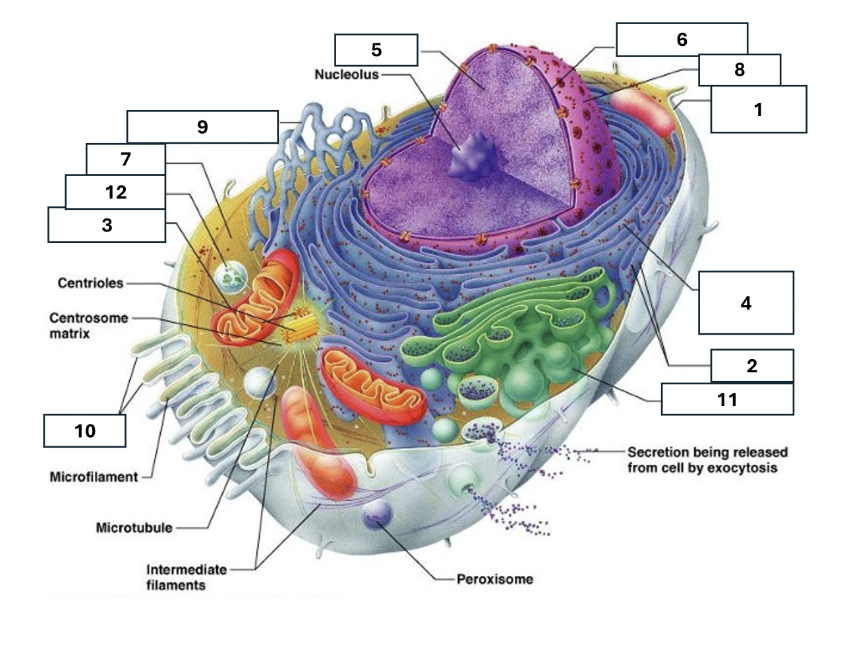
12
Lysosome
Nucleoli
Contains the genetic material of the cell, involved in assembling ribosomes and alteration of transfer (RNA)
Cytosol
Fluid in which all cytoplasmic elements are suspended
Microvilli
Folds in the cell membrane to increase cellular surface area
Mitochondria
the organelle that breaks down food molecules to produce energy ATP
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate - energy carrying molecule
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
makes lipids, cholesterol and other fatty compounds as well as breaking down drugs and other substances
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Proteins synthesised by ribosomes enter here for processing and sorting
Chromatin/Chromosomes
Compacted DNA and proteins that bears genetic information
Cell Membrane
A thin protective barrier surrounding every cell that separates the cells contents from its surroundings to allow cells to perform different functions and chemical reactions
Makes up a cell membrane
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Cholesterol, Phospholipid bilayer
Golgi Complex/Aparatus
Modifies, sorts and packages proteins and lipids from the Endoplasmic Reticulum to transport/secrete them to another location
Ribosome
in which amino acids are hooked together to make proteins (protein synthesis)
Nucleus
Contains the cells dna, other genetic material and is the control centre of the cell
Lysosomes
Digests food particles, wastes, cell parts and foreign invaders
Properties of Epithelial Tissue
consists of epithelial cells arranged in continuous sheets either in single or multiple layers
Epithelial Cells
Tightly packed together these cells make up epithelial tissue

Simple Epithelium Cells
A single layer of cells that functions in diffusion, osmosis, filtration, secretion or absorption.

