Lumbar Spine Special Tests - Mod 5 Ortho Study Guide
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
two stage treadmill test
tests for spinal stenosis
-10 minute level walking
-10 minute rest
-10 minute inclined walking
pt can walk longer and farther on incline than on flat surface (because they will lean forward and relieve symptoms as they walk)
segmental hypomobility testing
tests for presence of hypomobiliy
asses AROM, abnormality of segmental motion AbAROM, passive accessory intervertebral motion PAIVM, passive physiological intervertebral motion PPIVM
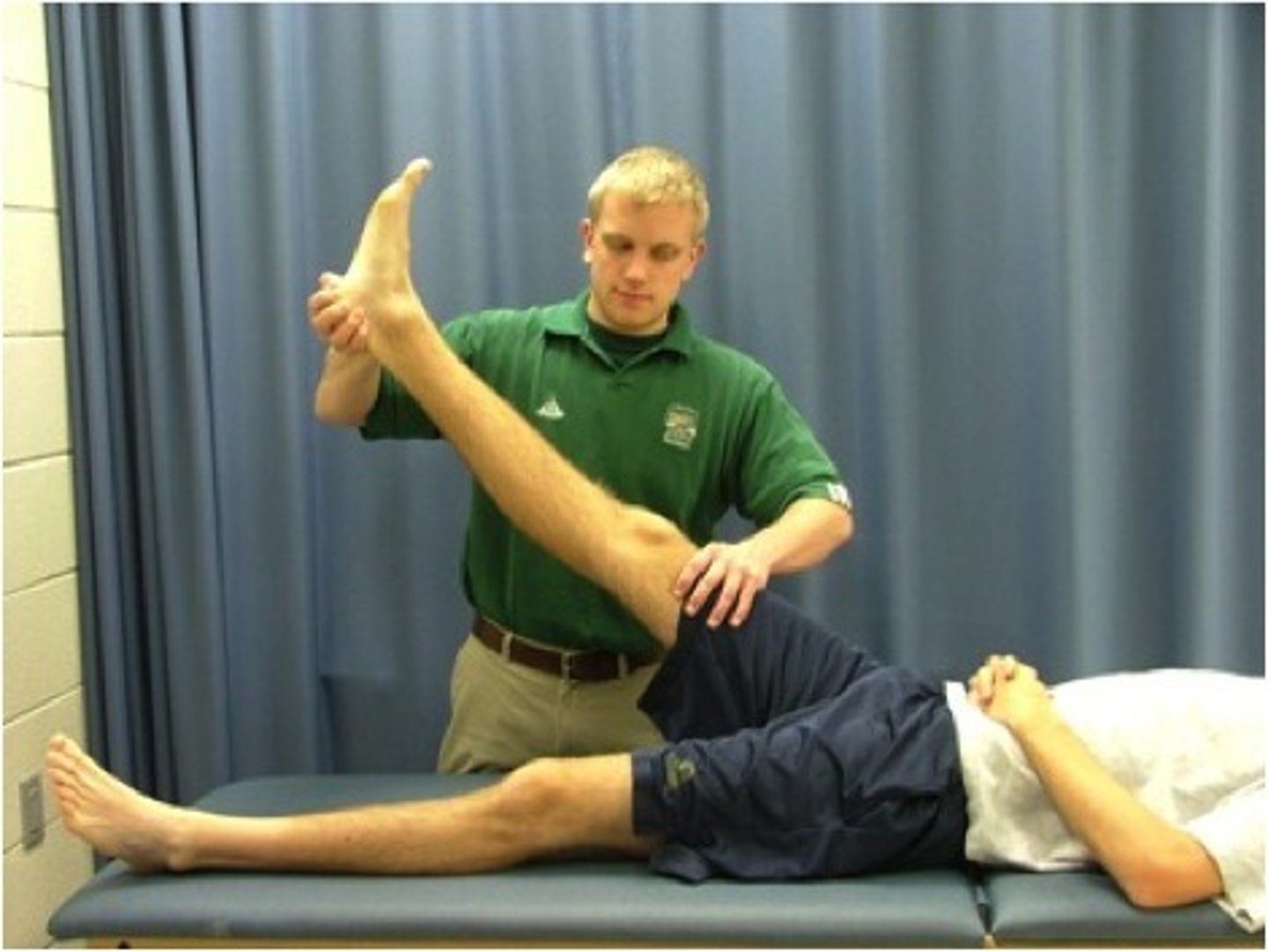
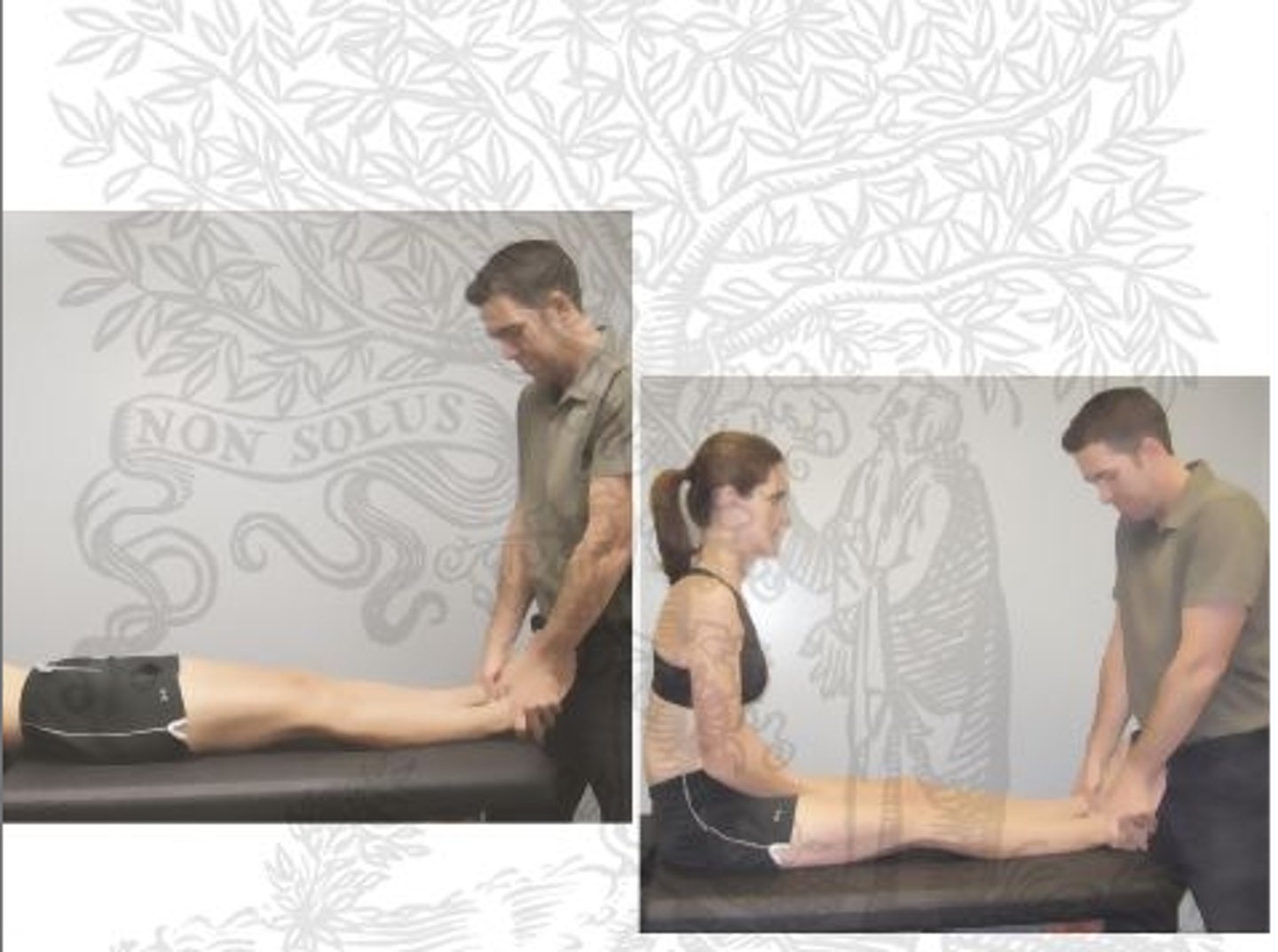
