Plant Histology 5: Secondary Vascular Tissues
1/160
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
cambium
gives rise to the primary plant body
vascular cambium
meristem whose presence results in the development of woody tissues; responsible for plant’s secondary growth
primary growth
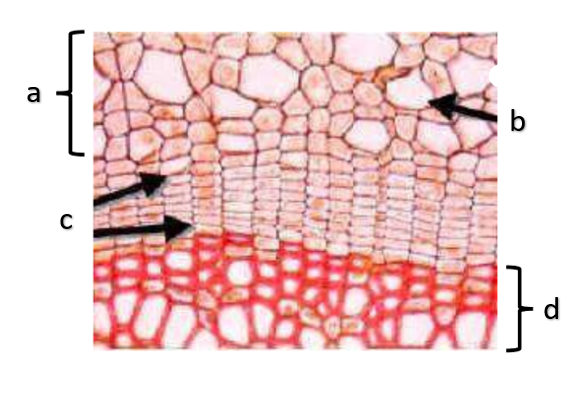
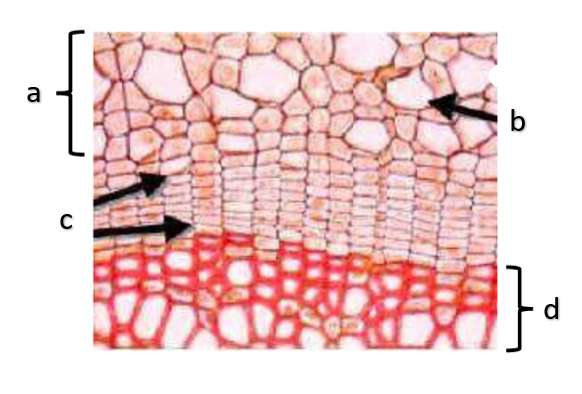
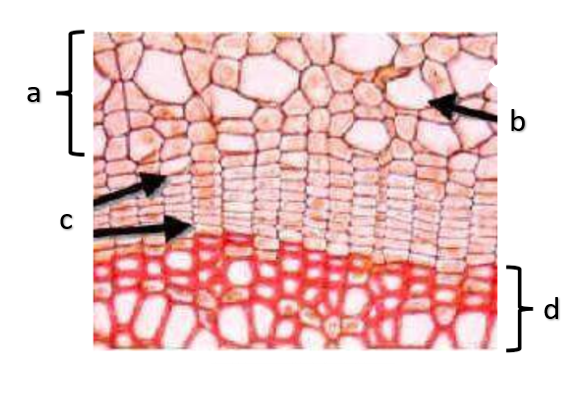
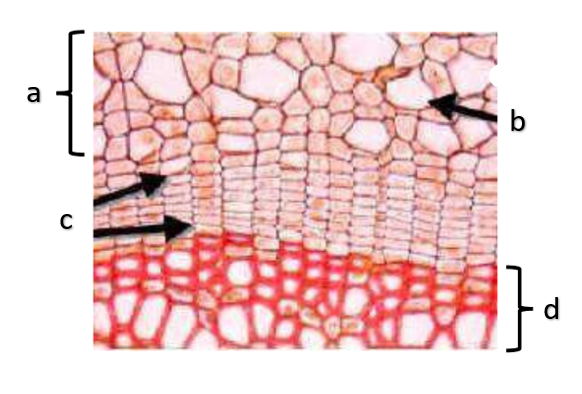
