Hospitality and Tourism
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Definition of Food Danger Zone
Temperature range where bacteria begins to multiply rapidly.
Definition of Cross Contamination
The transfer of bacteria to food from another food, piece of equipment or work surface.
What is the main cause of accidents in the cafeteria?
Carelessness.
5 Rules of carrying a knife
Hold knife firmly by the handle.
Knife tip points towards the floor.
Knife held firmly at your side (arms length).
Cutting edge facing behind you.
One free hand.
All accidents in the cafeteria can be divided into 5 groups.
Falls
Burns
Strains and sprains
Cuts
Electrocution
Assume every —— & —— is hot!
Pot and pan
A knife is falling! What should you do?
Let it fall. Don’t not touch it.
Never put a knife in a sink full of hot —— water.
Soapy
What class of fire involved combustible metals?
Class d
What class of fire deals with commercial kitchens?
Class K
Fire needs three things to live:
Food (igniters), oxygen, and temperature
Fire Extinguishers: PASS
P = pull the pin
A = aim the nozzle
S = squeeze the lever
A = sweep back and forth
Sanitation has three important guidelines:
How clean we keep the food service area
How to keep food free from contamination (food poisoning)
Understand and control bacteria
Salmonella
Raw chicken, eggs, unpasteurized dairy
E-coli
Ground beef
Staphylococcus
The food service worker (most common)
Botulism
Improper canning
Bacillus Cereus
Rice, potatoes or beans
Please list the following conditions for bacteria to grow & multiply FATTOM
F = food
A = Acid
T = Time
T = Temperature
O = Oxygen
M = Moisture
What’s the most deadly bacteria?
Botulism
What bacteria has spores forming bacterium?
Bacillus Cereus
What is the most common bacteria?
Staphylococcus
Bacteria multiply and doubles every —— minutes.
20
When you have a knife in your hands, always
Keep yours eyes on the blade.
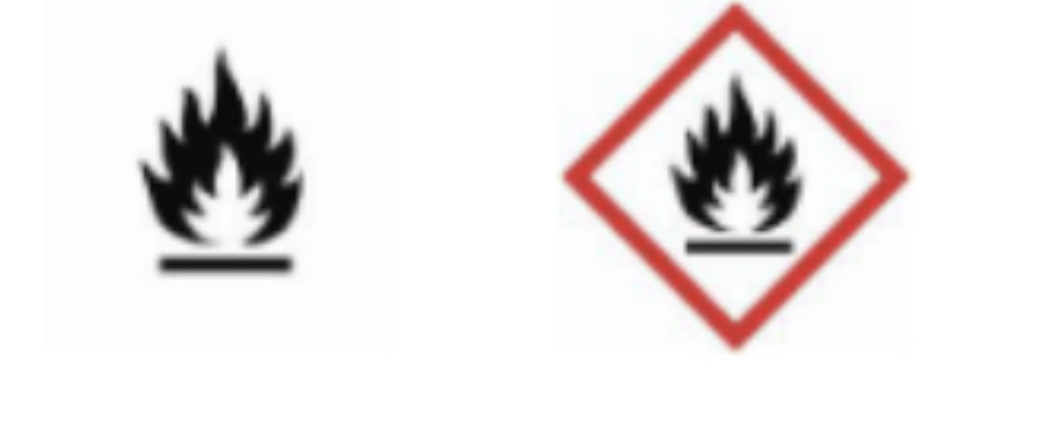

Flammable
It can catch on fire. Burns.

Oxyidier
This means it creates extra oxygen to fires. It starts easier and burns faster.

Explosive
It can explode. Extremely reactive.
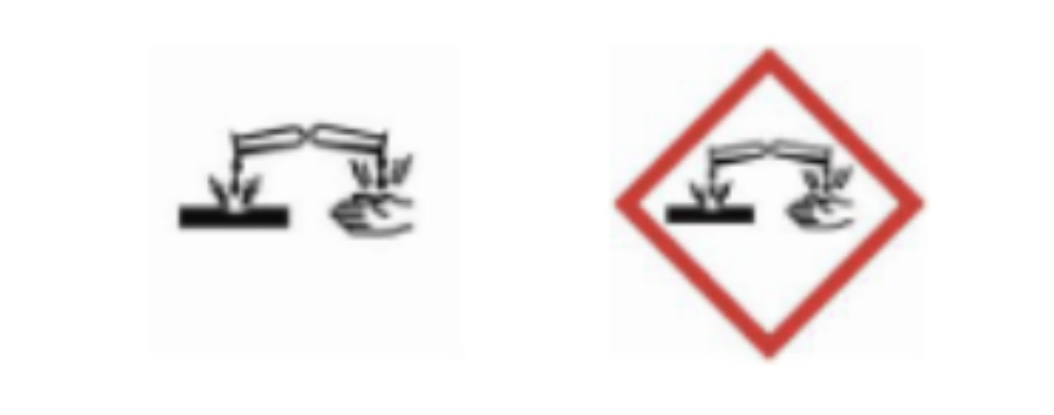
Corrosive
It causes damage to containers or people. Damages metals.
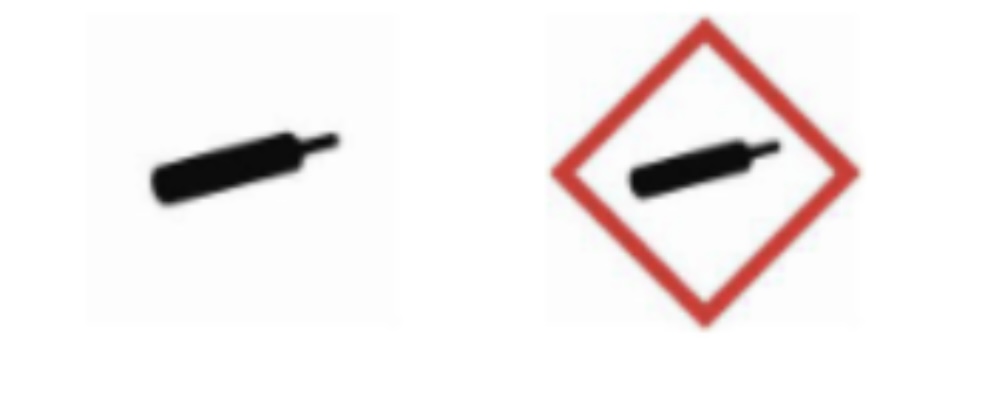