Straight Leg Raise Test
test to determine whether a patient with lower back pain has an underlying herniated disc
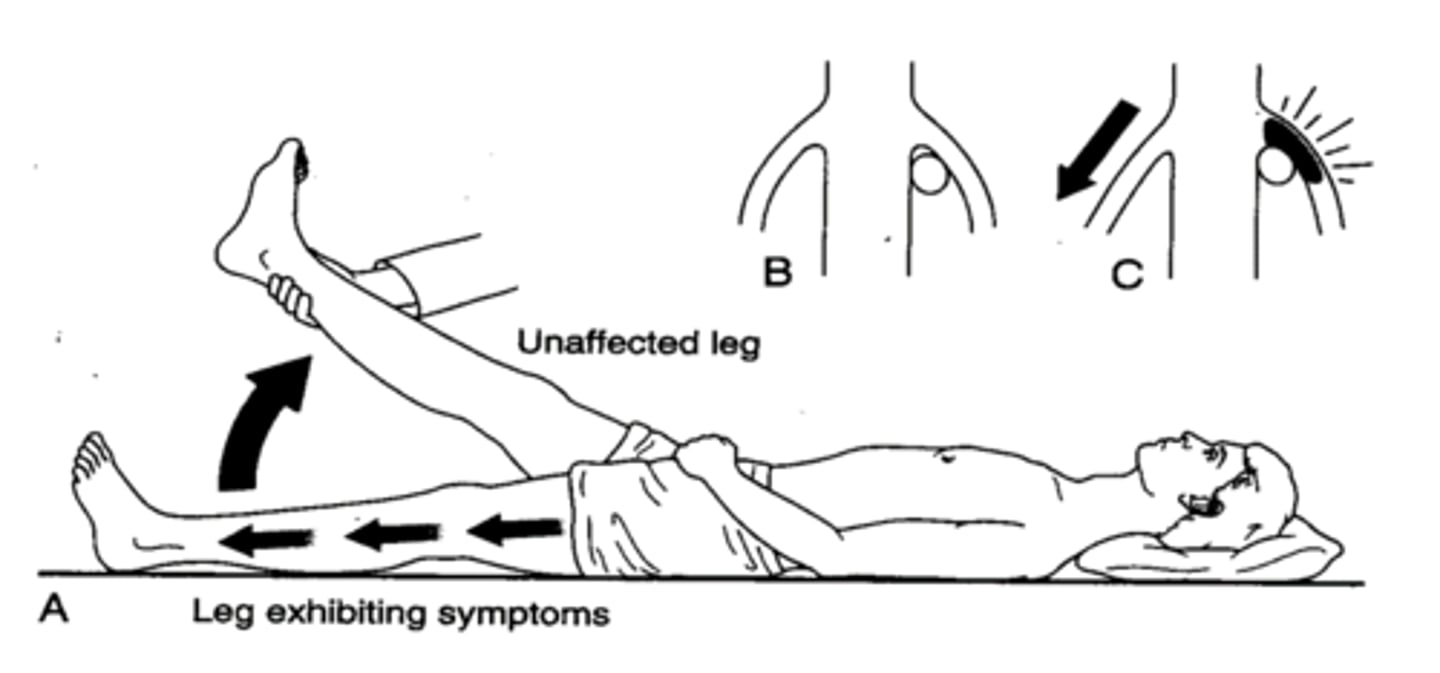
Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
test for herniation; have the patient lay supine. The examiner will passively flex the patient's uninvolved hip while maintaining the knee in full extension. A positive test is considered when the patient reports reproduction of pain in the involved limb at 40 degrees of hip flexion or less in the uninvolved limb. The examiner should make note of the degree of hip flexion where the patient reported pain or reproduction of symptoms.
