OS-CHAP-8-13: File Systems and Memory Management
1/395
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
396 Terms
File Concept
Logical address space for data and programs.
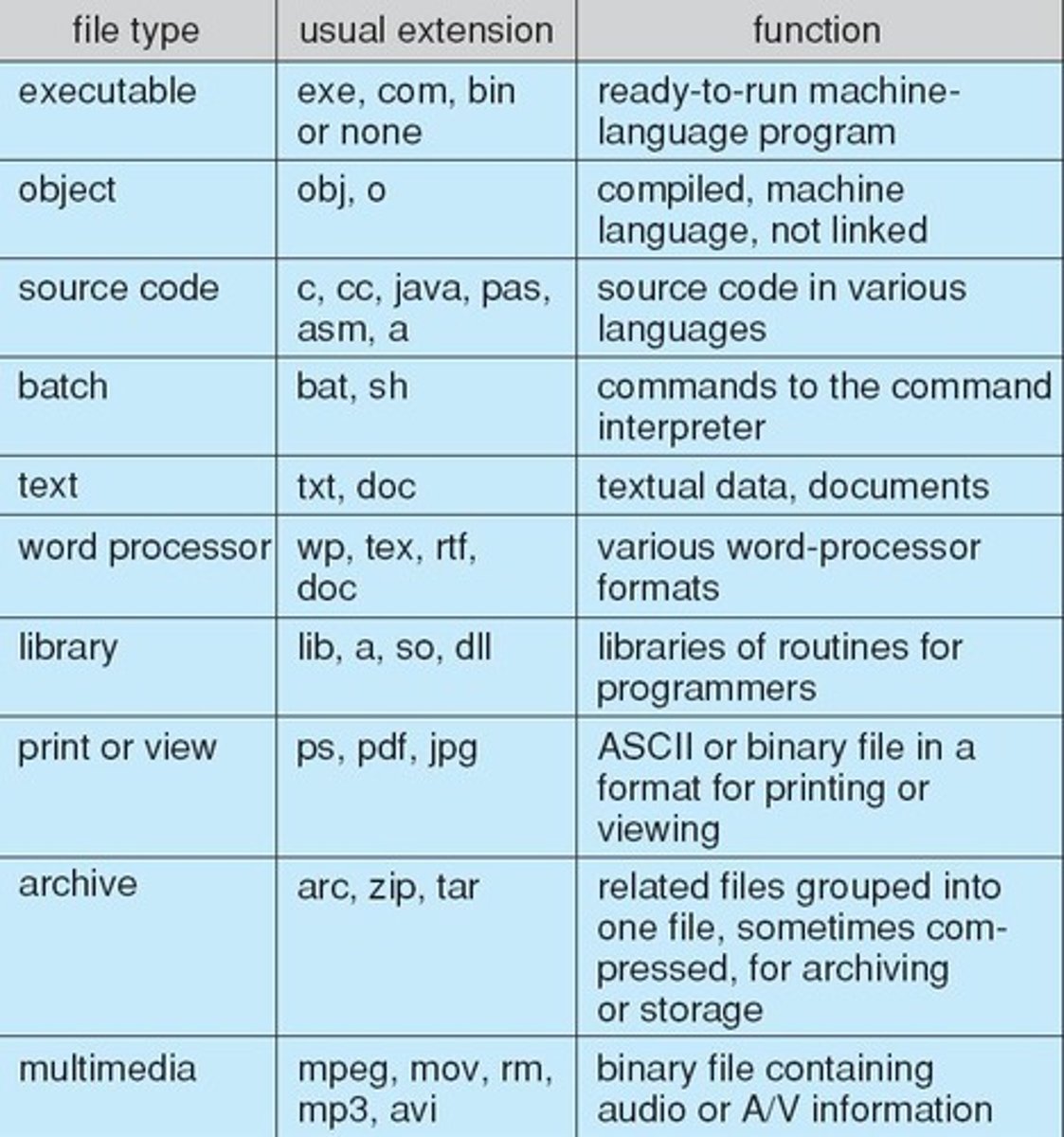
File Types
Includes data, program, text, source, executable.
File Attributes
Metadata describing files, like name and size.
File Identifier
Unique tag for file within the system.