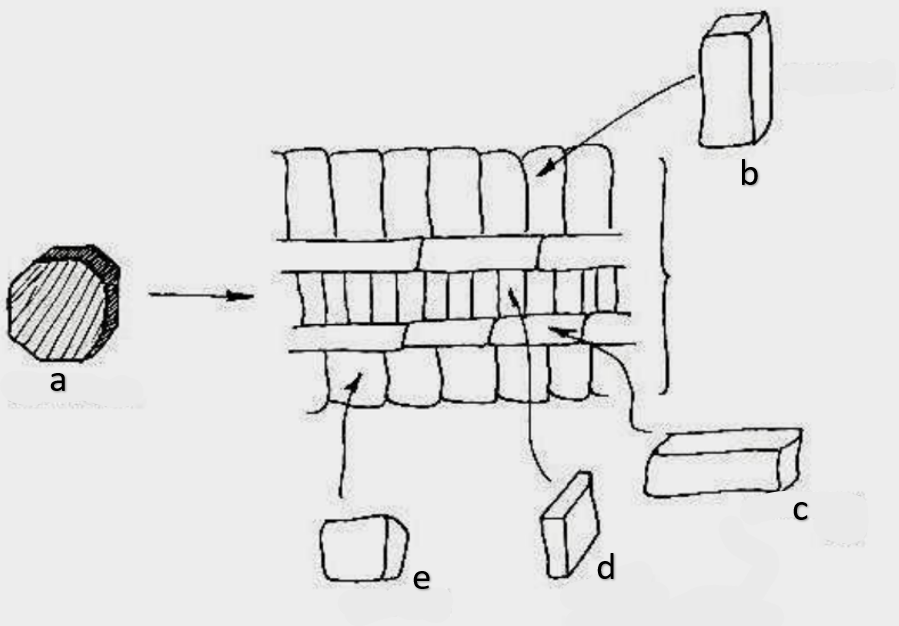
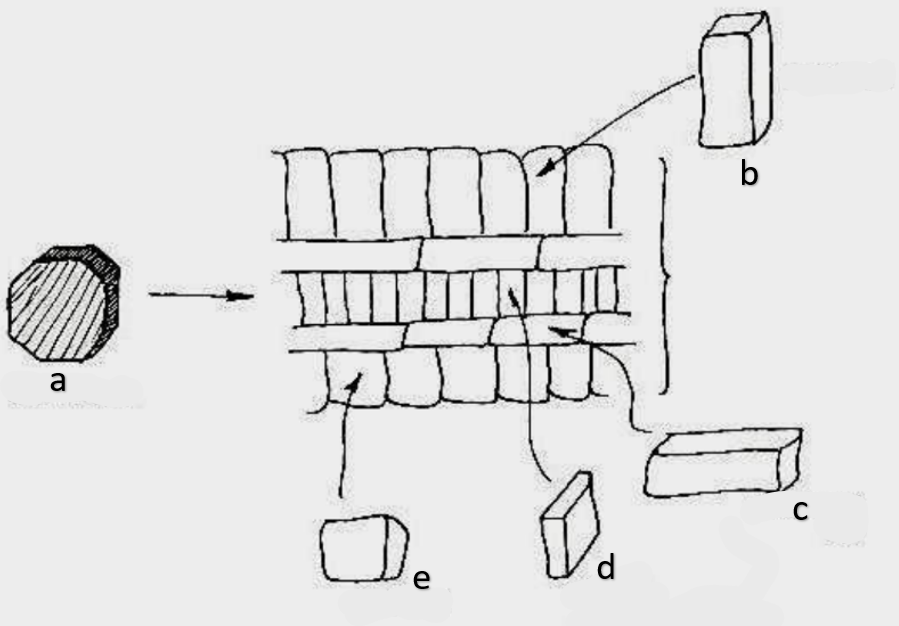
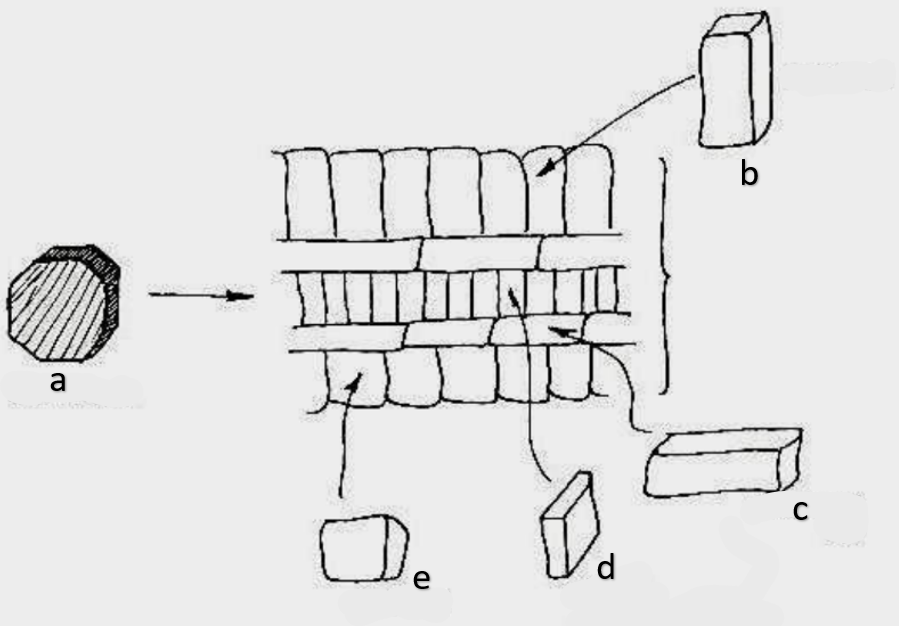
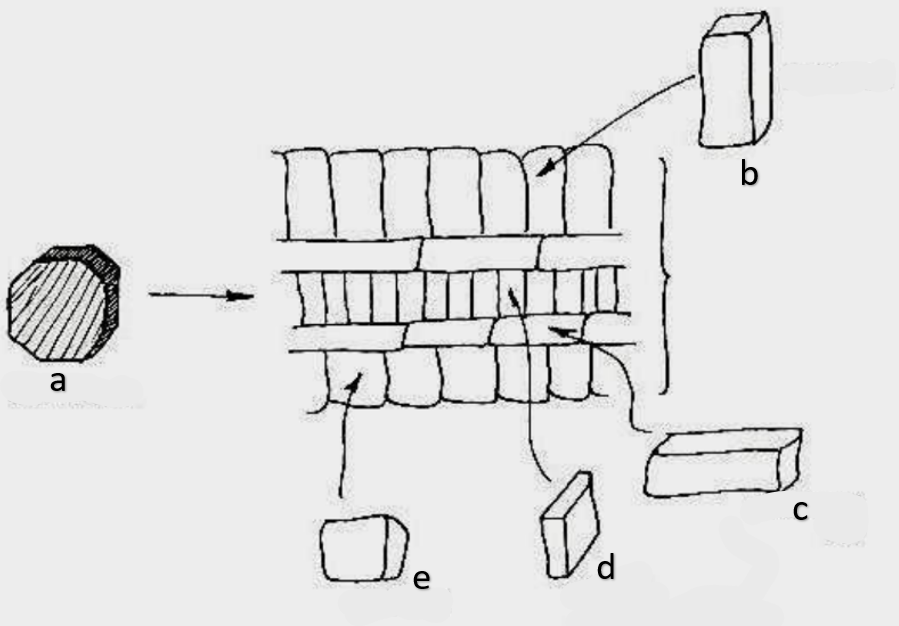
What type of growth is shown on the figure on the left?
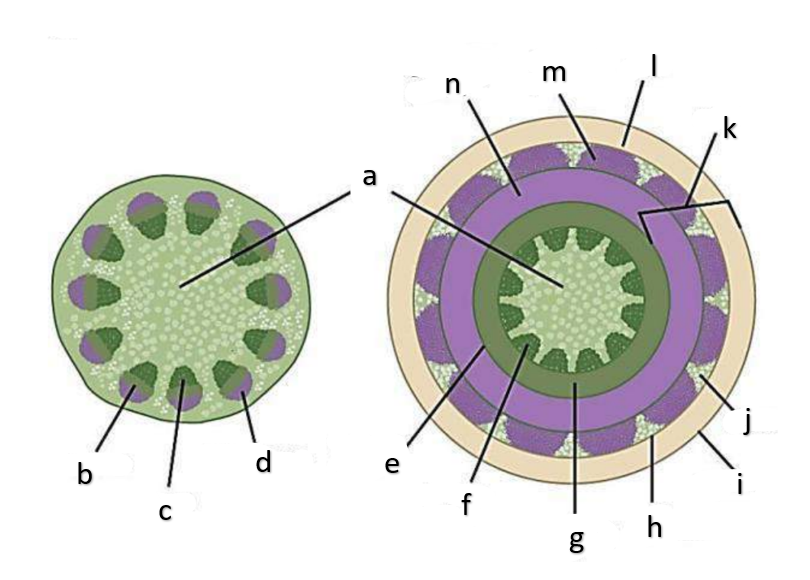
dicotyledons
The figure on the left is a cross section of what group of flowering plant?
secondary growth
What type of growth is shown on the figure on the right?
