Maintenance and blood sampling
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What does the centrifuge do
Spins a substance to separate the fluid portion from the solid content
Speeds up the natural process of gravity
What is the fluid portion alternatively known as
Supernatant
What is the solid content alternatively known as
Sediment
What can the centrifuge spin down
PCV
TP
Urine sediment
Blood
Faeces
Centrifuge safety rules
Do not open while still running
Don’t forget the plate
Must be balanced properly
How fast is blood spun and how long for
10,000 rpm
5 minutes
How fast is urine spun and how long for
1000-2000 rpm
3-5 minutes
How fast is serum spun and how long for
2.500-3,000 rpm
10-15 minutes
Must clot for 15-20 minutes before spinning
Centrifuge more info
Clean regularly
Check for broken glass
Replace the rubber ring (depending on use will depend on how often)
Flat strong surface required (ideally away from microscope)
Use of heparin tube
Taking blood directly from the patient
Use of plain tubes
Taking blood from a tube/sample
What is a Hawksley reader used for
To read a PCV
Normal PCV range for a cat
24%-35%
Normal PCV range for a dog
35%-45%
Sighthound- 45%-55%
What causes a high PCV
Dehydration (less serum = more RBCs and higher PCV)
Polycythaemia- produced more RBCs than normal (usually hypoxic patients)
Acute bleed- spleen contracts, PCV isn’t actually higher it will just read higher at first
What causes a low PCV
Anaemia
What does a refractometer measure
Specific gravity (SG) of urine
Total protein (g/L OR g/DL) of serum
What is the SG of diluted water
1.000
What is the prism
Glass screen of refractometer
How to calibrate a refractometer
Apply 2 drops of distilled water to prism
Adjust using a screwdriver if necessary
Ensure SG of distilled water is 1.000
Normal TP of cats
66-84 g/L
Normal TP of a dog
55-72 g/L
What does hyperprteinaemia mean
High protein
What does hypoproteinaemia mean
low protein
Why are blood samples taken
To determine if infection/inflammation is present
Organ function (liver/kidney)
Blood glucose
Hypotension
Clotting-platelet count and coag tests
Electrolytes
Blood typing
What happens when samples are put in a fridge
Cell activity reduces
What happens when a sample becomes ‘old’
Platelets break down (looks like there are none)
Cells will use up the glucose (will look like none, hypoglycaemic)