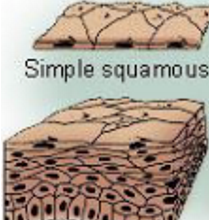
Squamous Epithelial Cells
thin allowing for the rapid passage of substances through them
Stratified Epithelial Cells
Consists of two or more layers of cells that protect underlying tissues in locations where there is considerable wear and tear
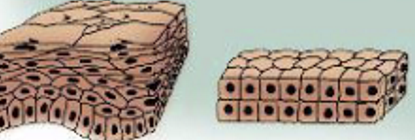

Pseudostratified Epilated Cells
Appear to have multiple layers of cells because the cell nuclei lie at different levels but are actually only a single layer

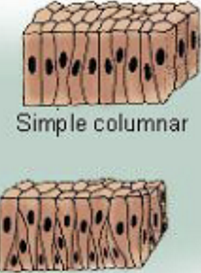
Columnar Epithelial Cells
Cells that are much taller than they are wide and protect underlying tissues, they often have cilia and microvilli specialised for secretion or absorption

Ciliated cells
Cells with cilia, fine hair-like extensions on the cells membrane, that reach the surface of a tissue and beats rhythmically to move substances across a surface e.g. continuously moving mucus our of airways


Goblet Cells
Modified columnar epithelial cells that secretes mucus to collect foreign objects

Homeostasis
The ability for all living systems to maintain stable internal conditions despite changes occurring outside of the body
Normal temp range
36-38
Temp above 38
usually means infection
Normal heart rate
60-100bpm
Bradycardia
slow heart rate less than 60bpm
Tachycardia
fast heart rate over 100bpm
Normal oxygen levels
94-100%
Other name for blood glucose
BM
Normal Respiratory Levels
12-20
Negative Feedback
this is when changes are reversed to bring internal conditions back to the norm
Examples of Negative feedback
thermoregulation, blood glucose regulation, breathing rates
Thermoregulation
the homeostatic regulation of body temperature even when the surrounding temp is different such as shivering or sweating
Positive Feedback
the physiological change that tends to strengthen or reinforce the initial change in one of the bodys controlled conditions increasing it further away from the norm
Examples of Positive Feedback
clotting during wound healing, during childbirth, platelets during cuts and wounds
Pyretic
abnormal, regulated elevation of an organism’s core body temperature known as a fever
Hypothalamus
a small vital structure deep within the brain that acts as the body’s control centre for homeostasis
Vasodilation
Blood vessels widening (dilating) to allow more blood to flow from the warm body core to increase heat loss through the surface of the skin in response to the body being too hot
Vasoconstriction
Blood vessels narrowing (constricting) to reduce blood flow and therefore heat loss through the surface of the skin in response to the body being too cold
Diaphoresis
a biological process in which sweat glands release an abnormally strong and excessive amount of sweat that may affect the entire body, evaporating it to the surrounding air helps cool down the body
Reasons for Diaphoresis
underlying medical conditions, hormone imbalance or strong emotional stimulus
To increase heat loss from the lungs
patient will breathe deeper through their mouth instead of the nasal passages
when too warm
hair erector muscles relax lowering the hair to prevent a layer of air being trapped to insulate heat
when too cold
hair erector muscles contract, raising the hair to trap a thick layer of air above the skin to prevent heat loss by insulating
Patient is pyretic - how would body temp get back down
The hypothalamus receives information from sensors in the skin and brain the body temperature is too high and begins to cool it down using vasodilation, diaphoresis, breathing deeper through the mouth, relaxing hair erector muscles - assisting the body achieve homeostasis
Osmosis
The movement of a solvent molecule across a semi permeable membrane down a concentration gradient/from a region of high solvent concentration to a region of low solvent concentration
Osmosis occurs in
Renal filtration, Gastrointestinal tract, Nerve conduction
Passive/Simple Diffusion
the free movement of molecules across a membrane going down a concentration gradient that does not cost energy and continues until equilibrium is reached
Facilitated Diffusion
the transport of molecules that cannot diffuse directly through a phospholipid bilayer, by a channel or carrier protein receptor down a concentration gradient that does not require atp and continues until equilibrium is reached
Active Transport
the movement of a substance from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration which costs ATP energy
Active Transport’s relationship with homeostasis
necessary for the homeostasis of ions and molecules with a significant portion of the available energy going toward maintaining these processes
Sodium Potassium Pump
Mechanism for active ion transport across the cellular membrane e.g. in cardiac tissue causes heart to contract
Sodium Potassium Pump alternative name
Na+K+ATPase