Unit 8 - Genes & Molecular Biology
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
DNA - structure
center of nucleus of a cell; organic molecule; contains very long strands
DNA - function
contains genetic info; has info to make proteins; has directions for all activities of the cell
DNA monomer
nucleotide
3 parts of nucleotides
sugar w/5 carbons
phosphate group
base (nitrogen and Adenine/Thymine/Cytosine/Guanine
2D shape vs 3D shape
like a ladder: base is the rungs and sugar/phosphate is the backbone; 3D shape is a double helix
How are bases held together?
hydrogen bonds
Chargaff’s Rule/Base Pairing Rule
amounts of adenine=amounts of thymine; amounts of guanine=amounts of cytosine
“Aunt Thelma Cooks Good!”
A-T and C-G
Melesons-Stahl’s experiment
proves how DNA replicates
processed DNA with two isotopes of nitrogen, N14 (light) and N15(heavy)
DNA was centrifuged, and bands formed on the tube based on the weight or dominance of the isotope
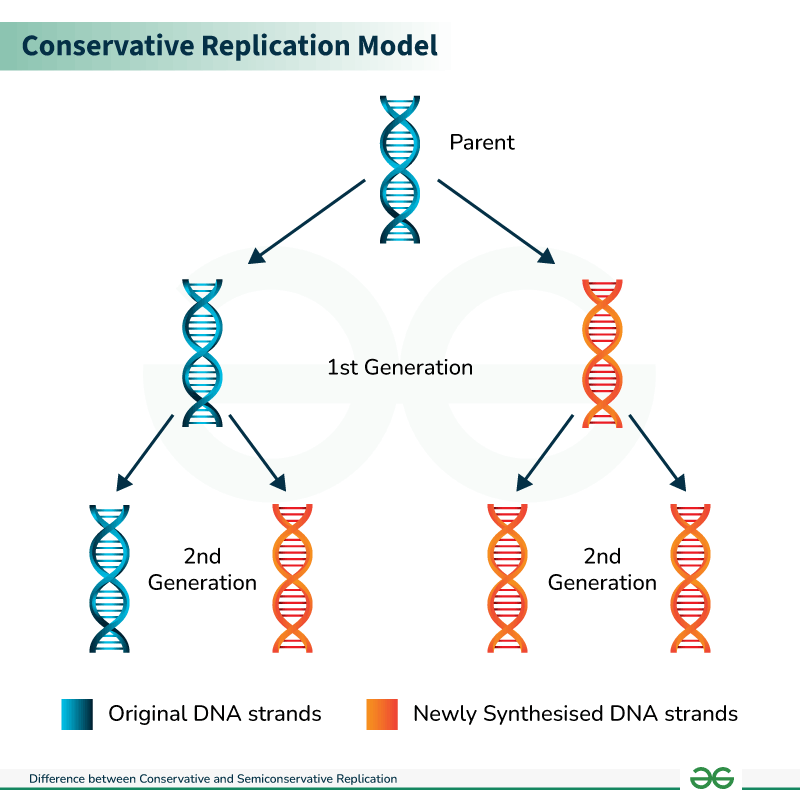
Conservative
possible method of DNA replication
og strands are conserved through out the process
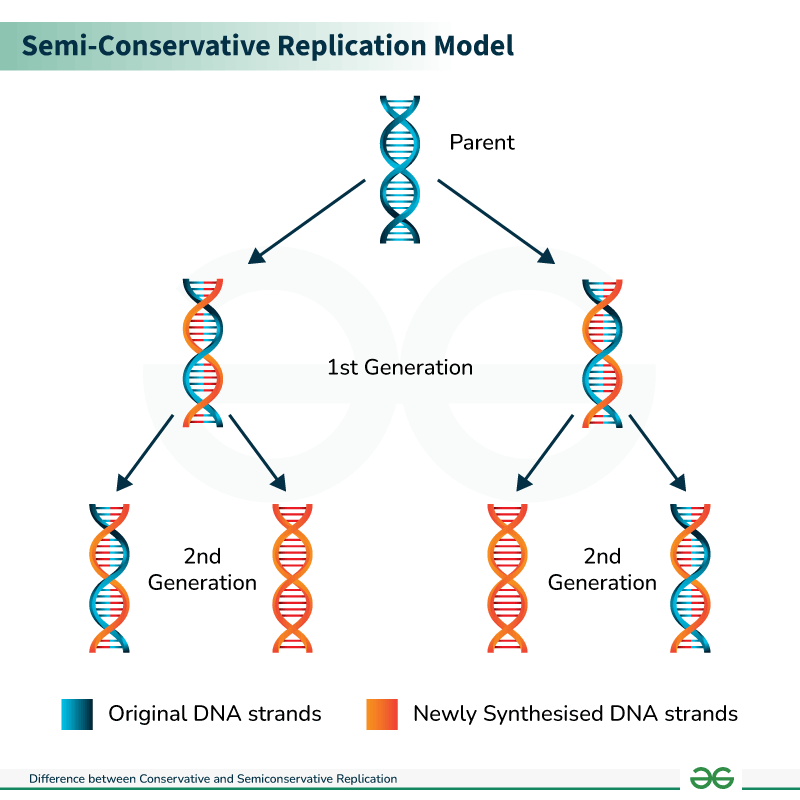
Semi-Conservative
possible method of DNA replication
DNA strand is halved after each replication
new strands are half new half old
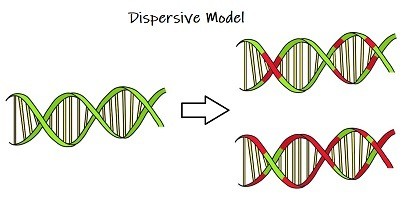
Dispersive
possible method of DNA replication
DNA strand is halved after each replication
replicated strands are chunked together and not in full pieces
results of Meleson-Stahl’s experiment
Semi-Conservative
When does DNA replicate?
