Genetics - Lecture 14: Transcription Regulation
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Attenuation
ribosomes in prokaryotic organisms can translate mRNA that is still being transcribed

Open reading frame (ORF)
prokaryotic organization of genes where a single ribosome can continue past a stop codon to translate co-regulated genes
Example of an open reading frame
lac operon

Polycystronic mRNA
one strand of mRNA that codes for multiple proteins
Example of attenuation in bacteria
trp operon
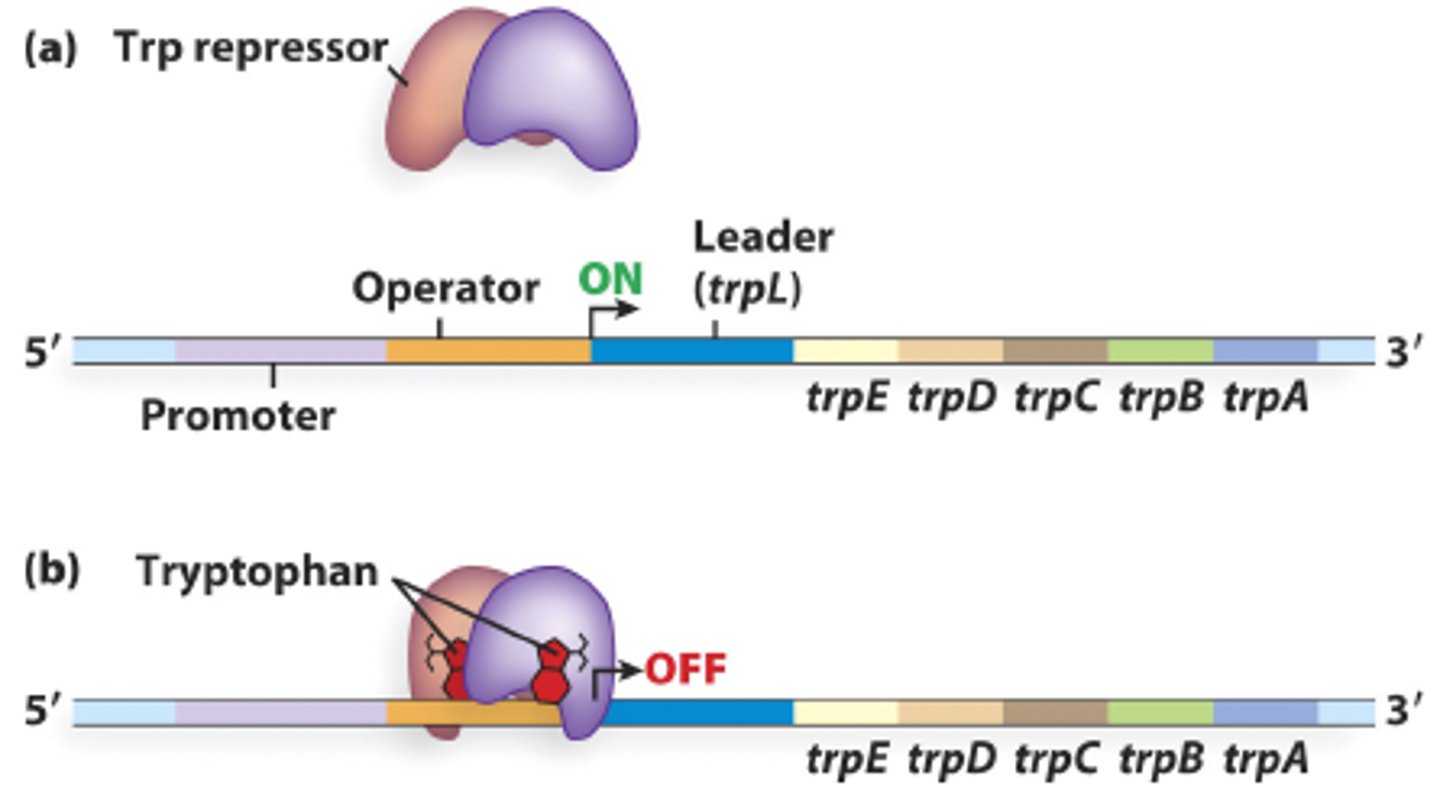
Trp operon
tryptophan binds to the repressor protein and enables it to repress gene transcription.
Major similarity between lac operon and trp operon
both are repressible via ligand-binding means
Major difference between lac operon and trp operon
the trp operon is normally ON, and is only turned off in the presence of excess tryptophan
lac operon is normally repressed (OFF), and is induced by the presence of lactose
Attenuator sequence in trp operon
trpL - codes for a "leader" peptide, whose sequence is used for attenuation
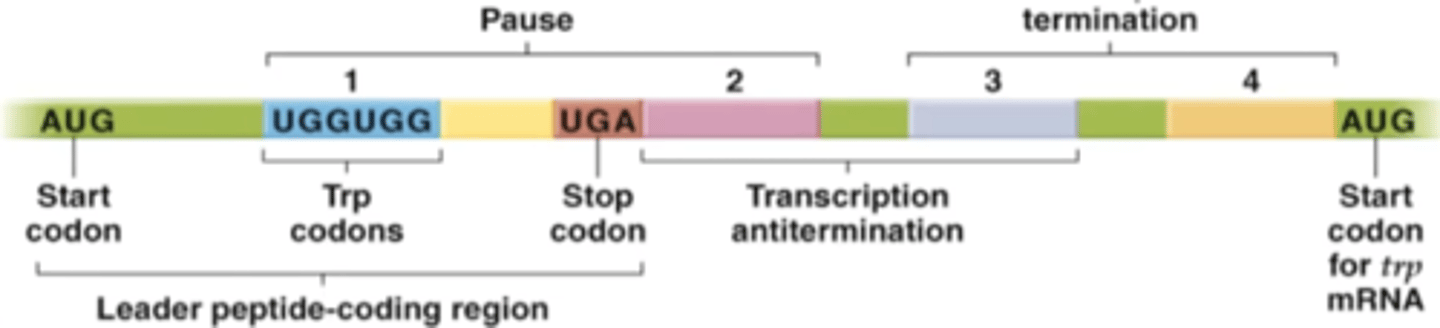
mRNA from trpL
can form several alternative hairpin structures that have different effects on RNA polymerase
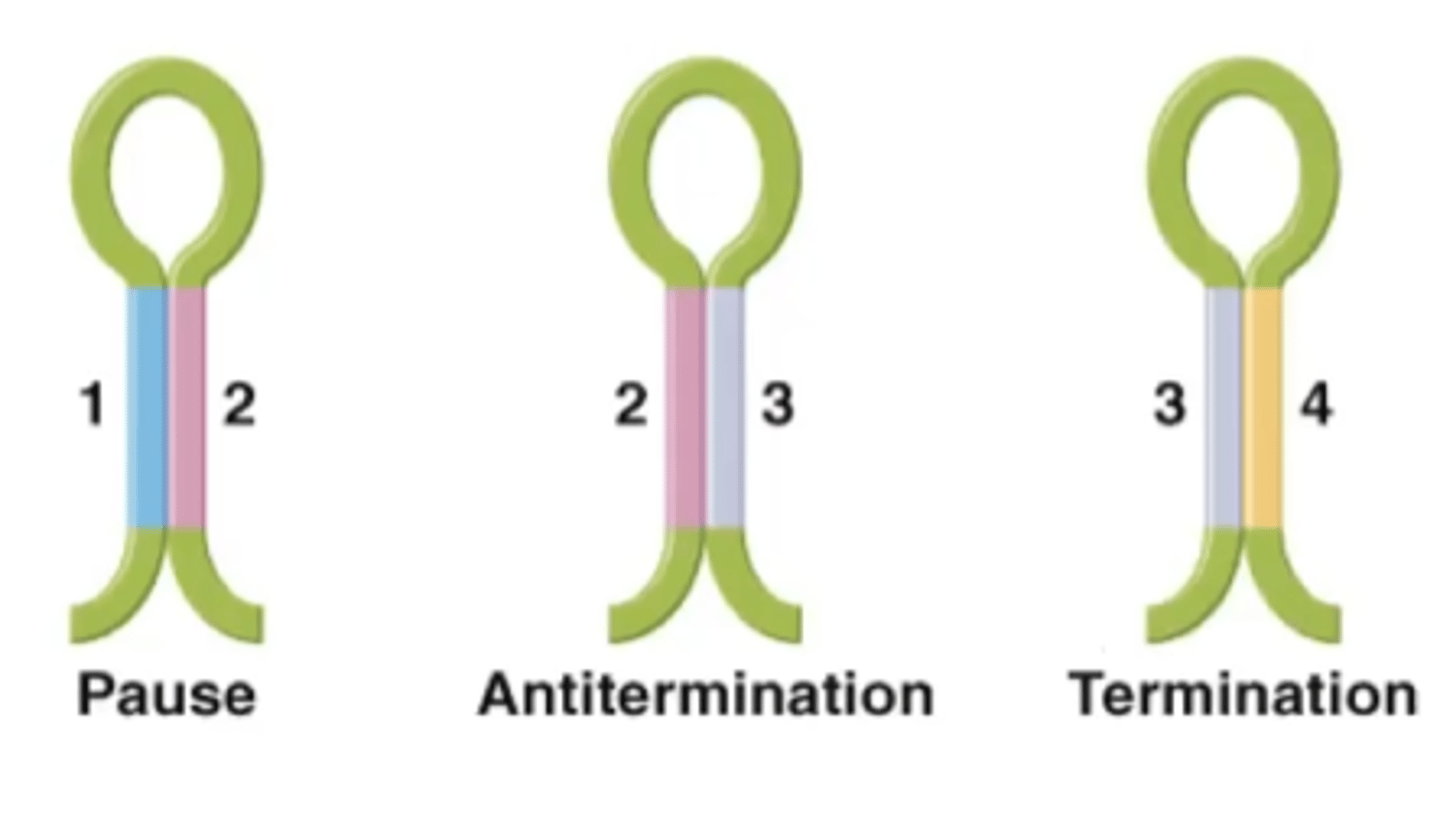
trp-starved
-not enough tryptophan in the system to start synthesis of the leader peptide so ribosome stalls
-while ribosome is stalled, sequences 2 and 3 of trpL are made and will pair up
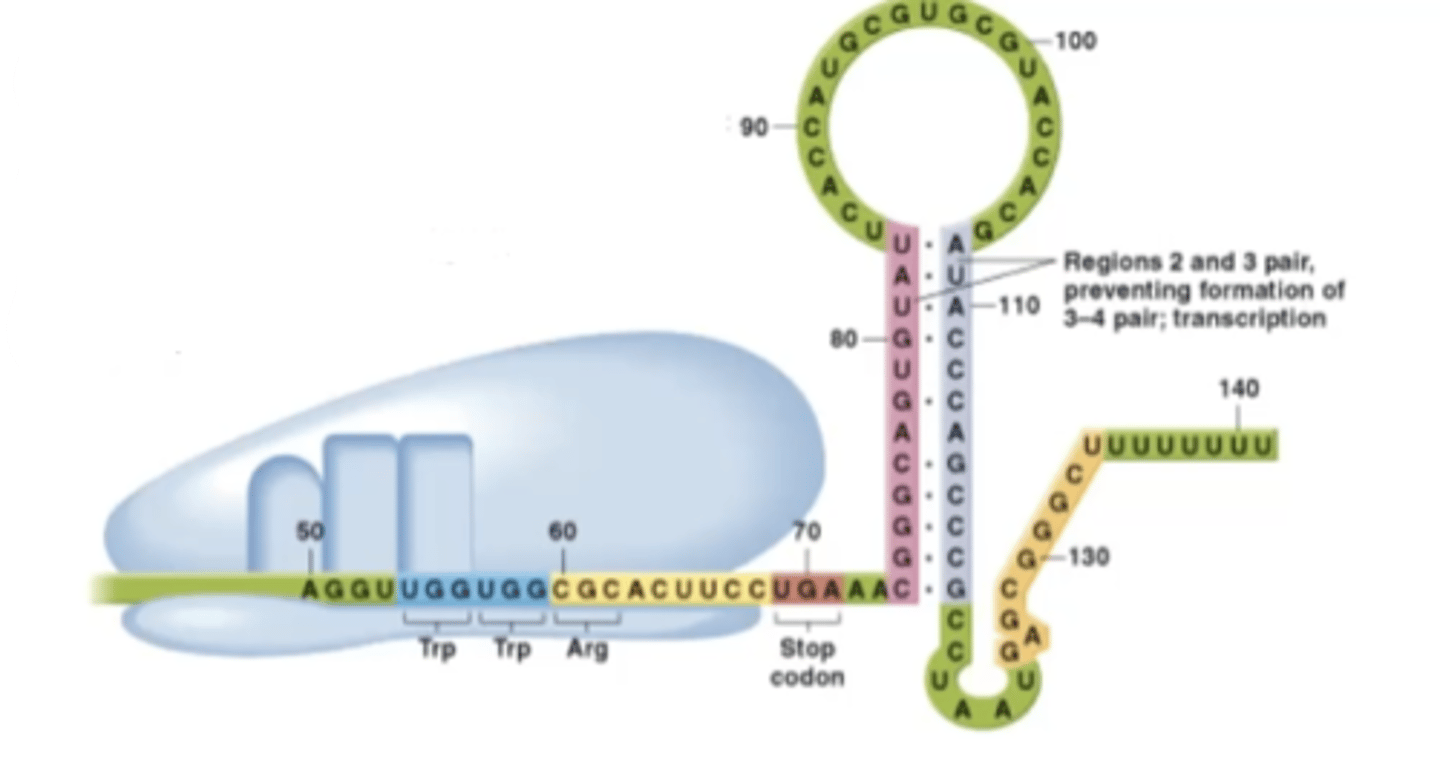
What structure is created in a trp-starved environment?