Bicycle test of van Gelderen
Have patient pedal against resistance on an upright stationary bike
1. Leg pain/paresthesia/cramping -> vascular claudication
2. lateral spinal stenosis will tolerate test well
3. intermittent cauda equina compression -> increased symptoms
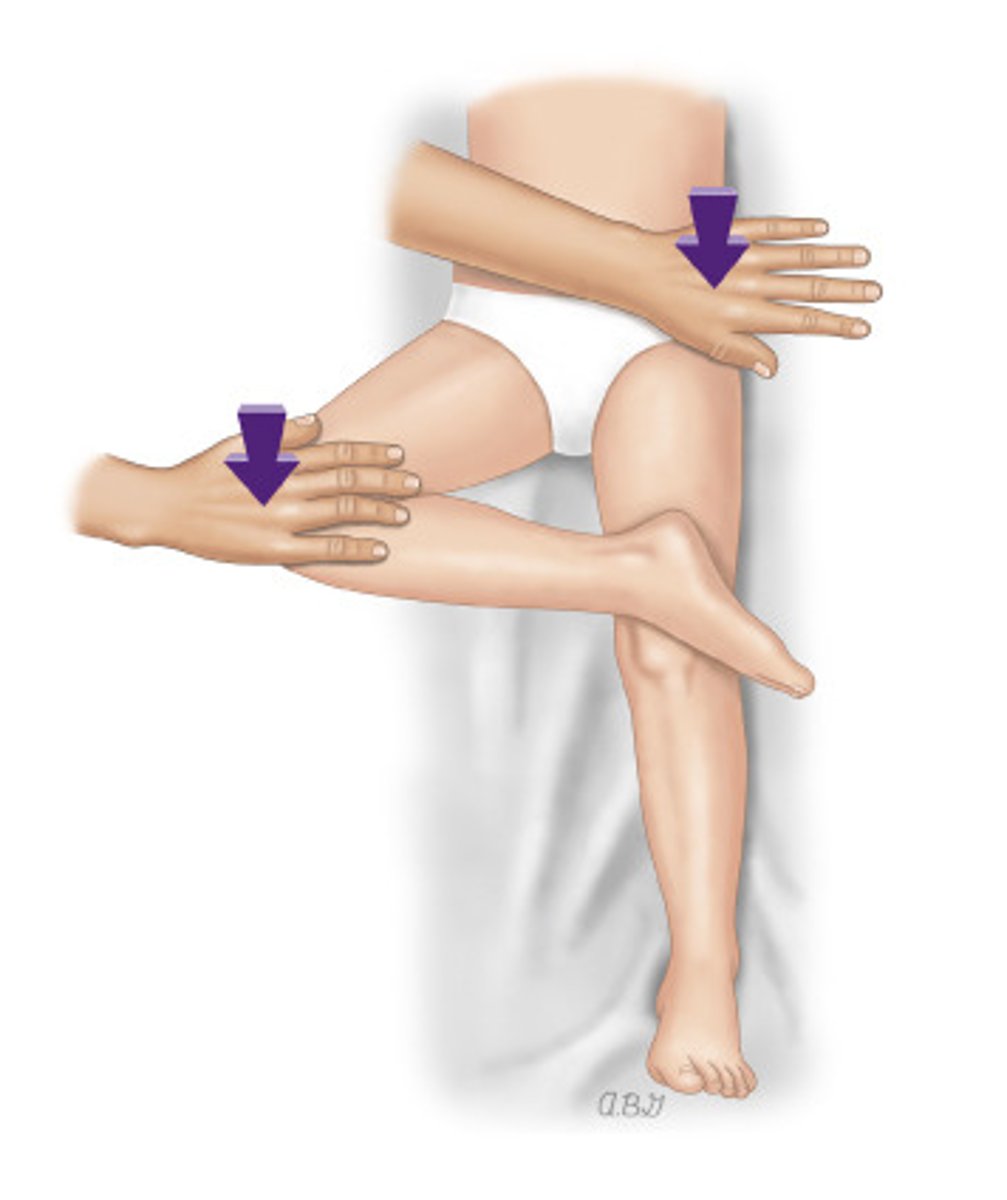
Patrick test / FABER
-Pt hip is flexed, abducted and externally rotated
-pelvis stabalized and overpressure applied to medial aspect of knee
-positive for SIJ if buttock and groin pain reproduced
