High risk pregnancy notes (class 13,
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:15 PM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
High risk pregnancy
* Condition/s which threaten maternal and/ or fetal health or interferes with normal fetal development, childbirth or transition to parenthood.
\
* Biophysical, socio-demographic, psychosocial, environmental factors
* Can become high risk at any point on the continuum.
\
\
2
New cards
high risk factors
\- Preexisting factors that are affected by pregnancy and affect the pregnancy and its outcomes e.g. diabetes, cardiac disease
\- Factors that are related to pregnancy only eg.) Gestational HTN
\- Factors that have nothing to do with pregnancy e.g. trauma, but have potential to affect it
\- Factors that are related to pregnancy only eg.) Gestational HTN
\- Factors that have nothing to do with pregnancy e.g. trauma, but have potential to affect it
3
New cards
what are some effects of high risk pregnancy
\-Physical effects on mother and/or baby
\-Psychological effects
\-Social effects
\-Spiritual
\-Effects on other family members
\-May be financial effects
\-Effects of long-term hospitalization
\-Psychological effects
\-Social effects
\-Spiritual
\-Effects on other family members
\-May be financial effects
\-Effects of long-term hospitalization
4
New cards
psychological effects of high risk pregnancy
\-Increased stress \n -Uncertainty about outcomes \n -Disruption of family routines, role changes, child care issues, work disruption etc... \n -May have difficulty establishing relationship with fetus if outcome is questionable
5
New cards
goals of care for a high risk pregnancy
\-Reduce the incidence of health problems affecting maternal/ fetal health and pregnancy outcomes by identifying the presence of risk factors and signs and symptoms of complications early.
\-Treat ASAP \n -Minimize effects of complications on pregnancy outcome
\-Monitor status of pregnancy \n -Emotional support
6
New cards
intimate partner violence / violence during pregnancy
high risk pregnancy
7
New cards
adolescent pregnancy
* Statistics - rate generally decreasing in last few years
* Can lead to physical, psychological, social & economic
problems for individuals and families
* Social/economic problem for society
* Individual differences
\
8
New cards
risks of adolescent pregnancy
\- Can affect education & career options
\- Many don’t seek antenatal and follow-up care
\- Often have poor nutritional status; many smoke,
substance abuse
\- Insufficient weight gain \n - increased Fe deficiency anemia \n - LBW; increased preterm birth \n -increased Risk of abuse to child especially if abandoned - increased Gestational Hypertension \n - Cephalopelvic Disproportion (CPD)
\- Many don’t seek antenatal and follow-up care
\- Often have poor nutritional status; many smoke,
substance abuse
\- Insufficient weight gain \n - increased Fe deficiency anemia \n - LBW; increased preterm birth \n -increased Risk of abuse to child especially if abandoned - increased Gestational Hypertension \n - Cephalopelvic Disproportion (CPD)
9
New cards
nursing care for adolescent pregnancy
* Goals - assist girl in experiencing a physically safe and emotionally satisfying pregnancy, promote optimal health for mother and baby
* Educate re: options. Provide support!! Treat with respect Don’t be judgmental
* Need to assess developmental level
* Encourage prenatal care and education
\
\-supports/community resources
* Educate re: options. Provide support!! Treat with respect Don’t be judgmental
* Need to assess developmental level
* Encourage prenatal care and education
\
\-supports/community resources
10
New cards
after age 35
After age 35, there's a higher risk of pregnancy-related complications that might lead to a C-section delivery. The risk of chromosomal conditions is higher. Babies born to older mothers have a higher risk of certain chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome. The risk of pregnancy loss is higher.
11
New cards
multiple pregnancy
\-Ideal outcomes – to reach 36-37 weeks of gestation with all fetuses growing and developing normally \n
\-Close monitoring (doppler studies, BPP, NST) useful in monitoring status of the pregnancy
\
\-Increased Risk for cord entanglement, fetal compromise, and placental abruption. \n
\-Method of childbirth depends on the position of the first fetus.
\
\-Important to monitor subsequent fetus/es after the birth of the first, as well as maternal bleeding and vital signs
\-Close monitoring (doppler studies, BPP, NST) useful in monitoring status of the pregnancy
\
\-Increased Risk for cord entanglement, fetal compromise, and placental abruption. \n
\-Method of childbirth depends on the position of the first fetus.
\
\-Important to monitor subsequent fetus/es after the birth of the first, as well as maternal bleeding and vital signs
12
New cards
cardiovascular disorders during pregnancy
* Normal changes during pregnancy impact woman with pre-existing cardiac disease.
* Normal heart can compensate for increased workload
* Diseased heart is hemodynamically challenged – if not
well tolerated, can lead to cardiac failure during
pregnancy, L&D, or postpartum period
* Consider degree of disability rather than the type of
diagnosis when considering treatment and prognosis during pregnancy
13
New cards
autoimmune disorders
\-Disrupt the function of the immune system
\-Occur more frequently during reproductive
years \n -Can affect the course of pregnancy or are
detrimental to the fetus \n -Close monitoring before, during and after
pregnancy
14
New cards
what is the presence of gallstones in the bladder
cholelithiasis
15
New cards
cholelithiasis
\-Presence of gallstones in the gallbladder.
\-Hypothesis during pregnancy: Estrogen causes increased
cholesterol secretion of bile; Progesterone promotes decreased gallbladder motility .
\-Increased hormone levels and pressure from uterus interfere with normal circulation and drainage of the gallbladder.
\-Most gallstones asymptomatic; may have epigastric (right upper quadrant pain) that radiates to back or shoulders.
\-May occur spontaneously, or after a high fat meal.
\-Hypothesis during pregnancy: Estrogen causes increased
cholesterol secretion of bile; Progesterone promotes decreased gallbladder motility .
\-Increased hormone levels and pressure from uterus interfere with normal circulation and drainage of the gallbladder.
\-Most gallstones asymptomatic; may have epigastric (right upper quadrant pain) that radiates to back or shoulders.
\-May occur spontaneously, or after a high fat meal.
16
New cards
what is inflammation of the gallbladder
cholecystitis
17
New cards
cholecytitis
\-Inflammation of the gallbladder \n -Causes: gallstone obstructs a cystic duct; pressure from
uterus interfere with normal circulation and drainage of the gallbladder. \n -Older pregnant women with several pregnancies and
history of previous attacks. \n -More severe epigastric pain than cholelithiasis.
\-Nausea, vomiting and fever may also be present.
18
New cards
treatment for cholecystitis
\-Antibiotics, analgesics, IV fluids, bowel rest, and N/G suctioning.
\-Surgery should be postponed until the puerperium.
\-Recurring may require immediate cholecystectomy – preferably during second trimester, but can be performed anytime during pregnancy.
19
New cards
Antepartal Hemorrhagic Disorders
In pregnancy, increases in plasma volume and RBC’s \n ✔meet metabolic demands of mother & fetus ✔protect against potentially deleterious impairment in venous return \n ✔safeguard the mother against the effects of blood loss at birth
\
• Maternal blood loss ↓ oxygen carrying capacity to tissues/organs / fetus.
