Comprehensive Guide on Second Semester Biology | Mr. Ingrum | 11th grade
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
What is a hypothesis
a testable prediction
What was Darwin & Darwin's hypothesis on phototropism?
The eyes of the plant are at the tip of the seedling.
What four things define plants?
1. Multicellular
2. Eukaryotic
3. Cell walls made from cellulose
4. Most are capable of photosynthesis
What did Anning do?
She discovered the Plesiosaurus
What did Cuvier do?
Discovered the concept of extinction.
What did E. Darwin do?
Believed all live came from one "single filament".
What did Hutton do?
proposes that Earth is millions of years old
What did Lamarck do?
He believed that evolution moved toward complexity, towards perfection.
What did Lyell do?
He popularized the concept of uniformitarianism
What did Malthus do?
He showed that population growth leads to competition for limited resources.
What did Smith do?
Described faunal succession
What did St. Hillarie do?
described homologous structures
What 3 characteristics do mosses have?
No vascular system
No seeds
No flowers
What 3 characteristics do ferns have?
Vascular system
No seeds
No flowers
What 3 characteristics do coned plants have?
Vascular system
Seeds
No flowers
What 3 characteristics do flowers have?
Vascular system
Seeds
Flowers
What do Green Algae and (most) plants have in common?
Same color
Multicellular
can photosynthesize
How do humans see?
Photoreceptor proteins in our pupils respond to the stimulus of electromagnetic waves on the color spectrum. We interpret these stimuli as sight, and our brains piece together the light we see to make a live image.
Where is the Retina?
Back of the eye, behind the Iris and Lens
What do photoreceptor proteins on rod cells do?
Rhodopsin is responsible for detecting light (brightness)
What do photoreceptor proteins on cone cells do?
Photopsin is responsible for seeing color
How does the ratio of rod to cone cells generally differ between diurnal and nocturnal animals? Why?
Nocturnal animals need more cone cells to help them see in the dark. Color isn't important at night because you can't really see color in low-light environments.
How many times have eyes independently evolved among the Animalia?
50
What is phototropism?
A plant's response to light; turning to face the source
How did Darwin & Darwin test their hypothesis?
5 seedlings:
control: bent towards light
tip cut: didn't bend
tip covered with opaque cap: didn't bend
tip covered with transparent cap: bent towards light
base covered with opaque cylinder: bent towards light
Did Darwin & Darwin's test support their hypothesis?
Yes, when the tip of the seedling was exposed to the light, it bent in that direction.
Why do plants turn toward light?
Plants need sunlight to synthesize food; needed for survival
What is photoperiodism?
Plants measure continuous periods of darkness
Explain the experiments that demonstrate that plants can measure continuous periods of darkness.
shining a light on a single leaf on a plant will cause it to flower if it's a summer flower, and not if it's a winter flower. Like a light switch, it turns the function on and off.
What does phototropin do?
blue light receptor, signals phototropism, found in stem tips
What does phytochrome do?
red / far red receptor, signals flowering, found in leaves
What does cryptochrome do?
establishes circadian rhythm
Chamovitz says, "Plant vision is much more complex than human sight at the level of perception." How can we justify this statement?
Because plants are rooted in one place, seeing light is much more important to them. In order to eat, they need to know where the light is coming from. It's not like they can get up and find food, so they grow towards the source instead.
What is the photosynthesis CHEMICAL formula?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight = Glucose (biproduct: oxygen)
What is a circadian rhythm?
A biological 24 hour clock in which bodily functions are most optimally executed. We use blue light levels to tell what time on the biological clock it is.
How do you work with your circadian rhythm?
People tend to function better when they follow their circadian rhythm. This means minimizing the amount of time spent using a screen closer to the optimal bedtime (9 - 10). Unnecessary use of screens can trick your body into thinking it's a different time of day, and can throw you off. The best time to wake up is from 6:45 to 7, meaning we should be getting 9 - 9.75 hours of sleep. The added blue light of screens can, again, throw off your sleep cycle.
Describe the function of a human olfactory receptor.
Olfactory receptors send signals to the brain when airborne molecules bind to them; they convert a chemical to an electrical signal.
What is the olfactory epithelium?
a thin layer of tissue, within the nasal cavity, that contains the receptors for smell and the mucus secretion glands
Why might poor human olfaction be a 19th century myth?
size of olfactory bulb / size of brain >>>does not necessarily equal>>> olfactory ability
How many unique olfactory protein receptors do we have?
400
What proportion of our protein-coding genes is dedicated to olfaction?
1/50 (400 unique proteins / 20,000 genes = 1/50)
How can humans smell 10,000 distinct odors?
different smells trigger different olfactory receptors (a combination of 40 million receptors), leading to our brain perceiving different smells.
What are pheromones?
chemicals used to communicate with other members of the same species
Why might you be suspicious of a date that shows up to your doorstep wearing lots and lots of cologne or perfume?
You won't have an idea of what they actually smell like. It is possible to smell if someone has desirable traits. Apparently, being fond of someone's natural smell is a sign that they would make a good life-partner.
What is the role of ethylene in ripening fruits?
Ethylene is a ripening hormone; when a plant smells ethylene, they make the fruit ripen much faster to match the rest of the nearby fruit.
Why might a plant with animal-dispersed seeds be interested in having all its fruits and the fruits of its neighbors ripen at the same time?
It's easier for an animal to notice a tree full of red, ripe apples. Having all of the fruits ripen at the same time means their seeds have a higher chance of being dispersed.
How is Cuscuta different from most plants?
Cuscuta, or the Dotter plant, is a parasite that feeds off of the water and nutrients of other plants. It uses nozzles to suck said nutrients out of the host plant, and will flower once it's matured.
Discuss the experiment that demonstrated Cuscuta showing a preference for a particular host plant.
When given the choice between a tomato plant and a wheat plant, the parasite prefers the tomato plant because of its scent.
Why do we think that Cuscuta chooses its host based on olfaction?
Airtight-sealed tomato plant vs vial of tomato scent | Scent Wins
Differentiate the terms "intraspecific communication" and "interspecific communication"
Intraspecific = within a species
interspecific = between species
How can a plant know that a neighbor is being attacked by herbivores?
The plant under attack will release a warning pheromone, telling their neighbors to be on high alert
Why might it increase an individual's fitness to know a neighbor is being eaten?
By being prepared for a foreign invasion, an organism is more likely to survive
What characterizes a bryophyte?
