Chapter 1- Introduction to Nursing and Professional Formation
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
Burnout
A state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged and excessive stress.
Compassion Fatigue
A condition characterized by emotional and physical exhaustion leading to a diminished ability to empathize or feel compassion for others.
Health
A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Healthy Nurse
A nurse who actively engages in practices that promote physical, mental, and emotional health.
Licensure
The process by which a governmental authority grants permission to an individual to practice a profession.
Mindfulness
The psychological process of bringing one's attention to the present moment.
Nurse Practice Acts
Laws enacted in each state to regulate the practice of nursing and protect public health.
Nursing
A profession focused on assisting people, families, and communities to attain, recover and maintain optimum health and function.
Nursing Process
A systematic method used by nurses to plan and provide care for patients.
Profession
A paid occupation, especially one that involves prolonged training and a formal qualification.
Reciprocity
The practice of exchanging things with others for mutual benefit.
Resilience
The capacity to recover quickly from difficulties; toughness.
Second Traumatic Stress
The stress experienced by individuals who witness or hear about traumatic events experienced by others.
Standards
Established criteria or benchmarks used to measure the quality of nursing care.
COVID pandemic
A global health crisis that placed nurses and healthcare professionals on the frontlines to save lives.
PPE
Personal Protective Equipment that was in short supply during the pandemic, affecting nurses' ability to care for patients.
Nursing care
Involves a wide range of activities, from complicated technical procedures to simple acts like holding a hand.
Science of nursing
The knowledge base for the care that is given.
Art of nursing
The skilled application of nursing knowledge to help others achieve maximum health and quality.
Scope of nursing practice
Describes the 'who', 'what', 'when', 'where', 'why', and 'how' of nursing practice.
4 million nurses