• Any bleeding in pregnancy↑ risk of maternal and/ or fetal morbidity & mortality
20
New cards
bleeding in pregnancy
\
• Hemorrhage - major cause of death
\
\
• Bleeding in early pregnancy (Trimester 1): mostly spontaneous abortion
\
\
• Causes of late bleeding (Trimester 2 & 3):
– placenta previa
– abruptio placentae
– abnormal implantation and/or development of placenta
– trauma
• Hemorrhage - major cause of death
\
\
• Bleeding in early pregnancy (Trimester 1): mostly spontaneous abortion
\
\
• Causes of late bleeding (Trimester 2 & 3):
– placenta previa
– abruptio placentae
– abnormal implantation and/or development of placenta
– trauma
21
New cards
what might be happening if someone is bleeding in early pregnancy (tri 1)
spontaneous abortion
22
New cards
what are some causes of bleeding in tri 2 and 3 during pregnancy
\-placenta previa
\-abruptio placentae
– abnormal implantation and/or development of placenta
– trauma
\-abruptio placentae
– abnormal implantation and/or development of placenta
– trauma
23
New cards
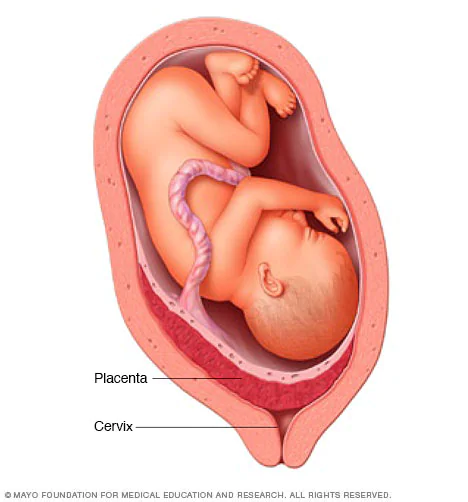
___________________ is a problem during pregnancy when the placenta completely or partially covers the opening of the uterus (cervix).
placenta previa
24
New cards
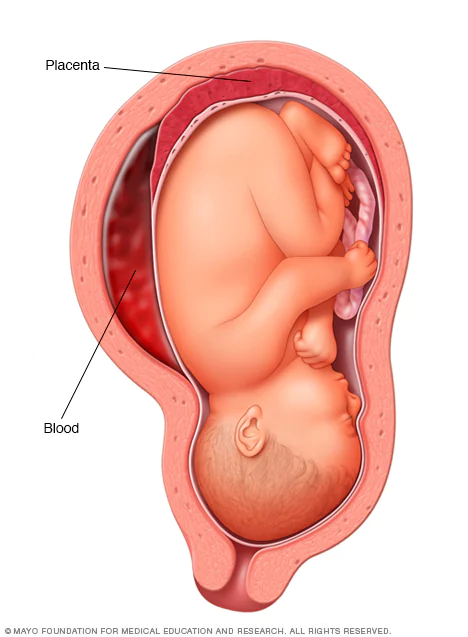
__________________ is defined as the premature separation of the placenta from the uterus.
abruptio placentae
25
New cards
a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks is _________
abortion
26
New cards
types of abortion
\-spontaneous
\-voluntary (elective, therapeutic )
\-voluntary (elective, therapeutic )
27
New cards
nursing care for induced/ elective / voluntary abortion
\-Confirmation of pregnancy and gestation- bimanual exam/US
\- Blood work \n -Pre-abortion counseling \n - Mostly dilatation and curettage and vacuum aspiration
\- Nursing support during procedure \n - Recovery 4-5 hours then home \n - RhoGAM to woman who is Rh negative
28
New cards
client teaching for induced/ elective / voluntary abortion
* Expect some cramping, bleeding like heavy period
* Often- prophylactic antibiotics
* NSAIDs for pain relief
* Avoid douches, sex, tampons for about 2 wks
* Next period- 4 to 6 wks
* Contact Dr if temp increases, chills, abdominal pain, tenderness, excessive or
prolonged bleeding, foul smelling vaginal discharge
* Info re birth control
* Follow up with Dr.
29
New cards
spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
* Incidence- approximately 10-15% of pregnancies
* Causes - genetic abnormalities, uterine or cervical problems,
infections, substance abuse, maternal medical conditions (e.g.
diabetes, hypothyroidism)
\
• Sub groups
\- threatened
\- inevitable \n - incomplete \n - complete \n - missed \n - recurrent (habitual)
\
30
New cards
nursing care for threatened abortion
\
\
THINK CONCEPTUALLY Bleeding/Infection/Pain
* Assessment of pain & bleeding. May require IV
* Blood work- Type, Rh, Hbg, Hct
* Date of LMP
* Obstetric history
* Vital signs
* Bed rest, nutritious diet, adequate hydration
* Decreased Stress
* Nosex
* hCG levels
* Ultrasound - confirmation
* Emotional support -determine meaning of this
pregnancy for woman
31
New cards
threatened abortion
When the symptoms indicate a miscarriage is possible, the condition is called a "threatened abortion."
(This refers to a natural event that is not due to a medical or surgical abortion.)
(This refers to a natural event that is not due to a medical or surgical abortion.)
32
New cards
following a spontaneous abortion
* May require dilatation and curettage (D&C)
* Follow up - phone calls
* Referral as necessary
* May have mood swings
* Expect cramping
* Monitor bleeding
* Assess pain
* Eat foods high in iron and protein
* Refer to support groups
* Avoid pregnancy for at least 2 months to allow recovery
* Other advice - see induced abortion
33
New cards
methods of abortion
\-Surgical and medical (meds) methods
\-Suction curettage or vacuum aspiration
\-Dilatation and Curettage
\-Misoprostol (Prostaglandins)
\-RU 486 (Mifepristone) - ”abortion pill” now available in Canada
\-Mifepristone with misoprostol
\-Suction curettage or vacuum aspiration
\-Dilatation and Curettage
\-Misoprostol (Prostaglandins)
\-RU 486 (Mifepristone) - ”abortion pill” now available in Canada
\-Mifepristone with misoprostol
34
New cards
second trimester abortions
\-Dilatation and Evacuation (surgical) \n -Induction of labour with Misoprostal and Oxytocin (medical)
35
New cards
molar pregnancy.
gestational trophoblastic disease
gestational trophoblastic disease
* Monitoring of hCG levels for 12 months
* Risk of Choriocarcinoma
* Avoidance of pregnancy for 12
months
36
New cards
ectopic pregnancy
* Life-threatening condition
* Products of conception implant anywhere other than the uterus
* Incidence - 1.5% pregnancies
* Sites- most in fallopian tubes, particularly in ampulla, Less common- abdominal cavity, ovary, cervix
* Leading cause of infertility
37
New cards
cuases / risk factors of ectopic pregnancy
(blocked or narrowed fallopian tubes)
* previous pelvic infection,
* history of chlamydia infection,
* previous appendicitis,
* history of infertility
* or cesarean birth,
* age greater than 35,
* smoking
38
New cards
management of ectopic pregnancy
* Non surgical- methotrexate (unruptured) disrupts growth of developing embryo → cessation of pregnancy
\
* Surgical - Removal by salping__ostomy__. Or If tube is ruptured→laparoscopic salping__ectomy__
\
* Surgical - Removal by salping__ostomy__. Or If tube is ruptured→laparoscopic salping__ectomy__
39
New cards
ectopic pregnancy
Diagnosis :
* – Rule out other conditions
* – Ultrasound – transvaginal, abdominal, laparoscopy
to dx
* – If previous positive pregnancy test, repeat hCG
levels over 48 hours
\
Treatment:
* Drugs (unruptured)
* Laparoscopic surgery
* Supportive nursing care – gentle upon palpation, may
fear for safety and express concern for future fertility, psychological health with pregnancy termination
\
safety and express
* – Rule out other conditions
* – Ultrasound – transvaginal, abdominal, laparoscopy
to dx
* – If previous positive pregnancy test, repeat hCG
levels over 48 hours
\
Treatment:
* Drugs (unruptured)
* Laparoscopic surgery
* Supportive nursing care – gentle upon palpation, may
fear for safety and express concern for future fertility, psychological health with pregnancy termination
\
safety and express
40
New cards
clinical manifestations of ectopic pregnancy
==-positive pregnancy==
==-vaginal bleeding==
==-abdominal pain==
\
\
If rupture occurs → Increased pain from blood in perineum. Typically referred shoulder tip pain caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm
Can lead to severe hemorrhage and shock
Cullen’s sign – ecchymotic blueness around umbilicus (ruptured ectopic pregnancy)
Bladder Pain \n Dizziness, pallor, and nausea
==-vaginal bleeding==
==-abdominal pain==
\
\
If rupture occurs → Increased pain from blood in perineum. Typically referred shoulder tip pain caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm
Can lead to severe hemorrhage and shock
Cullen’s sign – ecchymotic blueness around umbilicus (ruptured ectopic pregnancy)
Bladder Pain \n Dizziness, pallor, and nausea
41
New cards
Placenta and Cord anomalies can also be a significant source of __________ in pregnancy.