posterior gapping of the SIJ (compression test)
positive if symptoms are reproduced
pt in supine, cross-over pressure applied to both ASIS
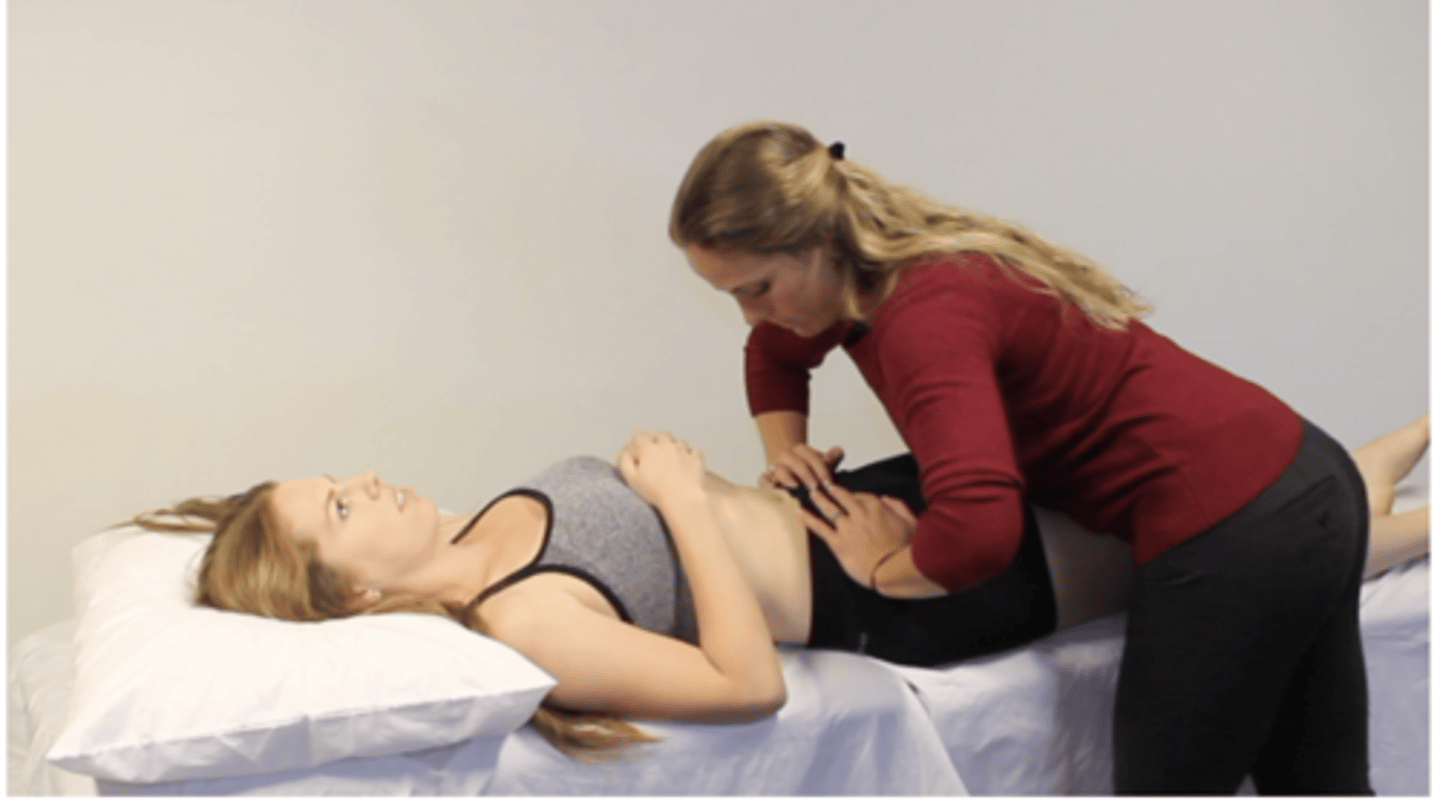
Gaenslen's Test
Patient is supine with the involved side near the edge of the examining table. The opposite knee and thigh are fully flexed and fixed against the abdomen by the patient. The involved leg is gradually extended off the table by the doctor. The doctor then applies downward pressure against clasped knee and knee of the extended hip.