File Location
Pointer indicating file's location on device.
File Size
Current size of the file in bytes.
File Protection
Controls read, write, execute permissions.
Directory Structure
Nodes containing information about all files.
File Operations
Actions like create, read, write, delete files.
Open File Table
Tracks all currently open files in memory.
File Pointer
Indicates last read/write position in file.
File Open Count
Counts how many processes have opened a file.
Disk Location
Cache for file access information on disk.
Access Rights
Permissions for processes accessing a file.
File Locking
Controls concurrent access to files by processes.
Shared Lock
Allows multiple processes to read simultaneously.
Exclusive Lock
Prevents other processes from accessing a file.
Mandatory Locking
Access denied based on existing locks.
Advisory Locking
Processes can check lock status before access.
File Locking Example
Java API example for file locking implementation.
Memory-Mapped Files
Maps file contents directly into memory space.
File Truncation
Reduces file size to zero or specified length.
Repositioning within File
Changing current read/write position using seek.
exclusiveLock
A lock preventing other threads from accessing data.
sharedLock
Allows multiple threads to read data simultaneously.
raf.length()
Returns the length of the file in bytes.
ch.lock()
Method to acquire a lock on a file region.
SHARED
Lock mode allowing concurrent read access.
Shared Lock
Allows multiple processes to read a file concurrently.
Exclusive Lock
Allows only one process to write to a file.
File Structure
Organization of data in a file.
Sequential Access
Read/write operations occur in order.
Direct Access
Access data at a specified location directly.
Relative Block Number
Indicates position of data in a file.
Access Methods
Techniques to read/write data in files.
Index File
A structure for fast data location.
ISAM
Indexed Sequential Access Method for file organization.
Disk Structure
Physical organization of data on a disk.
RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks for data protection.
Volume
Entity containing a file system.
File System
Manages how data is stored and retrieved.
Directory Operations
Functions like search, create, delete files.
Single-Level Directory
One directory for all users, causing naming issues.
Two-Level Directory
Separate directories for each user, improving organization.
Tree-Structured Directories
Hierarchical organization of directories and files.
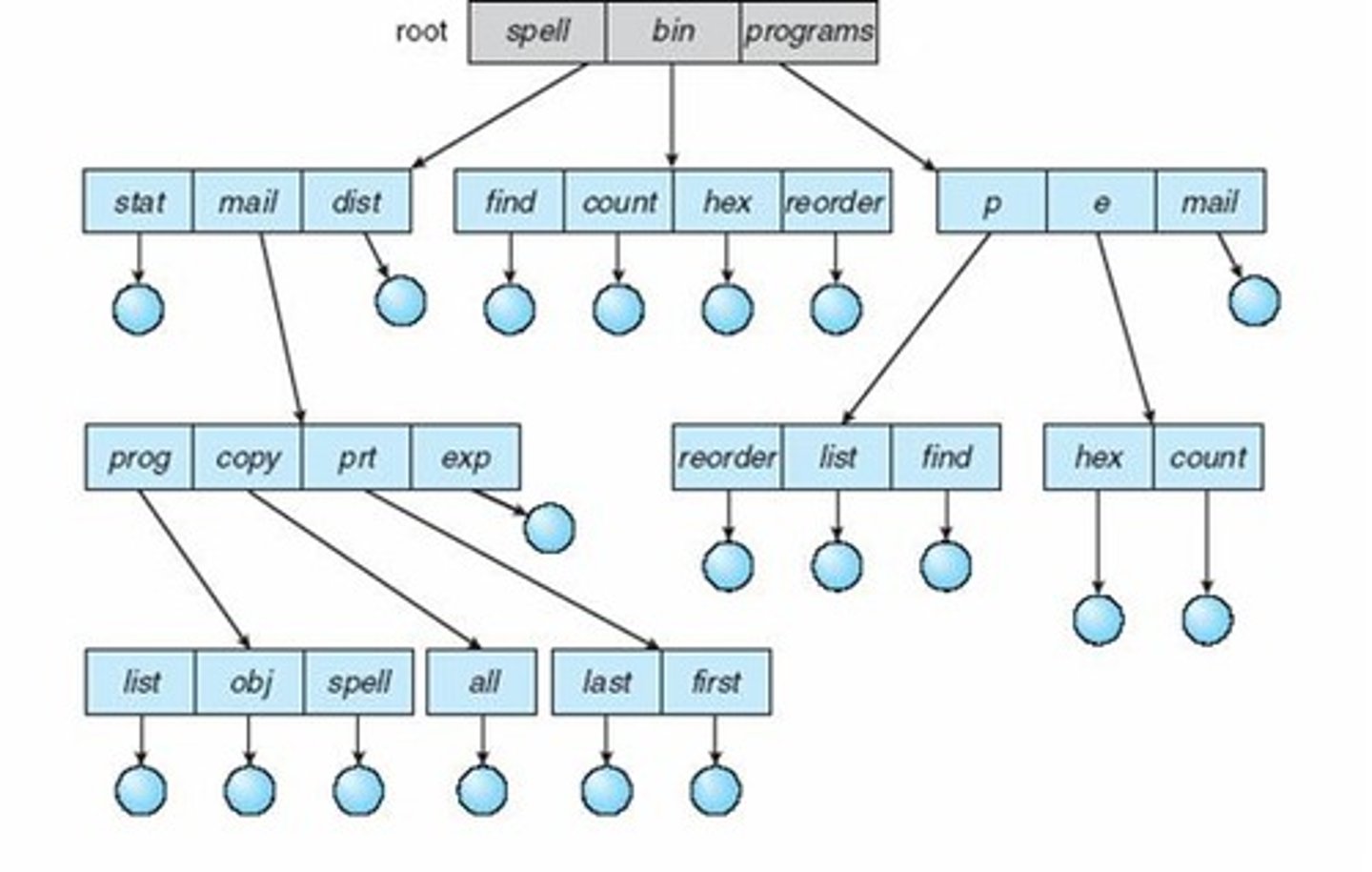
Acyclic-Graph Directories
Directories allowing shared subdirectories and files.
Dangling Pointer
Reference to a deleted file or directory.
Control Characters
Special characters used for formatting files.
File Types
Categorization based on name and extension.
Formatted Document
File with specific structure and layout.
Complex Structures
Files with advanced formatting beyond simple records.
Logical Grouping
Organizing files based on shared properties.
Variable Size Records
Records with varying lengths in storage.
Backpointers
Pointers linking to previous records in a chain.
Daisy Chain Organization
Method of linking records in a sequence.
Entry-Hold-Count Solution
Counts entries to manage directory space.
Directory Entry Type
New classification for storing directory information.
Link
Pointer referencing an existing file.
Resolve the Link
Follow pointer to find the actual file.
General Graph Directory
Directory structure allowing multiple links to files.
Cycle Detection Algorithm
Algorithm to prevent cycles in directory links.
Garbage Collection
Process of reclaiming unused directory entries.
Current Directory
Designated directory for file operations.
cd Command
Changes the current working directory.
Creating a File
Done within the current directory context.
Deleting a Directory
Removes entire subtree rooted by the directory.
File Protection
Control over file access by owner.
Types of Access
Permissions: read, write, execute, append, delete, list.
Access-Control List
List defining user permissions for file access.