bleeding
42
New cards
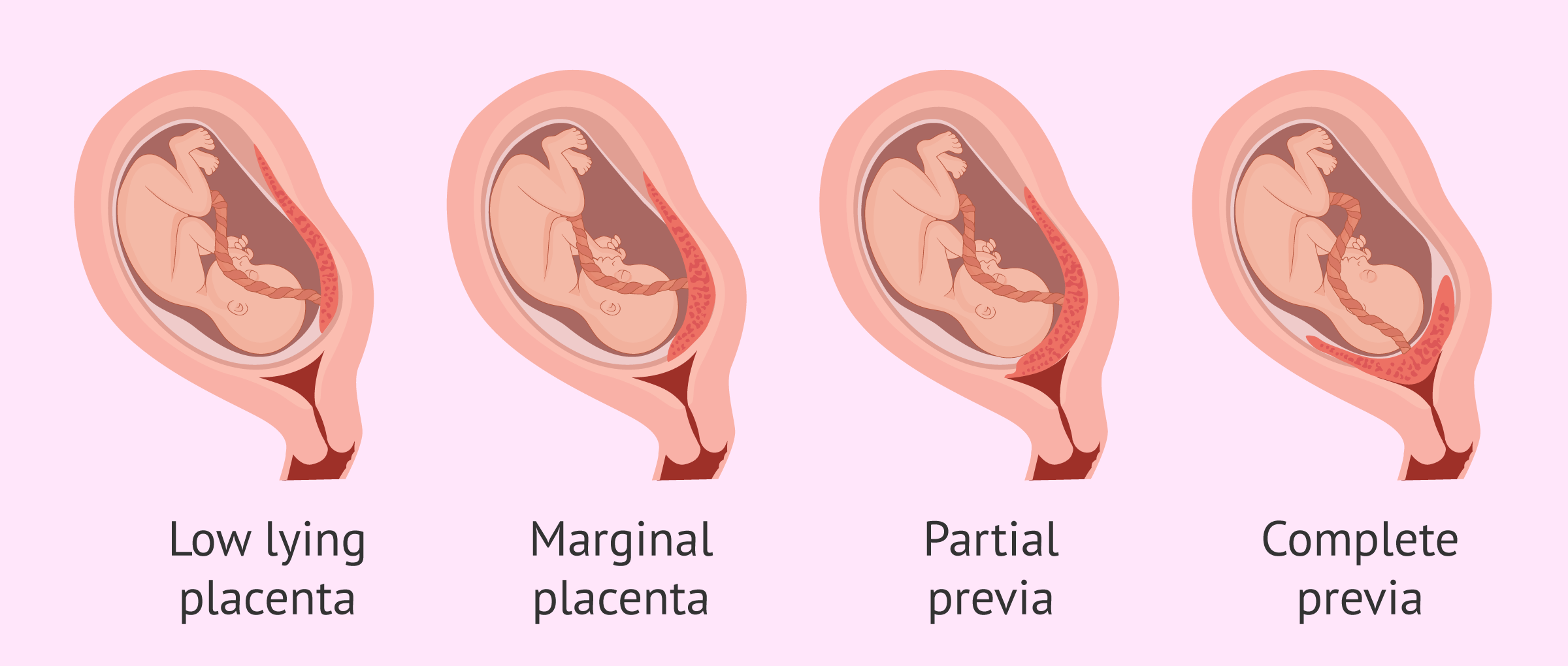
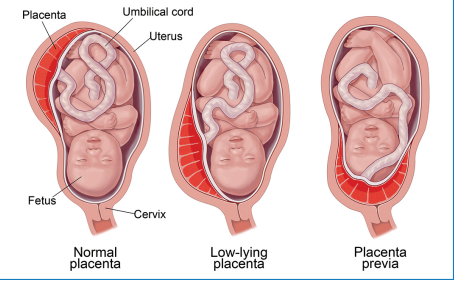
placenta previa
• Abnormal implantation of the placenta in the Lower uterine segment (LUS) , over or very close to the internal cervical os.
\
• Classified according to degree to which internal cervical os is covered by placenta:
⮚ Complete placenta previa
⮚ Partial Placenta previa \n ⮚ Marginal placenta previa
⮚ Low lying placenta
43
New cards
complete placenta previa
The placenta is completely covering your cervix, blocking your vagina.
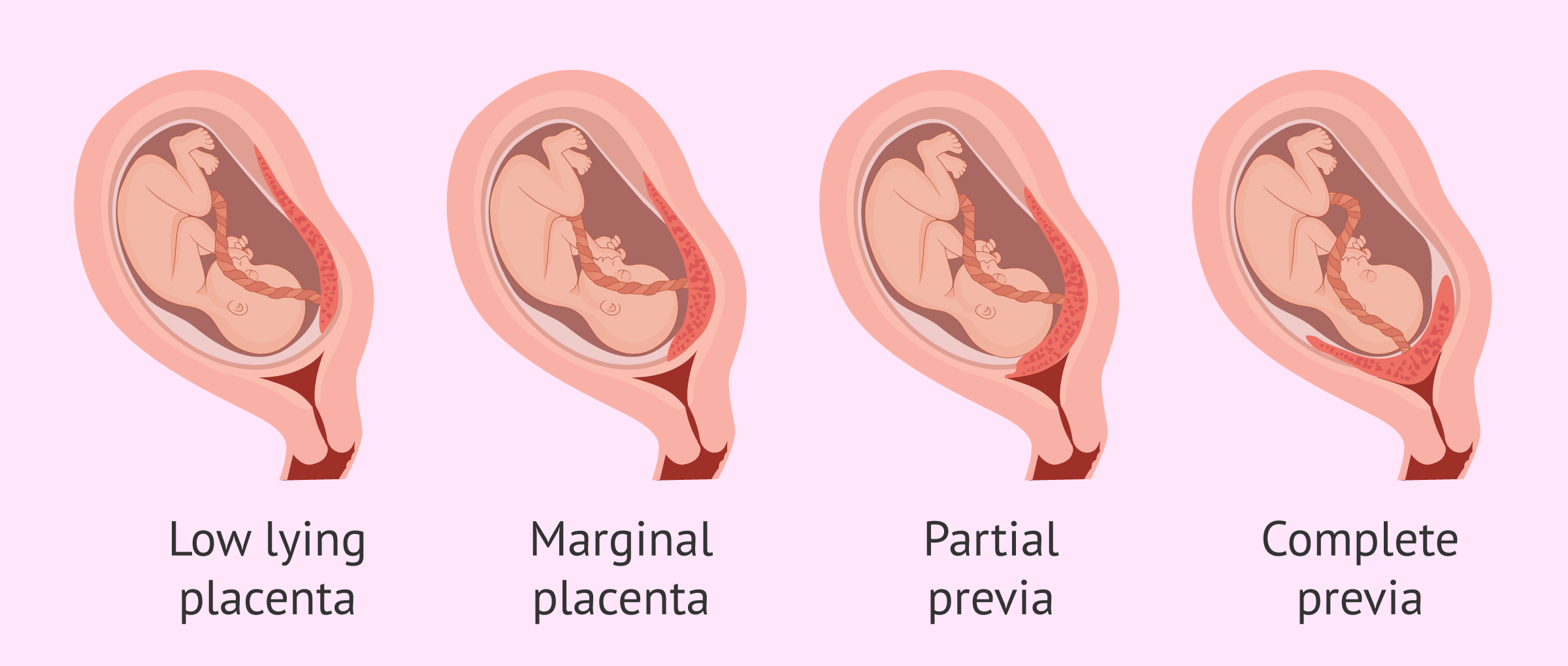
44
New cards
partial placenta previa
The placenta partially covers your cervix.