anti-attenuation structure
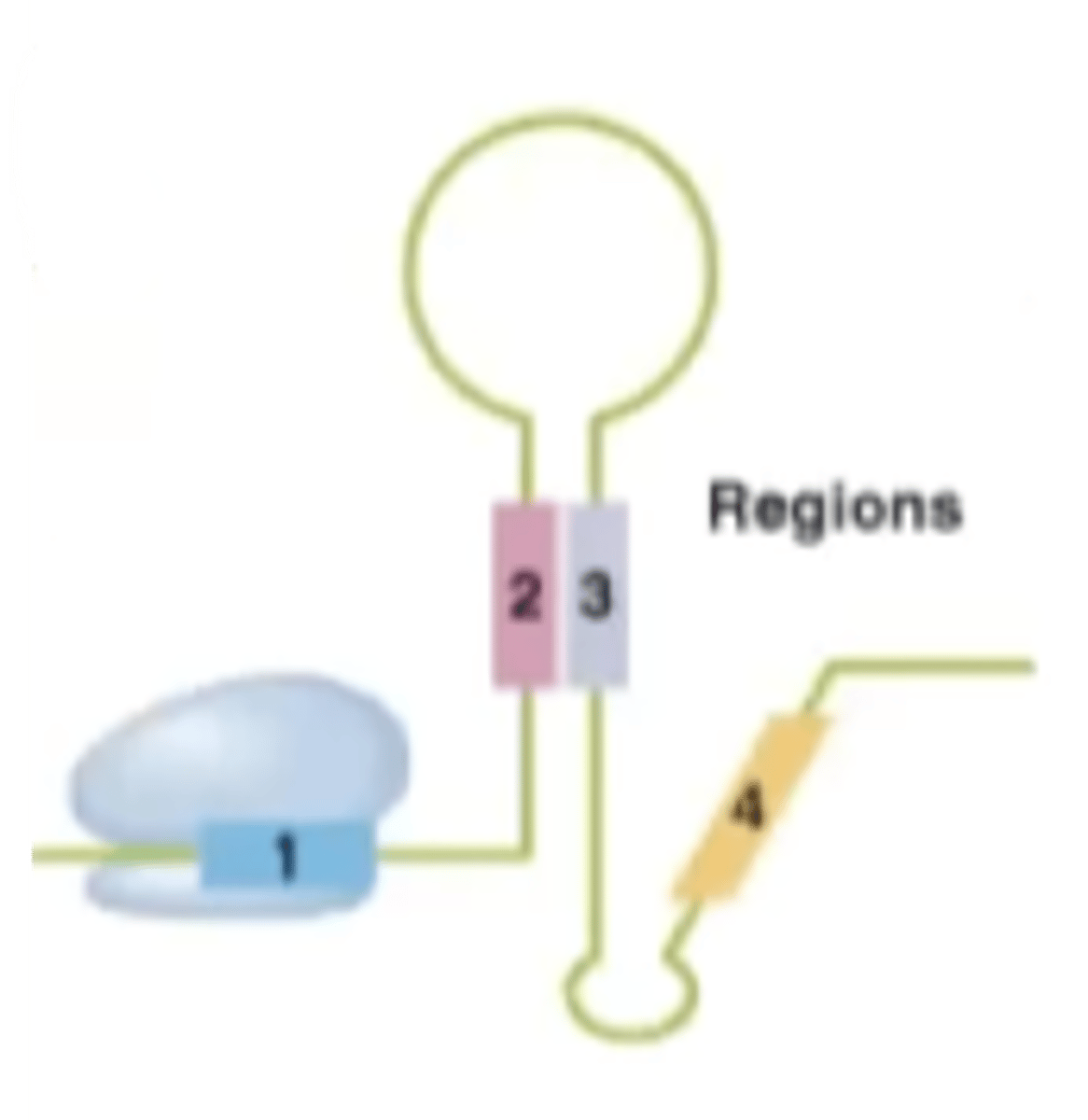
What does the anti-attenuation structure in the trp-operon do?
further stimulates RNA polymerase to transcribe trp-creating mRNA due to the lack of tryptophan in the cell
Excess-trp
-leader peptide will be sysnthesized quickly
-ribosome will block segment 2 from binding to segment 3
-segment 3 will then pair up with segment 4
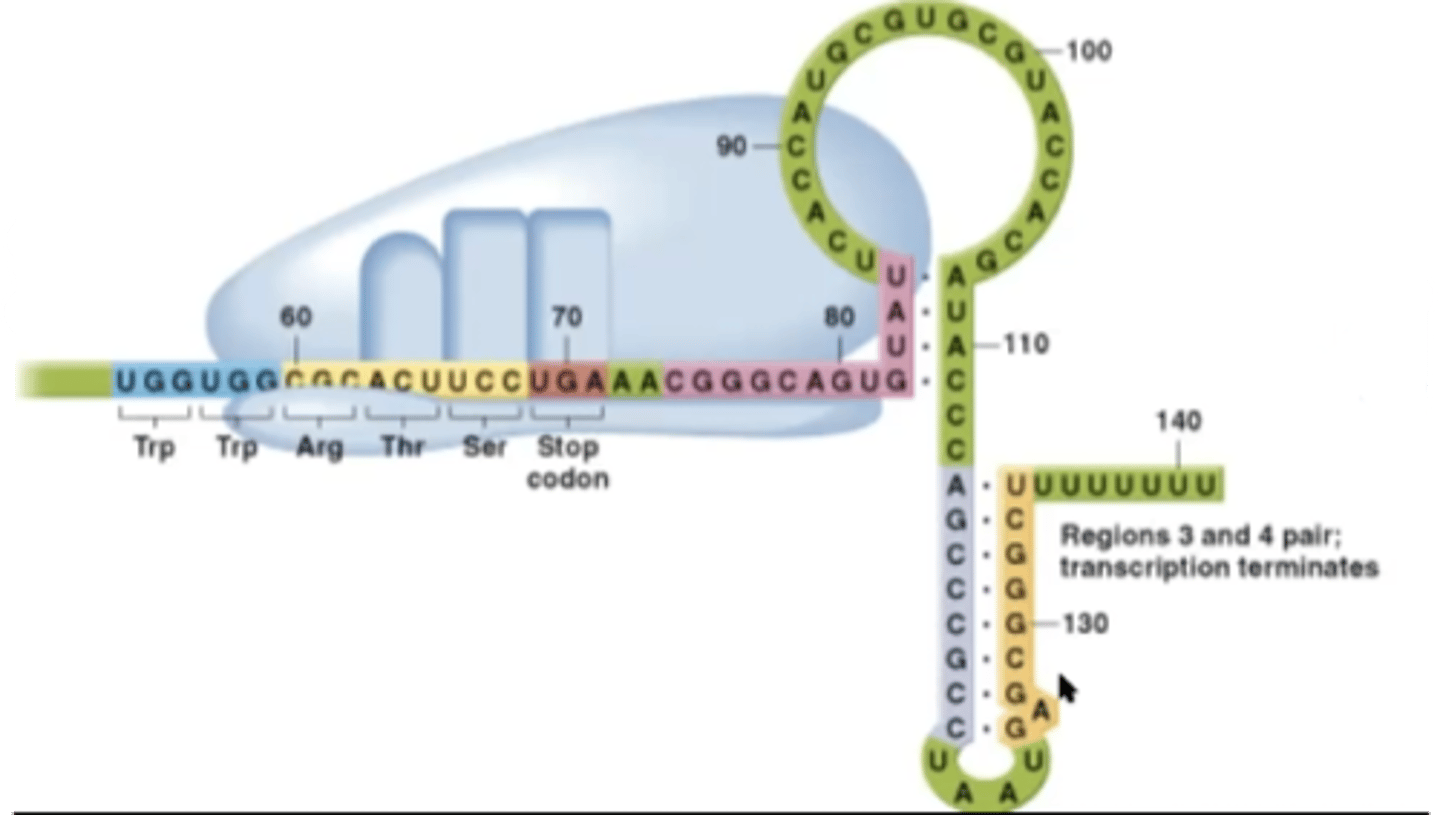
What structure is created in an environment with excess tryptophan?