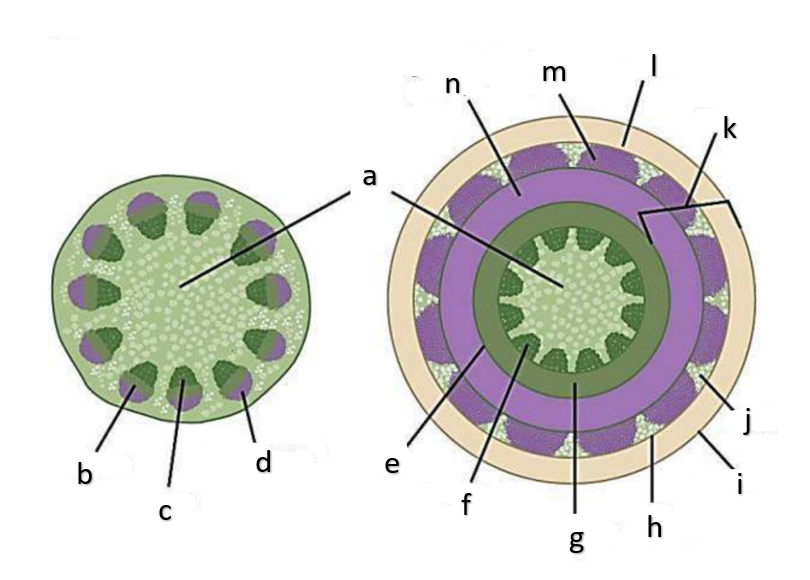
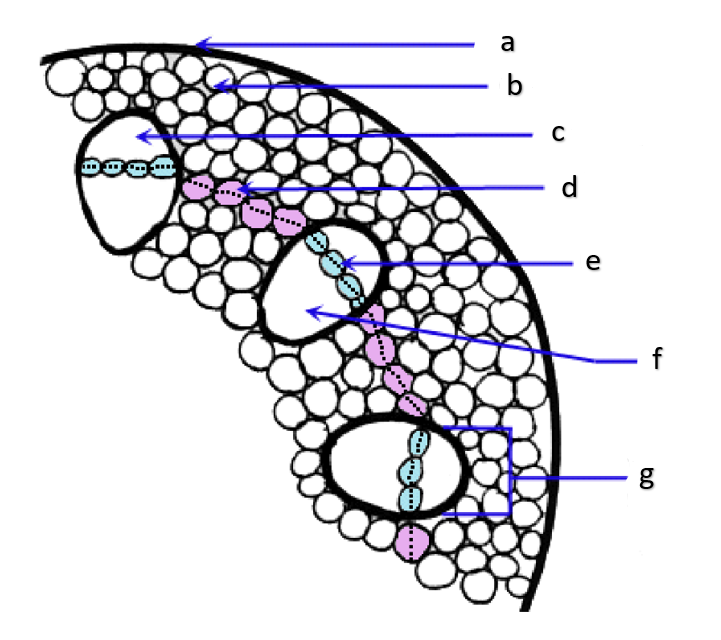
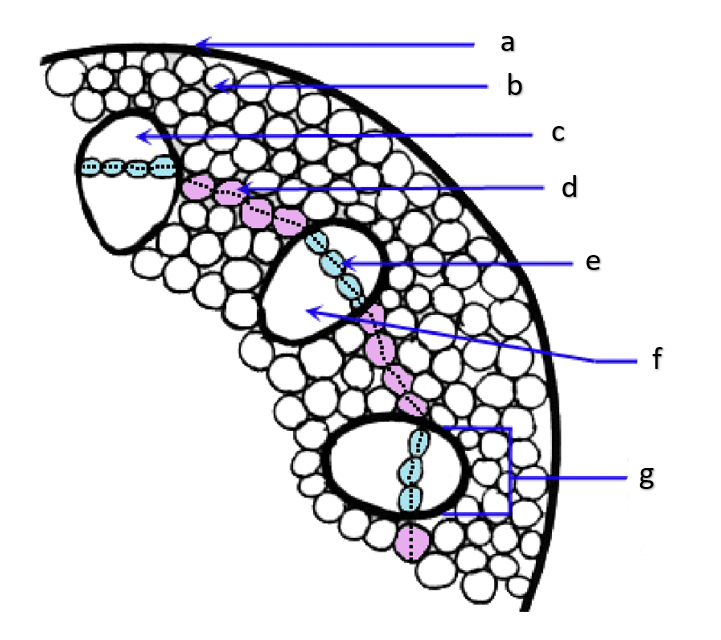
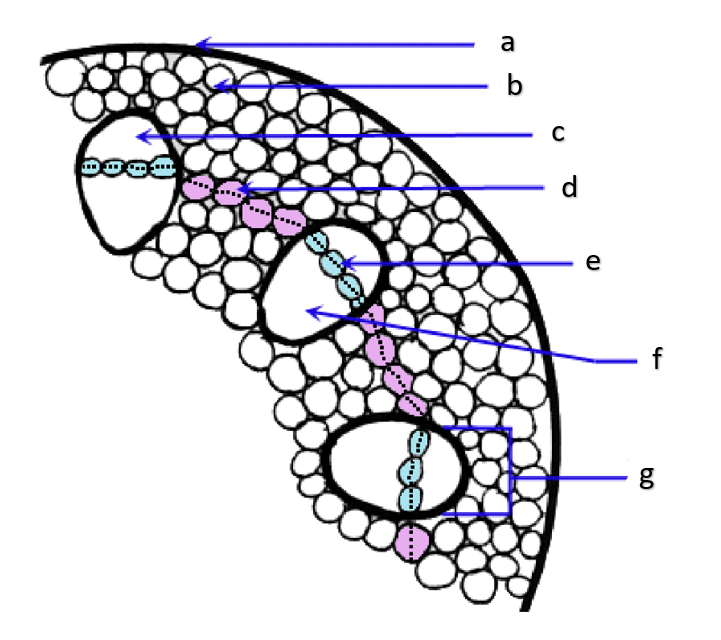
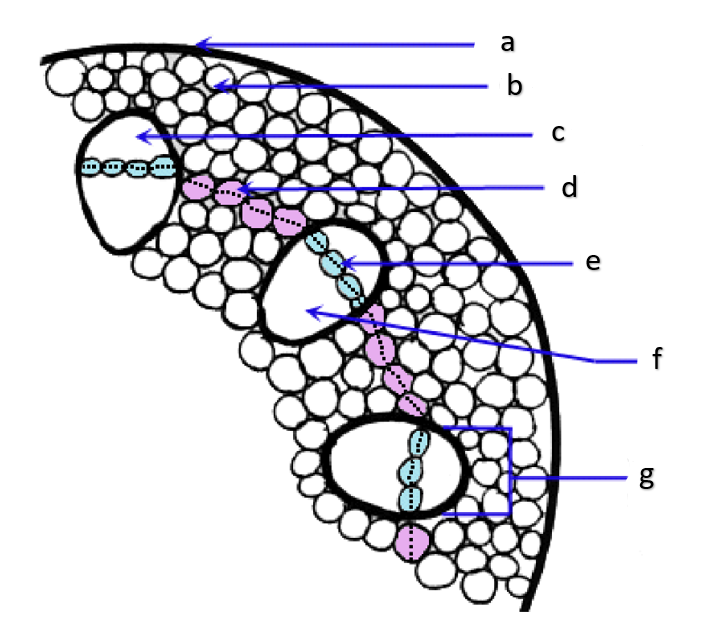
pith
a
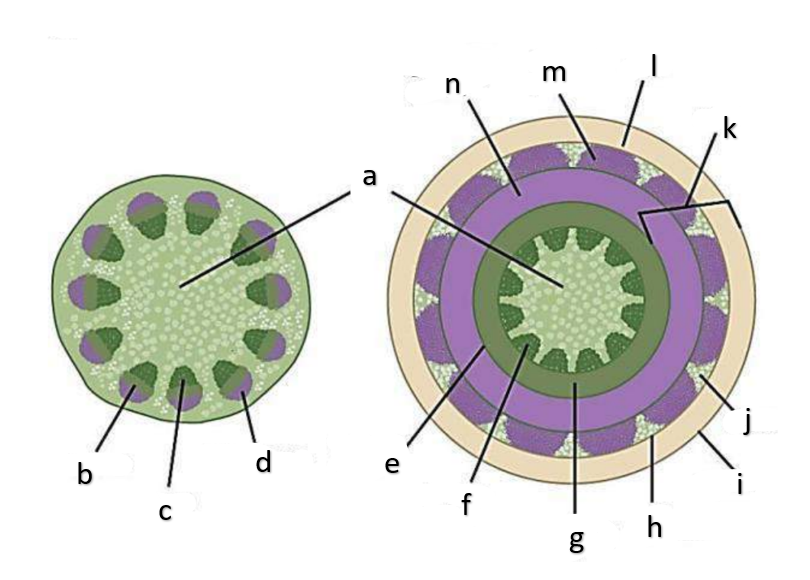
phloem
b
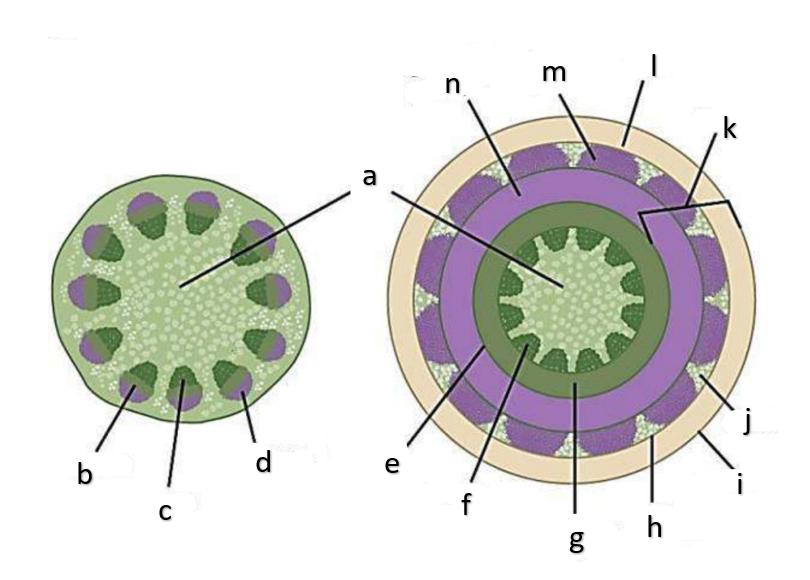
xylem
c
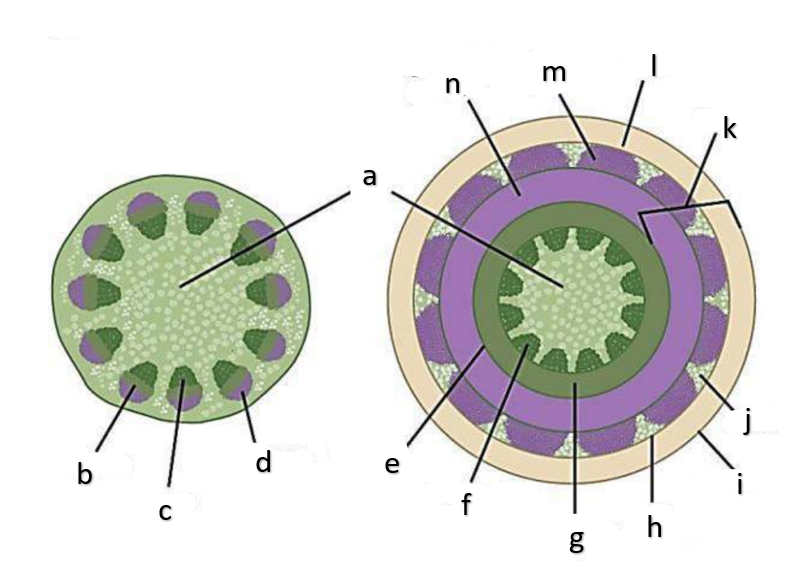
sclerenchyma, fibers
d
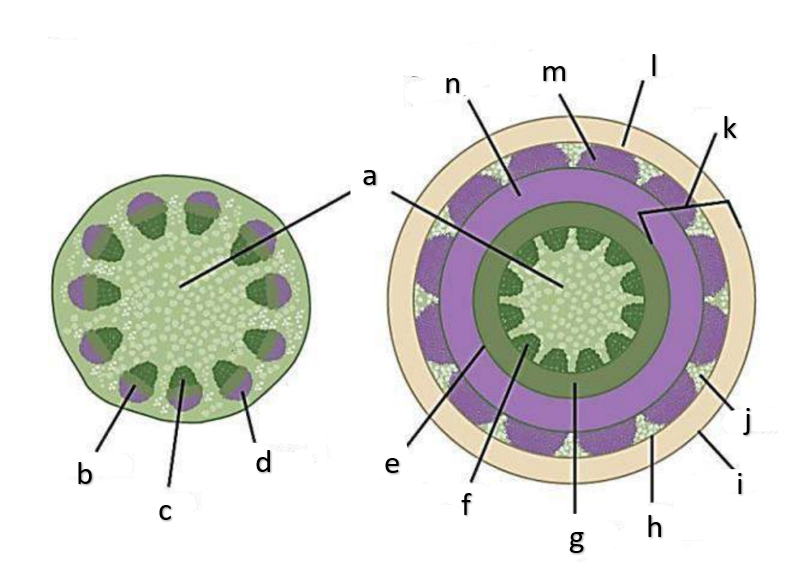
vascular cambium
e
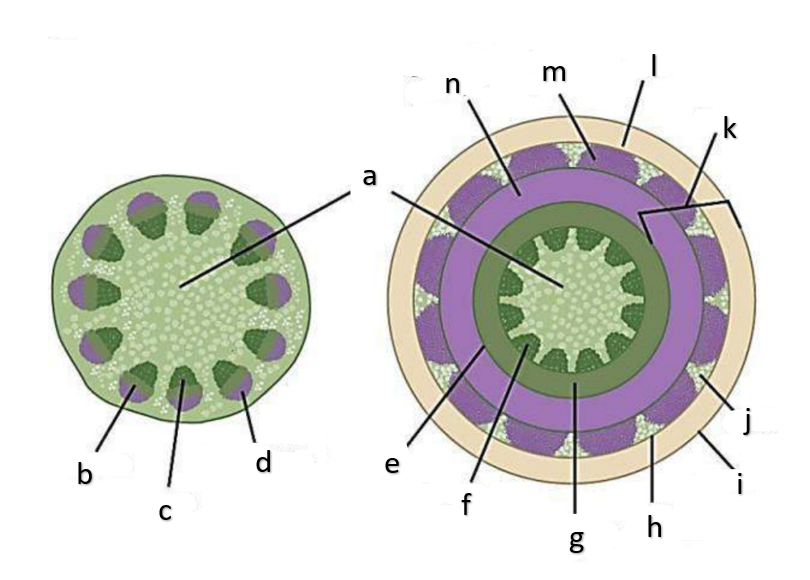
primary xylem
f