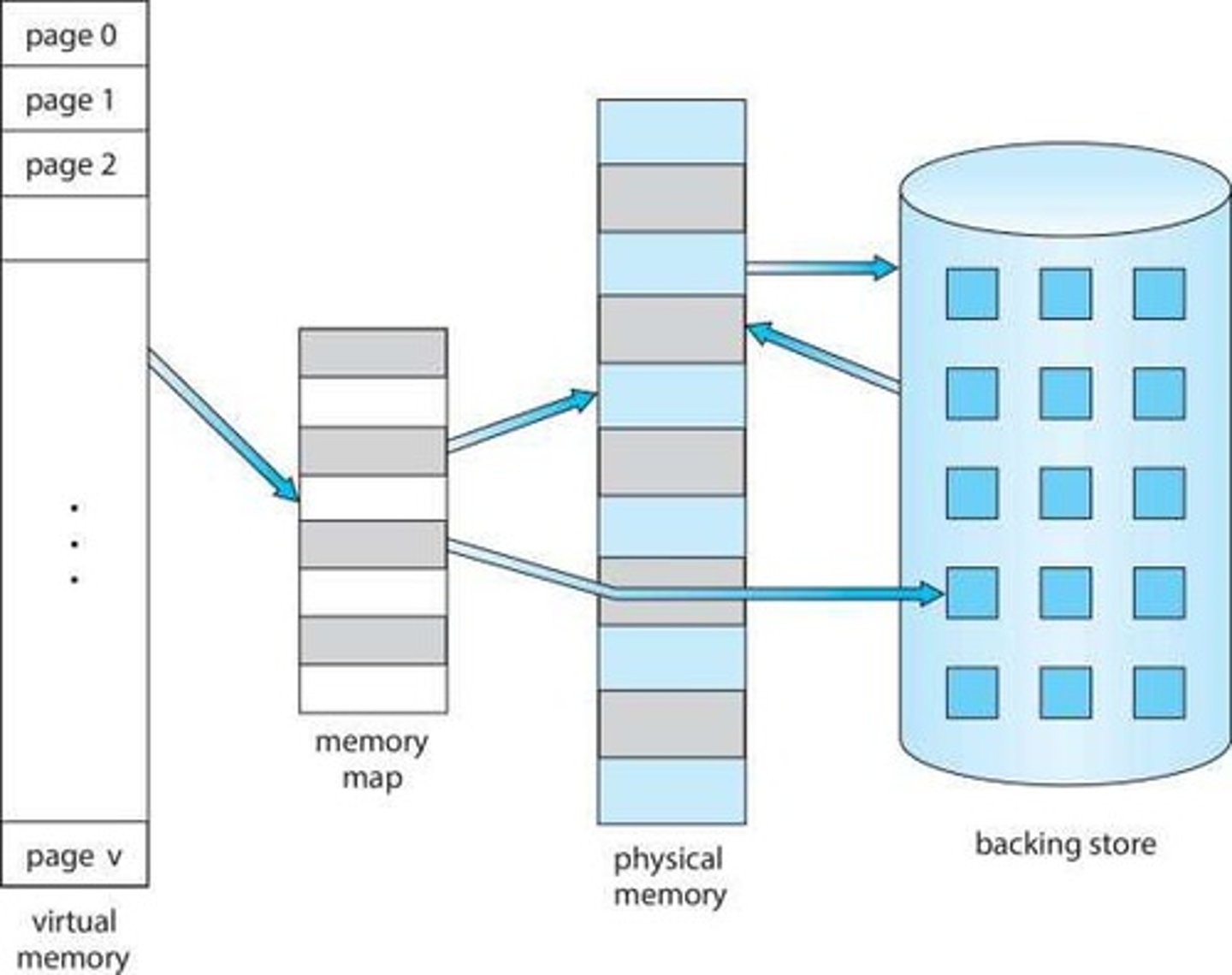
Virtual Memory
Memory management technique using disk space.
Demand Paging
Loading pages into memory on demand.
Copy-on-Write
Technique to delay copying until necessary.
Page Replacement
Algorithm for replacing pages in memory.
Thrashing
Excessive paging causing performance degradation.
Memory-Mapped Files
Files mapped into memory for access.
Allocating Kernel Memory
Managing memory for operating system kernel.
Working Set
Set of pages actively used by a process.
Virtual Memory
Separation of user logical memory from physical memory.
Logical Address Space
View of memory space larger than physical memory.
Physical Memory
Actual memory hardware where data is stored.
Demand Paging
Loading pages into memory only when needed.
Page Frame
Fixed-size block of physical memory.
Memory Management Unit (MMU)
Maps logical addresses to physical addresses.
Concurrent Programs
Multiple programs running simultaneously in memory.
Swapping
Moving processes between physical memory and disk.