Positive sign is pain the SI joint indicating an SI lesion
Long Sitting Test
SIJ dysfunction due to functional leg length discrepancy. Have patient come from Supine to long sitting. Observe change in medial malleolar positions
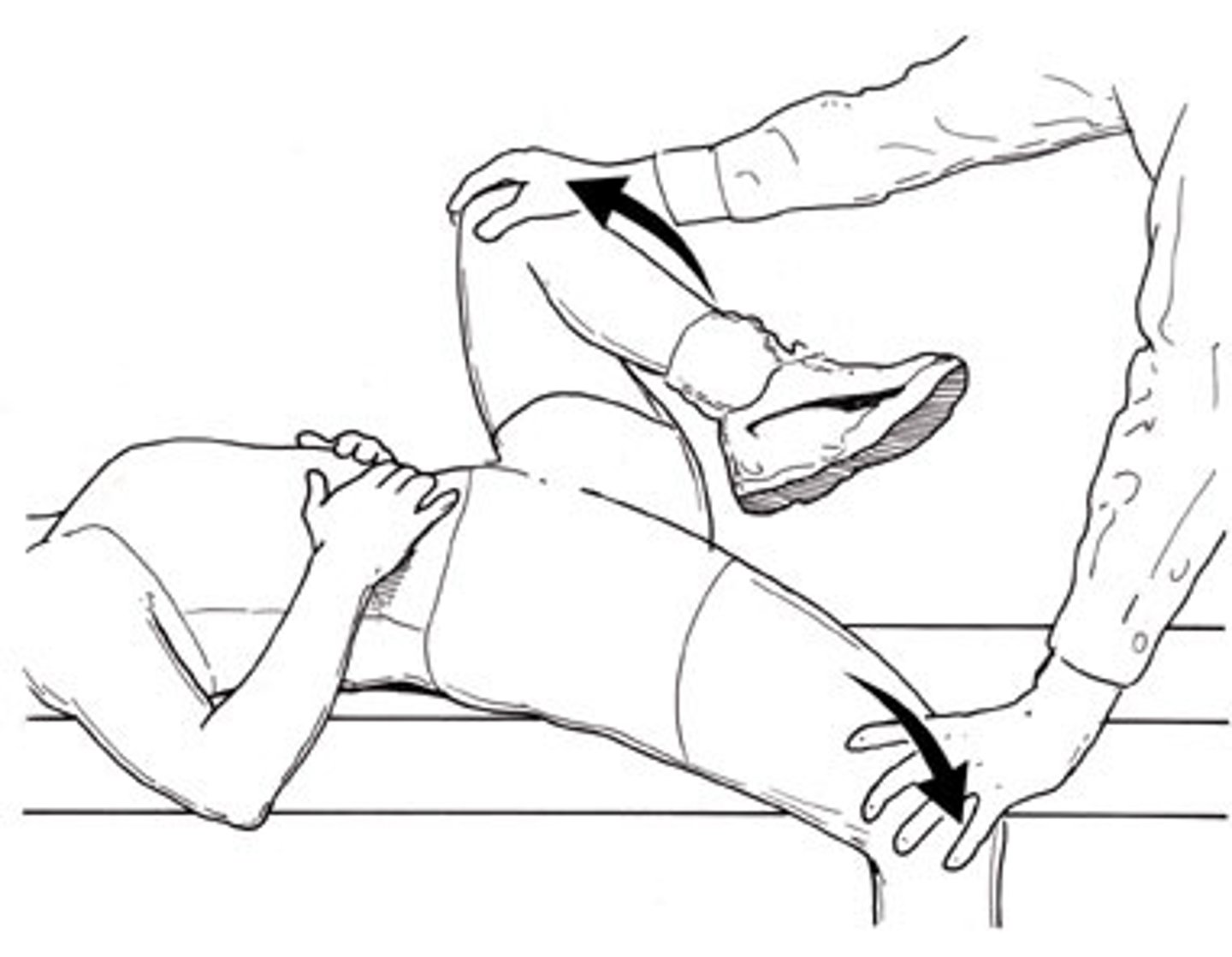
Thigh Thrust Test
___Pt is supine & examiner passively flexes hip to 90 degrees
___One hand palpates the SI joint while the other hand thrusts (pushes) down through the knee and hip (long axis compression)