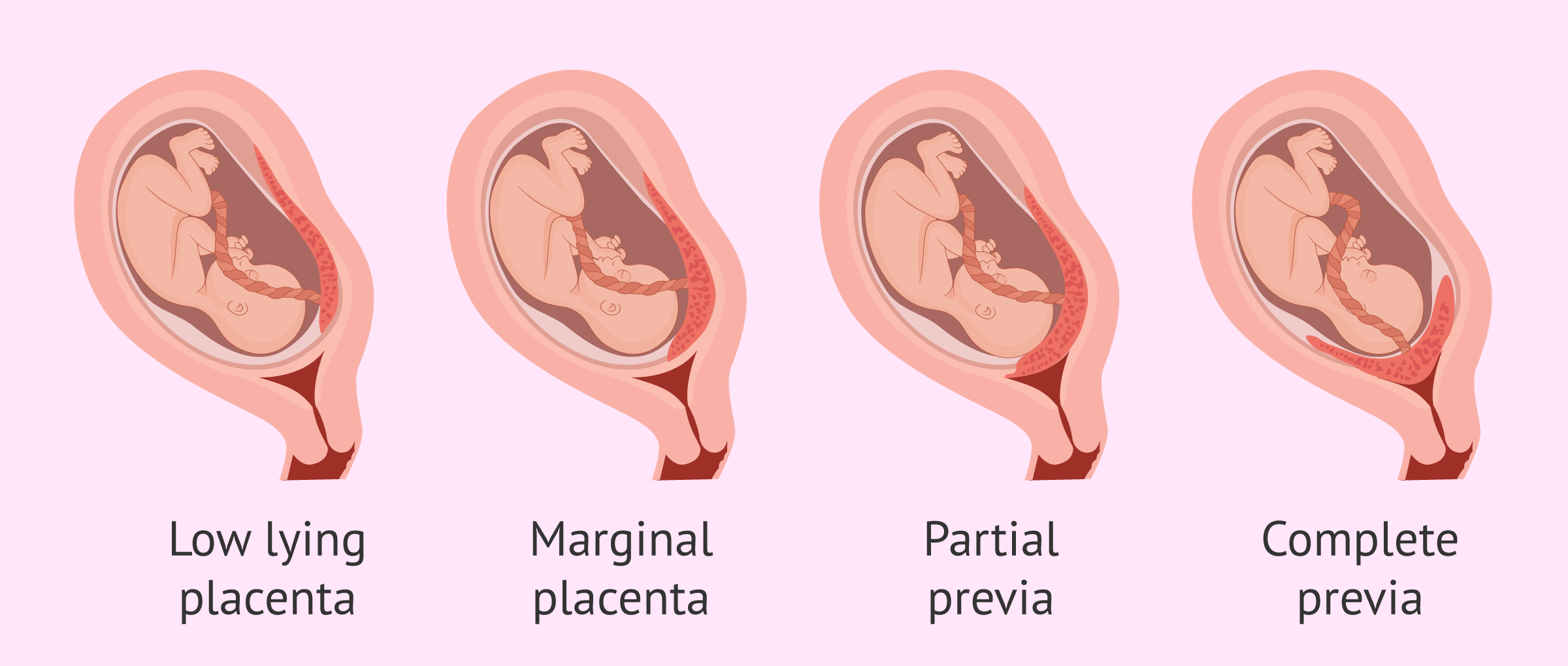
45
New cards
__________ placenta previa is when The placenta is positioned at the edge of your cervix.
marginal
46
New cards
low lying placenta
47
New cards
out of these placenta previas:
⮚ Complete placenta previa
⮚ Partial Placenta previa \n ⮚ Marginal placenta previa
⮚ Low lying placenta
\
which 2 are not as risky
⮚ Complete placenta previa
⮚ Partial Placenta previa \n ⮚ Marginal placenta previa
⮚ Low lying placenta
\
which 2 are not as risky
⮚ Marginal placenta previa
⮚ Low lying placenta
⮚ Low lying placenta
48
New cards
placenta previa manifestations
usually ==**painless, vaginal bleeding, bright red.** ==
With stretching and thinning of LUS, there is a disruption in placental blood vessels. Risk of bleeding ↑ as term approaches & effacement & dilatation occur. This disrupts the placental attachment. Uterus isn’t able to contract & stop blood flow. May have several bleeding episodes
▪ Uterus - soft and non tender
\-vital signs may be normal because we have 40-45% extra blood during pregnancy.