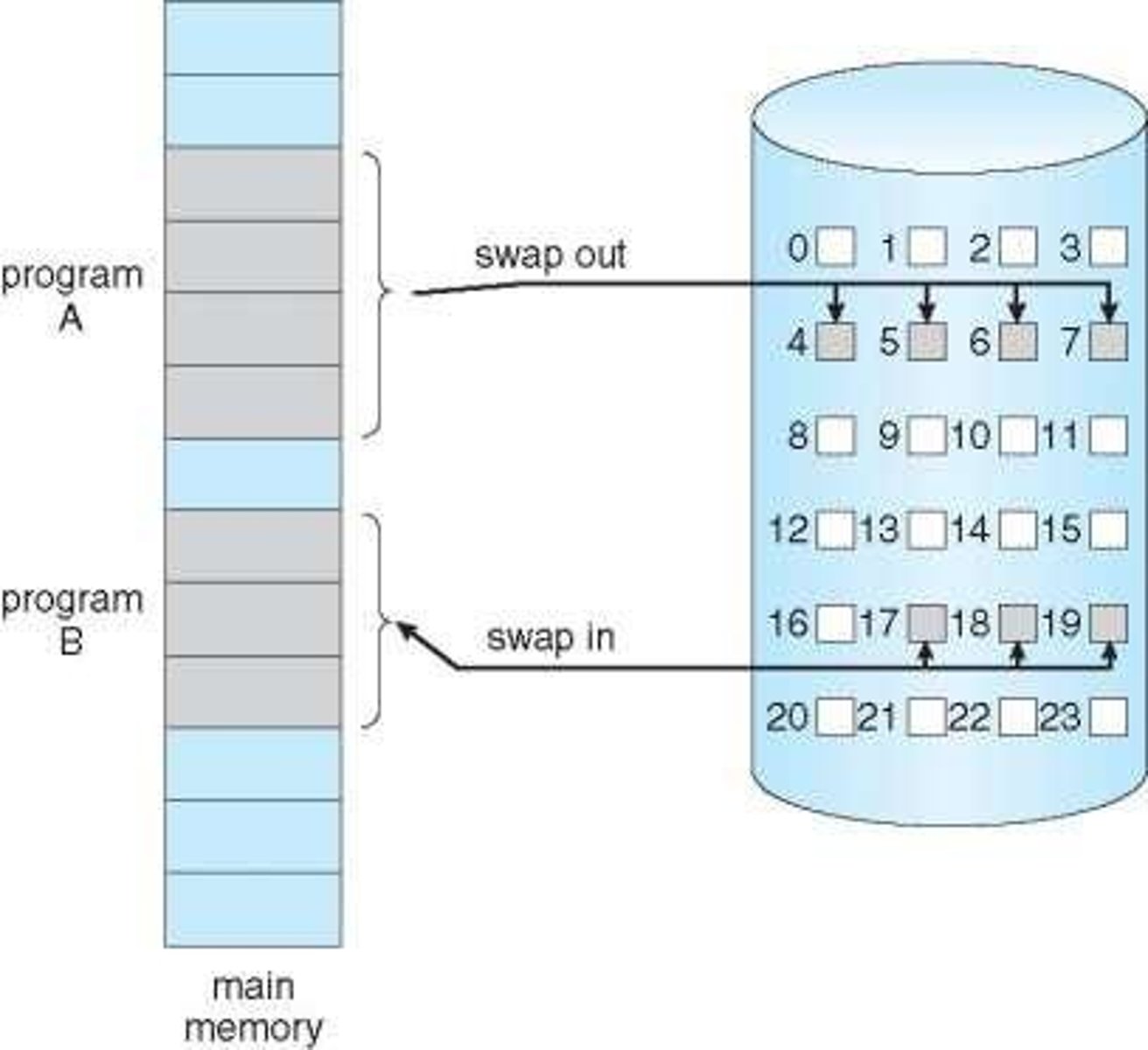
Lazy Swapper
Only loads pages when they are required.
Shared Memory
Memory accessible by multiple processes.
Heap
Dynamic memory allocation area growing upwards.
Stack
Memory area for function calls growing downwards.
Holes in Address Space
Unused memory space between stack and heap.
Throughput
Number of processes completed in a given time.
CPU Utilization
Percentage of time CPU is actively processing.
I/O Operations
Input/Output tasks involving data transfer.
Process Creation
Generating new processes in the operating system.
Virtual Address Space
Logical view of how a process is stored.
Error Code
Code indicating an error during program execution.
Unusual Routines
Non-standard code paths in program execution.
Data Structures
Organized formats for storing and managing data.
Demand Segmentation
Loading segments into memory as needed.
MMU Functionality
Memory Management Unit's role in demand paging.