___Bilaterally performed
___Positive finding: SIJ pain on the same side
___Indication: SIJ syndrome
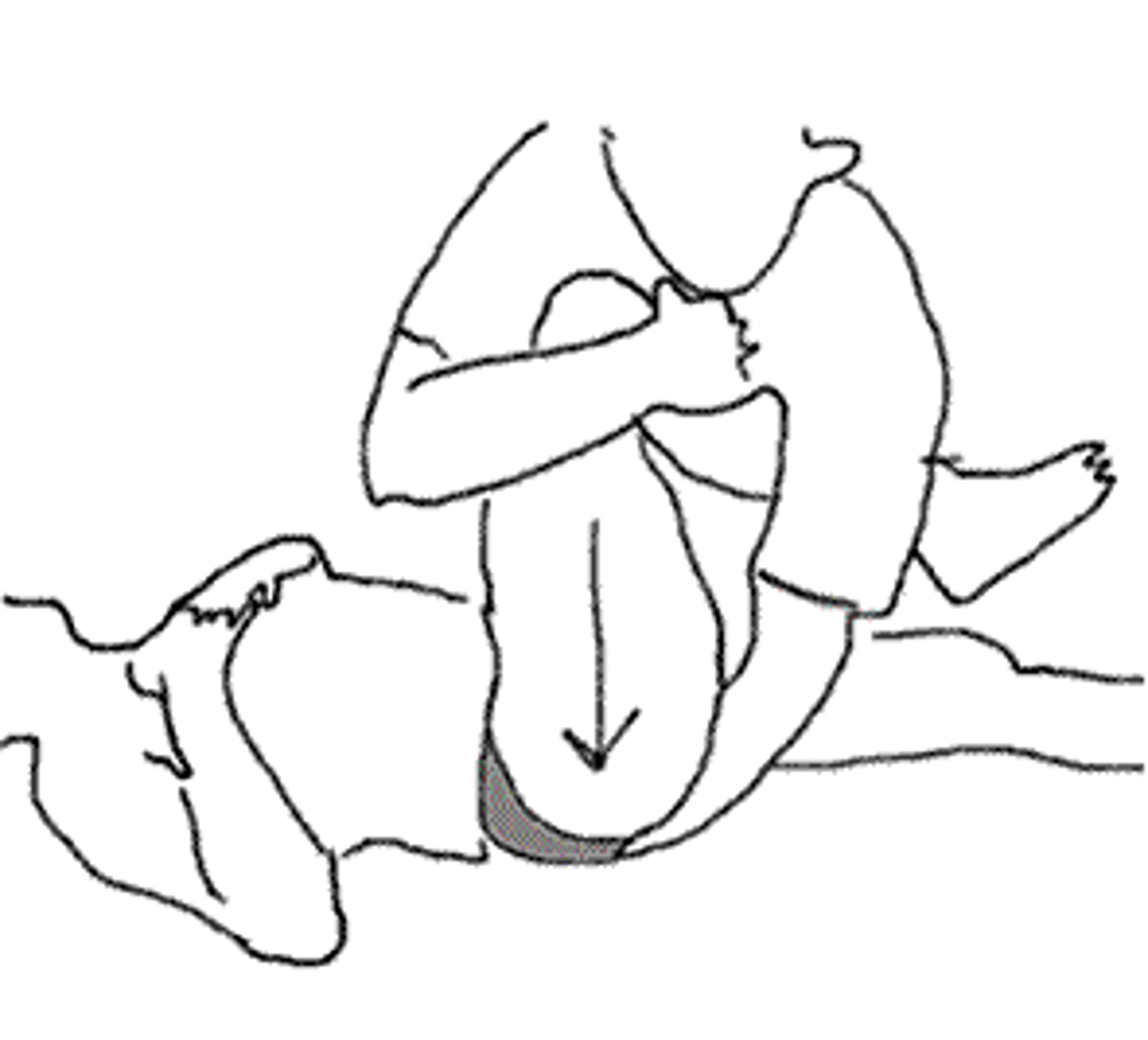
Sacral Thrust Test
Also called Prone Springing & Sacral apex pressure
___Pt is prone
___Examiner puts base of their hand on the center of sacrum and applies a P-A force
___Positive finding: pain over the SIJ
___Indication: SIJ syndrome
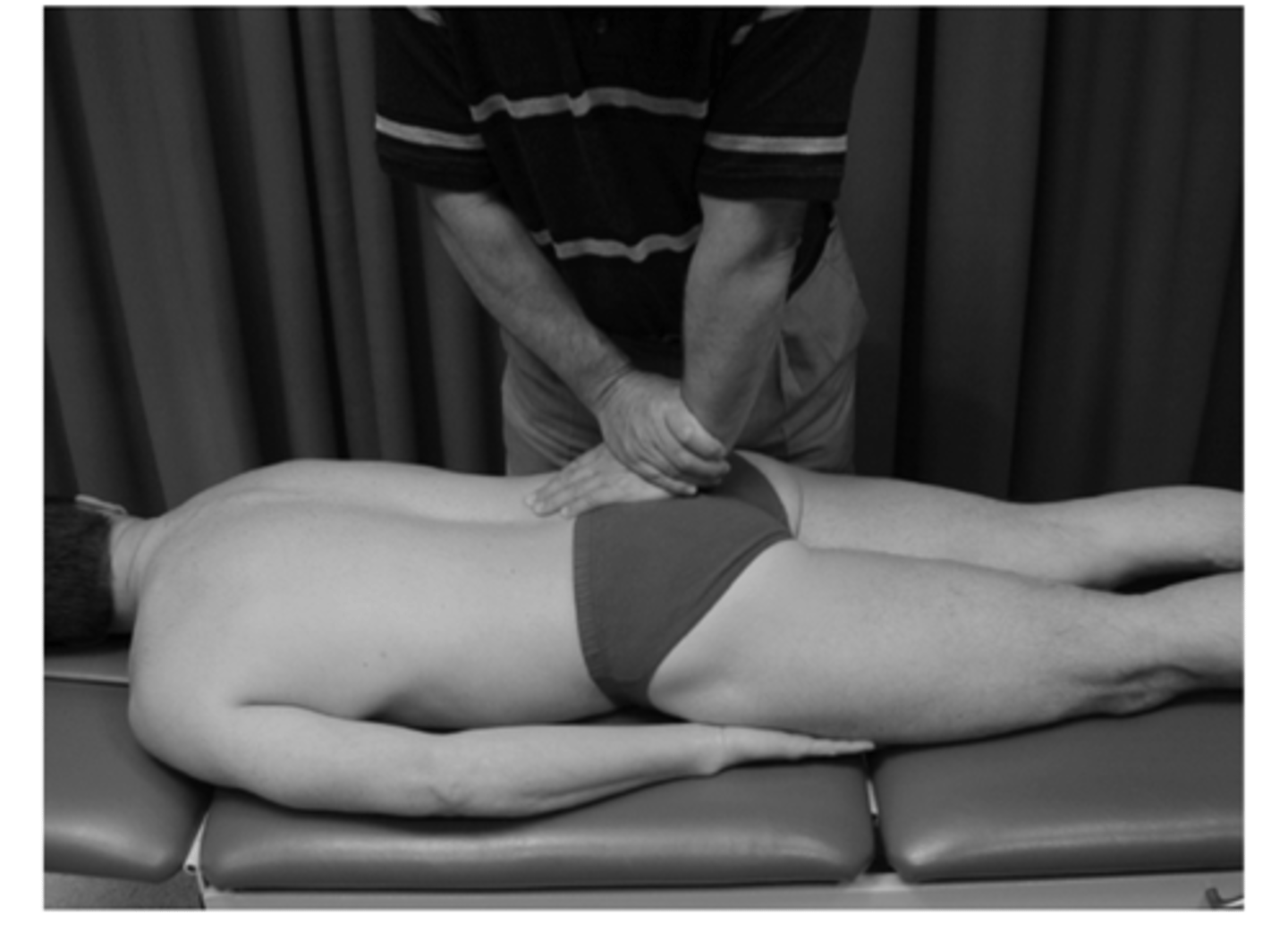
Mennell's Test
+Exacerbation of SI pain
Myofascial involvement of gluteal muscles