Nonvascularity; the inability to carry water and nutrients throughout a plant via vascular tissue
Why are bryophytes so small?
they lack vascular tissue, and need to stay low to the ground
Distinguish between the gametophyte and sporophyte stages of the bryophyta.
Gametophyte stage: pre-fertilization stage. Rhizoids grow into the ground (roots, of sorts), and a stalk grows upwards. Then, the female and male organs are introduced: Archegonia creates the egg, antheridia creates the sperm.
Sporophyte stage; post-fertilization stage. Zygote grows to make the sporangium, that will eventually release spores.
How is water essential in the life cycle of a bryophyte?
The bryophyte sperm swims through water to reach the egg
Name the differences between Liverworts, Hornworts, and Mosses.
Liverworts: ~9000 species, umbrella shaped sporophyte, lobed thalli
Hornworts: ~200 species, horn-shaped sporophyte, lobed thalli
Mosses: ~12000 species, look comfortable and soft, highly differentiated thalli
What is the bryophyte thallus (plural = thalli)?
Leaf-like structures without any vascularity
What is paleobotany?
The study of ancient plant life
What do the coal deposits dating to the Carboniferous period that we burn for energy have to do with seedless vascular plants?
All of the plants that were around 300-350 million years ago eventually turned into coal
Describe the organization and function of vascular tissue (xylem & phloem) in plants.
The xylem is found at the center of the roots and stem, and serves to send water and nutrients up to the leaves.
The phloem is situated towards the outside of the stem, and carries sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Describe the structure and function of roots, stems, and leaves.
Roots draw water and nutrients from the ground, the stem carries those nutrients to the leaves, and the leaves use the nutrients (along with the sun) to photosynthesize and create sugars, which the stem distributes to the rest of the plant.
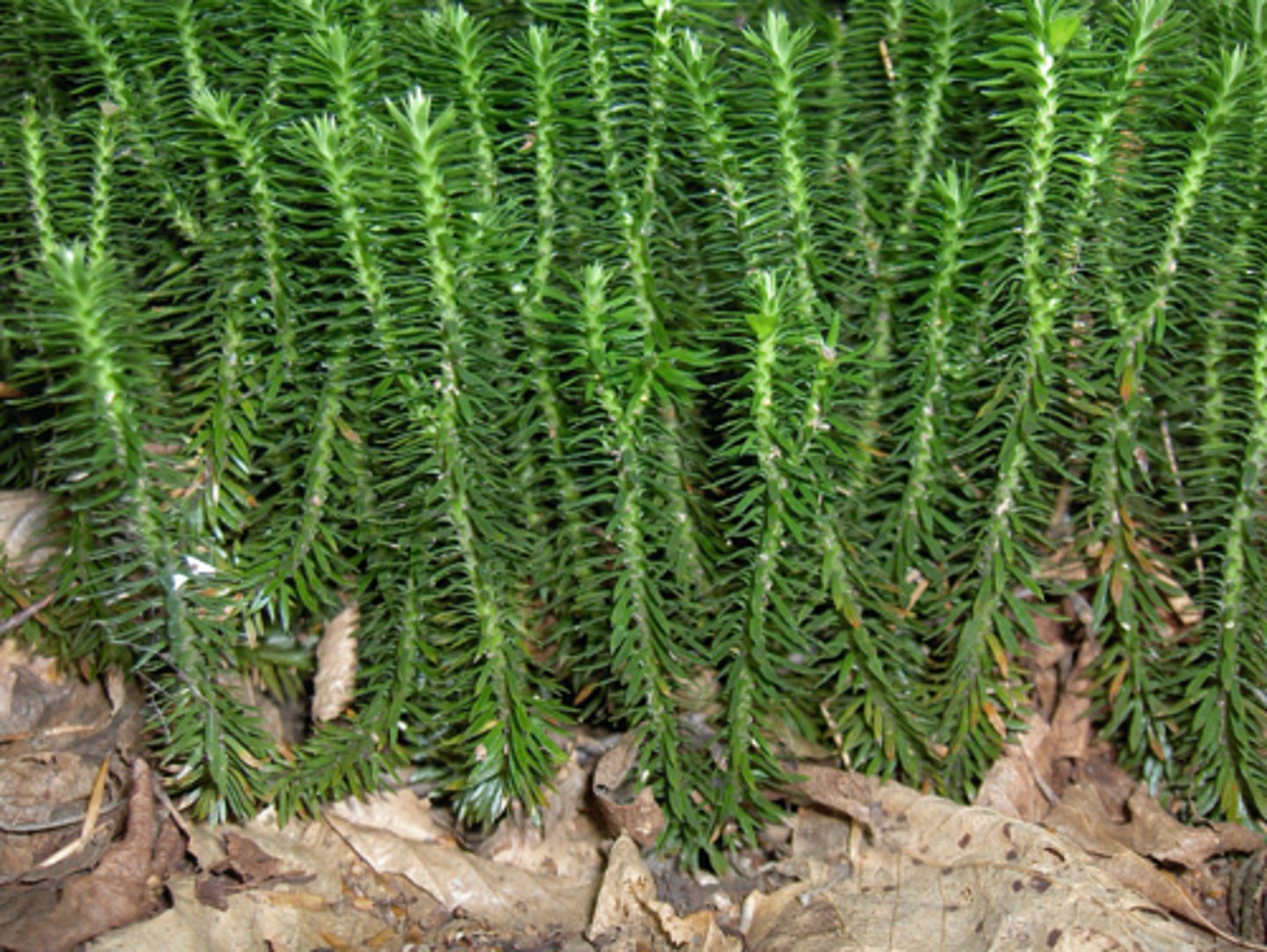
Describe Lycophyta
Vascular, seedless, short, bristly plant: "club moss"

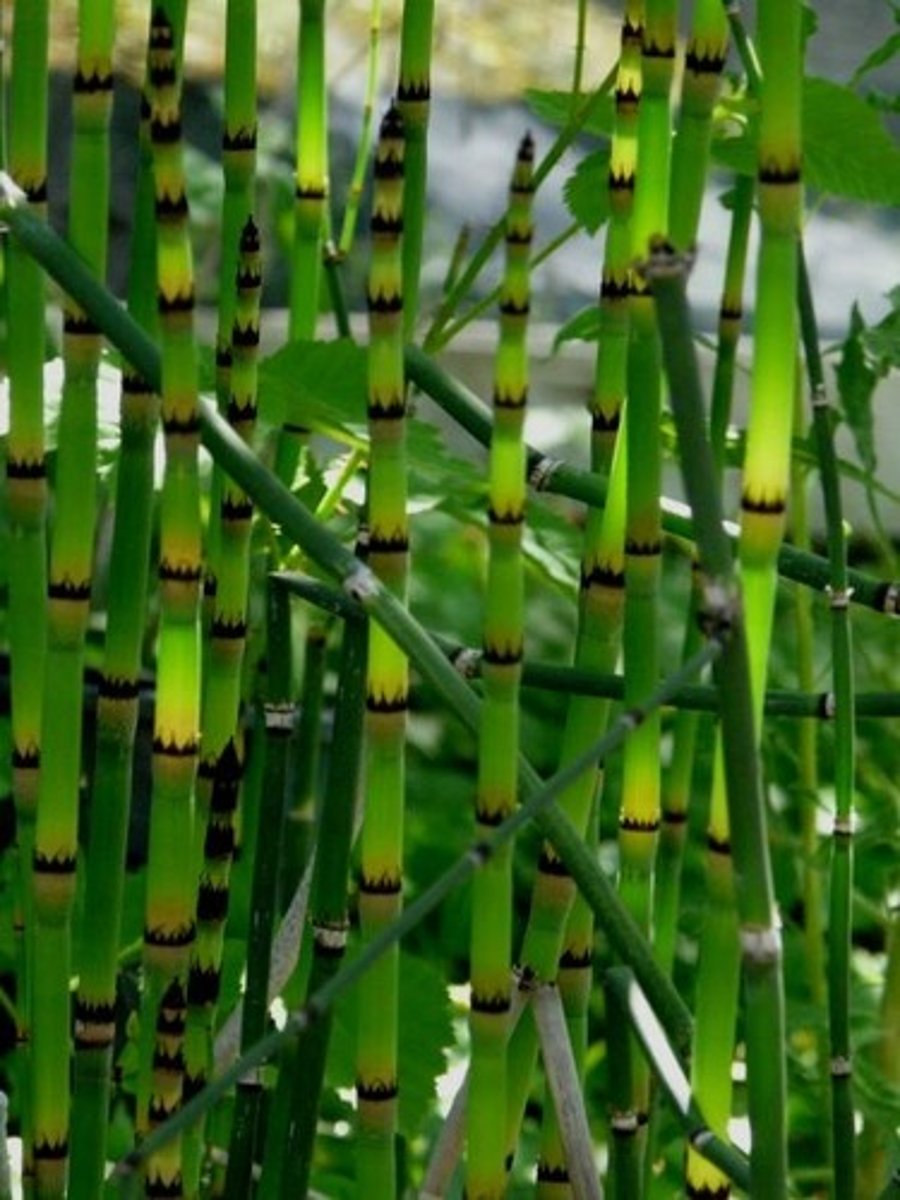
Describe Arthrophyta
Vascular, seedless, superficial bamboo-like exterior; has a jointed look to it

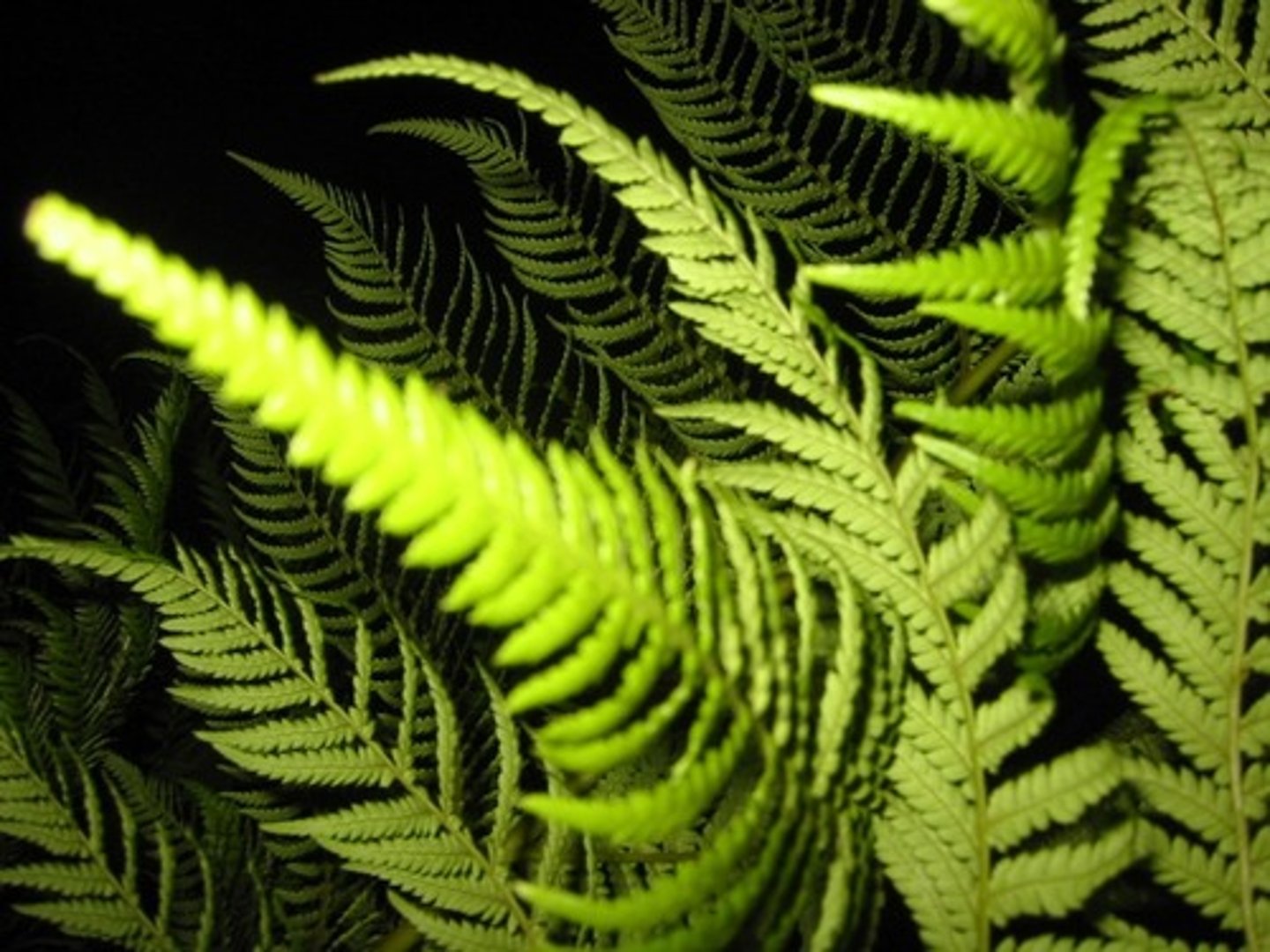
Describe Pterophyta
Vascular, seedless, has fronds with varying levels of division

What's the difference between the gametophyte and sporophyte stages of the Pterophyta?