during the S phase of interphase
Helicase
enzyme that breaks H-bonds of the bases and allows the DNA to unwind
Topoisomerase
enzyme that reduces tension as the coiled double helix unwinds itself
primer
short section of RNA that helps DNA begin the replication
Primase
enzyme that builds RNA primer
Elongation
adding new nucleotides to the single DNA strand
DNA Polymerase III
adds in the new bases to pair up with the old ones (requires energy)
Antiparallel Elongation
the two DNA strands in a double helix run in opposite directions → DNA Polymerase III needs to build in different directions
top goes from 5’ to 3’ (forward, faster)
bottom goes from 3’ to 5’ (backward, slower)
Leading Strand
the new strand that builds on the “top” strand
continuous
only needs one RNA primer
Lagging Strand
the new strand that builds on the “bottom” strand
built in sections, backward — not continuous
needs multiple RNA primers
Okazaki fragments
sections the lagging strand is build out of
DNA Polymerase I
replaces RNA primer bases with the proper DNA
Ligase
enzyme that joins nucleotides together
Examples of how you can damage your DNA
smoking, x-rays, wearing no sunscreen/tanning, etc
DNA Polymerase II
fills in missing nucleotides that were removed because they were damaged or incorrect
Gene expression
process of transcribing genes to RNA then translating that to make proteins
Transcription
RNA molecule is made from a DNA sequence
aka, mRNA synthesis (only in nucleus)
Translation
RNA message assembles amino acids into protein at the ribosome (only in cytoplasm)
Why RNA
because DNA can’t leave the nucleus
Structure of RNA (5)
single stranded
polymer of nucleotides
has a ribose, phosphate group, and base
found in nucleus + cytoplasm
Bases = G, C, A, and U (uracil)
mRNA (3)
carries instructions
long strand of bases
found in nucleus and cytoplasm
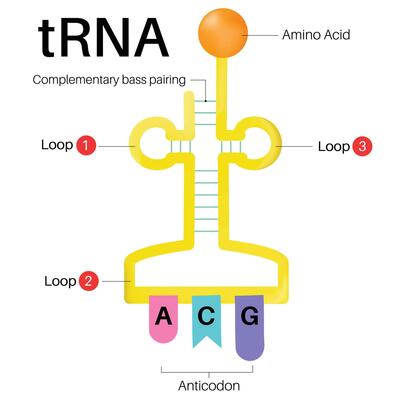
tRNA (3)
carries amino acids
“t” shape w/ 3 bases on one end
only in cytoplasm
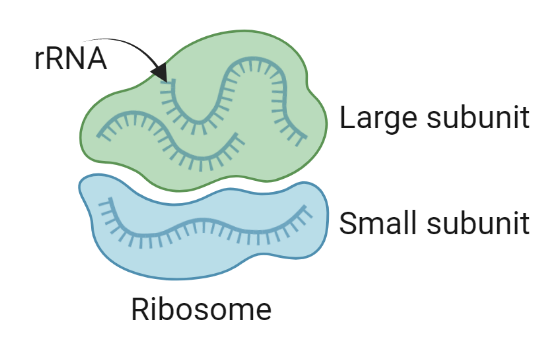
rRNA (3)
connects amino acids
small (binds to mRNA) and large (forms peptide bonds) subunits
only in cytoplasm
Promoter
enzyme that tells where the gene for a protein is