Gas under pressure OR Gas cylinder
Catches fire or explodes. Dangerous to breath.

Acute Toxicity
It can make poison or kill you. If you touch it, swallow or breath it.

Exclamation Mark OR Skin/eye irritation
Can cause skin or eye problems. Reminds you to wear protective wear.
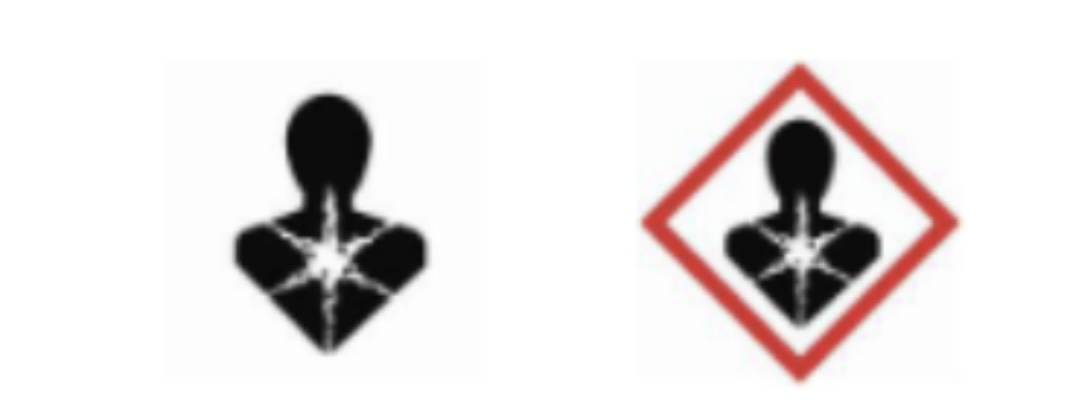

Health Hazard
Products you make not see (in air). Small exposures over a long period of time may cause health issues.

Biohazard
It can cause disease or sickness in humans or animals.
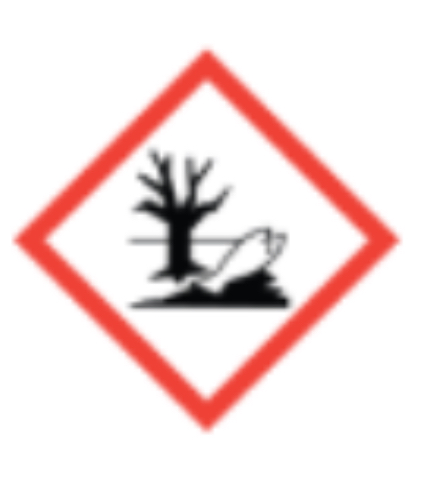

Environment
It can damage water and it’s wildlife.
Types of workplace hazards
Physical hazards
Chemical hazards
Biological hazards
Psychosocial hazards
Safety Hazards
Fire hazards
Environmental hazards
Radiological hazards
Other hazards
Classes of fires
Class A
Class B
Class C
Class D
Class K
Class A
Involves ordinary combustibles such as wood, paper, and cloth
Class B
Includes flammable liquids like gasoline, oil, grease
Class C
Involves electrical fires
Class D
Encompasses fires involving combustible metals
Class K
Specifically designed for fires involving commercial kitchens involving cooking oils and fast
Safe food storage
Refrigerate perishable foods promptly at or below 40F (4C) to slow the growth of bacteria
Keep the freezer at 0F (-18C) or lower for long-term food storage
Cooking to Safe Temperatures
Chicken and turkey: 165F (74C)
Ground meats: 160F (71C)
Pork, veal, and lamb: 145F (63C)
Fish: 145F (63C)
Reheat leftovers to at least 165F (74C)
Hot and Cold Holding
Keep hot foods hot (above 140F or 60C) and cold foods cold (below 40F or 4C) to prevent bacterial growth.
Time and Temperature Contol
The Temperature Danger Zone is the temperature range where bacteria multiplies rapidly and produces toxins (between 40F or 4C and 140F or 60C).
TOXIN: a poisonous chemical produced by a microorganism.
Limit the time that perishable foods spend in the danger zone (between 40F or 4C and 140F or 60C).
Discard food that has been left in the danger zone for more than two hours (or one hour if the temperature is above 90F or 32C).
Proper Hand Washing
Wet Hands
Apply Soap
Lather Hands
Scrub Hands (20 seconds)
Rinse thoroughly
Dry hands
Use a paper towel to turn off faucet
What a food borne illness
A food borne illness is a disease acquired from eating or drinking contaminated food or water
Symptoms of a food borne illness
Fever
Headache
Nausea
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Stomach cramps
What 6 things does bacteria need to grow
Food
Acid
Time
Temperature
Oxygen
Moisture
What 4 most common ways bacteria can contaminate food products
People
Raw food
Insects/Rosents
Soil