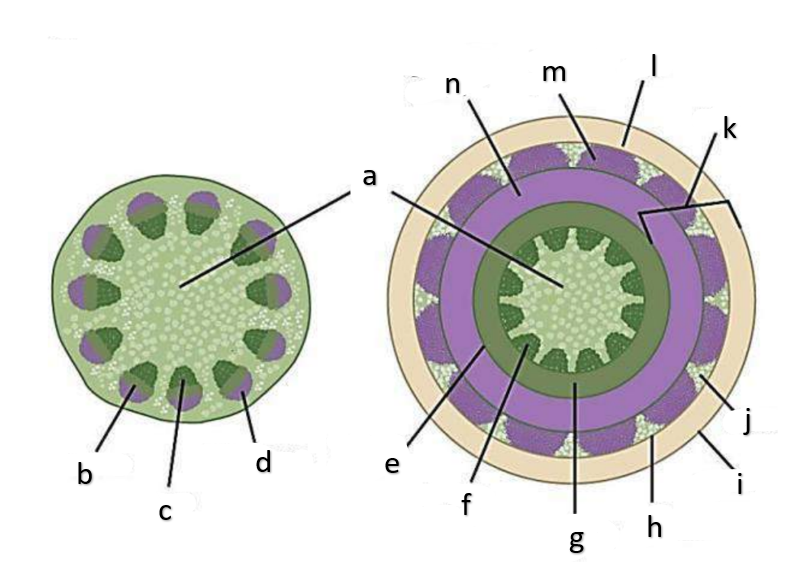
secondary xylem
g
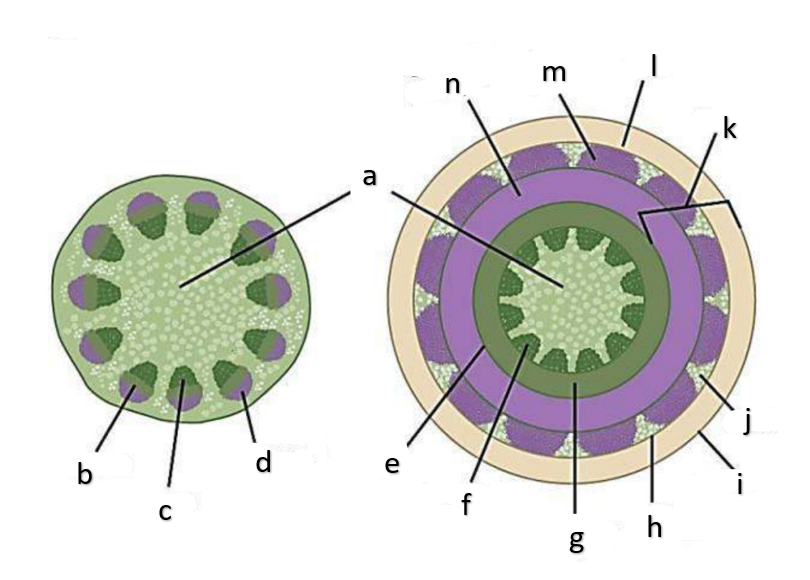
cork cambium
h
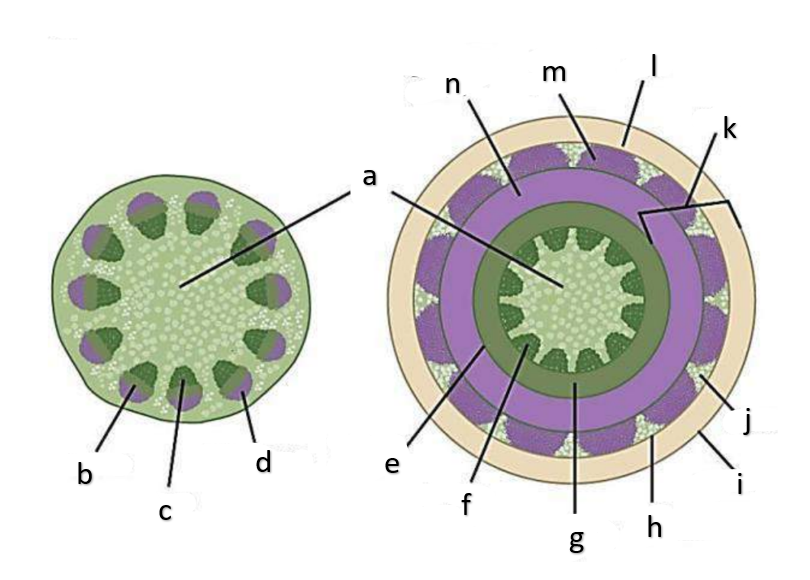
epidermis
i
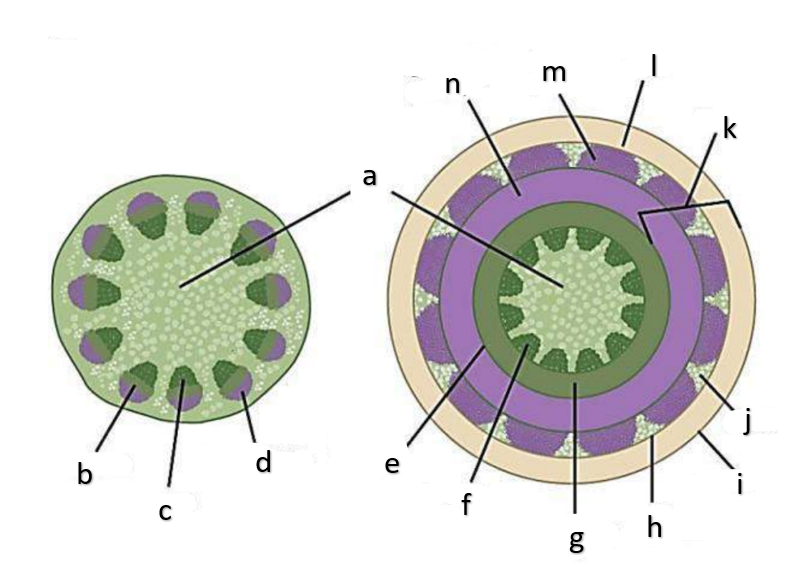
cortex
j
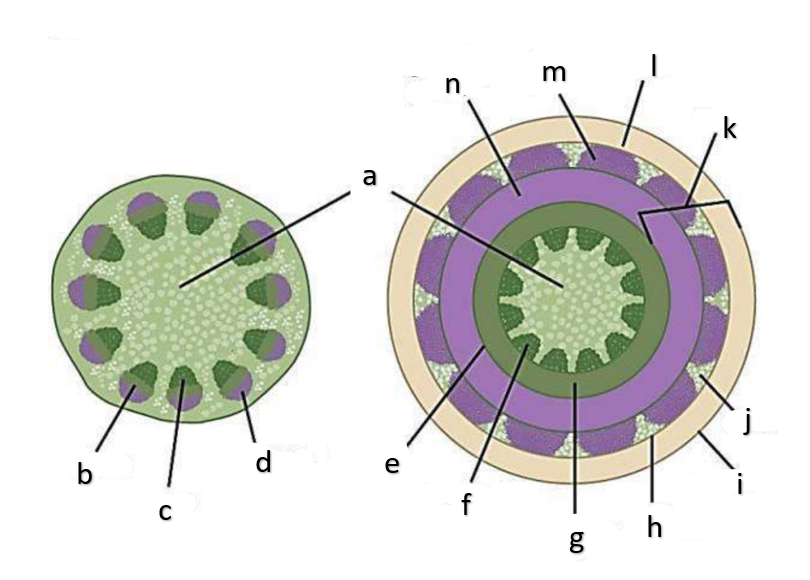
bark
k
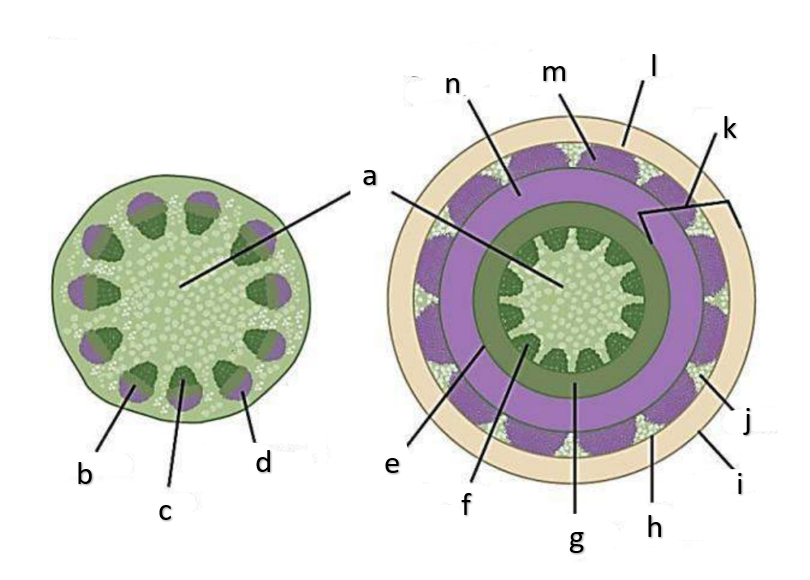
cork
l
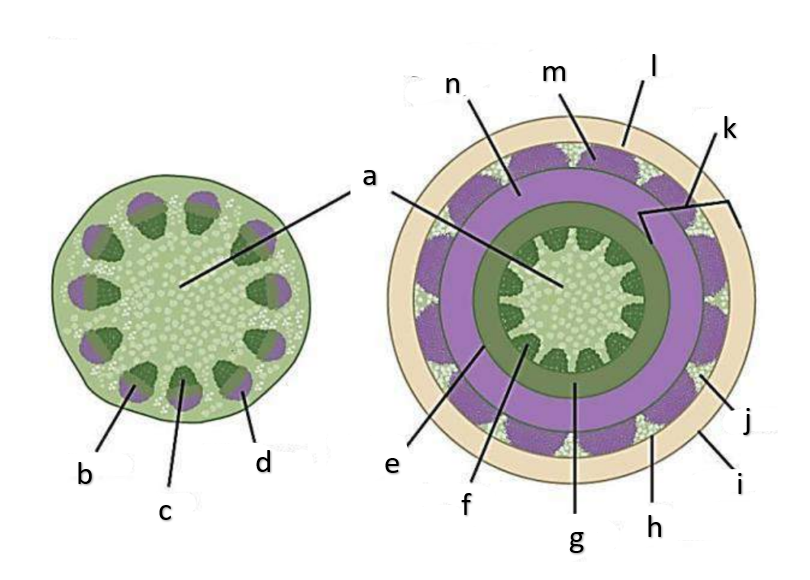
primary phloem
m
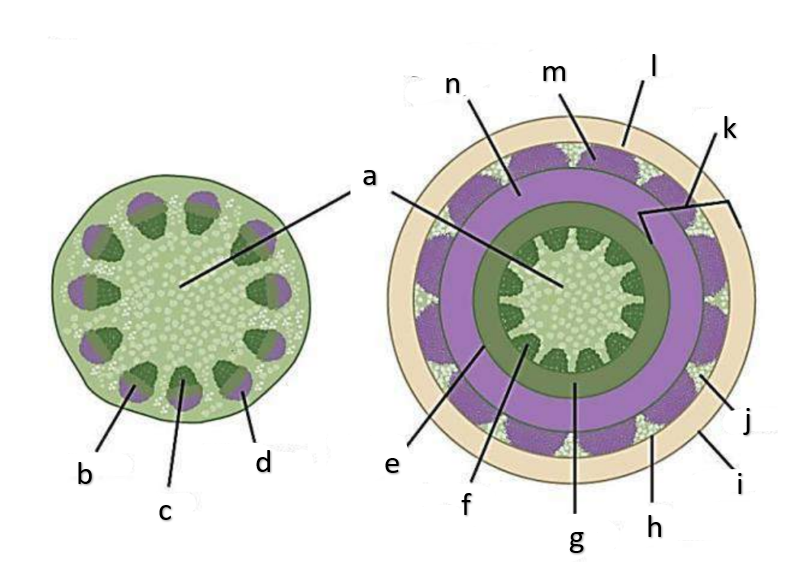
secondary phloem
n
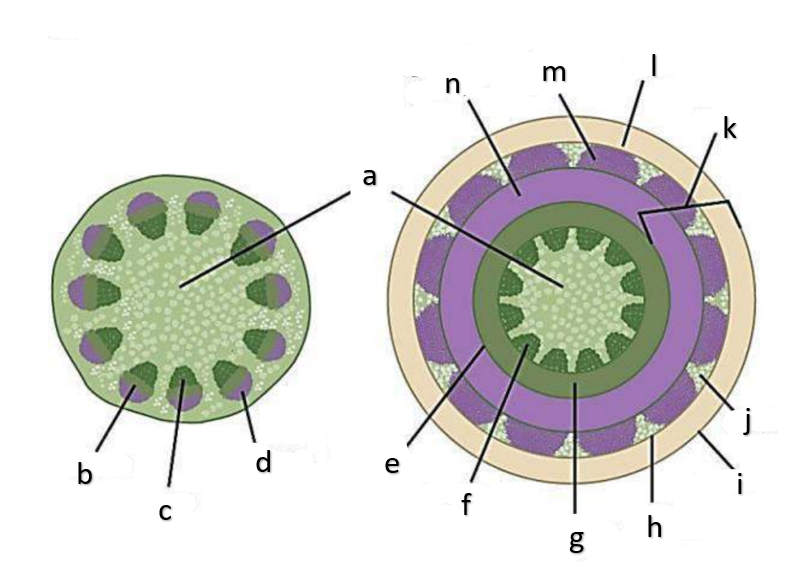
procambium