The number of nurses practicing in the US today across over 200 different specialties.
Specialties of nursing
Include areas such as anesthesia, mental health, school nursing, cardiac care, pediatrics, surgery, oncology, obstetrics, and geriatrics.
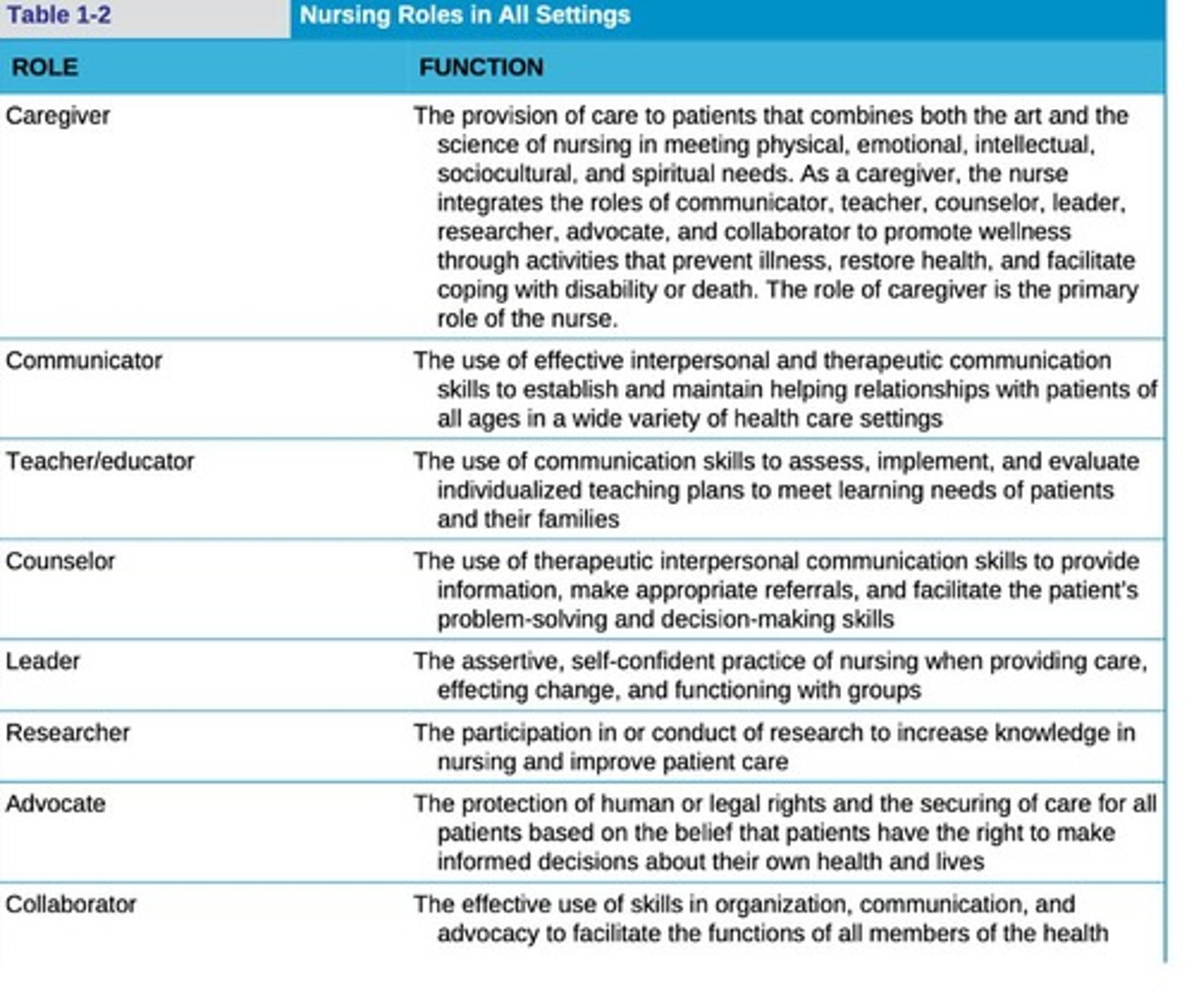
Roles of nurses
Nurses serve as caregivers, administrators, researchers, innovators, and policy makers.
Projected RN positions
The federal government projects that more than 200,000 new RN positions will be created each year from 2016 to 2026.
Largest health profession
Nursing is the largest of the health professions and the foundation of the nation's healthcare workforce.
Professional nursing
Includes a brief history of nursing, definitions, and aims of the profession.
Educational preparation for nursing
Discusses the training and education required for professional nursing.
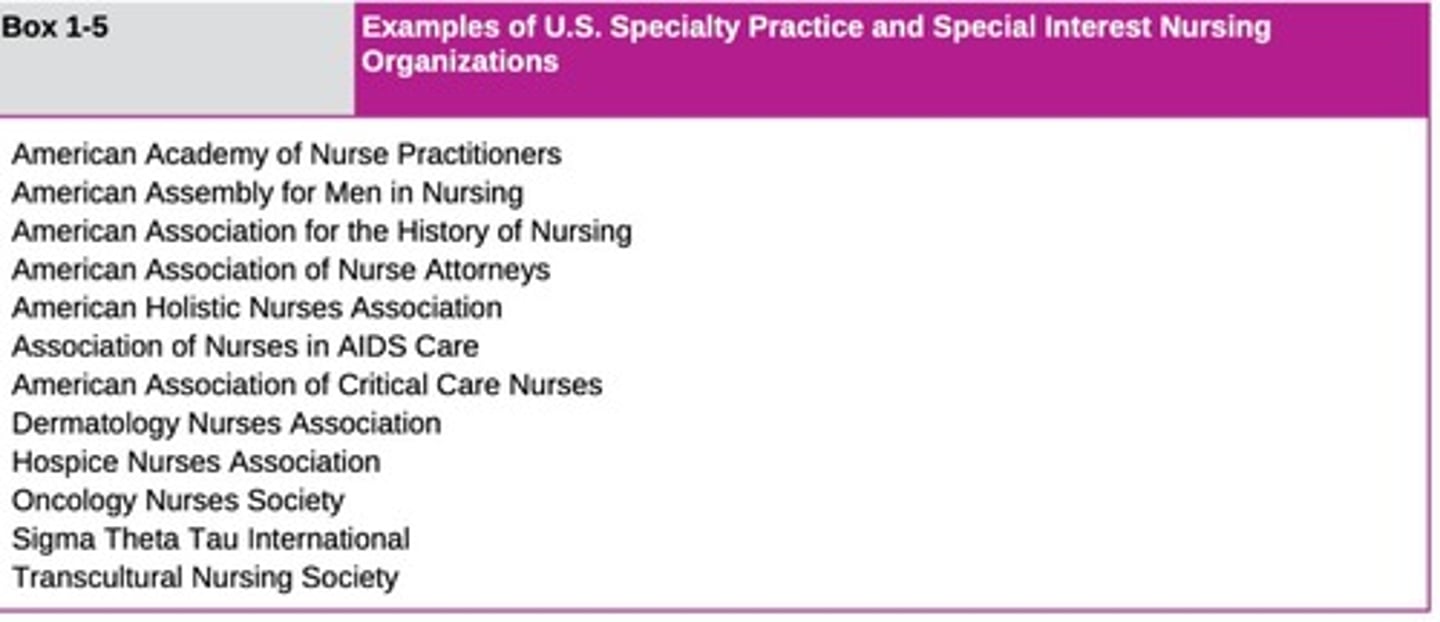
Professional nursing organizations
Groups that support and guide nursing practice and education.
Guidelines for nursing practice
Standards and protocols that help define how nursing is organized and practiced.
Nursing as a profession
A field that is organized with specific practices, standards, and educational requirements.
Public appreciation of nurses
During the pandemic, the public showed increased appreciation for nurses' contributions.
Nurses as superheroes
A term used to describe the elevated status and recognition of nurses during the pandemic.
Challenges faced by nurses
Included shortages of PPE and the emotional toll of caring for dying patients.
Nursing history
A brief overview of the evolution of nursing from its beginnings to the present.
Nursing activities
Range from technical procedures to emotional support for patients.
Historical Perspectives on Nursing
Care givers for the ill and injured have always been part of history.
Development of Nursing from Early Civilizations to the 16th Century
Most early civilizations believed that illness had supernatural causes.
Theory of Animism
Attempted to explain the cause of mysterious changes in bodily functions based on the belief that everything in nature was alive with invisible forces.
Good Spirits
Brought health.
Evil Spirits
Brought sickness and death.
Roles of Health Care Provider and Nurse
