Marketing Management Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:55 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Marketing
is about identifying and meeting human needs
2
New cards
* Goods
* Events
* Experiences
* Persons
* Properties
* Organizations
* Information
* Ideas
* Events
* Experiences
* Persons
* Properties
* Organizations
* Information
* Ideas
What is Marketed? 8
3
New cards
Segmentation
Divide market into distinct groups of customers
4
New cards
Target Market
determine which customer group to focus your marketing efforts on
5
New cards
Positioning
Determining how a brand is to be perceived to fit into the lives of its target customers
6
New cards
* Product
* Place
* Promotion
* Price
* Place
* Promotion
* Price
Marketing Mix 4 P’s
7
New cards
* People
* Processes
* Programs
* Performance
* Processes
* Programs
* Performance
Modern Management Marketing 4 P’s
8
New cards
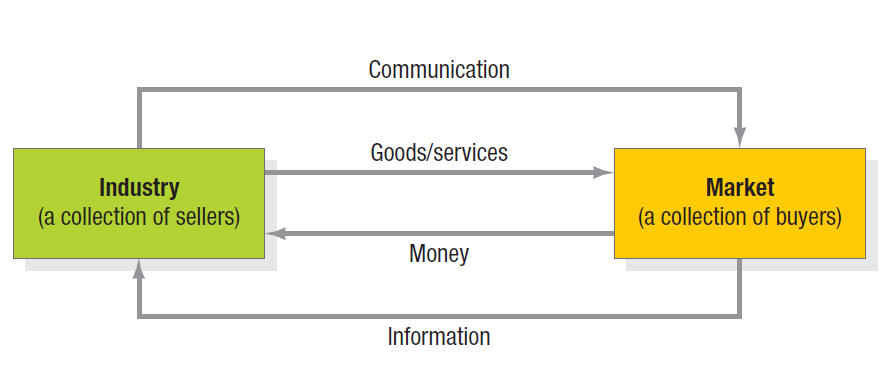
Simple Marketing System
9
New cards
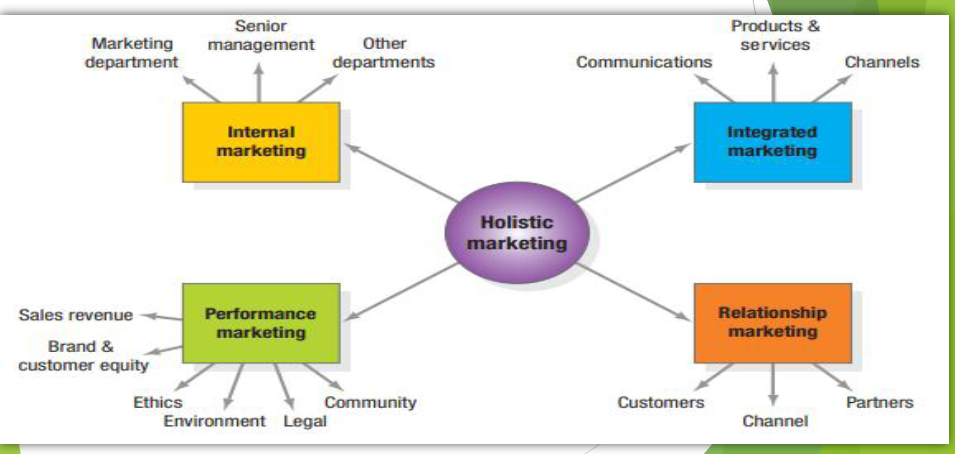
Holistic Marketing Dimensions
10
New cards
Holistic Marketing
* concept is based on the development, design, and implementation of marketing programs, processes, and activities that recognize their breadth and interdependencies.
* acknowledges that everything matters in marketing—and that a broad, integrated perspective is often necessary.
* acknowledges that everything matters in marketing—and that a broad, integrated perspective is often necessary.
11
New cards
* Internal Marketing
* Integrated Marketing
* Performance Marketing
* Relationship Marketing
* Integrated Marketing
* Performance Marketing
* Relationship Marketing
Holistic Marketing is composed of
12
New cards
* Marketing Department
* Senior Department
* Other Departments
* Senior Department
* Other Departments
Internal Marketing includes
13
New cards
* Communications
* Products & Services
* Channels
* Products & Services
* Channels
Integrated Marketing includes
14
New cards
* Sales Revenue
* Brand and Customer Equity
* Ethics
* Environment
* Legal
* Community
* Brand and Customer Equity
* Ethics
* Environment
* Legal
* Community
Performance Marketing includes
15
New cards
* Customers
* Channels
* Partners
* Channels
* Partners
Relationship Marketing includes
16
New cards
Relationship Marketing
aims to build mutually satisfying long-term relationships with key constituents in order to earn and retain their business.