termination structure
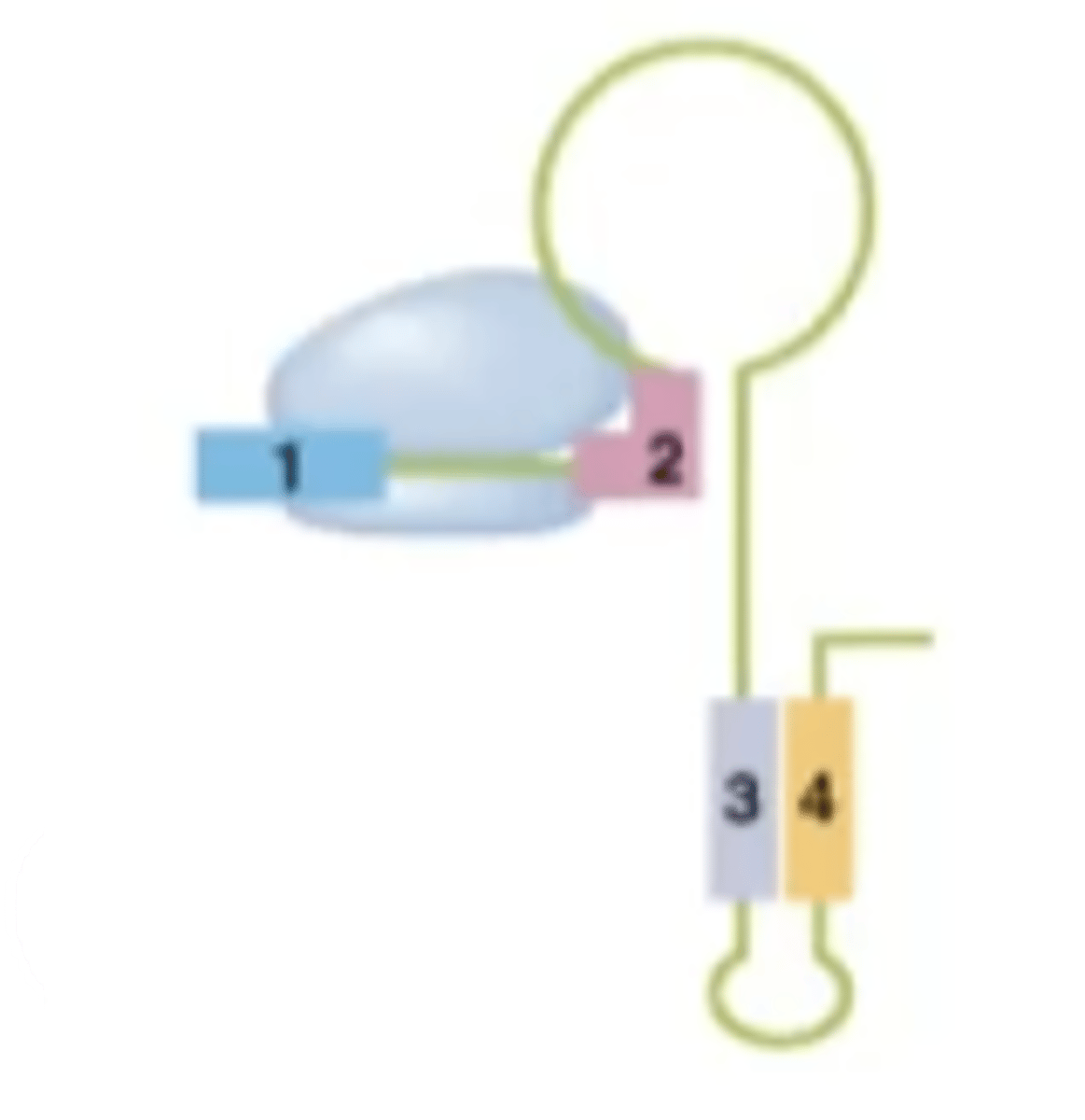
What does the termination structure in the trp operon do?
The termination hairpin structure binds to the RNA polymerase transcribing the DNA and kicks it off, stopping synthesis of trp operon mRNA.
What is the purpose of the termination structure?
To prevent the cell from wasting energy by expressing trp-operon genes in the presence of excess tryptophan
Which type of biosynthesis pathways is attenuation commonly found in (prokaryotes).
amino acid biosynthesis pathways (like trp-operon)
Why is attenuation commonly found in amino acid biosynthesis pathways?
Because the RNA hairpins are much easier to form (just simple base pairing), while building specific regulator proteins to bind to specific DNA AND some other ligand is hard.
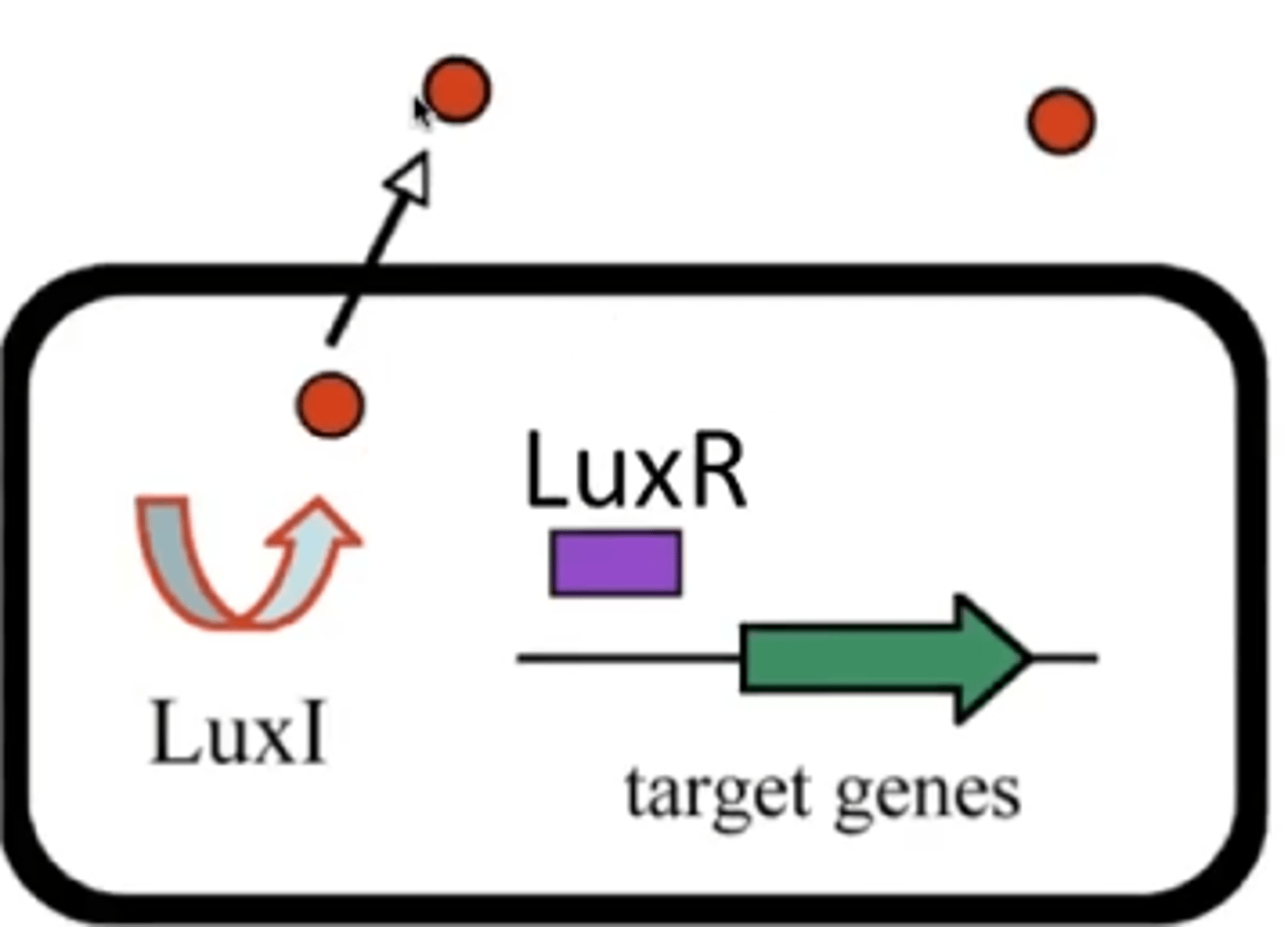
Qorum Sensing
bacteria cooperating in mutually beneficial collective behaviors
Autoinducer