Steps of Transcription (6)
RNA Polymerase finds promoter
Initiation (DNA unwinds)
Elongation (new RNA nucleotides are added)
Termination (end of instructions)
mRNA leaves
DNA rezips
types of RNA in translation
mRNA carries instructions
tRNA delivers amino acids to ribosomes
rRNA connects the amino acids
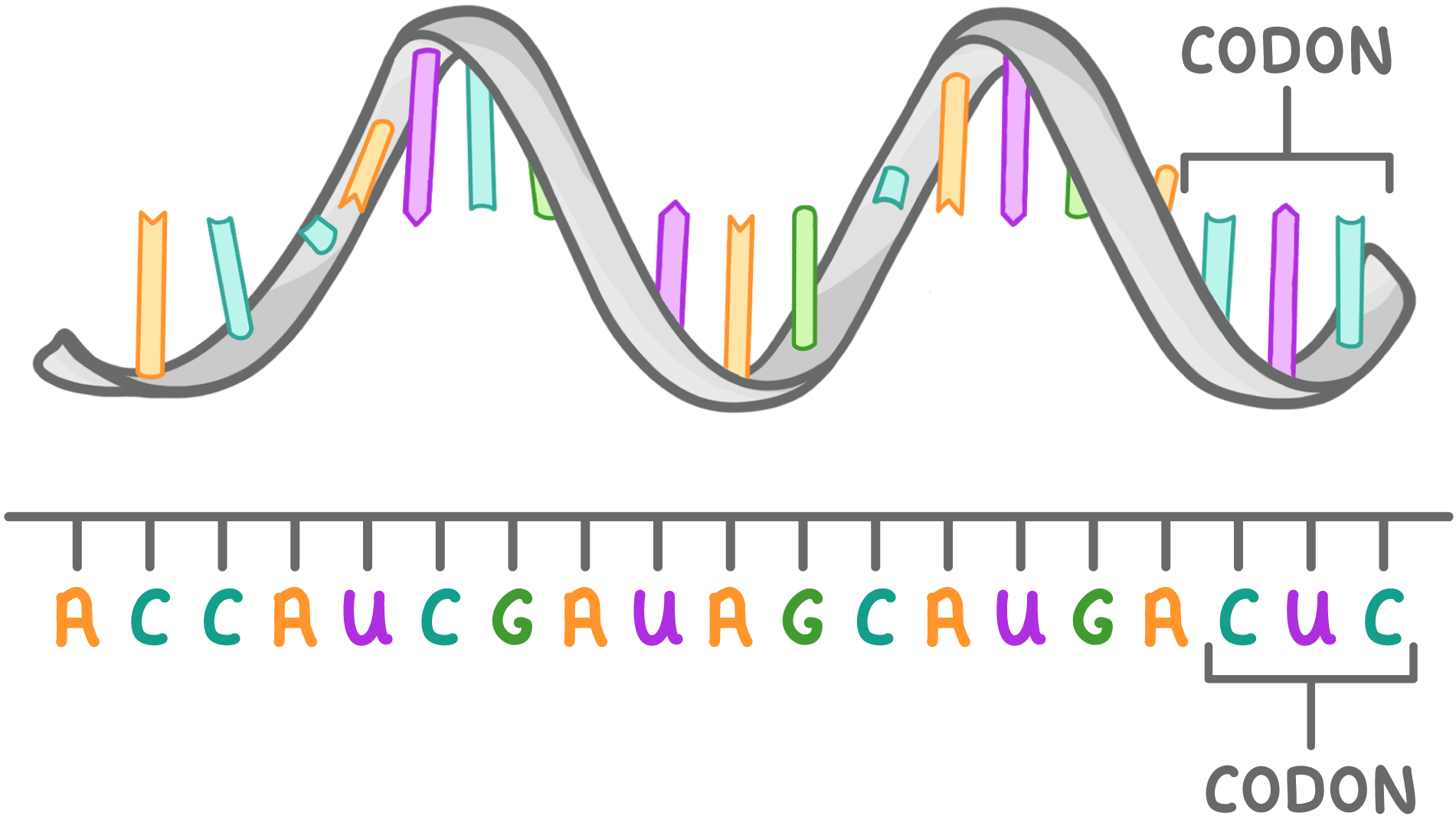
codon
sets of three bases on mRNA that ribosomes read (1 codon = 1 amino acid)
Start Codon
AUG (could also be an amino acid)
Stop Codons
UAA UAG UGA
Steps of Translation (6)
mRNA attaches to ribosome
Ribosome reads codons and tRNA binds to mRNA
tRNA corrects the codons on mRNA w/ anticodon
specific amino acids hangout on the other end of tRNA
rRNA connects amino acids w/ peptide bonds
protein is made
Gene Mutations
changes in one or a few nucleotides (aka point mutations)
Substitution
base pair is replaced (may or may not cause problem)
insertion
additional base pair is inserted (dangerous)
deletion
base pair is deleted from the sequence (dangerous)
Fram shift exampeles
silent (no change)
nonsense (stop codon is made)
missense (another amino acid/ protein is made)
Frame Shift Mutation
the more dramatic gene mutations are, the more a template frame is going to shift and mess up everything
Griffith
organisms can get new properties and noninhertiable gene exchange is possible
Avery, McCarty, and Macleod
nucleic acids are molecules of heredity
Hershey and Chase
DNA is the genetic material and carries genetic info
Chargaff
Frequency of bases in DNA vaires
Franklin
DNA has a helix structure
Watson and Crick
DNA has an anti-parallel structure
Kariko and Weissman
mRNA can be used therapeutically in meds like vaccines
Langer
RNA can be protected from enzymes by inserting them in a nanoparticle
how are mRNA vaccines different?
they use genetic info of the virus, specifically they code for proteins found on viruses to warn cells of the body what to watch out for
side effects of mRNA vaccines
Inflammation, destroyed the RNA before it could do anything
how did they fix the inflammation of RNA vaccines?
altered uridine to be a pseudouridine; also helped make more proteins
disadvantages of RNA
fragile and can be destroyed by enzymes of the body