17
New cards
* customers
* employees
* marketing partners (channels, suppliers, distributors, dealers, agencies)
* members of the financial community (shareholders, investors, analysts).
* employees
* marketing partners (channels, suppliers, distributors, dealers, agencies)
* members of the financial community (shareholders, investors, analysts).
Four key constituents for relationship marketing are
18
New cards
Marketing Network
The ultimate outcome of relationship marketing is a unique company asset called a __________, consisting of the company and its supporting stakeholders—customers, employees, suppliers, distributors, retailers, and others—with whom it has built mutually profitable business relationships.
19
New cards
build an effective network of relationships with key stakeholders, and profits will follow
The operating principle is simple:
20
New cards
Integrated Marketing
occurs when the marketer devises marketing activities and assembles marketing programs to create, communicate, and deliver value for consumers such that “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.”
21
New cards
* many different marketing activities can create, communicate, and deliver value
* marketers should design and implement any one marketing activity with all other activities in mind.
* marketers should design and implement any one marketing activity with all other activities in mind.
Integrated Marketing two key themes are
22
New cards
Internal Marketing
is the task of hiring, training, and motivating able employees who want to serve customers well.
23
New cards
Performance Marketing
requires understanding the financial and nonfinancial returns to business and society from marketing activities and programs.
24
New cards
* Executive Summary
* Current Marketing Situation
* Threats and Opportunity Analysis
* Objectives and Issues
* Marketing Strategy
* Action Programs
* Budgets
* Controls
* Current Marketing Situation
* Threats and Opportunity Analysis
* Objectives and Issues
* Marketing Strategy
* Action Programs
* Budgets
* Controls
Contents of Marketing Plan
25
New cards
Executive Summary
presents a brief overview of the proposed plan for quick management review
26
New cards
Current Marketing Situation
presents relevant background data on the market product, competition, and distribution.
27
New cards
Threats and Opportunity Analysis
identifies the main threats and opportunities that might impact the product
28
New cards
Objectives and Issues
defines the company’s objectives for the product in sales, market share and profit, and the issues that will affect these objectives
29
New cards
Marketing Strategy
presents the broad marketing approach that will be used to achieve the plan’s objectives
30
New cards
Action Programs
specifies what will be done, who will do it, when it is done, and how much it will cost.
31
New cards
Budgets
a projected profit and loss statement that forecasts the expected financial outcomes from the plan.
32
New cards
Controls
indicates how the progress of the plan will be monitored.
33
New cards
Internal Marketing
ensuring everyone in the organization embraces appropriate marketing principles, especially senior management
34
New cards
Integrated Marketing
ensuring that multiple means of creating, delivering, and communicating value are employed and combined in the best way
35
New cards
Relationship Marketing
having rich, multifaceted relationships with customers, channel members, and other marketing partners.
36
New cards
Performance Marketing
understanding returns to the business from marketing activities and programs, as well as addressing broader concerns and their legal, ethical, social, and environmental effects.
37
New cards
Fad
is “unpredictable, short-lived, and without social, economic, and political significance.”
38
New cards
Trend
* A direction or sequence of events with momentum and - durability
* is more predictable and durable than a fad
* reveals the shape of the future and can provide strategic direction.
* is more predictable and durable than a fad
* reveals the shape of the future and can provide strategic direction.
39
New cards
Megatrend
is a “large social, economic, political, and technological change \[that\] is slow to form, and once in place, influences us for some time—between seven and ten years, or longer.”
40
New cards
* Demographic
* Economic
* Social - Cultural
* Natural
* Technological
* Political - Legal
* Economic
* Social - Cultural
* Natural
* Technological
* Political - Legal
6 Major Forces in the Broad Environment:
41
New cards
Demographic Environment
The main one marketers monitor is population, including the size and growth rate of population in cities, regions, and nations; age distribution and ethnic mix; educational levels; household patterns; and regional characteristics and movements.
42
New cards
* Worldwide Population Growth
* Population Age Mix
* Ethnic and Other Markets
* Educational Groups
* Household Patterns
* Population Age Mix
* Ethnic and Other Markets
* Educational Groups
* Household Patterns
Demographic Environment includes
43
New cards
Economic Environment
The available purchasing power in an economy depends on current income, prices, savings, debt, and credit availability.
44
New cards
* Consumer Psychology
* Income Distribution
* Income, Savings, Debt, and Credit
* Income Distribution
* Income, Savings, Debt, and Credit
Economic Environment includes
45
New cards
Sociocultural
a world view that defines our relationships to ourselves, others, organizations, society, nature, and the universe
46
New cards
* Views of ourselves.
* Views of others
* Views of organizations
* Views of society
* Views of nature
* Views of the universe
* Views of others
* Views of organizations
* Views of society
* Views of nature
* Views of the universe
Sociocultural Environment includes
47
New cards
* The high persistence of core cultural values
* The existence of subcultures.