The gametophyte stage disappears once the fern reaches adulthood; only existing until its sporophyte starts growing and it shoots roots into the ground
The fern we see is the sporophyte
Why did seedless vascular plants comprise the very first forests of the earth?
After having evolved vascular tissue, ferns were able to dominate the scene.
What is the petiole of a leaf?
The stem of a leaf
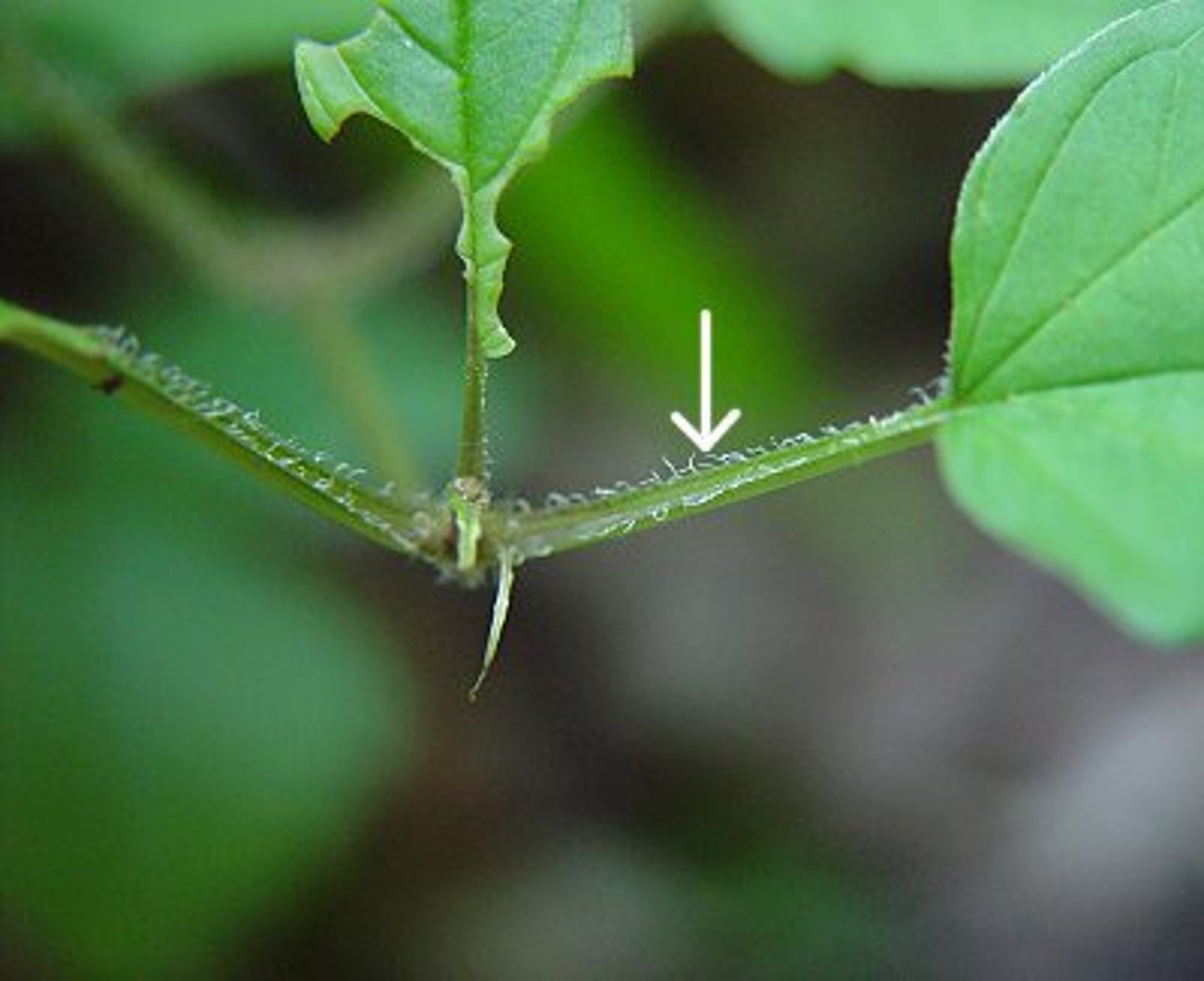

What is the blade of a leaf?
The flat part of the leaf that conducts photosynthesis
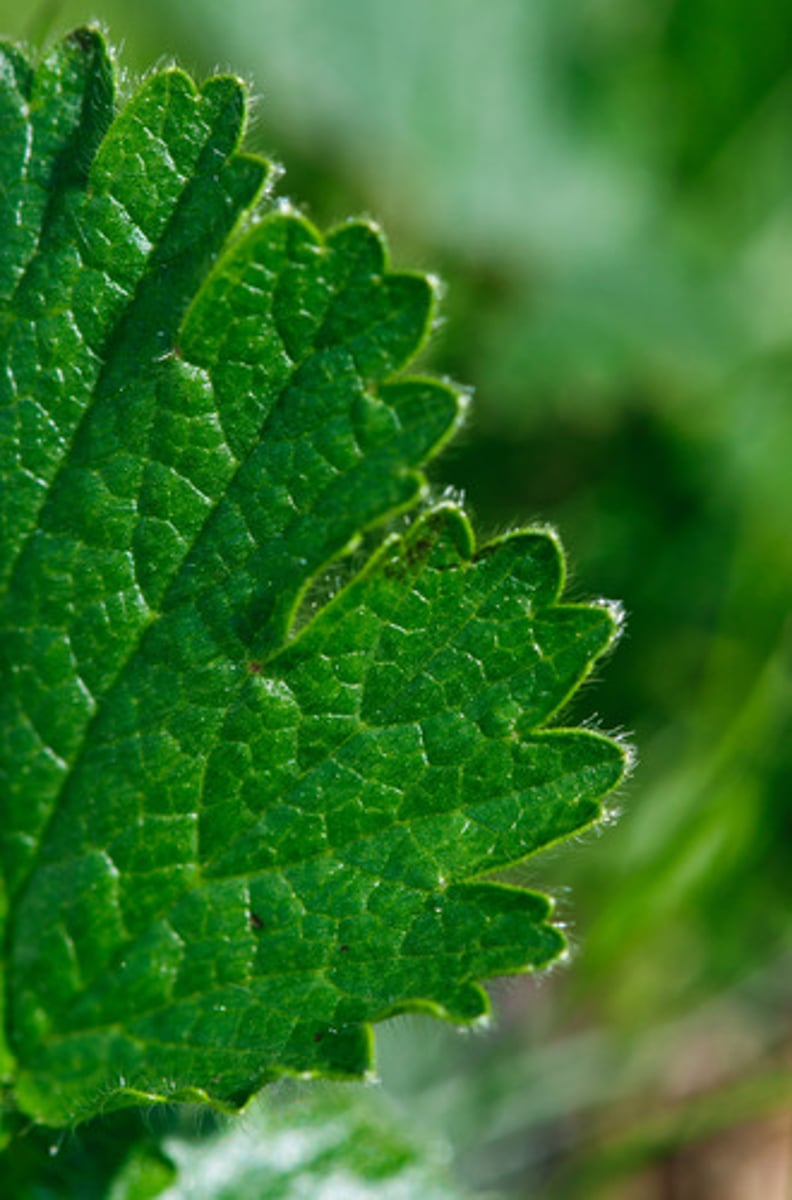

What is a frond?