signaling molecule secreted by bacteria to communicate with other bacteria of its kind and others
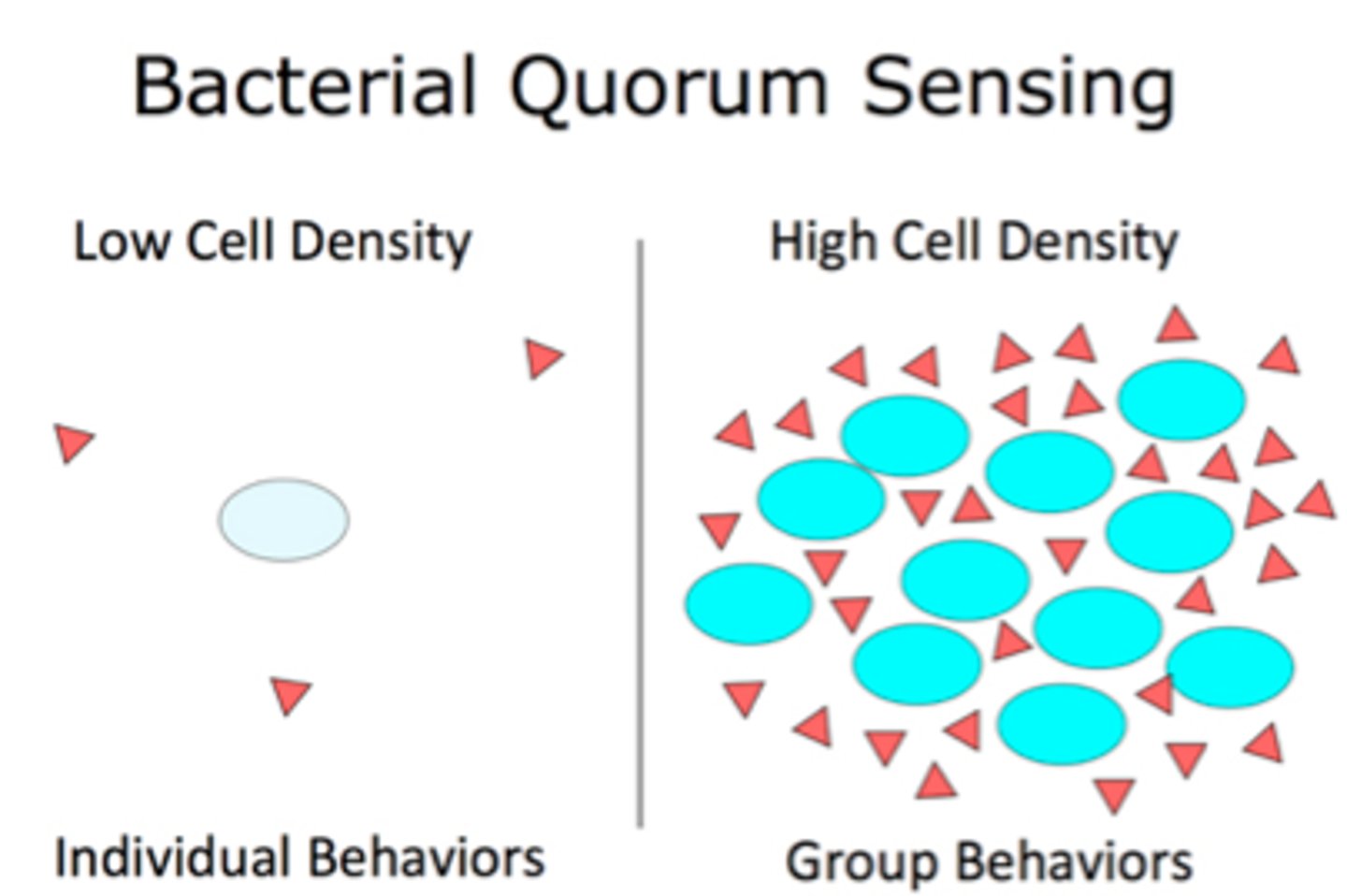
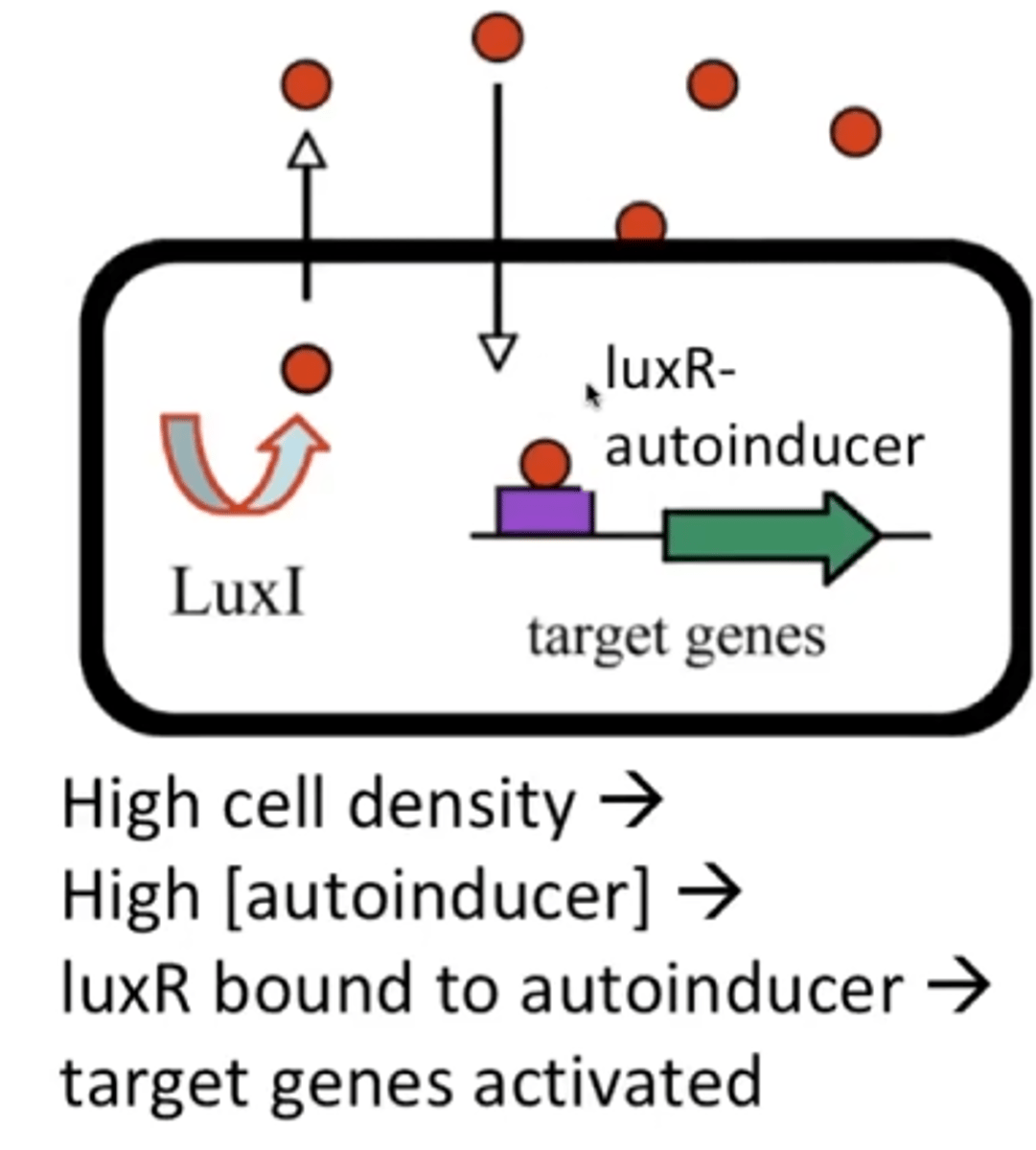
At high autoinducer concentration...
autoinducer re-enters cells and regulates gene expression
LuxI
produces autoinducer under low systemic autoinducer concentration
LuxR
A DNA binding transcriptional activator but needs high concentrations of autoinducer.
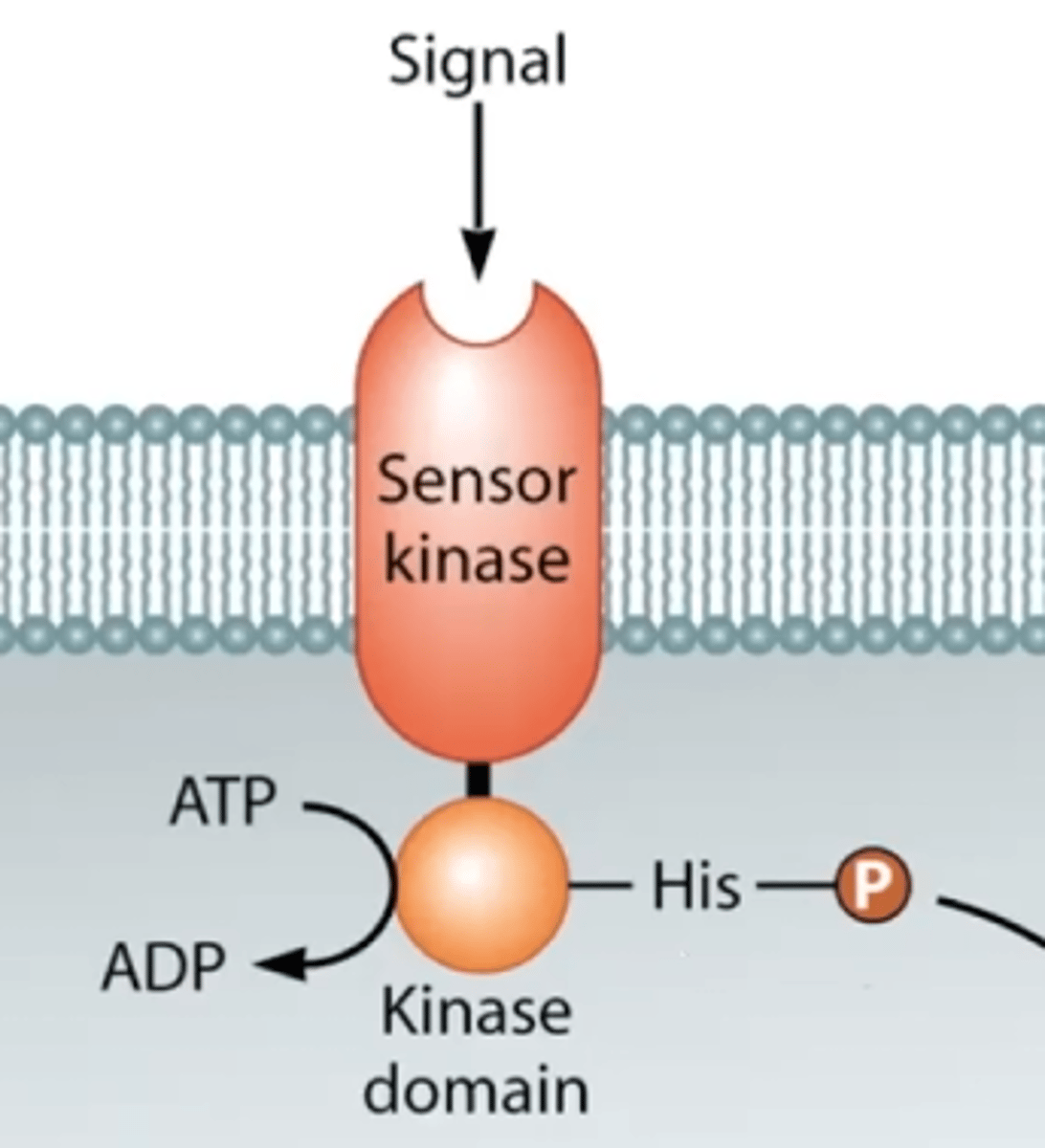
Two-component pathways
Another method of bacterial transcription regulation
Parts of a two component regulatory system
Sensor with a kinase domain
Response regulator
What happens when a sensor in a two component pathways recieves a signal?
It undergoes a 3-D conformational shift and its intracellular kinase domain autophosphorylates.
What happens after the kinase domain of a two component pathway is autophosphorylated?
The phosphate group is transferred to a response regulator, which can bind to DNA and regulate transcription.