* The existence of subcultures.
Other cultural characteristics of interest to marketers are
48
New cards
Natural Environment
In Western Europe, “green” parties have pressed for public action to reduce industrial pollution. In the United States, experts have documented ecological deterioration, and watchdog groups such as the Sierra Club and Friends of the Earth carry these concerns into political and social action.
49
New cards
Technological Environment
It is the essence of market capitalism to be dynamic and tolerate the creative destructiveness of technology as the price of progress.
50
New cards
* ACCELERATING PACE OF CHANGE
* UNLIMITED OPPORTUNITIES FOR INNOVATION
* VARYING R&D BUDGETS
* INCREASED REGULATION OF TECHNOLOGICAL CHANGE
* UNLIMITED OPPORTUNITIES FOR INNOVATION
* VARYING R&D BUDGETS
* INCREASED REGULATION OF TECHNOLOGICAL CHANGE
Technological Environment includes
51
New cards
Political-Legal Environment
consists of laws, government agencies, and pressure groups that influence various organizations and individuals. Sometimes these laws create new business opportunities
52
New cards
* INCREASE IN BUSINESS LEGISLATION
* GROWTH OF SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP
* GROWTH OF SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP
Political-Legal Environment includes
53
New cards
* Introduction
* Growth
* Maturity
* Decline
* Growth
* Maturity
* Decline
Product Life Cycle
54
New cards
Introduction
A period of slow sales growth as the product is introduced in the market
55
New cards
Growth
A period of rapid market acceptance and substantial profit improvement
56
New cards
Maturity
A slowdown in sales growth because the product has achieved acceptance by most potential buyers.
57
New cards
Decline
Sales show a downward drift and profits erode
58
New cards
* Growth-Slump-Maturity Pattern
* Cycle-Recycle Pattern
* Scalloped Pattern
* Cycle-Recycle Pattern
* Scalloped Pattern
Common Product Life-Cycle Patterns
59
New cards
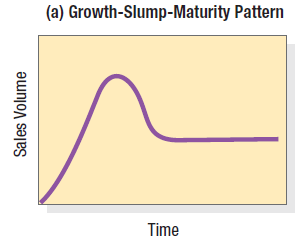
growth-slump-maturity pattern
characteristic of small kitchen appliances, for example, such as handheld mixers and bread makers. Sales grow rapidly when the product is first introduced and then fall to a “petrified” level sustained by late adopters buying the product for the first time and early adopters replacing it.
60
New cards
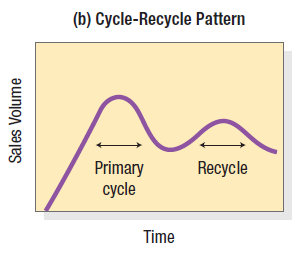
cycle-recycle pattern
often describes the sales of new drugs. The pharmaceutical company aggressively promotes its new drug, producing the first cycle. Later, sales start declining, and another promotion push produces a second cycle (usually of smaller magnitude and duration)
61
New cards
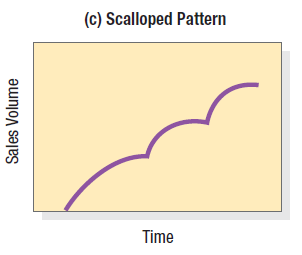
scalloped pattern
sales pass through a succession of life cycles based on the discovery of new-product characteristics, uses, or users. Sales of nylon have shown a scalloped pattern because of the many new uses—parachutes, hosiery, shirts, carpeting, boat sails, automobile tires—discovered over time
62
New cards
Style
is a basic and distinctive mode of expression appearing in a field of human endeavor
63
New cards
* homes (colonial, ranch, Cape Cod)
* clothing (formal, business casual, sporty)
* art (realistic, surrealistic, abstract).
* clothing (formal, business casual, sporty)
* art (realistic, surrealistic, abstract).
Styles appear in
64
New cards
Fashion
is a currently accepted or popular style in a given field.
65
New cards
* distinctiveness,
* emulation,
* mass fashion,
* decline
* emulation,
* mass fashion,
* decline
Fashions pass through four stages:
66
New cards
Fads
are fashions that come quickly into public view, are adopted with great zeal, peak early, and decline very fast
67
New cards
Porter’s Value Chain
According to this model, every firm is a synthesis of activities performed to design, produce, market, deliver, and support its product
68
New cards
9 strategically relevant activities
* 5 primary activities
* 4 support activities
* 5 primary activities
* 4 support activities
The value chain identifies
69
New cards
* inbound logistics, or bringing materials into the business;
* operations, or converting materials into final products;
* outbound logistics, or shipping out final products;
* marketing, which includes sales;
* service
* operations, or converting materials into final products;
* outbound logistics, or shipping out final products;
* marketing, which includes sales;
* service
5 Primary Activities
70
New cards
* procurement,
* technology development,
* human resource management,
* firm infrastructure.