The leaf of a fern; responsible for both photosynthesis and reproduction
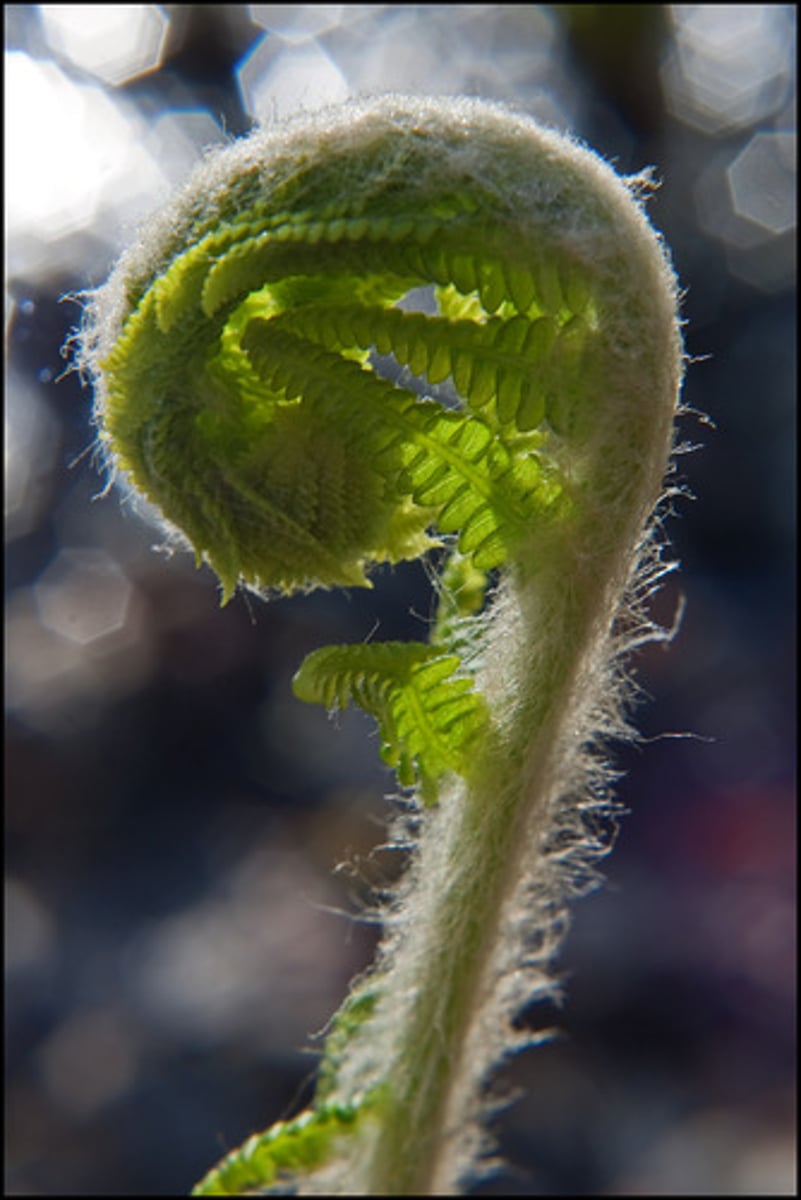
Describe a fiddlehead
the frond of a fern as it is unrolling

Label the image on the back using these terms: sorus, indusium, sporangium (ignore d)
Answers sold separately (on separate card)
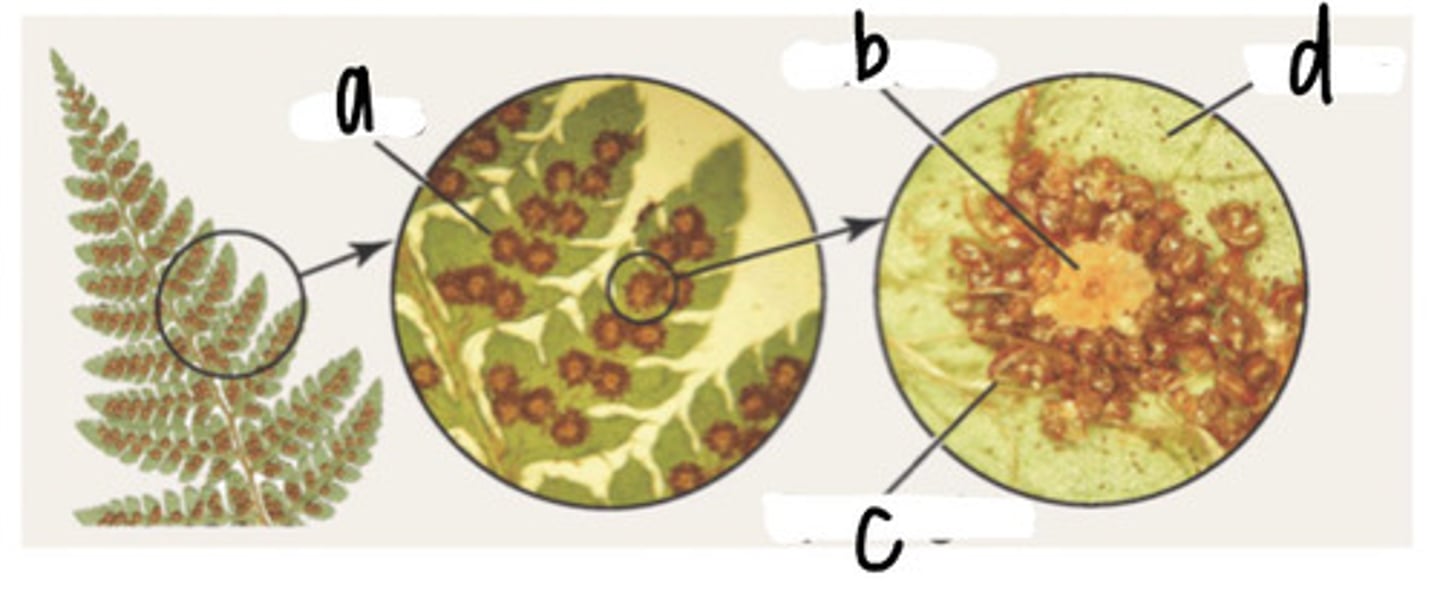
Answer to fern reproduction mix/match
a: sorus
b: indusium
c: sporangium
What is a rhizome?
