Chapter 1
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Movement
An action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place
Respiration
describes the chemical reaction in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism
Sensitivity
the ability to detected respond to change in the internal or external environment
Growth
a permanent increase in size and dry mass
Reproduction
the process that makes more of the same kind of organism
Excretion
the removal of waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Nutrition
the taking in of materials for energy, growth and development
Species
a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring
Genus ⦅𝑃𝑙𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑙: genera⦆
a group of closely related species
Binomial system
an internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and species
Population
a group of organisms of the same species populating a given area
Dichotomous key
a step by step approach to identify unfamiliar organisms. Each key is made up of pairs of contrasting features
Evolution
the gradual change in a species over time
Autotrophic
produces their own food through photosynthesis (or chemical energy
Heterotrophic
organisms that cannot make their own food
Kingdom
a category of living organisms
Arthropods
the arthropods include crustacea, insects, myriapods and arachnids. They have jointed limbs, antennae, compound eyes, an exoskeleton and a cuticle.
Insects
insects have a segmented body with a exoskeleton, 3 pairs of jointed limbs, compound eyes and usually wings. the segments are grouped into head, thorax and abdomen.
Arachnids
arachnids have a body that is divided into 2 regions; a combined head and thorax known as the 𝐜𝐞𝐩𝐡𝐥𝐨𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐱; and the abdomen. they have 4 pairs of limbs on their cephalothorax.
they also have 2 pairs of 𝐩𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐩𝐚𝐥𝐩𝐬. one pair is used in reproduction; the other is used pierce their prey and paralyze it with a poison secreted by a 𝐠𝐥𝐚𝐧𝐝 at the base.
There are usually several pairs of 𝐬𝐢𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐞𝐲𝐞𝐬.