\-fetus may be in abnormal presentation
\-blood clotting usually normal
\-signs of fetal compromise (hypoxia) if maternal shock or extensive placental detachment
\-fetal/neonatal anemia possibly
\
49
New cards
complications of placenta previa
• Preterm rupture of membranes
• Preterm labour and birth
• Anemia
• Uterine rupture
• Postpartum infection
• Postpartum hemorrhage
• Fetal death
• Preterm labour and birth
• Anemia
• Uterine rupture
• Postpartum infection
• Postpartum hemorrhage
• Fetal death
50
New cards
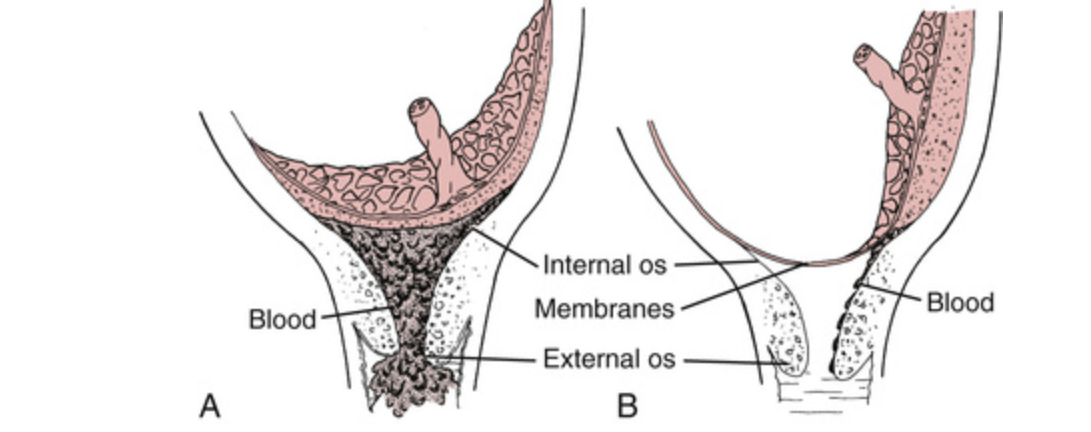
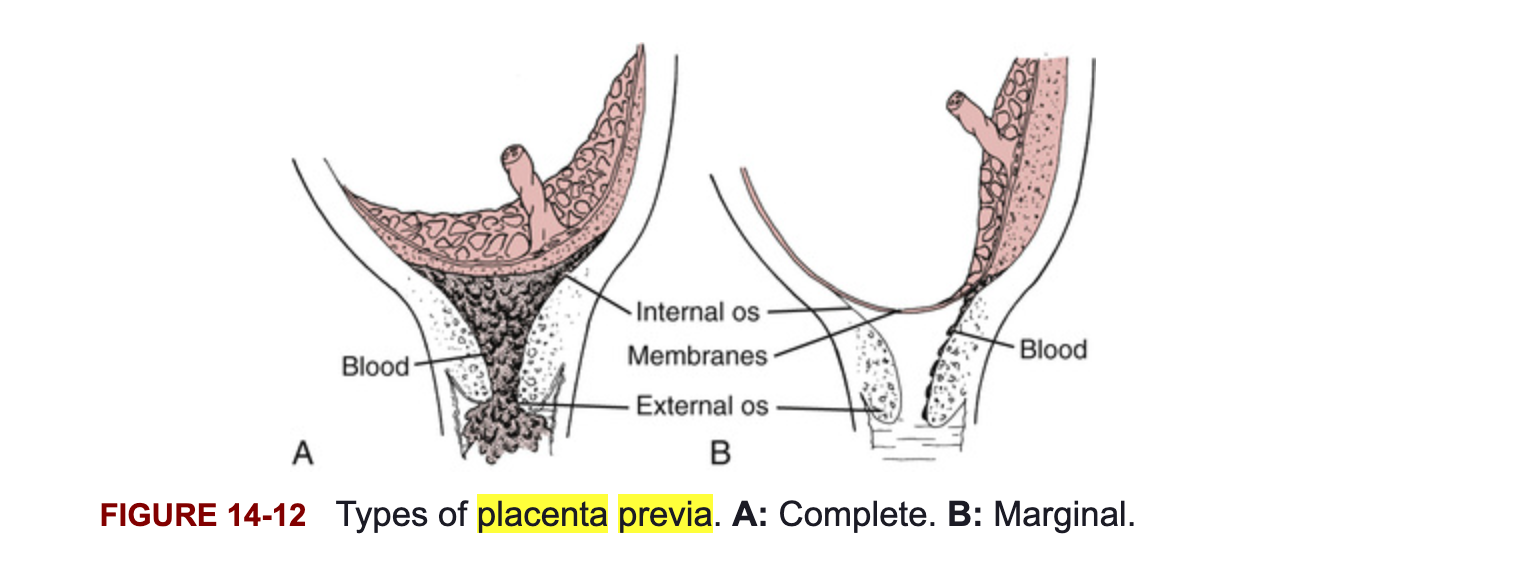
what is B
Marginal placenta previa
51
New cards
placenta previa management
* **Management- depends on length of gestation and amount of bleeding:**
* **Home care possibly if stable, no active bleeding and can get to hospital quickly. Otherwise - hospitalization**
* **C/S for complete Placenta Previa**
* **Delivery is necessary if bleeding is sufficient to jeopardize mother or**
**baby - C/S**
* **If woman is less than 36 weeks and is not in labour, bleeding has**
**stopped – rest and close observation to allow time for fetus to**
**mature.**
\
* Monitor pads for amt of bleeding
* Bed rest or bed rest with BRP if not
bleeding; limited activity
* Vitals
* Oxygen if required
\
* Monitor fetus i.e., electronic fetal monitoring, NST, BPP
* Assess blood loss, symptoms of shock, any contractions?
* IV fluids
* Have blood X matched
* Corticosteroids if < 34/40
* No PV exam
* Psychosocial support
52
New cards
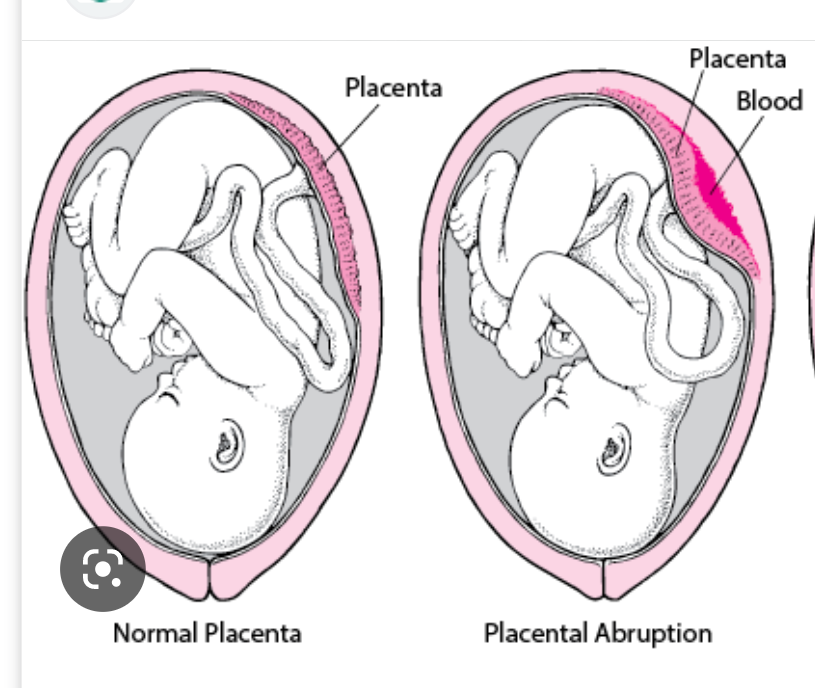
abruptio placentae
• Premature separation of a normally implanted placenta from the uterine wall
• Accounts for significant maternal & fetal morbidity and mortality
\
• Risk factors : -trauma, smoking, cocain use, multiple pregnancy, too much amnionitic fluid, diabeteies
53
New cards
abruptio placentae
• Various Degrees of placental abruption. May be a Partial abruption or Complete Abruption.
\
• It also occurs in various places of placental attachment. Therefore, there are several types:
• Marginal (partial: around edges) / Apparent
• Central / Concealed \n • Mixed or combined
54
New cards
clinical manifestations of placental abruption
* **Sudden, sharp, and severe onset of abdominal or back pain**
* **Uterus- firm and board like**
* **May be visible bleeding (dark red blood or port**
**wine stained amniotic fluid) or concealed**
* **Vital signs**
* **May have signs of shock (maternal**
**hypovolemia)**
* **Uterine contractility**
* ▪ **Often impaired clotting**
* ▪ **Fetal presentation - usually normal \**
* **Fetal response depends on amount of**
**blood loss and extent of uteroplacental insufficiency. Often decreased variability or late/variable decels on FHR**
55
New cards
complications of abruptio placentae
* **Complications - preterm birth, SGA baby, neuro damage to baby from hypoxia, DIC, PPH, infection**
* **Management – depends on maternal and fetal status**
* **Mother may need to be stabilized**
* **If preterm, try to preserve pregnancy as long as possible. Steroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity if bleeding is stabilized or mild abruption**
* **If condition deteriorates, cesearean birth.**
* **Management – depends on maternal and fetal status**
* **Mother may need to be stabilized**
* **If preterm, try to preserve pregnancy as long as possible. Steroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity if bleeding is stabilized or mild abruption**
* **If condition deteriorates, cesearean birth.**
56
New cards
nursing care for abruptio placentae
* • **Close monitoring of mother & fetus**
* **Observe for shock, bleeding**
* **Measure abdomen/ fundal**
**height- accumulation of blood Assess discomfort**
* **Assess for contractions**
* **Establish IV access and give IV**
**fluids**
* **Catheter - intake & output**
* **Monitor fetal status**
* **Oxygen if fetal distress**
* **May need corticosteroids**
* **Psychosocial support**
* **Observe for shock, bleeding**
* **Measure abdomen/ fundal**
**height- accumulation of blood Assess discomfort**
* **Assess for contractions**
* **Establish IV access and give IV**
**fluids**
* **Catheter - intake & output**
* **Monitor fetal status**
* **Oxygen if fetal distress**
* **May need corticosteroids**
* **Psychosocial support**
57
New cards
• **Abruptio placentae and placenta previa are differentiated by:**
* type of bleeding :Bright red (periva); Dark red (abruption)
\
\
* uterine tonicity: Soft non tender (pervia); Board like (abruption)
\
* presence or absence of pain: Sharp sudden pain (abruption); Painless (Previa)
\
\
* uterine tonicity: Soft non tender (pervia); Board like (abruption)
\
* presence or absence of pain: Sharp sudden pain (abruption); Painless (Previa)
58
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
bright red bleeding
bright red bleeding
placenta previa
59
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
dark red bleeding
dark red bleeding
abruptio placenta
60
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
uterine atony: soft non tender
uterine atony: soft non tender
placenta previa
61
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
uterine atony: board like
uterine atony: board like
abruptio placentae
62
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
sharpe sudden pain
sharpe sudden pain
abruptio placentea
63
New cards
Abruptio placentae or placenta previa?