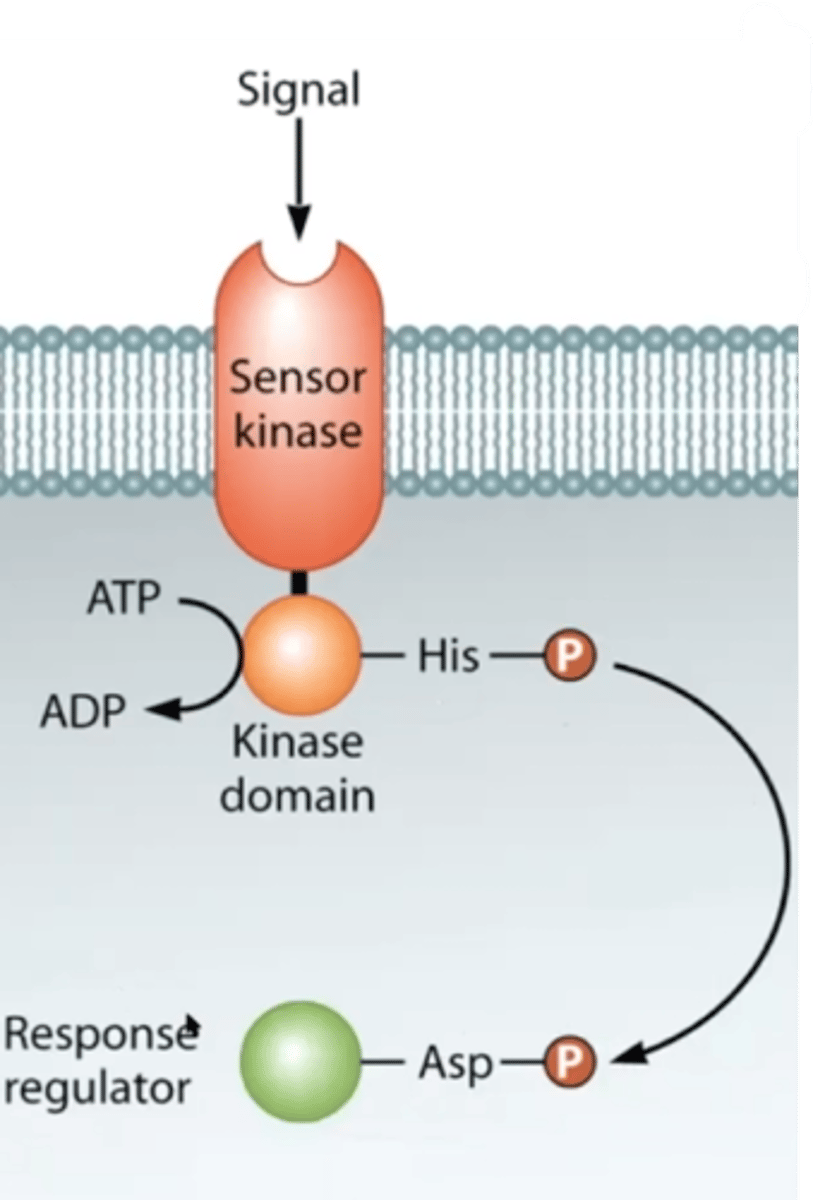
Common two component regulatory system
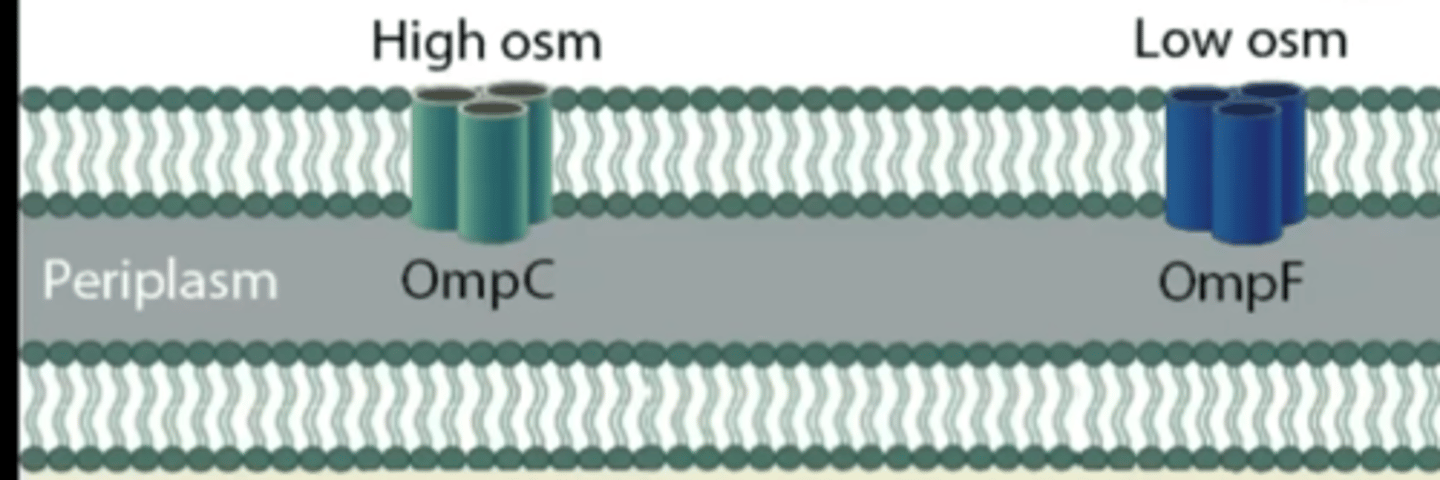
OmpC and OmpF porin protein regulation to respond to changes in osmotic environment
OmpC
smaller pores, used for higher osmolarity environments

OmpF
larger porin protein
dominant when E. coli is in dilute environment
allows more diffusion of solutes
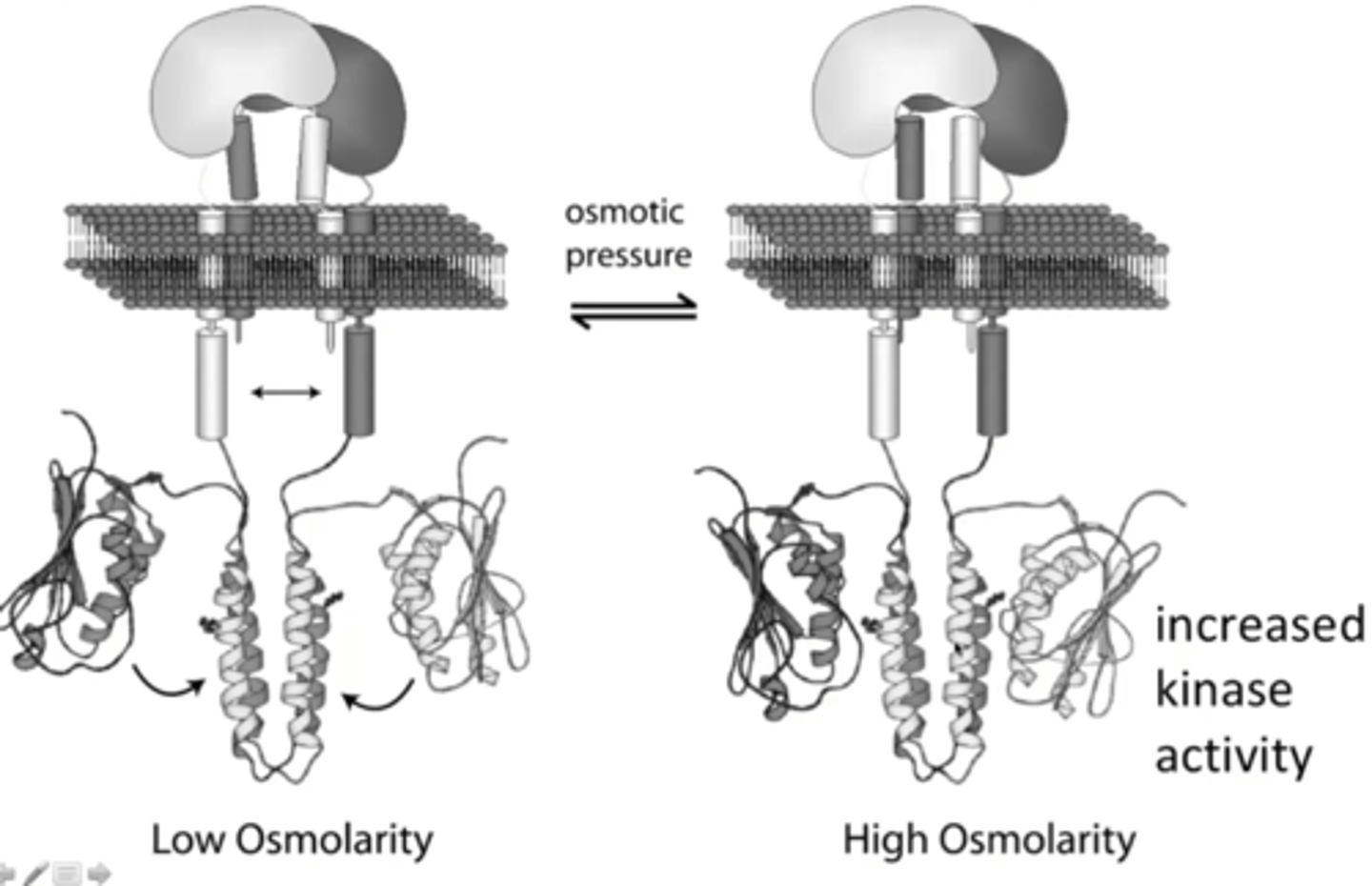
EnvZ
Receptor in the Omp regulatory pathway
How does EnvZ work?
Under high osmolarity conditions, the shrinking of the cell membrane causes a conformational change in EnvZ, and it autophosphorylates
What happens after EnvZ autophosphorylates?