horizontal underground stem
How are the seeds of gymnosperms fundamentally different from the seeds of flowering plants?
They have naked seeds; they aren't surrounded by an ovary.
As opposed to angiosperms, which have their seeds encased in a fruit.
In the Coniferophyta, male and female cones may occur on the same tree. How does the distribution of cones on a tree favor cross-pollination rather than self-pollination?
Male cones are on the bottom of the tree, and female cones are on the top of the tree.
The wind will carry the pollen away from the tree, instead of having it fall straight down (will almost guarantee self pollination).
Describe Gnetophyta
Vascular, has seeds, rhizome, leathery leaves
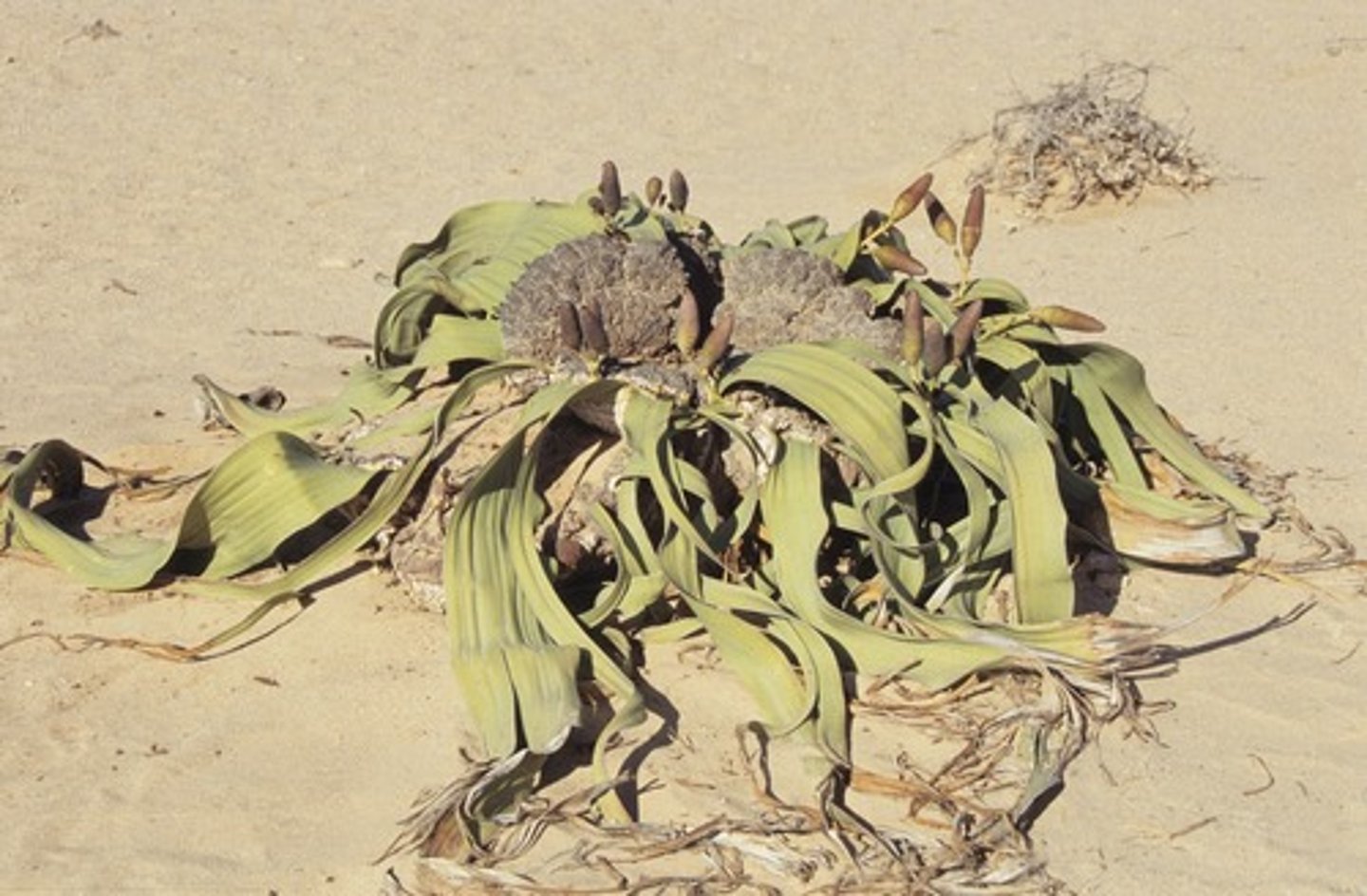

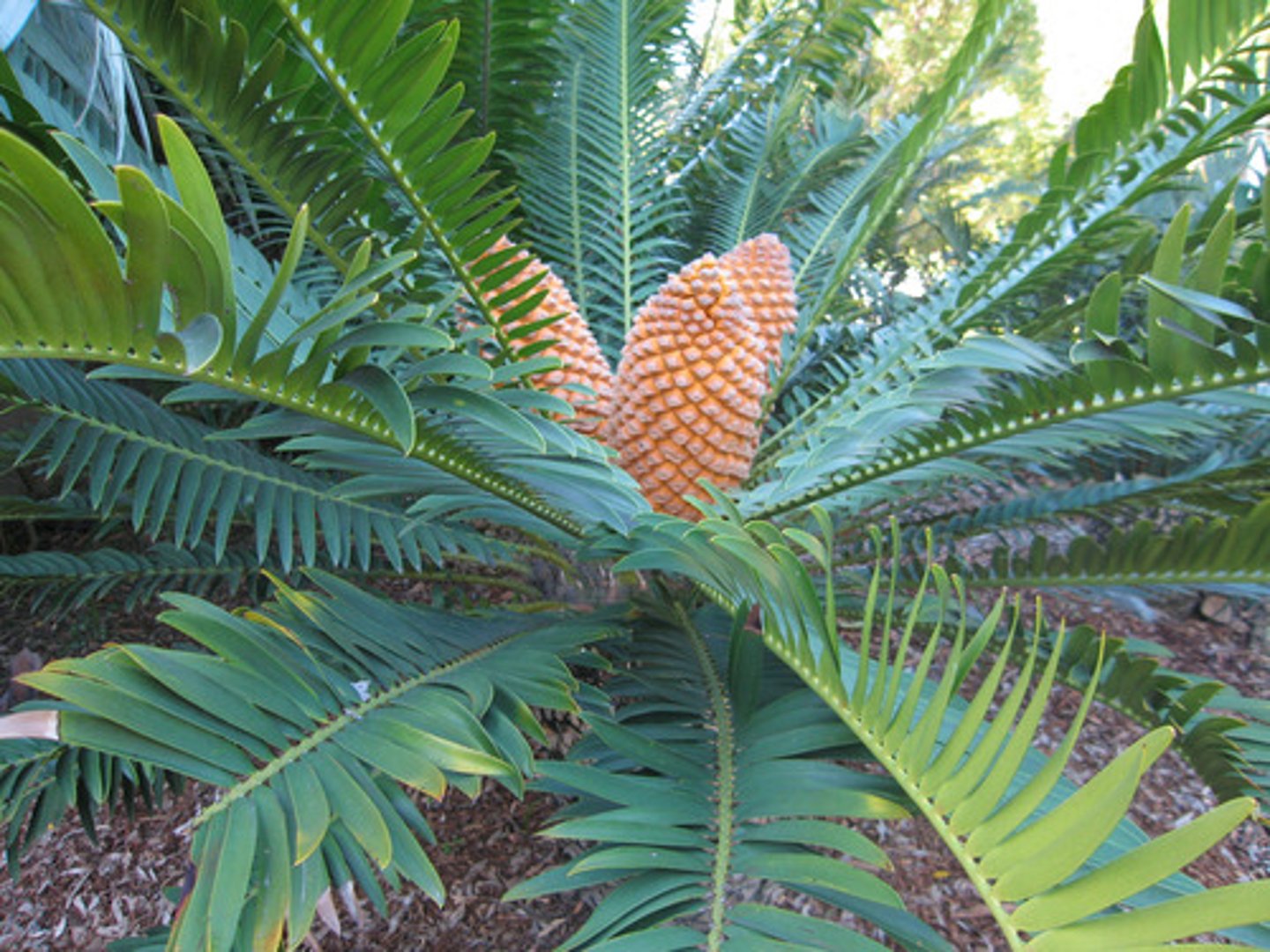
Describe Cycadophyta
Vascular, has seeds, palm-like leaves, carries seeds in the cone near the center of the plant