painless
painless
placenta previa
64
New cards
management of late pregnancy bleeding requires immediate evaluation
• **Care based on:** \n **> Gestational age** \n **> Amount of bleeding**
**> Fetal condition**
65
New cards
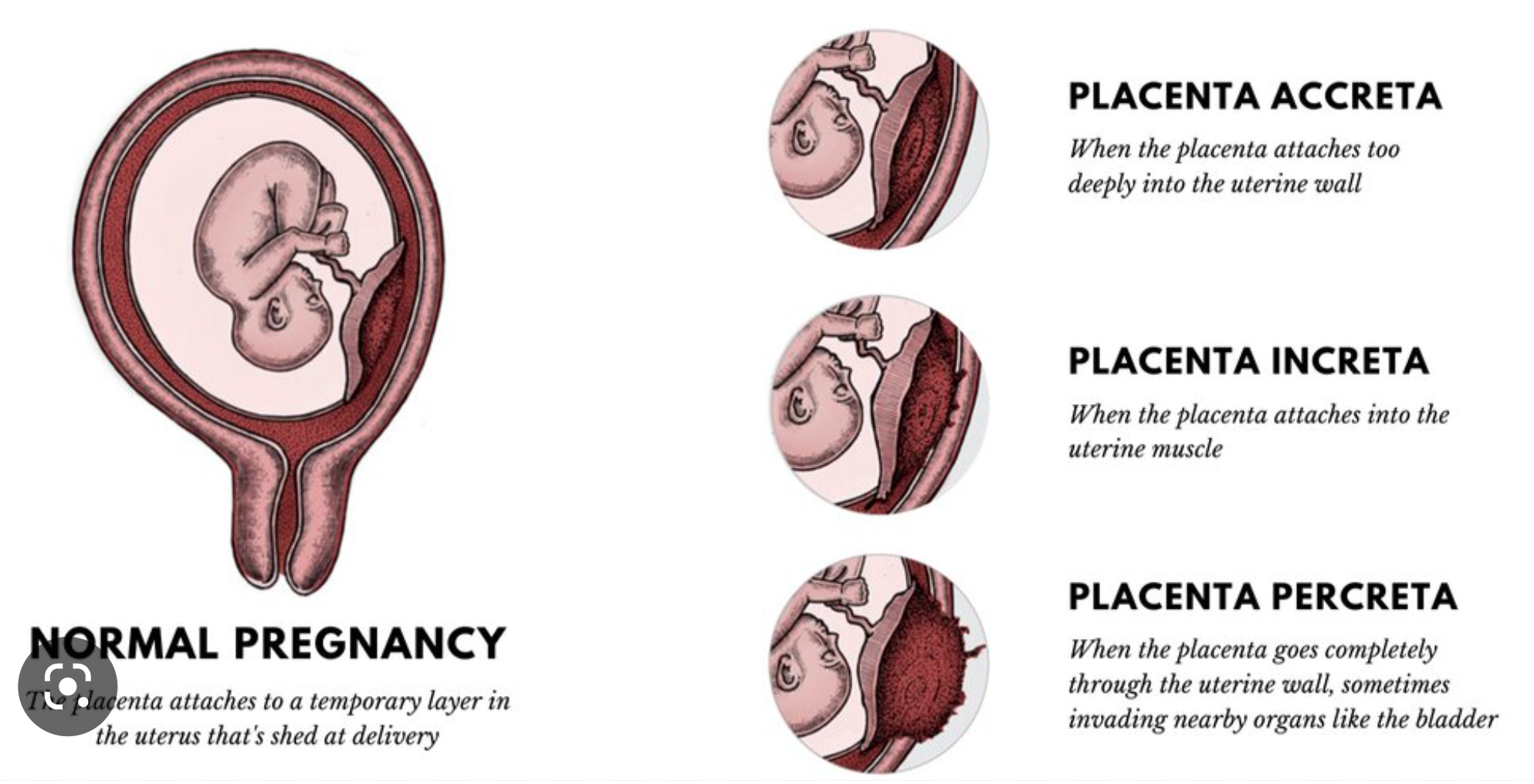
invasive placentas
placenta impants deeper than normal.
\
Invasive placenta is the term used to describe the condition when the whole or part of the placenta grows into the uterine wall and fails to detach from it during the delivery.
placenta has to be delivered (usually a c/s). hysterectomy if they can’t get placenta out.
\
• **Three types of invasive placentas:**
• Placenta Accreta \\n • Placenta Increta \\n • Placenta Percreta
\
Invasive placenta is the term used to describe the condition when the whole or part of the placenta grows into the uterine wall and fails to detach from it during the delivery.
placenta has to be delivered (usually a c/s). hysterectomy if they can’t get placenta out.
