Drug Stability FULL
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what is drug stability
the capacity of a drug to remain within established specifications of identiy for a specified time
what problems arise due to instablity
loss of drug through chemical reaction
loss of efficacy
poor bioavaliability
what is shelf life
time taken to reduce concentration of drig to 90% of original value
what type of drug form can lose activity
liquid and solid
types of physical instability
volatility
uptake or loss of solvent
polymorphusim
denaturation
chemical instability examples
hydrolysis
oxidation
elimination
racemisation + isomerisatiomn
what factors affecr hydrolysis
ph
temperature
solvent
structure
what dosage forms does pH affect
liquid and solid form
what can the pH rate profile be affected by in liquid doses
buffers
how can you activate the carbonyl carbon for nucleophilic attack by the water molecule
protonation
what is the process called when reversing acid hydrolysis
esterification
what can make a good leaving group
alcohol
what does an increase in temprature do in regards to the hydrolysis rate
increases it
why are stability studies carried out at high tempratures 60-80 celcius
as the hydrolysis rate can be measured more easily
how can you measure the hydrolysis rate
using the arrhenius equation
what is the arrhenius equation
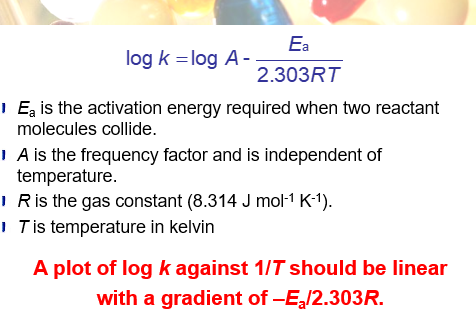
what should you do if a particular drug formulation is unstable at room temprature
label with storage instructions
what is a complication of using the arrhenius equation for solid forms
melts on temprature release
changing of polymorphic form
loosley bound to water which is lost at a higher temprature.
equation to predict the effect of solvent on hydrolysis rate
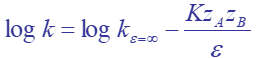
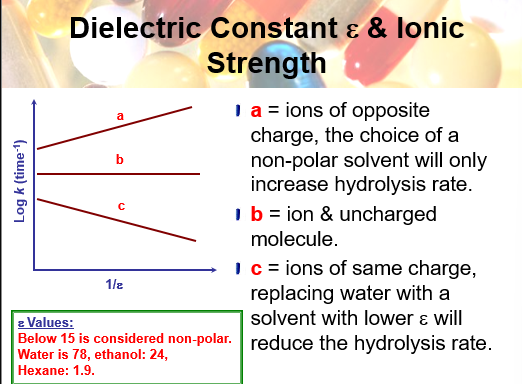
dielecctric constant and ionic strength
what does greater electronegativity lead to in terms of polarisation
increased polarisation
why do esters hydrolyse more readily than amides
as oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen
what can infulence the rate of hydrolysis
inductive and mesomeric effects
what shape is the transistion state
tetrahedral
what may bulky groups do to the hydrolysable group
block or shield it from attack
what is tafts steric factor a measure of
steric effect
what are hydrolysis rates measured under
acidic and basic conditions
what factors are measured under basic conditions
steric and electronic factors
what factors are measured under acidic conditions
only steric factors
how can you protect against hydrolysis
solubilising in surfactants
how can oxative degregation occur
by autoxidation
what is autoxidation
a slow irreversible oxidation in the presence of atmospheric 02
what are the 3 chain processes of autoxidation
initiation propagation and termination including free radicals
what can autoxidation be catalysed by
light and trace metals
what are the factors affecting autoxidation
light
sensitizers
catalysts
hydrogen ion concentration
temprature
how does light affect autoxidation
the energy achived from a light source is capable of forming radical species
how do sensitizers affect autoxidation
upon recieving energy from another molecule they become excited and release light
how does temprature affect autoxidation
generally the rate increases with increasing temprature
how does pH affect autoxidation
by lowering it, it slows it down
what are free radicals?
species with one unpaired electron in their outer shell
what is a heterolytic bond cleavage
both electrons making up the bond move together when the bond is broken

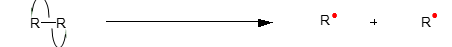
what is homolytic bond cleavage
when the two electrons making up the bond gets distributed equally between the two atoms so each atom gets one electron
what is an enantiomer
they rotate the plane of polarised light by an equal amount in opposite direction
whats an equal mixture of enantiomers called
racemate
how can structures be chiral
if they cannot be superimposed on their mirror image
what is a chiral centre
when a molecule contains a carbon atom containing 4 different groups it will not have a plane of symmetry
how to create a 50:50 mixture of enantiomers using racemisation
inversion of stereochemistry at a chiral centre
a change at one chiral centre gives rise to what
diastereomers
whats the difference between optically active and optically inactive enantiomers
idk there is a Hydrogen bond near the OH bond when its optically active
when does inversion at a chiral centre occur
when the centre is adjecent to a carbonyl group