SI subluxation or sprain.
pt sidelying involved side down and in hip and knee flexion. clinician places one hand on the ipsilateral buttock and iliac crest and other hand on the semiflexed knee and lightly forces leg into extension
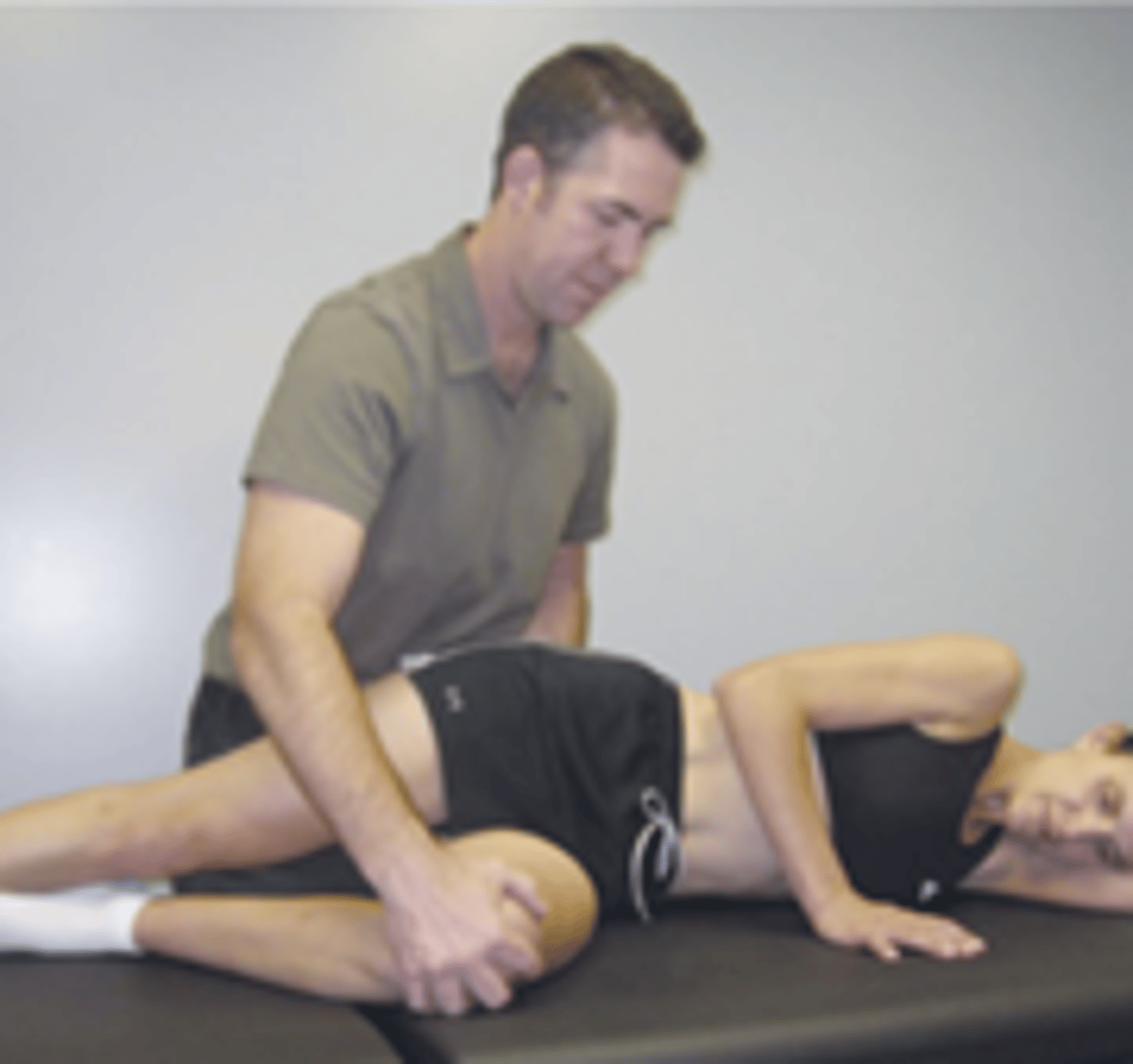
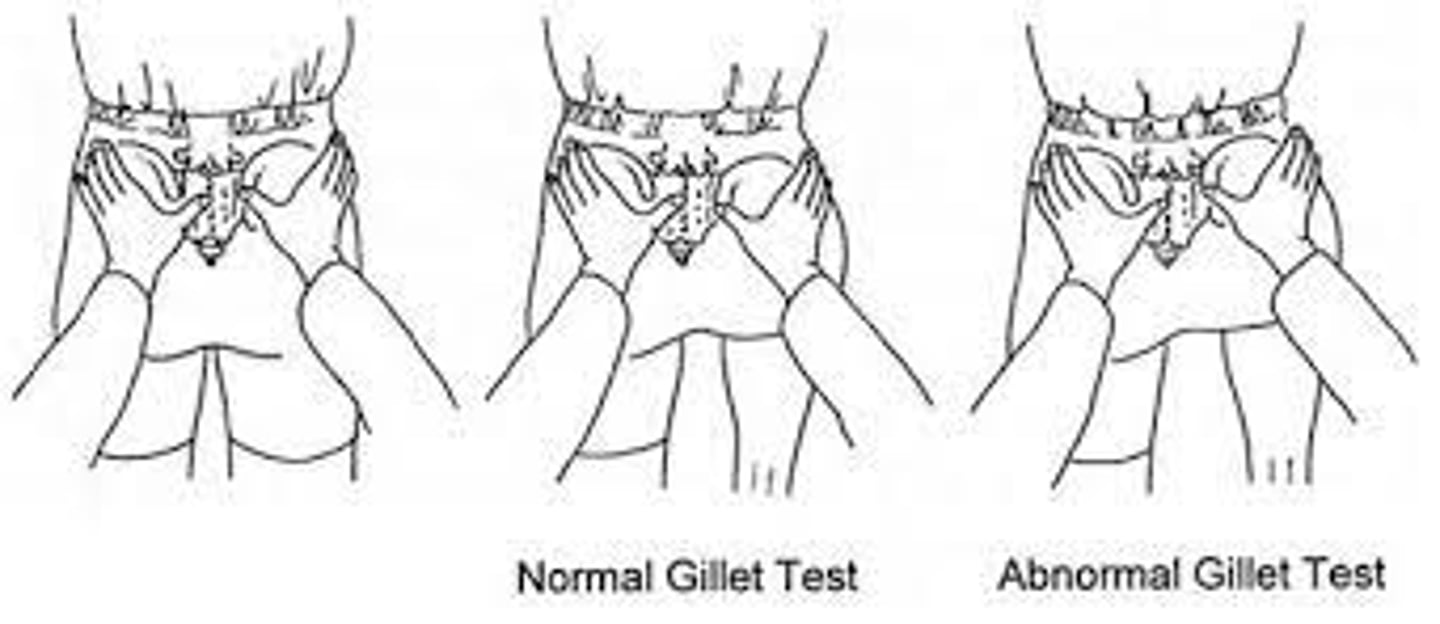
Gillet test
pt standing feet spread 12 inches apart, clinician palpates S2 spinous process with one hand and PSIS with other. pt then flexes the hip and knee on the side being tested.