Myriapods
myriapods have a head and a segmented body with pair of legs
The plant kingdom
vascular plants (well developed xylem and phloem)
cell wall made up of cellulose + photosynthesis
Division
Red Algae, brown algae, green algae
- seaweeds and filamentous forms; mostly aquatic
(class) Bryophytes
no specialized conducting tissue
Classes of plant kingdoms
Ferns
Conifers (seeds not enclosed in fruits)
Flowering plants (seeds enclosed in fruits)
Liverworts
Mosses
rhizoid is ?
Subclasses of plant kingdoms
Monocotyledons (grass, lilies)
Dicotyledons (trees, shrubs, herbaceous plants)
Family of plant kingdom
e.g. Ramunculaceae
(genus and species name of this is: Ramunculus)
Vascular tissue
means they have vessels
used to distinguish between vascular & non- vascular plants
Reproduction method
used to distinguish between spore producing & seed producing plants
Flowers
used to distinguish between flowering & non-flowering plants
Plant body structure
used to distinguish between simple & complex plants
Type of roots
used to distinguish between true rots & rhizoids
Leaves
used to distinguish between true roots & leaf-like structures
Habitat
used to distinguish between aquatic & terrestrial plants
Monocotyledon
one cotyledon (seed leaves)
parallel leaf veins
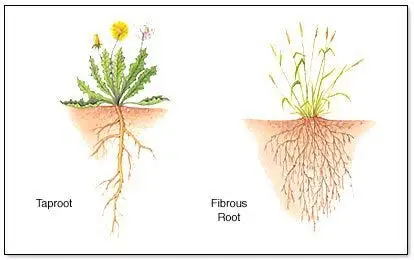
Fibrous roots
Flower parts: usually in multiples of 3
Dicotyledons
two cotyledons
branched or net-like veins
tap root system
flower parts: usually in multiples of 4 or 5
Fibrous roots vs tap root system
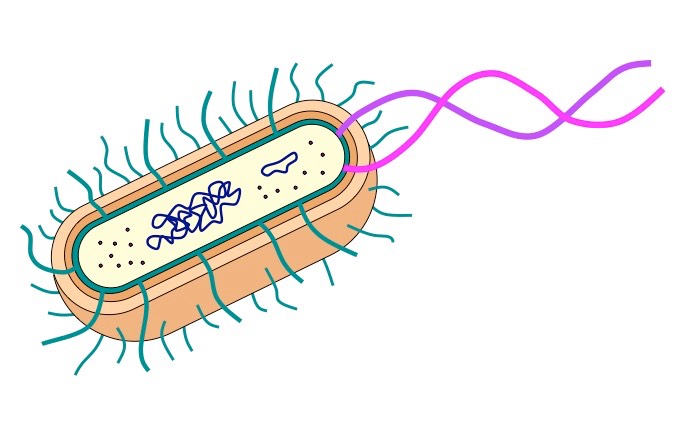
Bacteria (prokaryote)
prokaryotic
has a cell wall
unicellular
heterotrophic or autotrophic
asexual reproduction
Dog (animalia)
eukaryotic
no cell wall
heterotrophic
multicellular
sexual reproduction
Mushroom
eukaryotic
cell wall
heterotrophic
multicellular
spores
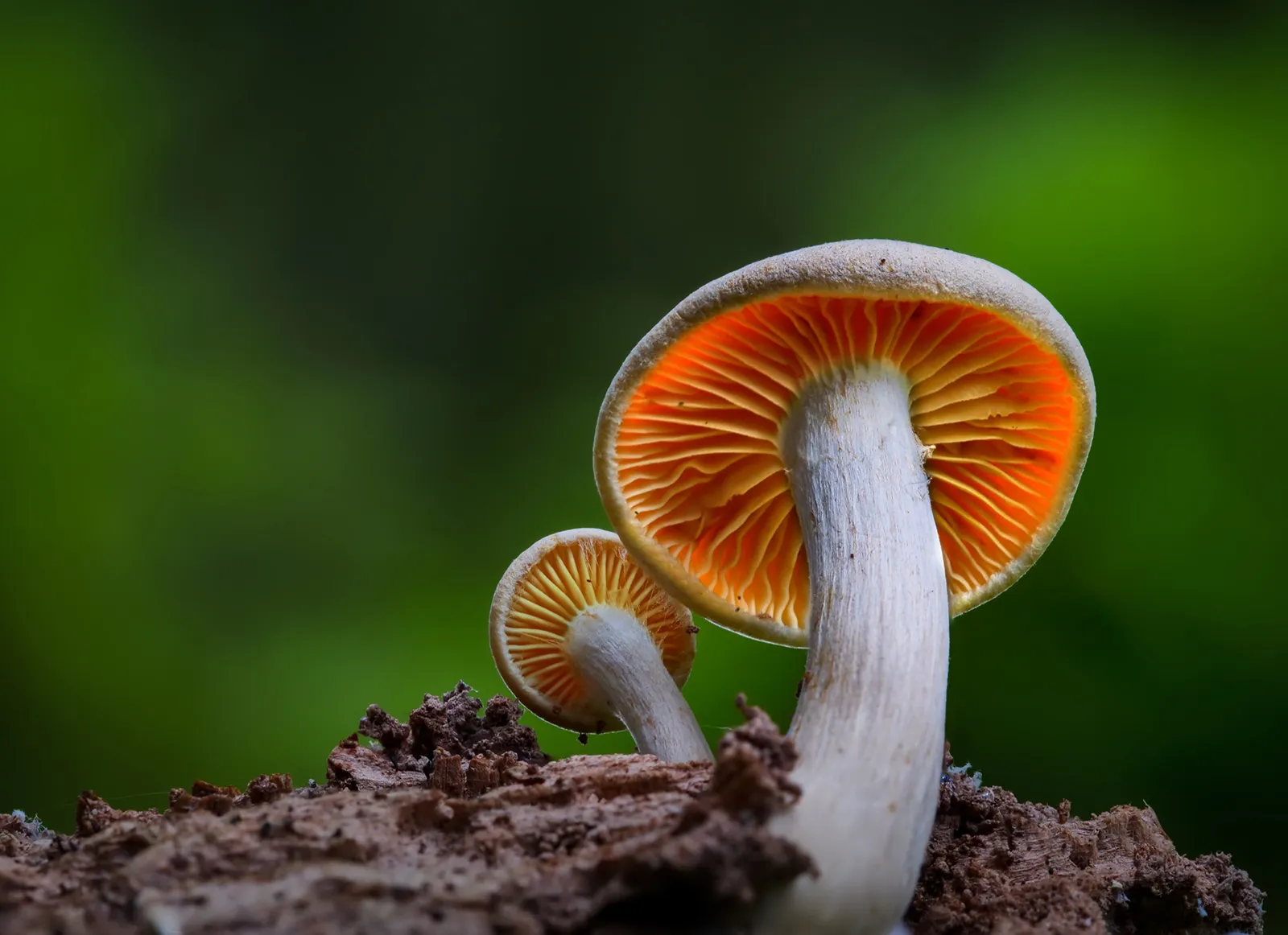

Fern (Plantae)
eukaryotic
cell wall
autotrophic
multicellular
vascular tissue
spores

Amoeba (protocista)
eukaryotic
no cell wall
heterotrophic
unicellular
asexual reproduction
Ferns
known for their large feathery leaves known as fronds.
