Week 9 - suture patterns
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the three classifications for pulling skin together?
Opposing
Everting
Inverting
Opposing
The suture bring the tissue together end on end
What are opposing sutures good for?
The ideal suture for normal stitches
Everting
The suture tend to turn the edges outwards
What are everting sutures good for?
Helps with stability if the wound won’t be still and high tension is required
Inverting
The sutures tend to turn the edge inwards
What are inverting sutures good for?
Used for lumen of the intestine to reduce the rusk of adhering other structures in abdomen

How is the skin pulled together here?
Opposing

How is the skin pulled together here?
Everting

How is the skin pulled together here?
Inverting
What is the ideal stitch length?
1cm
What is the ideal stitch spacing?
0.5cm
What is the ideal stitch depth?
0.5cm
Where should a knot be placed?
All knots on the same on the inferior side
What is important about putting the knots on the inferior side
They’re place where gravity would take it
What is the basic knot used for suturing?
Square knot
What is better than a square knot
Surgeons knot
What’s a square knot?
A two-throw knot tied in opposite directions to create a stable, non-slipping closure.
What is a surgeons knot?
A double first throw followed up to 5 single throws
What are the 3 main components of a surgical knot?
Loop
Knot
Ears
What is the loop?
The part of the suture material within the opposed or ligated tissue
What is the knot?
Composed of a number of throws - each throw being the linking of two strands of material around each other
What are the ears?
The cut end of the suture which prevents the knot coming untied

What knot is this?
Surgeons
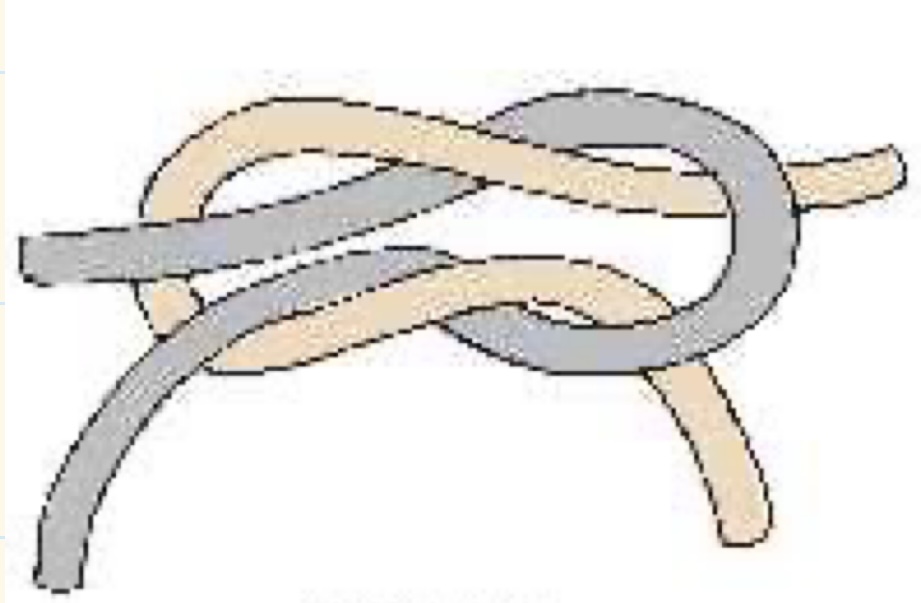
What knot is this?
Square
What are the 8 surgical patterns?
Simple interrupted
Simple continuous
Vertical mattress
Horizontal mattress
Ford interlocking
Cruciate suture
Purse string suture
Subcuticular suture
Simple interrupted
A interrupted suture pattern
Holds the wound edges in opposition
What is a con of Simple interrupted?
Time consuming
What is a pro of Simple interrupted?
If an individual suture falls the integrity of the suture line is maintained
Simple continuous
A continuous suture pattern with one knot at either end
Holds the wound edges in opposition
What is a pro of Simple continuous
Quick and simple to place/remove
What is a con of Simple continuous
If one knot/part of the suture line fails wound support across the whole suture line will be compromised
Vertical mattress
An interrupted suture pattern
Wound edges have a tendency to evert
What is a pro of Vertical mattress
Effective for use in skin under tension
What is a con of Vertical mattress
Can be time consuming to place/remove
If an individual suture fails the integrity of the suture line is maintained
Horizontal mattress
Can be continuous or interrupted
Wound edges have a tendency to evert
Ford interlocking
A continuous suture pattern with one knot at either end
The interlocking suture helps to hold the wound edges in opposition
What is a pro of Ford interlocking
Quick to place/remove
What is a con of Ford interlocking
More time consuming than a simple continuous
The one knot/part of the suture line fails wound support across the whole suture line will be compromised
Cruciate suture
An interrupted suture pattern
Holds the wound edges in opposition
What is a pro of Cruciate suture
Effective for closing wounds that will be under tension due to a skin deficit e.g. when a large skin margin has been taken when removing a mast cell tumour
What is a con of Cruciate suture
Time consuming to place/remove
If an individual suture fails the integrity of the suture line is maintained
Purse string suture
A continuous suture pattern
What is a pro of Purse string suture
Quick to place/remove
Use to tie off hollow organs or to close orifices to facilitate surgery e.g. to temporarily close the anus to allow for surgery in the anal region
Subcuticular suture
Can be continuous or interrupted
No part of the suture is visible on the skin surface
What are 9 rules of suturing?
Handle tissue gently
Minimal handling of suture material
Use correct needle size
Correct use of needle holders
Even tension of each suture
Sutures should always be placed at least 5mm from the wound edge and placed squarely across the wound
Opposition without crushing
The wound should never be gapping or overlapping