Receptor kinase catalyzes phosphorylation of response-
regulator OmpR
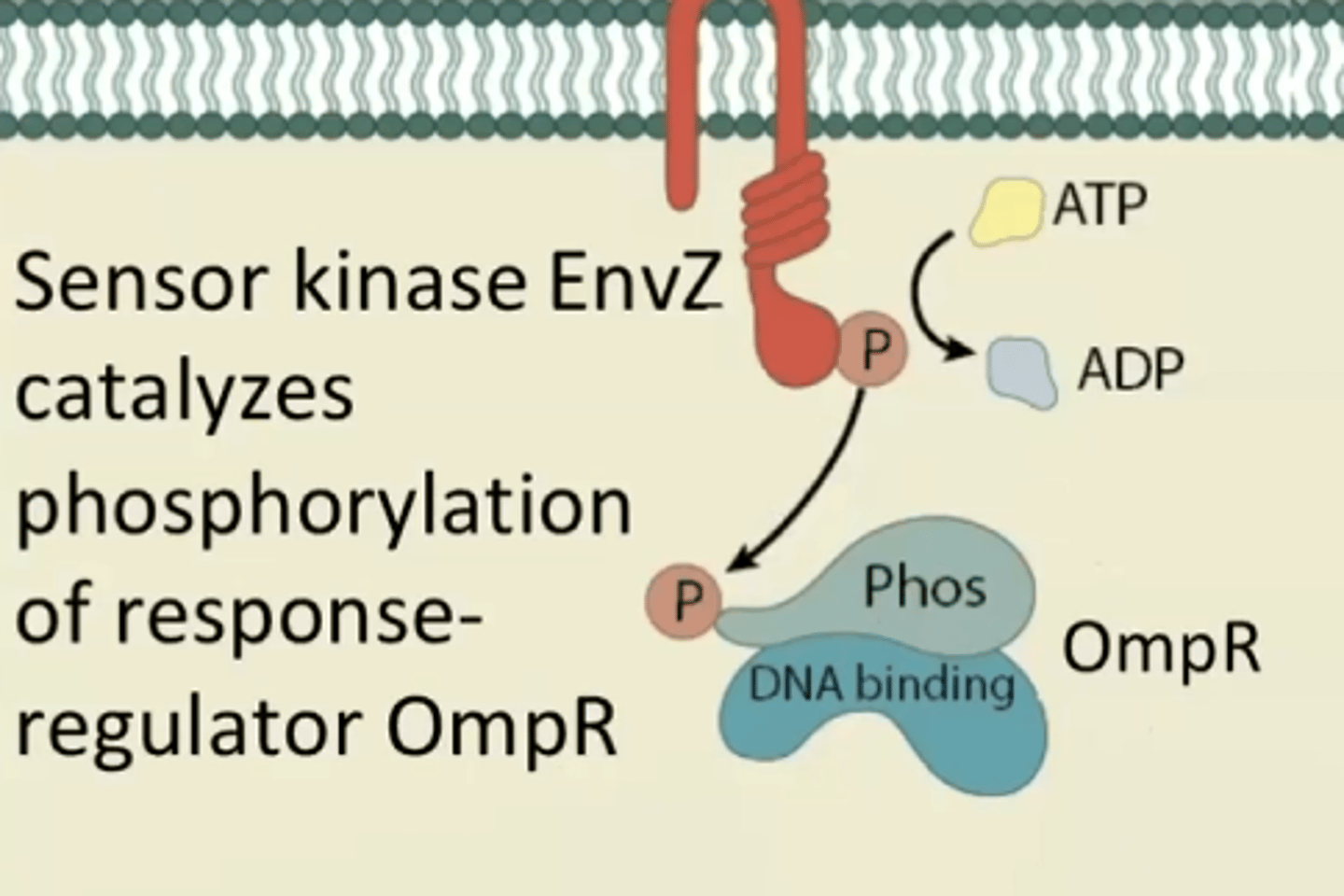
OmpR
(response regulator) phosphorylated and regulates transcription via DNA binding
Unphosphorylated OmpR
binds weakly to DNA and therefore only binds to HIGH affinity binding sites on the Omp promoters
Phosphorylated OmpR
can bind to both high and low affinity sites on the Omp promoters
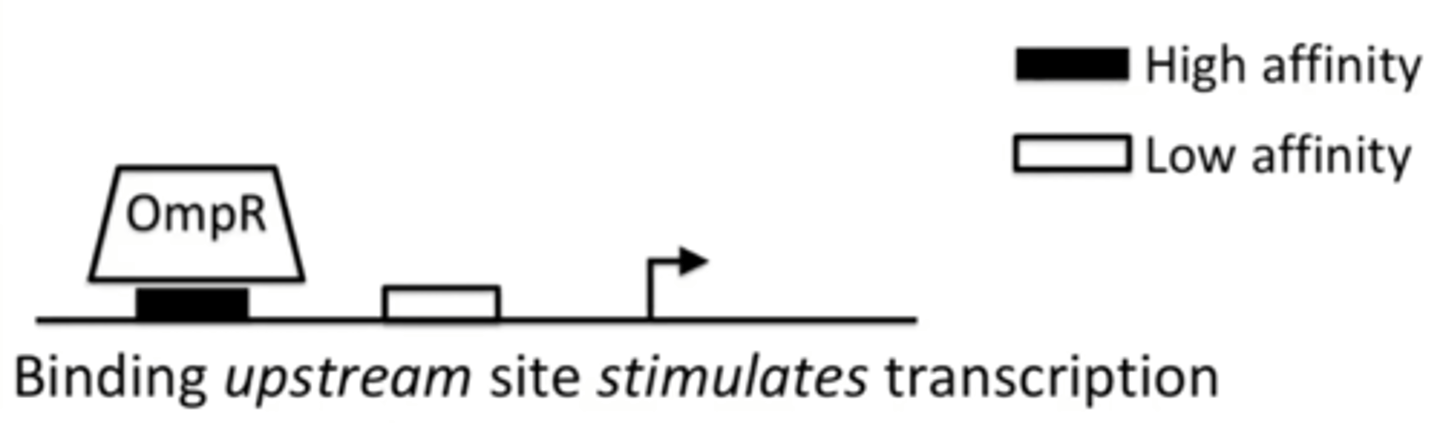
What does OmpR do when it is UNPHOSPHORYLATED?
It stimulates transcription of a gene
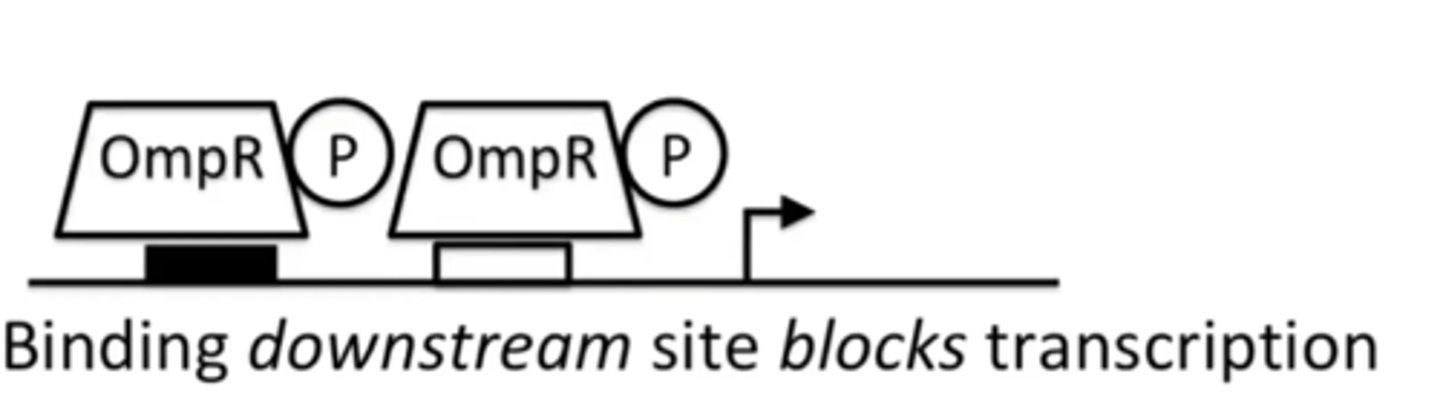
What does OmpR do when it is PHOSPHORYLATED?
It acts as a transcriptional repressor and blocks transcription
Which binding sites does OmpF have?
Both high and low affinity binding sites
Which binding site does OmpC have?
ONLY low affinity binding site
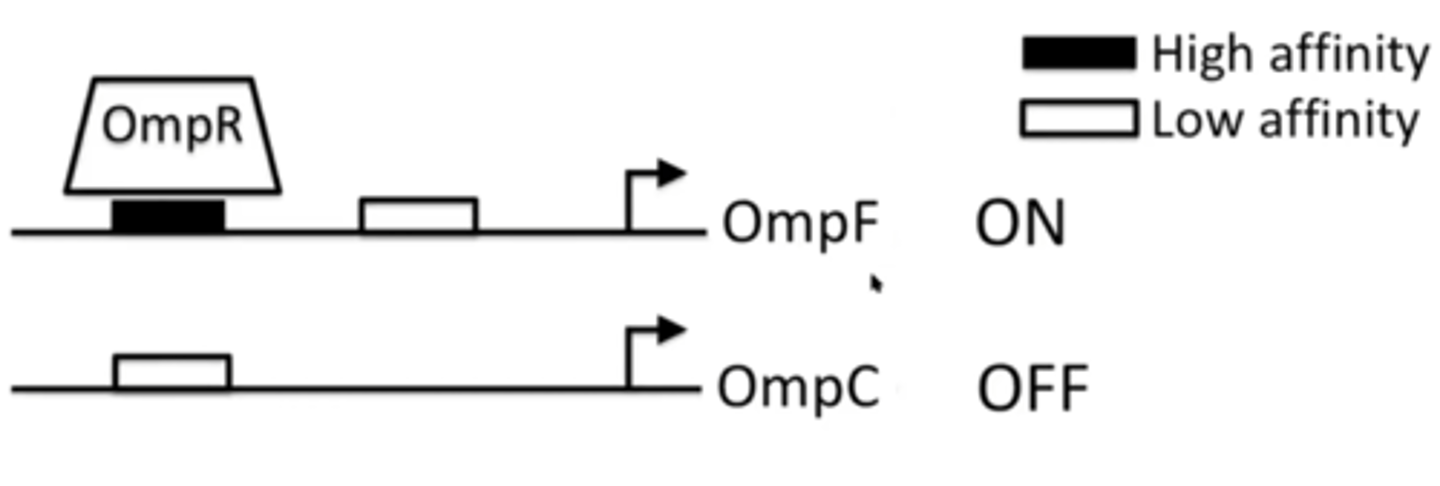
Omp-regulatory pathway under low osmolarity conditions
OmpR is unphosphorylated and can only bind to high affinity sites, located on the OmpF promoter
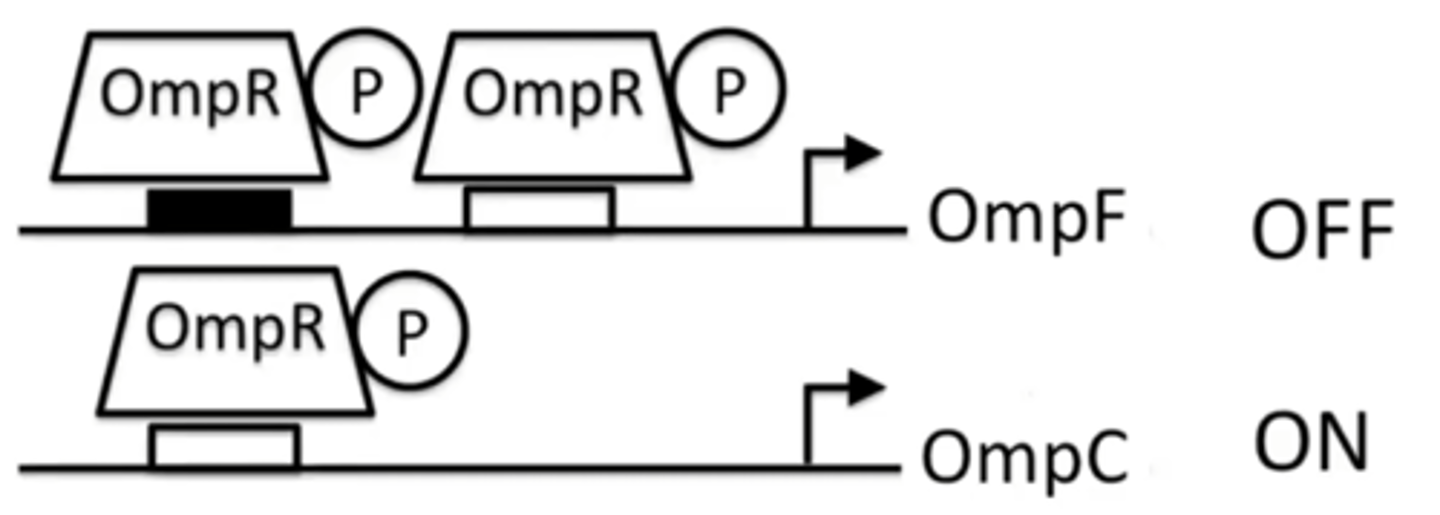
Omp-regulatory pathway under high osmolarity conditions
OmpR is phosphorylated and can bind to both high and low affinity sites
OmpR will bind to both sites in OmpF promoter, shutting it down
OmpR will also bind to only binding site in OmpC promoter, and activate transcription of OmpC
How can two component regulatory systems be used in genetics?