present in herbaceous plants, which remain herbaceous all throughout
parenchyma
What type of tissue is found at the pith?
procambium
positioned between xylem and phloem
first
primary cells refer to cells that were formed ______.
last
secondary cells refer to cells that were formed ______.
secondary, secondary
vascular cambium is positioned between ________ xylem and__________ phloem.
primary phloem
very first tissue to form
secondary phloem
very last tissue to form
epidermis
will eventually be sloughed off and replaced with bark
secondary cortex
associated with bark
secondary phloem
a
sieve tube member
b
vascular cambium
c
secondary xylem
d
flattened
in procambium and vascular cambium, the cells are usually __________.
sieve tube member
main component of phloem that transports or translocates sugar
procambium and interfascicular parenchyma cells
gives rise to the vascular cambium
monocots, monocotyledons
some of these may increase in height and diameter, but its “wood” is not a product of the vascular cambium
dicots, dicotyledons
produce true wood
anomalous secondary growth
in place of vascular cambium, other tissues are responsible for wood found in monocot families; caused by active parenchyma cells give rise to wood or girth increase (example: palm family)
interfascicular parenchyma
“between” + “fascicle”; tissue located in between two vascular bundles
epidermis
a
cortex
b
phloem
c
interfascicular parenchyma
d
procambium
e
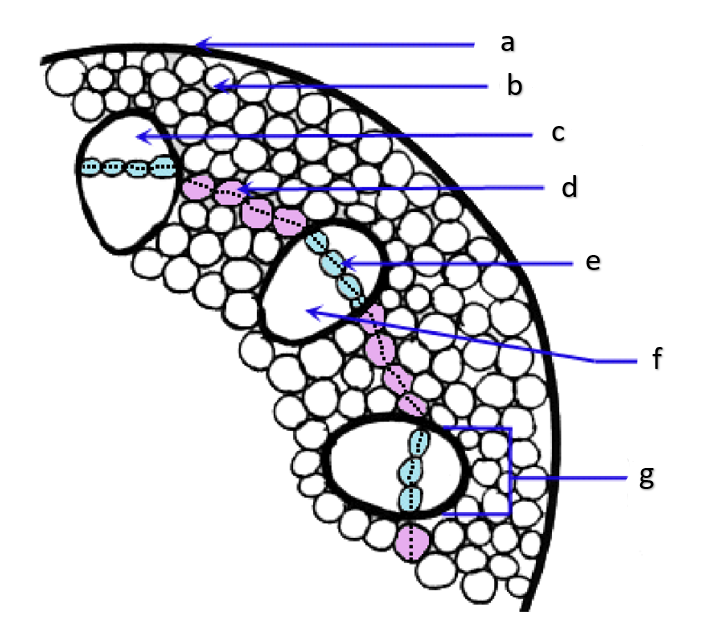