The health care provider was the medicine man who treated disease, while the nurse usually was the mother who cared for her family.
Ancient Greek Civilizations
Temples became the centers of medical care due to the belief that illness was caused by sin and the gods' displeasure.
Mosaic Health Code
Developed rules for ethical human relationships, mental health, and disease control.
Deaconesses
Women who made the first organized visits to sick people in the early Christian period.
Crusades
Both male and female nursing orders were founded during this time.
Florence Nightingale
Established the first training school for nurses and wrote books about healthcare and nursing education.
Nursing Education
Based on many of the beliefs of Florence Nightingale.
Nursing Roles
Range from direct patient care and case management to establishing nursing practice standards.
Four Spheres of Care
Include disease prevention, chronic disease care, regenerative or restorative care, and hospice/palliative/supportive care.

Definitions of Nursing
Nursing encompasses autonomous and collaborative care of individuals of all ages, families, groups, and communities.
ICN Definition of Nursing
Includes the promotion of health, prevention of illness, and care of ill, disabled, and dying people.
ANA Definition of Nursing
Describes the social context of nursing, the knowledge base for nursing practice, and the scope of nursing practice.
Nursing Aims
To promote health, prevent illness, restore health, and facilitate coping with disability or death.
Blended Competencies
Include cognitive, technical, interpersonal, and ethical/legal competencies.
QSEN Project Competencies
Include patient-centered care, teamwork and collaboration, quality improvement, safety, EBP, and informatics.
Health Promotion
Motivated by the desire to increase a person's well-being and health potential.
Health Literacy
The ability of people to obtain, process, and understand basic health information.
Healthy People 2030
Establishes health promotion guidelines focused on achieving health equity and eliminating health disparities.
Preventing Illness
Objectives include reducing the risk of illness, promoting good health habits, and maintaining optimal functioning.