\
• **Three types of invasive placentas:**
• Placenta Accreta \\n • Placenta Increta \\n • Placenta Percreta
66
New cards
placenta accreta
Slight penetration of myometrium
67
New cards
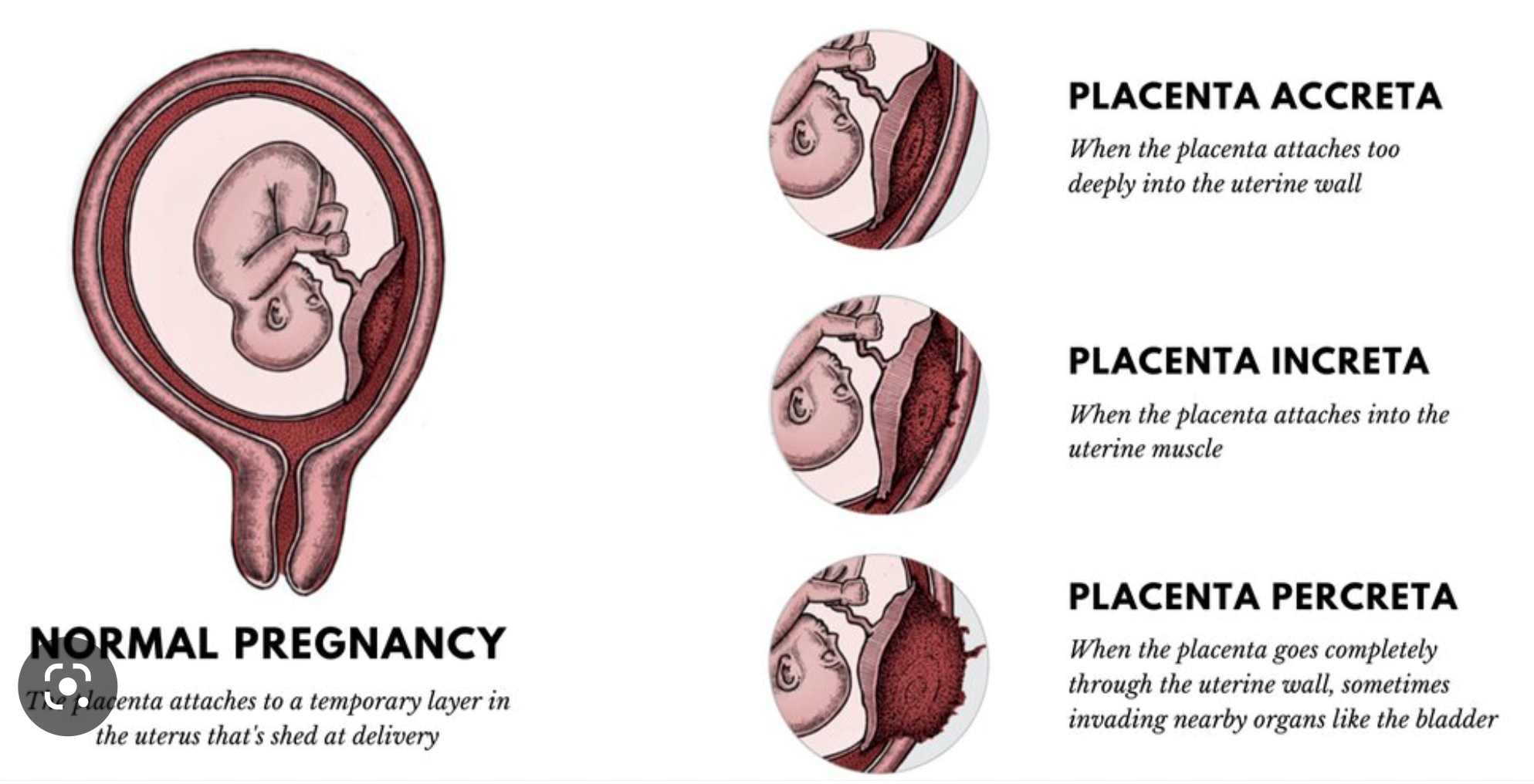
placenta increta
Deep penetration of myometrium
68
New cards
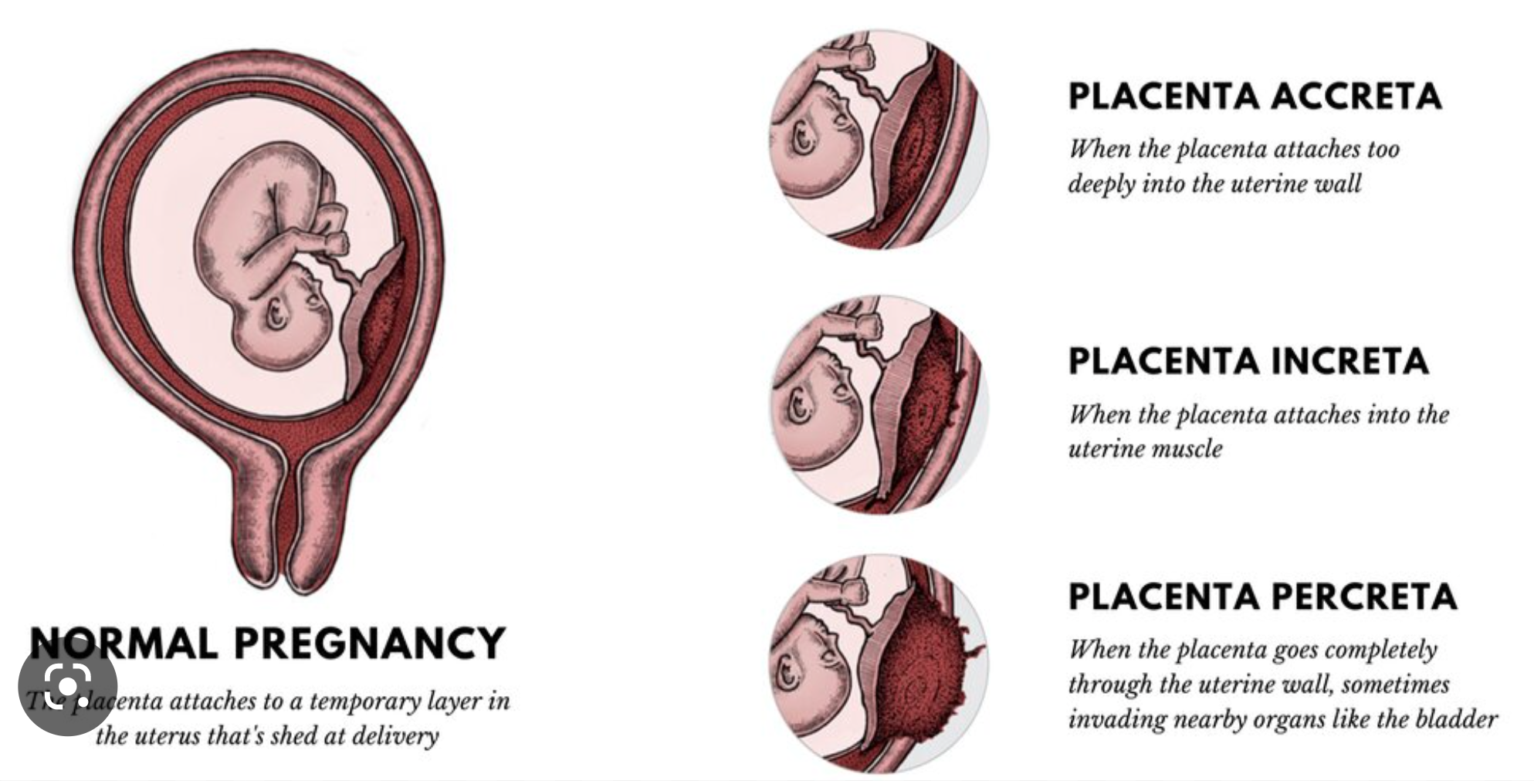
placenta percreta
Perforation of uterus
69
New cards
cord insertion anomalies
• **Velamentous cord insertion (Vasa Previa) – fetal vessels running into or coming within close proximity to the internal cervical os**
70
New cards
clotting disorders in pregnancy
**• Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)**
\
\-An over activation of the clotting cascade and the fibrinolytic system resulting in depletion of platelets and clotting factors
\-Always a secondary diagnosis
\-Often triggered by release of large amounts of thromboplastin:-abruptio placentae, retained demised fetus, amniotic fluid embolus, severe pre- eclampsia and sepsis also damage vasculature integrity
\
\-An over activation of the clotting cascade and the fibrinolytic system resulting in depletion of platelets and clotting factors
\-Always a secondary diagnosis
\-Often triggered by release of large amounts of thromboplastin:-abruptio placentae, retained demised fetus, amniotic fluid embolus, severe pre- eclampsia and sepsis also damage vasculature integrity
71
New cards
S&S of clotting disorders in pregnancy
• unusual spontaneous bleeding ie.) gums or nose \n • petechaie (especially after blood pressure cuff inflation)
• excessive bleeding from puncture sites ie.) IV,
venipuncture site \n • tachycardia and diaphoresis
72
New cards
management of clotting disorders in pregnancy
• correction of underlying cause \n • IV fluids to replace losses, \n • Packed RBC’s to maintain circulation and oxygen delivery
• Fresh frozen plasma to replace clotting factors \n • Administration of platelets
73
New cards
insulin is a growth hormone… so if the baby produces more insulin.. they get ?
big
74
New cards
pre-gestational diabetes
type 1 or 2 diabetes present prior to pregnancy
75
New cards
* Normal pregnancy-diabetogenic state in latter part of second trimester and third trimester-need for glucose increased
.