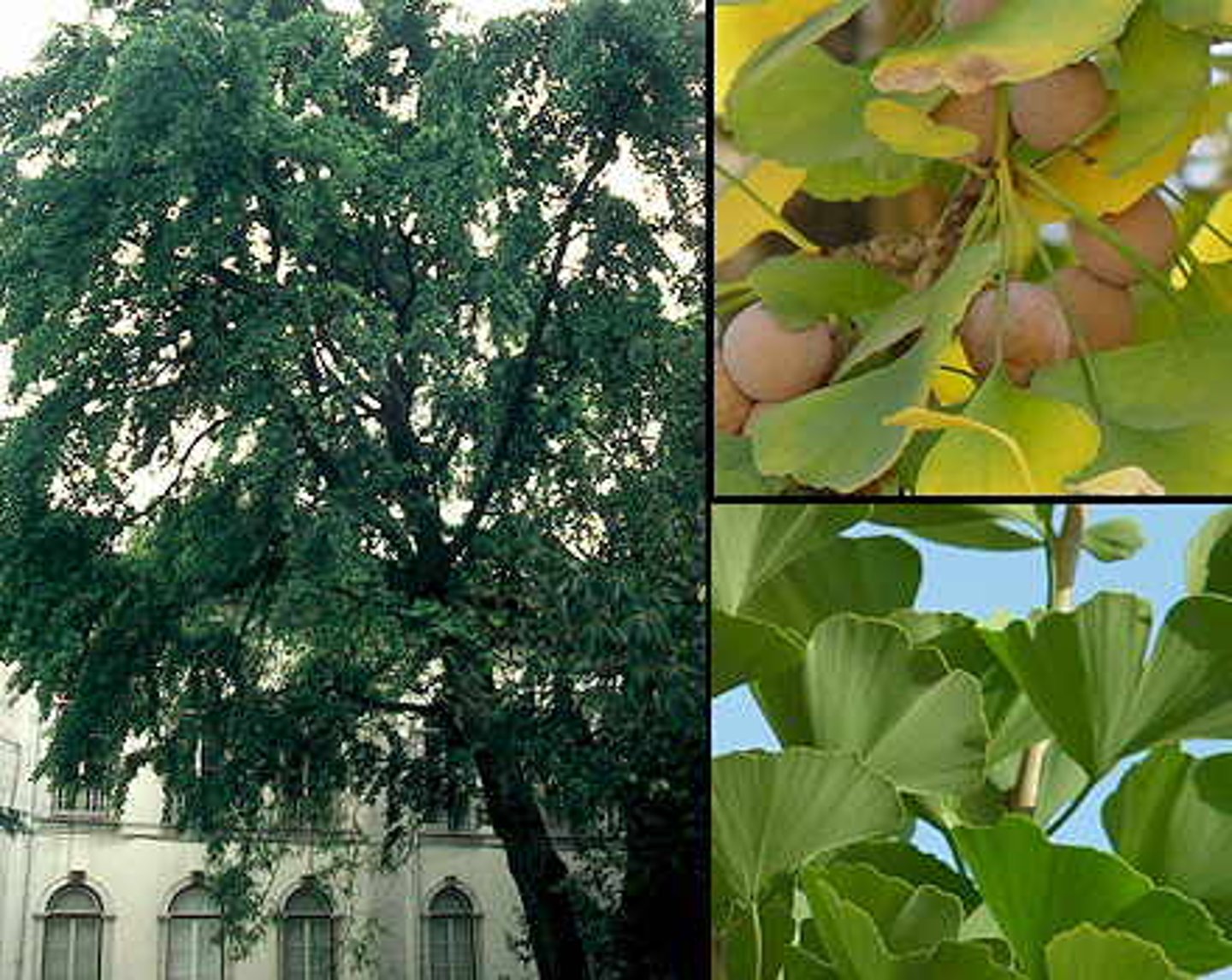
Describe Ginkgophyta
Vascular, has seeds, fan-shaped leaves, fruits smell like parmesan cheese, oldest genus that is extant

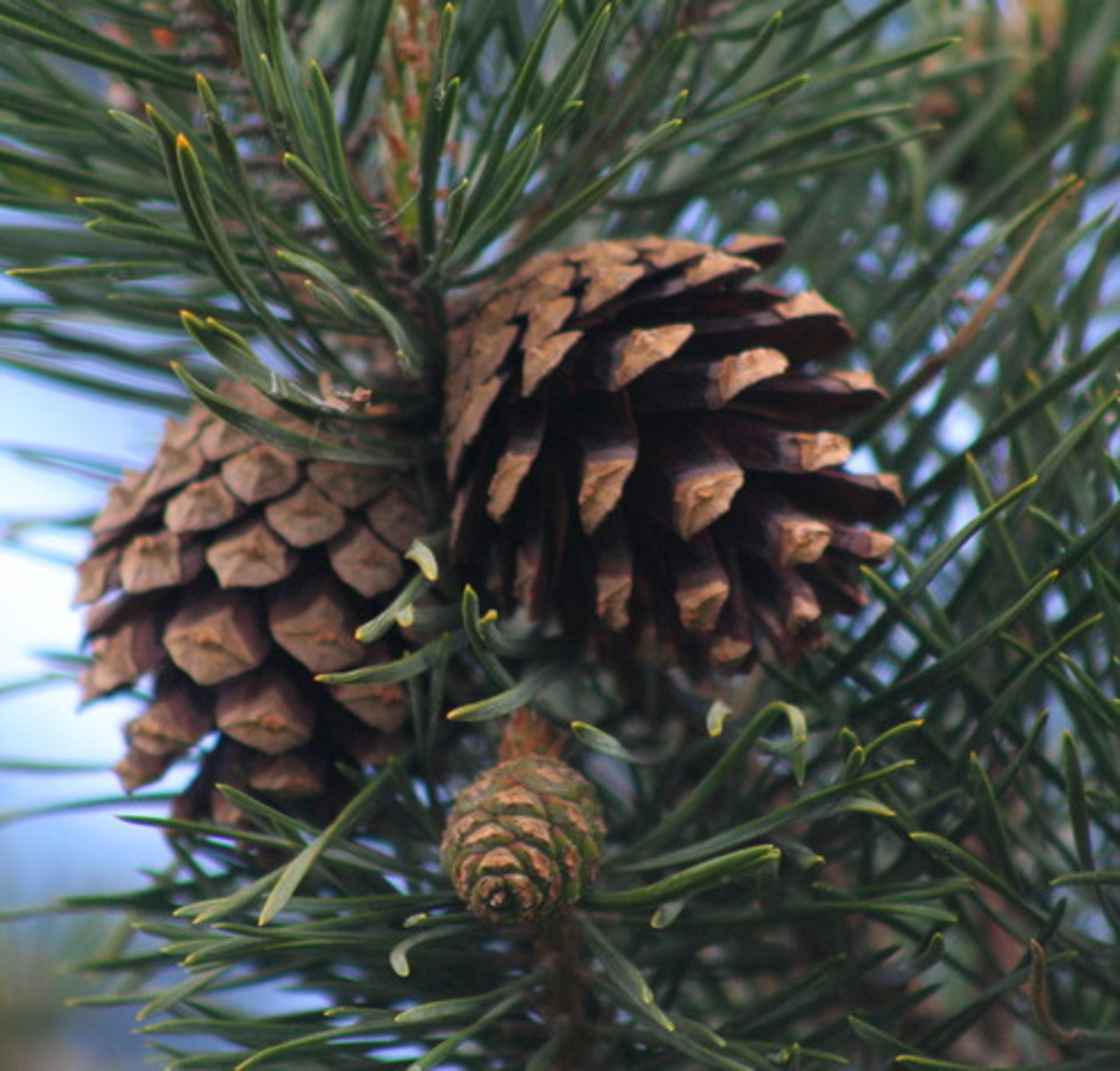
Describe Coniferophyta
Vascular, has seeds, carries seeds in cones (e.g pine tree)

A monocot has _____ cotyledon(s)
1
A monocot has _____ veins
parallel
A monocot has floral parts in groups of _____
3
A monocot has vascular tissue _____ in their stems
scattered
A monocot has _____ roots
fibrous
A dicot has _____ cotyledon(s)
2
A dicot has _____ veins
branched
A dicot has floral parts in groups of _____
4 or 5
A dicot has _____ vascular tissue in their stems
peripherally arranged (organized such they are all arranged at the perimeter of the stem, towards the surface of the epidermis)
A dicot has a _____ root system
taproot (the type of root that a carrot has)
What is a flower?
The reproductive structure of an angiosperm
What is a fruit?
A flower's enlarged ovary
What is the cotyledon?
an embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first leaves to appear from a germinating seed.
What is a woody plant?
a plant that produces wood as its structural tissue
What is a herbaceous plant?
a plant that does not have much wood and its stems are green and soft
What is unique about an annual plant?
They typically go through their life cycle in one growing season (1 year lifespan)
What is unique about a biennial plant?
They typically go through their life cycle in two growing seasons (2 year lifespan)
What is unique about a perennial plant?
They typically live longer than 2 years
What does the endodermis do?
"It regulates the uptake of certain minerals to vascular tissue in roots"
-quiz 4
What does transpiration do?
"Allows for the movement of water in the xylem"
-quiz 4