==>this allows them to capture sunlight effectively

Spore formation
when an asexual reproductive body grows on the plant & grows as an individual plant when the spores are ready they’re often able to grow into new plants
Spongaria
where spores are produced and stored.
Sori (sorus)
brown clusters on the underside of fern leaf
sorus contains many spongaria until it it’s ready to reproduce
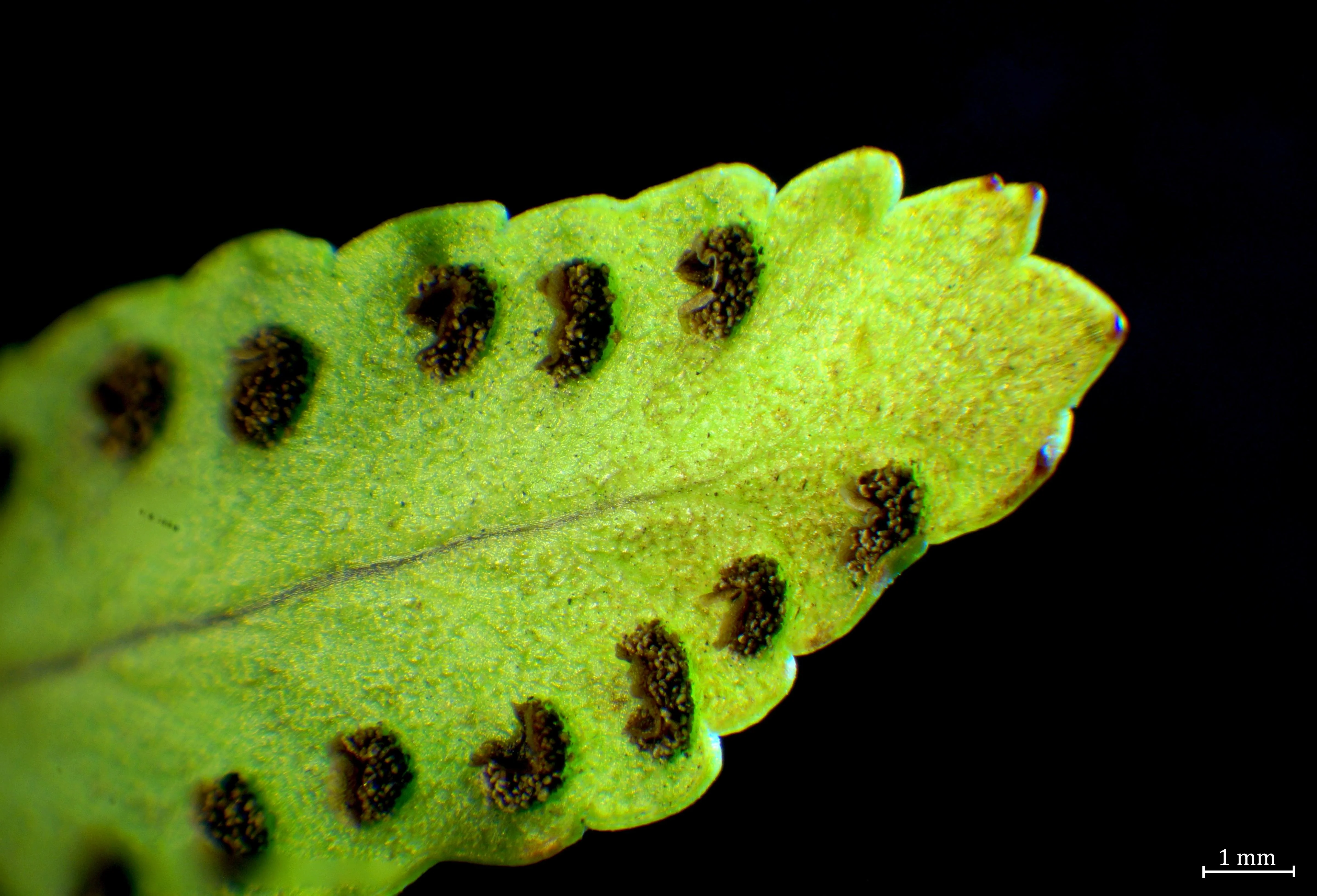

Spores
tiny reproductive cells inside the sori
Fronds
allows leaves to capture sunlight
known for their large feathery leaves known as fronds
Rachis
supports the leaflets and transports water, nutrients and sugar
The Fungi kingdom
Most organisms are made up of an hyphae rather than cells, and there are many nuclei distributed throughout the cytoplasm in their hyphae