* technology development,
* human resource management,
* firm infrastructure.
4 Support Activities
71
New cards
* Connecting with customers
* Building strong brands
* Shaping the market offerings
* Delivering value
* Communicating value
* Creating successful and long-term growth
* Building strong brands
* Shaping the market offerings
* Delivering value
* Communicating value
* Creating successful and long-term growth
Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans
72
New cards
Marketing Information System (MIS)
consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers. It
73
New cards
* Internal Records
* Marketing Intelligence System
* Marketing Decision Support System
* Marketing Research
* Marketing Intelligence System
* Marketing Decision Support System
* Marketing Research
Marketing Information System
74
New cards
Internal Records
To spot important opportunities and potential problems, marketing managers rely on internal reports of orders, sales, prices, costs, inventory levels, receivables, and payables.
75
New cards
Internal Records
which includes information on the order-to-payment cycle and sales information systems
76
New cards
Marketing Intelligence System
is a set of procedures and sources that managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environment.
77
New cards
Marketing Decision Support System (MDSS)
MIT’s John Little define this as a coordinated collection of data, systems, tools, and techniques, with supporting software and hardware, by which an organization gathers and interprets relevant information from business and environment and turns it into a basis for marketing action.
78
New cards
Marketing Intelligence System
a set of procedures and sources used by managers to obtain everyday information about pertinent developments in the marketing environment
79
New cards
Marketing Research System
allows for the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data
80
New cards
Marketing Information System (MIS)
To carry out their analysis, planning, implementation, and control responsibilities, marketing managers need this.
\
\
81
New cards
Marketing Information System (MIS)
is to assess the managers’ information needs, develop the needed information, and distribute that information in a timely manner.
82
New cards
* Step 1: Define the Problem, the Decision Alternatives, and the Research Objectives
* Step 2: Develop the Research Plan
* Step 3: Collect the Information
* Step 4: Analyze the Information
* Step 5: Present the Findings
* Step 6: Make the Decision
* Step 2: Develop the Research Plan
* Step 3: Collect the Information
* Step 4: Analyze the Information
* Step 5: Present the Findings
* Step 6: Make the Decision
Marketing Research Process
83
New cards
Customer Loyalty
an ongoing emotional relationship between you and your customer
84
New cards
* Frequency Programs
* Club Membership Programs
* Club Membership Programs
Developing Loyalty Programs
85
New cards
Frequency programs (FPs)
are designed to reward customers who buy frequently and in substantial amounts.
86
New cards
Club membership programs
can be open to everyone who purchases a product or service, or limited to an affinity group or those willing to pay a small fee.
87
New cards
Value Proposition
consists of the whole cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver
88
New cards
Value Delivery System
all experiences the customers will have on the way to obtaining and using the offering
89
New cards
* To identify prospects
* To decide which customers should receive a particular offer
* to deepen customer loyalty
* To reactivate customer purchases
* To avoid serous customer mistakes
* To decide which customers should receive a particular offer
* to deepen customer loyalty
* To reactivate customer purchases
* To avoid serous customer mistakes
Uses of Database
90
New cards
* Feud’s Theory
* Maslow’s Theory
* Herzberg’s Theory
* Maslow’s Theory
* Herzberg’s Theory
3 Theories of Motivation in Key Psychological Processes
91
New cards
Sigmund Feud’s Theory
assumed the psychological forces shaping people’s behavior are largely unconscious, and that a person cannot fully understand his or her own motivations.
92
New cards
Abraham Maslow’s Theory
explain why people are driven by particular needs at particular times. His answer is that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy from most to least pressing—physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
93
New cards
1. Problem Recognition
2. Information Search
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
4. Purchase Decision
5. Post-purchase behavior
5 Stage Model of the Consumer Buying Process
94
New cards
Frederick Herzberg’s Theory
developed a two-factor theory that distinguishes dissatisfiers (factors that cause dissatisfaction) from satisfiers (factors that cause satisfaction).
95
New cards
* Food
* Water
* Shelter
* Water
* Shelter
Examples of Psychological Needs
96
New cards
* Security
* Protection
* Protection
Examples of safety Needs
97
New cards
* Sense of Belonging
* Love
* Love
Examples of Social Needs
98
New cards
* Self-Esteem
* Recognition
* Status
* Recognition
* Status
Examples of Esteem Needs
99
New cards
* Self-Development
* Realization
* Realization
Examples of Self-Actualization Needs
100
New cards
* The availability heuristic
* The representativeness heuristic
* The representativeness heuristic
2 Kinds of Heuristics