Educational Programs
Include prenatal care for pregnant people, smoking-cessation programs, and stress reduction seminars.
Community Programs
Encourage healthy lifestyles, such as aerobic exercise classes and physical fitness programs.
Health Assessments
Identify areas of strength and risks for illness in institutions, clinics, and community settings.
COVID-19 Pandemic
Highlighted the critical importance of frequent handwashing, social distancing, and wearing masks.
Nursing Research
Recognized as the beginnings of nursing research by maintaining accurate records.
Nursing Roles in Healthcare
Include communicator, teacher, counselor, leader, researcher, advocate, and collaborator.
Case Manager
One of the specialized roles nurses play in today's evolving healthcare environment.
Navigator
A specialized role of nurses that assists patients in navigating the healthcare system.
Ethicist
A specialized role of nurses that involves addressing ethical issues in patient care.
Promoting Health
Involves identifying, analyzing, and maximizing each patient's individual strengths.
Wellness
An active state of being healthy by living a lifestyle that promotes good physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health.
95% mask wearing
If 95% of Americans wore masks in public, we could prevent 33,000 deaths by October 1, 2020.
US nurses
AT 4 million strong, US nurses have the potential to be a real powerhouse if we reach out in our personal spheres of influence to encourage healthy behaviors.
Activities to restore health
Activities to restore health encompass those historically considered to be the nurse's responsibility, focusing on the person with an illness.
Early detection
Early detection of a disease is one of the activities to restore health.
Performing assessments
Performing assessments that detect an illness includes taking BP and measuring blood sugars.
Referring questions
Referring questions and abnormal findings to other healthcare providers as appropriate is part of nursing responsibilities.
Direct care
Providing direct care of the person who is ill includes giving physical care, administering medications, and carrying out procedures and treatments.
Collaborating with healthcare providers
Collaborating with other health care providers in providing care is essential in nursing.
Rehabilitation planning
Planning, teaching, and carrying out rehabilitation for illnesses such as heart attacks, arthritis, and strokes is part of nursing.
Facilitating coping
Nurses facilitate patient and family coping with altered function, life, crisis, and death.
Altered function
Altered function decreases a person's ability to carry out activities of daily living (ADLs) and expected roles.
Optimal level of function
Nurses facilitate an optimal level of function through maximizing the person's strengths and potentials.
Hospice programs
Nurses are active in hospice programs, which assist patients and their families in preparing for death.
Nursing as a professional discipline
Nursing is recognized as a profession based on a well-defined body of specific and unique knowledge.
Service orientation
Nursing has a strong service orientation.
Professional authority
Nursing has recognized authority by a professional group.
Code of ethics
Nursing is guided by a code of ethics.
Ongoing research
Ongoing research is a criterion for nursing as a profession.
Autonomy and self-regulation
Nursing involves autonomy and self-regulation.
Evidence-based practice (EBP)
Nursing interventions are focused on EBP, which is practice based on research and not intuition.
LPN
Students may choose to enter a practical nursing program and become a LPN.
RN
Students may enter a diploma, an associate degree, or a baccalaureate program to be licensed as a registered nurse (RN).
AACN
The AACN believes that baccalaureate education should be the minimum level required for entry into professional nursing practice.
Employment of New Nurse Graduates
Findings from the AACN's latest survey show that 46% of employers require new hires to have a bachelor's degree.
Continuing education
The ANA defines continuing education as those professional development experiences designed to enrich the nurse's contribution to health.
Practical nursing programs
Practical nursing programs were established to teach graduates to give bedside nursing care to patients.
NCLEX-PN
On completion of the practical nursing program, graduates can take the National Council Licensure Examination-Practical Nurse (NCLEX-PN) for licensure as an LPN.
Registered Nursing Education
Three types of educational programs traditionally lead to licensure as an RN: Diploma, Associate Degree, Baccalaureate Program.
NCLEX-RN
Graduates of all three RN programs take the NCLEX-RN examination.
BLS report
As of 2020, the BLS reports that employment of registered nurses is projected to grow 12% from 2018 to 2028.