positive if PSIS fails to move in posteroinferior direction relative to S2
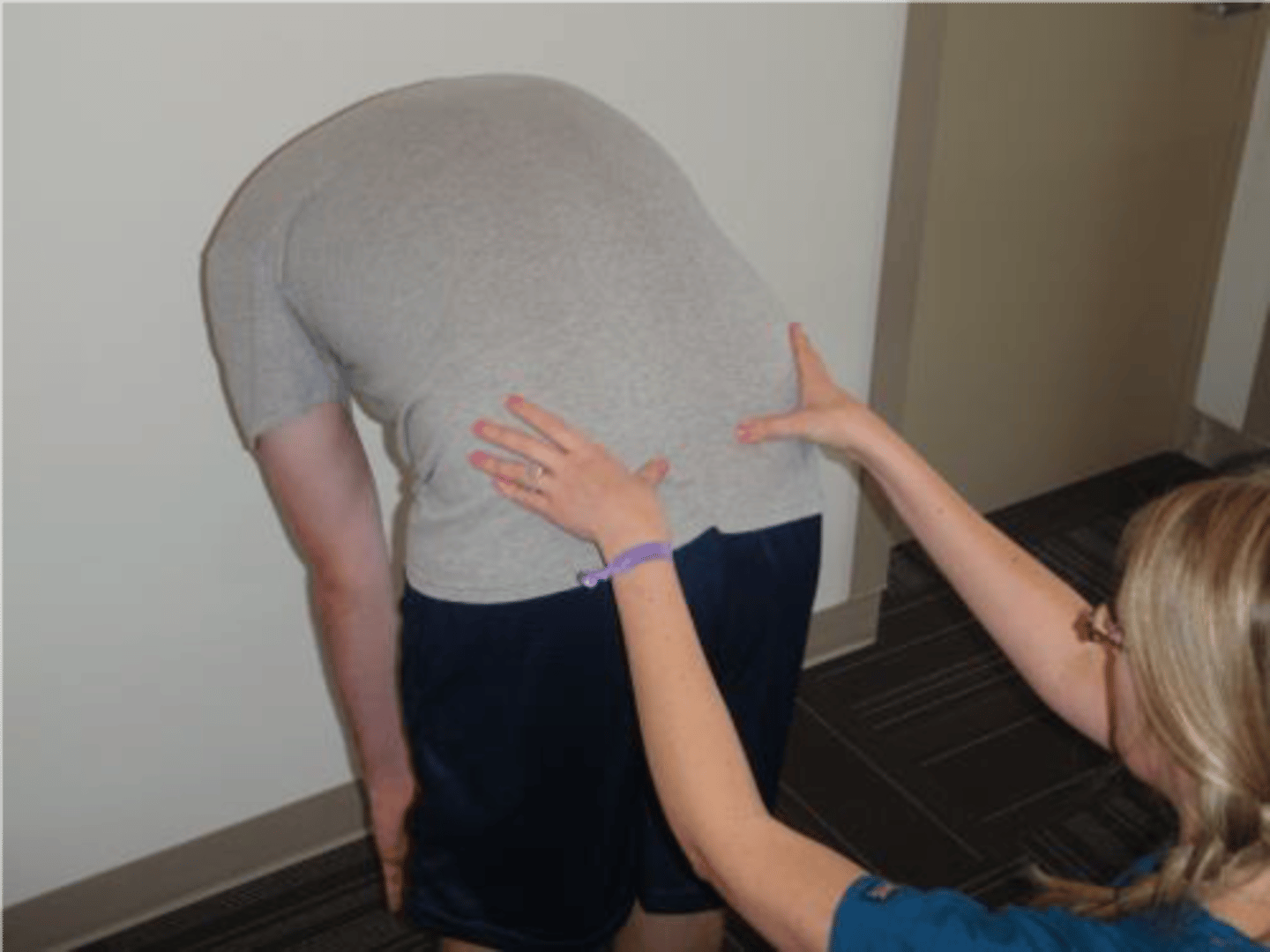
Standing flexion test
Purpose: Sacroiliac articular restriction
Method: Pt is standing. PT palpates PSIS and monitors its movement as pt bends forward
Positive Test: One PSIS moves farther in the cranial direction than the other PSIS.
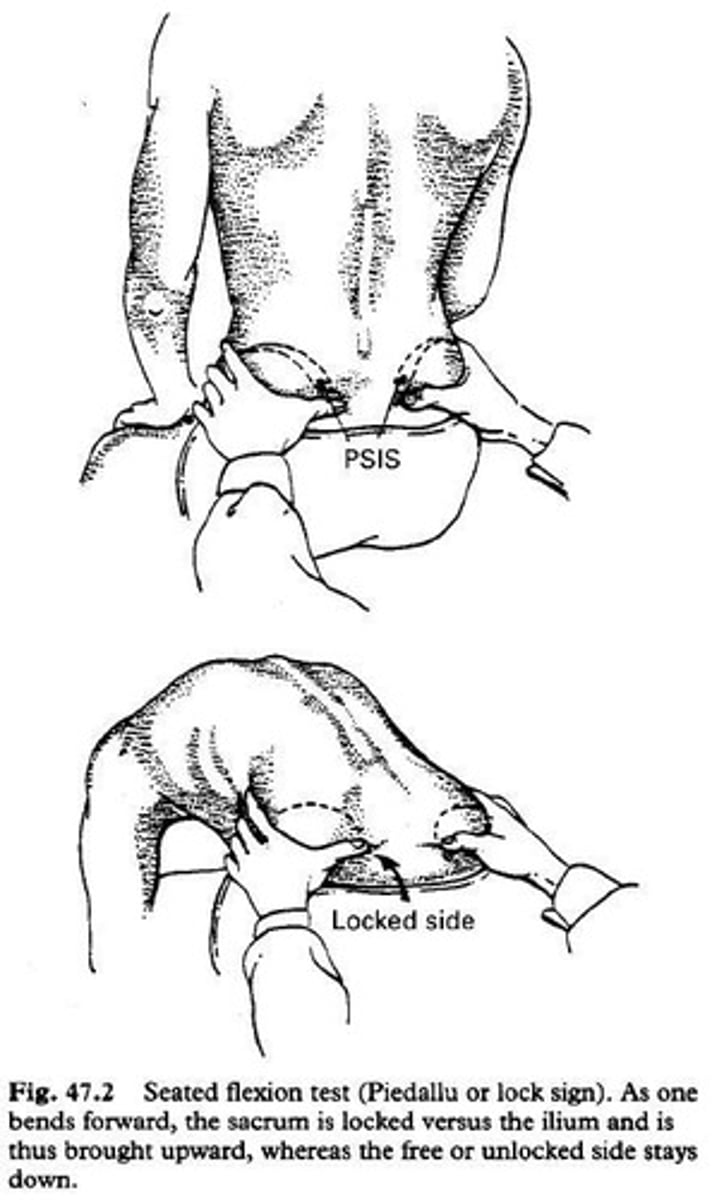
Sitting flexion test
Purpose: Sacroiliac articular restriction
Method: Pt is sitting with feet on floor. PT palpates PSIS and monitors its movement as pt bends forward and touches the floor.
Positive Test: inequality of PSIS movement is found