If blood smear is done the cells will appear shrivelled
Blood sites in cats
Jugular
Cephalic
Medial saphenous
Blood sites in dogs
Jugular
Cephalic
Lateral saphenous
Blood sites in Rabbit
Jugular
Marginal ear vein
Cephalic
Blood sites in exotics
Ventral tail
Jugular
Blood sites in birds
Jugular
Brachial (wing)
Metatarsal
When would you not use a jugular vein for bloods?
If the patient has a clotting problem
Equipment needed for blood samples
Needles (depending on animal depends on gauge)
Syringes
Blood tube/vacutainer
Hibiscrub
Spirit
Advantages of using a bigger needle
Better flow
Minimal pressure required
No haemolysis
Increased bleeding risk
Advantages of smaller needles
Haemolysis
Lower bleeding risk
Higher pressure required
Slower flow- higher clotting risk
Haematology terminology
RBCs-red blood cells
HCT- haematocrit aka PCV
HGB- haemoglobin (x3 is PCV)
RETIC- reticulocyte
WBC- white blood cells
NEU-neutrophils
LYM-lymphocytes
MONO-monophils
EOS-eosinophils
BASO-basophil
PLT-platelets
What does polycythaemia mean
High RBCs
What does anaemia mean
Low RBCs
What does leukocytosis mean
High WBCs
What does leukocytosis mean
High WBCs
What does leukopenia mean
Low WBCs
What does thrombocytosis mean
High platelets
What does thrombocytopenia mean
Low platelets
What can BioChem tell us
Electrolytes
ALT/ALP
Kidney values e.g. creatine and urea
Bile acids
Thyroid markers (T4)
Plasma vs serum
Plasma
Anticoagulated blood
Contains fibrinogen or clotting factors
Serum
Coagulated blood
Doesn’t contain fibrinogen or clotting factors
What are the 2 plasma proteins
Albumin
Globulin
What are the 6 electrolytes
Magnesium (MG2+)
Sodium (Na+)
Phosphate (PO4)
Calcium (2+)
Chloride (CL-)
Potassium (K+)
Glucose
Neonates and small patients are at risk of hyperglycaemia
Hyperglycaemia caused by diabetes
Lactate
Patients with high lactate have low BP and poor perfusion
Oxygen delivery is compromised so tissues anaerobically respire producing more lactate
E.g. GDV, hypovolaemic shock, septic patients
Renal biomarkers
Urea
SDMA
Creatinine-increase only occurs when 70% of nephrons stop working (stop producing urine)
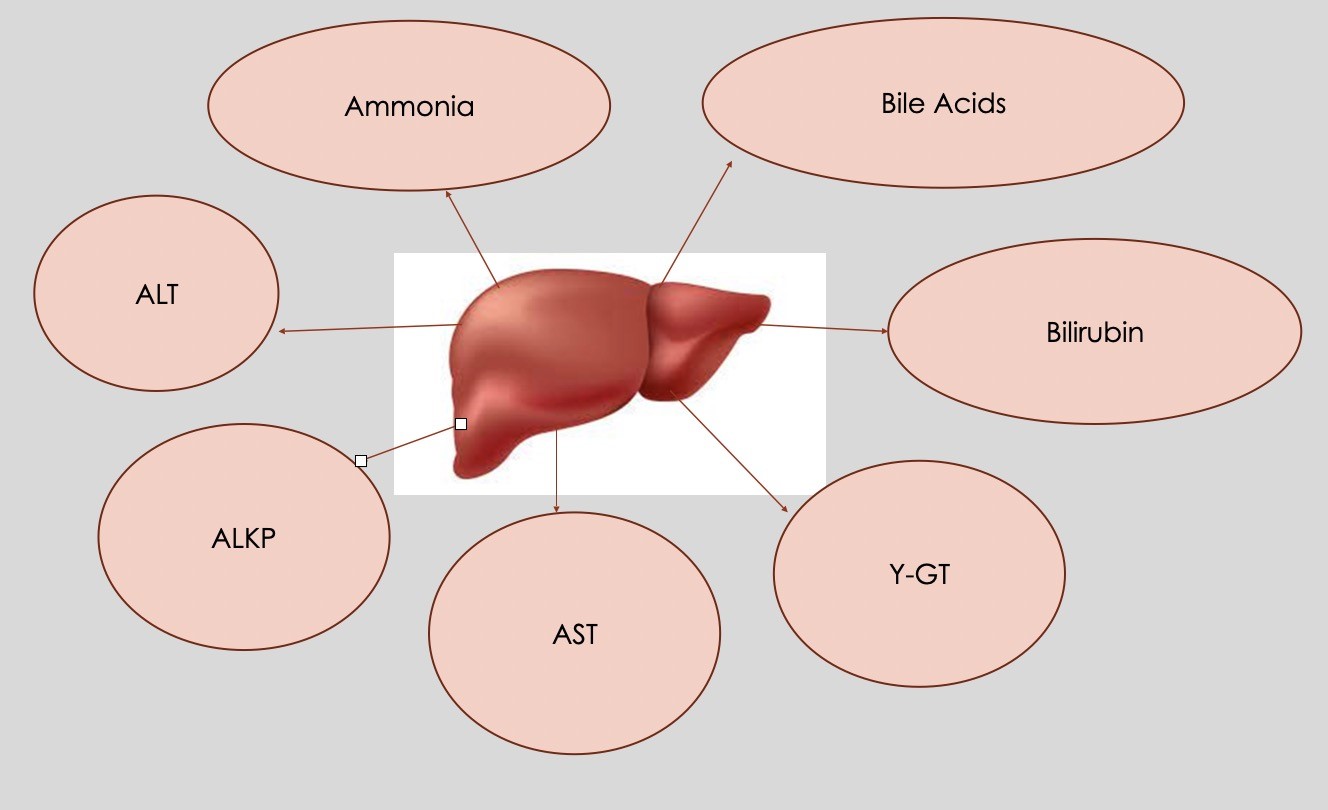
Hepatic biomarkers
AST
ALKP
ALT
Ammonia
Bile acids
Bilirubin
Y-GT
Where are the hepatic biomarkers found
What are the 2 fats
Triglycerides
Cholesterol
Pancreatic biomarkers
Amylase
Lipase
FPLI (snap test)
CPLI (snap test)