A sensory domain from one species can be fused to a
kinase in a second species, generating a new sensation for that species
Plaque
hole in a bacterial lawn due to cells being lysed by a phage
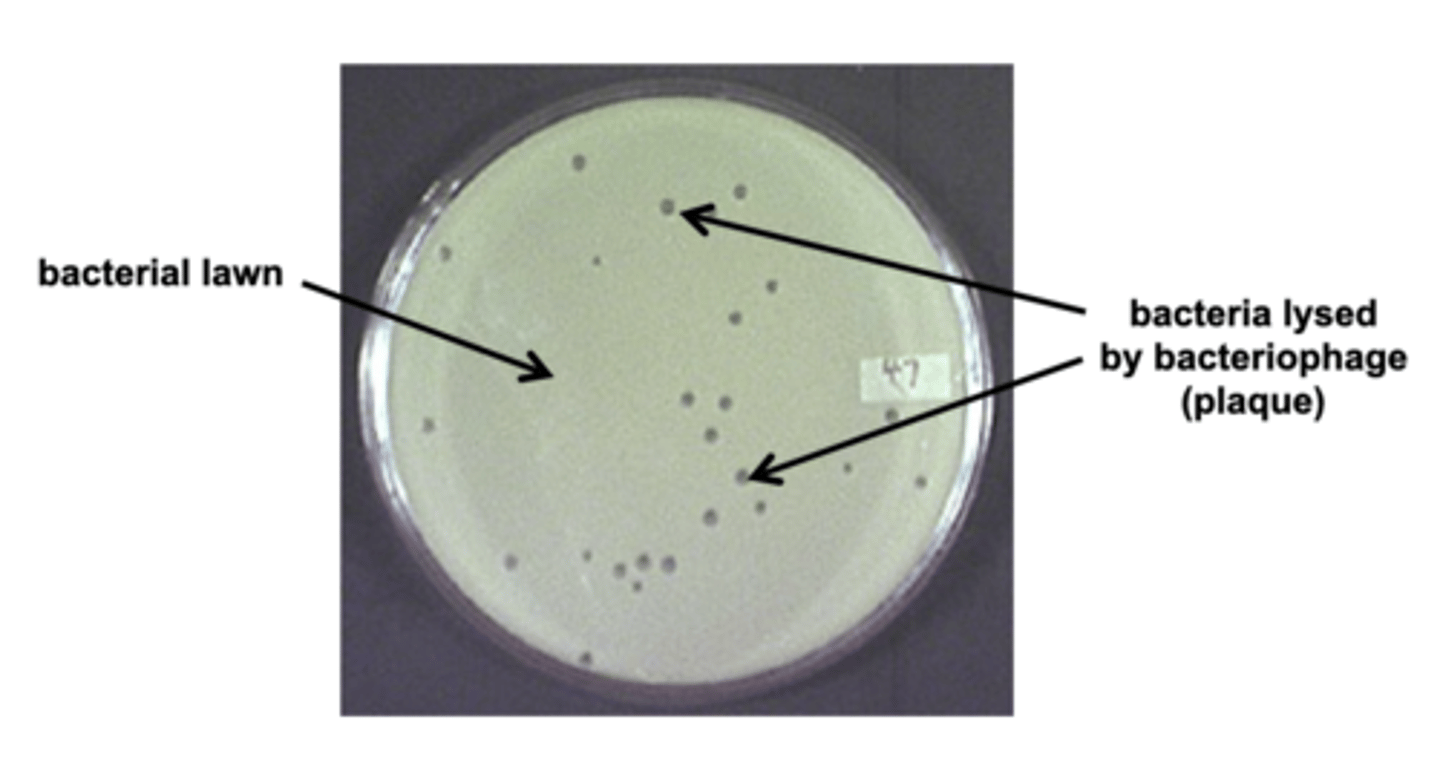
Lambda phage
bacteria virus used as vector, storage package for DNA that is going to be sequenced
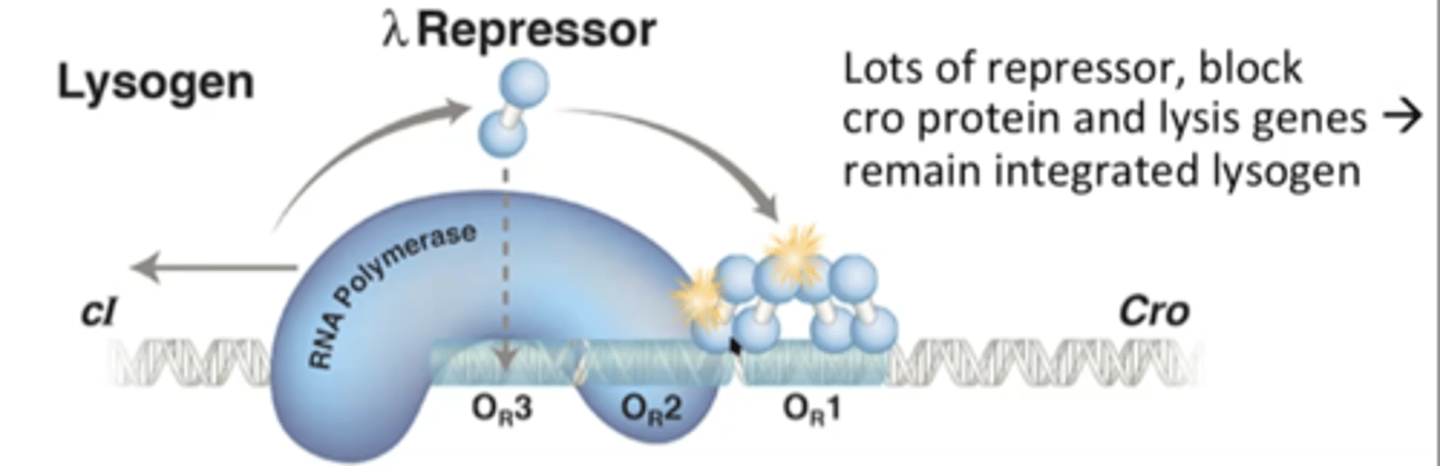
What is the lambda phage lysis vs lysogeny decision determined by?
levels of lambda repressor (cI gene) and cro DNA binding proteins
High levels of lambda repressor
Lambda Repressor molecules bind to DNA and prevent RNA polymerase from transcribing cro (lytic genes)
RNA polymerase is forced to go in the other direction, transcribing genes that make more lambda repressor
Low levels of lambda repressor
No lambda repressor binding to DNA, RNA polymerase transcribes cro, which further blocks expression of cI
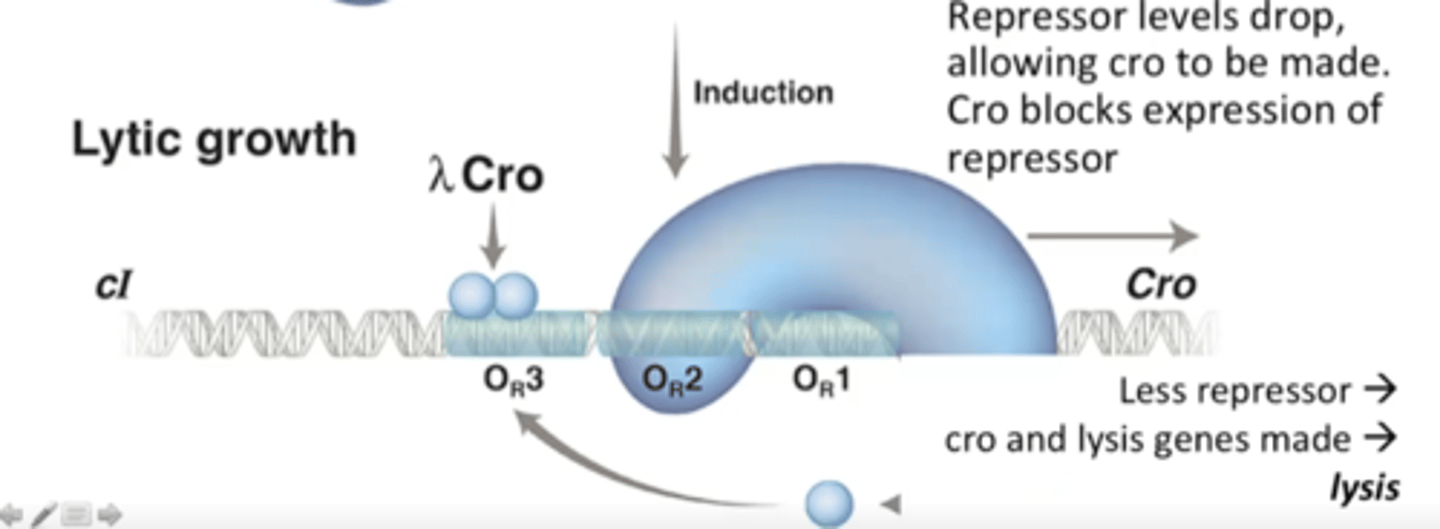
What causes a lambda phage to spontaneously enter the lytic cycle, if it was originally in the lysogenic cycle?
UV DNA damage causes a protease to destroy the repressor of the Uvr pathway but the protease also detroys lambda repressor

RNA polymerase II
all eukaryotic protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase I
transcribes rRNA
RNA polymerase III
transcribes tRNA
Where does RNA pol II bind?
TATA box
General transcription factors
RNA pol II can only bind if these proteins have already bound to the DNA
TATA-binding protein (TBP)
binds to the TATA box and attracts the TFIID complex
bends the DNA double helix
Transcription initiation complex
The assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase.
Besides the RNA polymerase and general transcription factors, in eukaryotes, what else is required to initiate transcription?