76
New cards
* Glucose transport to fetus facilitated by diffusion
* Maternal insulin does not cross placenta
* By 10 weeks, fetus secretes own _____ to use Mom’s _____
insuline.
glucose
glucose
77
New cards
Trimester 1
* Maternal glucose levels ^^drop below non pregnant values^^
* Influence of estrogen & progesterone → increased insulin production → increased peripheral glucose utilization. Fetus also using more glucose so leads to decreasing maternal levels
* Also possible N&V and appetite loss
* Increased chance of hypoglycemia
* Decreased need for insulin
78
New cards
trimester 2 & 3
* Hormonal changes→**decreased tolerance to glucose**
* Increased levels of human placental lactogen, estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, prolactin & insulinase→**increase insulin resistance** (glucose sparing mechanism ensuring abundant supply of glucose to fetus)
* Placenta begins to manufacture insulinase
* Results in **increased need for insulin** at beginning of Trimester 2 and increased
danger of hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis
79
New cards
normal glucose level for someone
4-7
80
New cards
complications of diabetes during L&D
* Labour is a form of exercise and has a glucose lowering effect. In addition, laboring mother is often maintained on an NPO status, further complicating hypoglycemia. May be given IV therapy to maintain normoglycemic state.
* No additional insulin is needed during labour; sufficient glucose should be infused to keep the woman from becoming ketotic from the prolonged period of starvation.
* There is clear evidence that neonatal hypoglycemia is directly related to maternal hyperglycemia during labour
* Birth Trauma from larger than average size newborn
* Higher incidence of failure to progress, Cesarean delivery
81
New cards
diabetes during L&D:
birth trauma from larger than average newborn size
birth trauma from larger than average newborn size
bigger baby.. more risk for tears, dystocia, c section, bigger baby = more risk for post partum hemorrhage
82
New cards
pre-gestational diabetes
* Labour
* Postpartum-abrupt drop in placental hormones, cortisol and
insulinase
* Should be encouraged to breastfeed. Protective effect
* Substantial decrease in insulin requirements
* Takes 7-10 days to re-establish CHO homeostasis if not
breastfeeding
* Lactation uses increased glucose so insulin requirements low until weaning
83
New cards
influence of pregnancy on pre-existing diabetes
* May have drastic alteration in insulin requirements
* Insulin requirements may double or quadruple by the end of
pregnancy
* May be more difficult to control
* May accelerate progress of vascular disease
84
New cards
most womens bodies can compensant for the extra needed insulin during pregnancy. some cant…. so then get ?
gestational diabetes (GDM)
85
New cards
Gestational Diabetes (GDM)
* Carbohydrate intolerance of variable severity with onset or first recognition during pregnancy
* Incidence approximately 3-5% of pregnancies in non-aboriginal women, 8-18% in aboriginal women
* Usually diagnosed after week 20 of gestation
* Fetal nutrient demands increase in later T2 and T3
* Maternal nutrient ingestion also increases→raises blood glucose. At the
same time, maternal insulin resistance increases. Insulin demands –> Increase 3-fold
\
* Usually disappears after pregnancy but may develop diabetes later
* Risk factors (obesity, bad eating habits, family hx)
* Many are asymptomatic- detected by glucose testing 24-28 weeks
gestation
* Treatment- diet mostly, possibly insulin
* Need to teach about S & S of hypo and hyperglycemia
86
New cards
Dx of gestational diabetes
\-50 GM Glucose Challenge test given at 24 – 28 weeks pregnancy 1 hr Post Glucose taken
\-If < 7.8 mmol/L→Normal value \n
\-7.8 – 11 mmol/L→retest with 75 gm Glucose challenge test with fasting PG, 1hrPG, 2hrPG. If
one of the three blood levels meets or exceeds \n (FPG > 5.3 mmol/L; 1hrPG > 10.6; 2 hrPG > 9 mmol/L)→ Gestational Diabetes
\
\-> 11.1 mmol/L →Gestational Diabetes
\-If < 7.8 mmol/L→Normal value \n
\-7.8 – 11 mmol/L→retest with 75 gm Glucose challenge test with fasting PG, 1hrPG, 2hrPG. If
one of the three blood levels meets or exceeds \n (FPG > 5.3 mmol/L; 1hrPG > 10.6; 2 hrPG > 9 mmol/L)→ Gestational Diabetes
\
\-> 11.1 mmol/L →Gestational Diabetes
87
New cards
management of pre-gestational / gestational diabetes
\
Preconception counselling
Nutrition
Urine testing
Fetal surveillance
Glucose checks
Insulin
Exercise
\
88
New cards
Lack of maternal glycemic control before conception and in T1 of pregnancy may be responsible for fetal congenital __________
malformations
89
New cards
\
key point - diabetes
key point - diabetes
Maternal insulin requirements increase as pregnancy progresses and may double to quadruple by term as a result of insulin resistance, created by placental hormones, insulinase, and cortisol
90
New cards
Key Points - diabetes
* After birth levels decrease dramatically
* Breastfeeding affects insulin needs
* Poor glycemic control before and during pregnancy can lead to maternal complications such as miscarriage, infection and dystocia caused by fetal macrosomia
* Careful glucose monitoring, insulin administration when necessary, and dietary counseling are used to create a normal intrauterine environment for fetal growth and development in pregnancy complicated by diabetes mellitus
* Because GDM is asymptomatic mostly, routine screening during pregnancy is necessary
.
91
New cards
Infant of a mother with diabetes
▪Good glucose/A1C control prior to conception is essential
\
▪Appearance
\-**May be** **LGA** - at @@risk for injury@@ at delivery \n -**May be** **SGA** due to @@impaired uterine flow@@ causing compromised placental functioning
92
New cards
an infant of a mother with diabetes will be at risk for ?
poor glucose control post birth
93
New cards
hypoglycemia
• Sustained state of hyperglycemia in pregnancy leads to hyperinsulinism.
• At birth, glucose supply is cut.
• Glucose depleted and leads to hypoglycemia in NB
94
New cards
infant of a mother with diabetes
▪At risk for developing respiratory distress & RDS (hyperinsulinemia in fetus alters surfactant production)
▪Increased risk of congenital abnormalities e.g., CHDs, spinal defects
▪Risk of hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, hypomagnesemia, polycythemia, cardiomyopathy
95
New cards
______________ is the most common medical complication in pregnancy
hypertension (High blood pressure)
96
New cards
pre-existing hypertension is hypertension present before pregnancy or diagnosed before week ___ of gestation
20
97
New cards
gestational hypertension
\- Onset of hypertension @@**after week 20** @@of pregnancy in a **previously normotensive** woman
\n - Systolic BP ≥140, diastolic BP ≥90
98
New cards
blood pressure of gestational hypertension
Systolic BP ≥140, diastolic BP ≥90
99
New cards
__________ is hypertension in pregnancy after week 20 + proteinuria ( high levels of protein in your urine)
preeclampsia
100
New cards
high levels of protein in urine indicate ________ damage
kidney