more abt fungi kingdom
Fungi include organisms such as mushrooms, toadstools, puffballs, etc
Some fungal species are parasites, where they cause diseases which can affect crops. e.g. mildew
To feed, fungi secrete digestive enzymes in their surroundings and absorb the digestive molecules as a source of nutrients (decomposers)
Septate hyphae
Septate hyphae are fungal filaments with cross-walls (septa) that divide them into individual cells.
These septa create a segmented or "bamboo stalk" appearance.
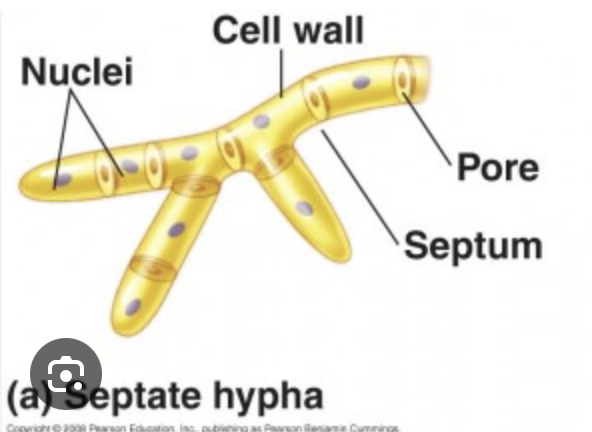
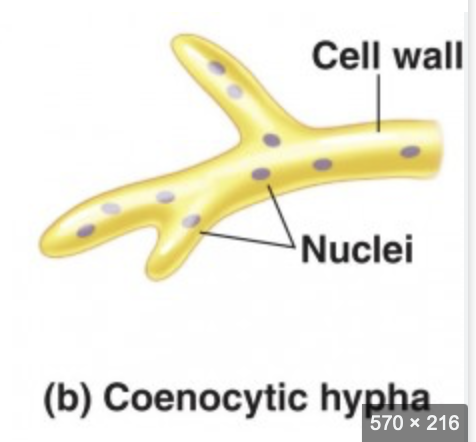
Coenocytic hyphae
Coenocytic hyphae, also known as aseptate hyphae, are a type of fungal filament that lacks septa (cross-walls) and are characterized by being multinucleate.
The Prokaryotic kingdom
Pro