cis-regulatory modules
Two types of cis-acting elements
enhancers and silencers
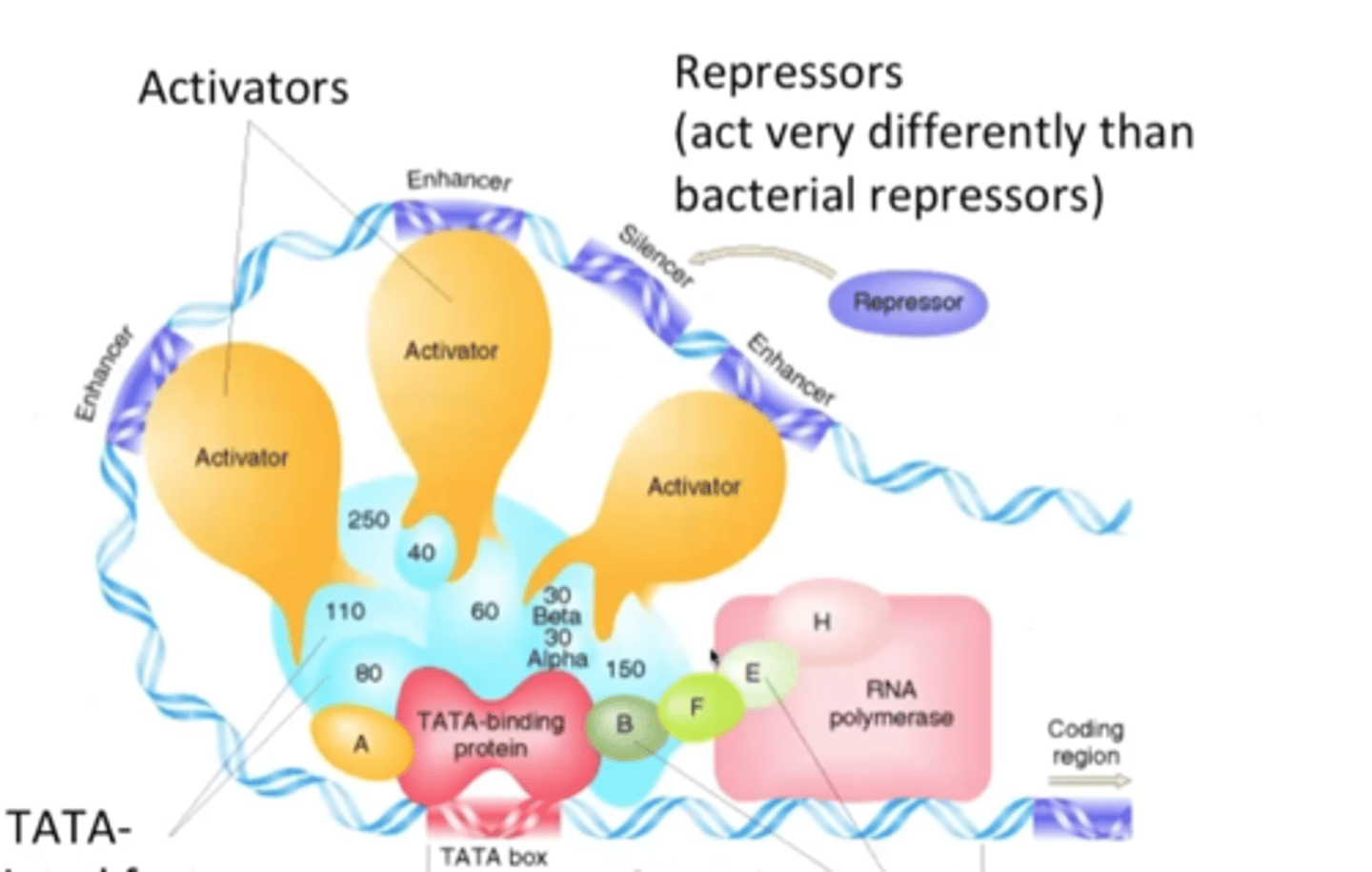
Enhancers
A segment of eukaryotic DNA containing multiple control elements, usually located far from the gene whose transcription it regulates.
Silencers
bound by proteins that inhibit RNA polymerase recruitment or activity at the promoter
Mediator complex
A complex of proteins that interacts with the Pol II complex and allows transcription to begin.
How can reporter genes be used to map promoters?
promoter bashing - deleting segments of a promoter for a gene of interest that is connected to lacZ
measure beta-gal activity after different deletions
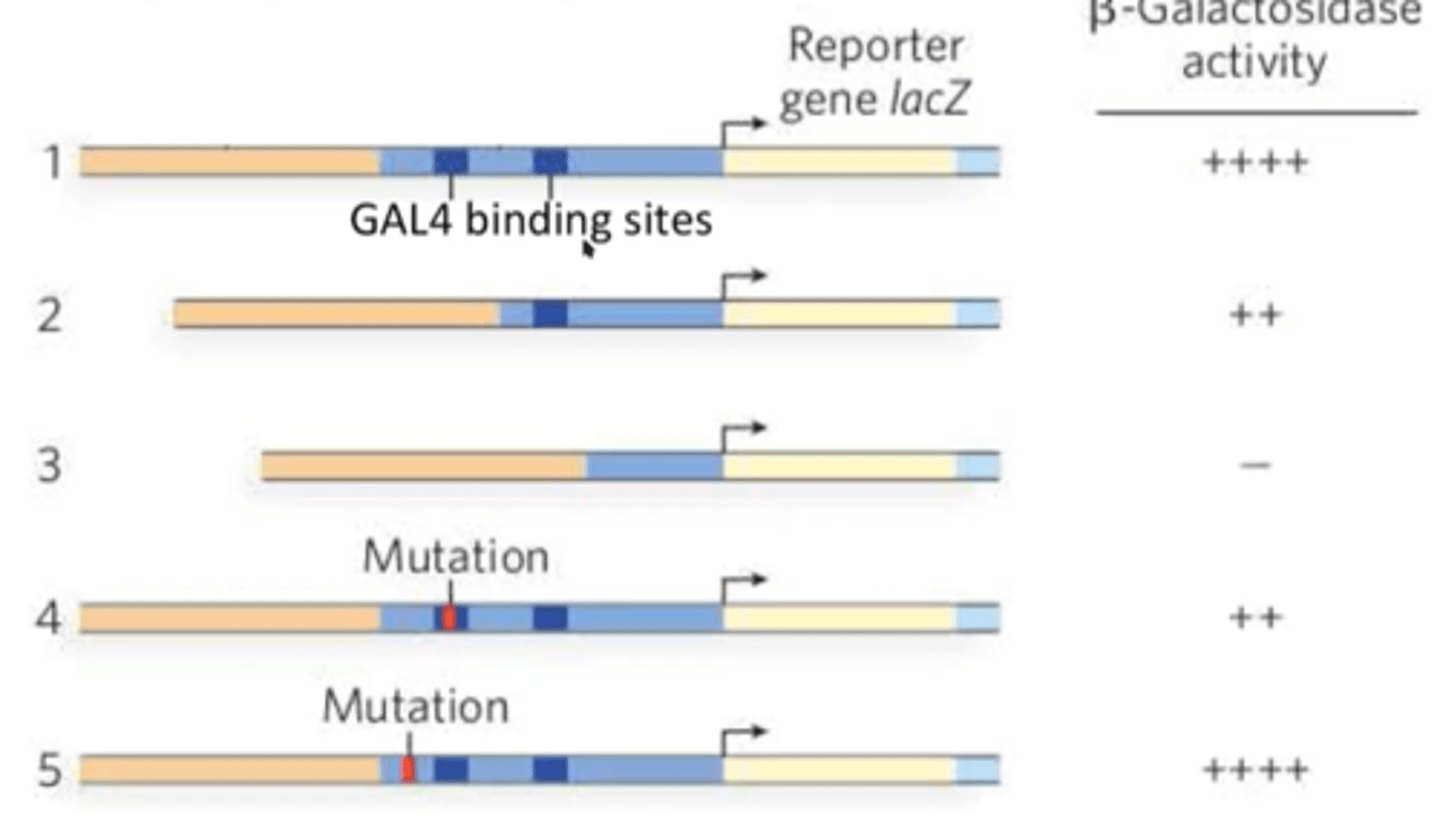
Combinatorial control of gene expression
involves groups of transcriptional regulators working together to determine the expression of a gene
ChIP assay (chromatin immunoprecipitation assay)
a method used to find specific interactions of DNA with proteins.
-break up DNA, use an antibody to pull down specific proteins (along with any associated DNA), then purify the DNA fragments and determine their sequence.
Termination of transcription in eukaryotes
RNA polymerase II transcribes the polyadenylation signal sequence; the RNA transcript is released 10-35 nucleotides past this polyadenylation sequence
5' end of mRNA
recieves a modified guanine methyl cap
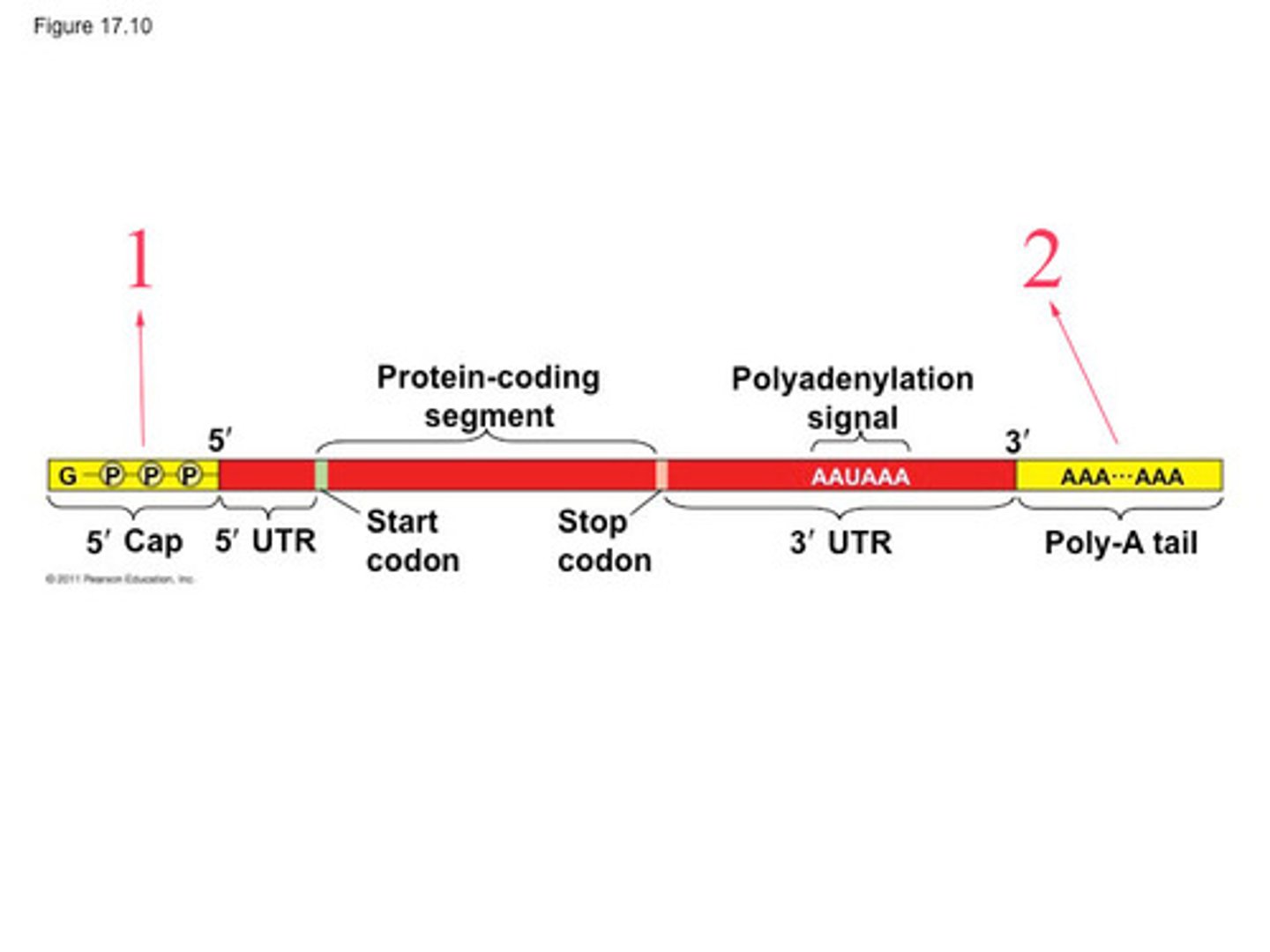
3' end of mRNA
poly A tail