xylem
f
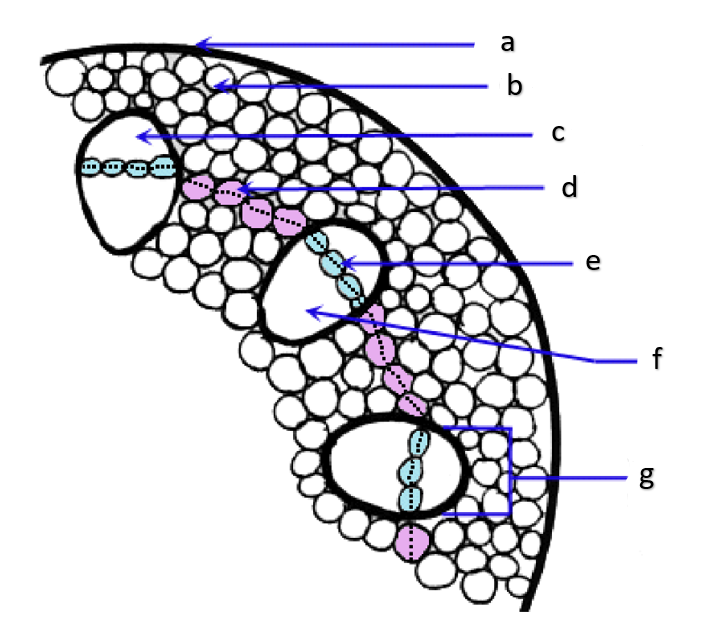
vascular bundle
g
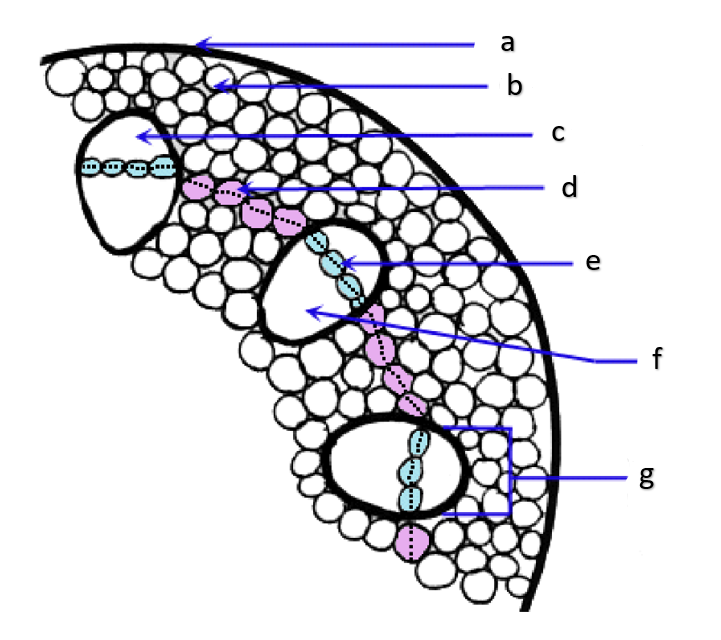
cortical region
cortex; usually includes parenchyma, collenchyma, and fibers
periclinal
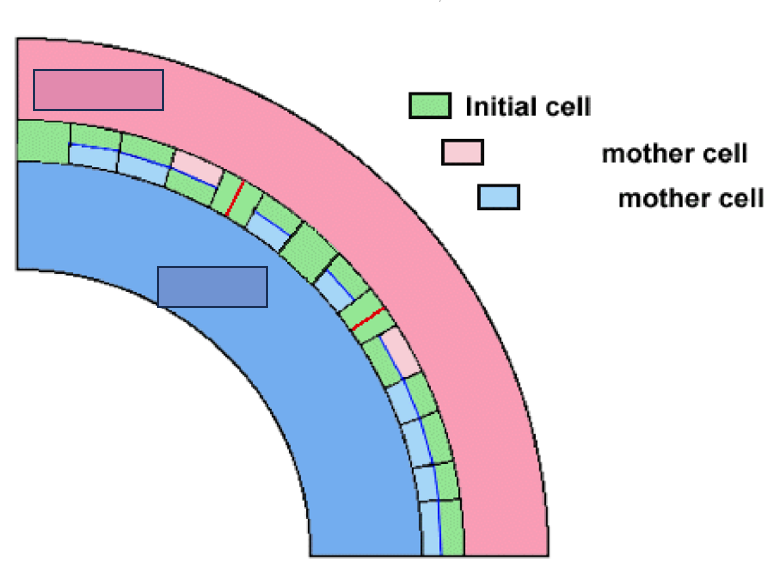
What is the interfascicular cambium’s manner of division?
Multiplicative division
What kind of division is portrayed as the red line?
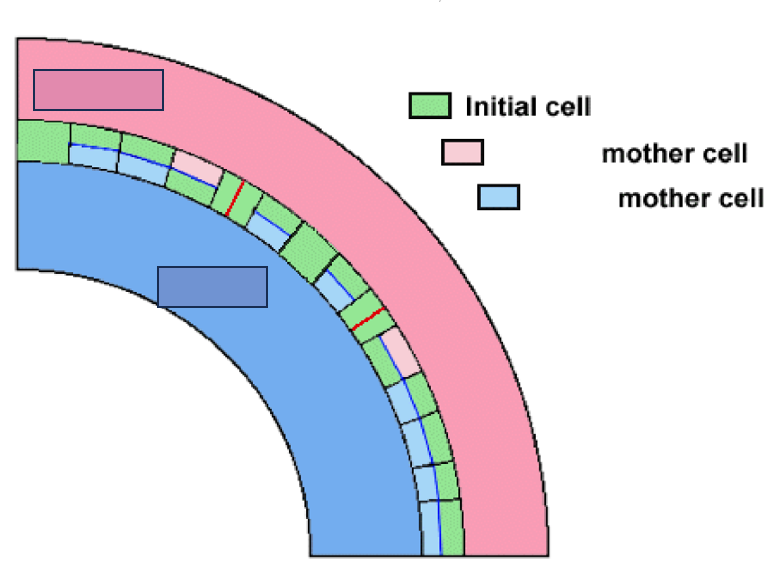
Additive division
What kind of division is portrayed as the blue line?
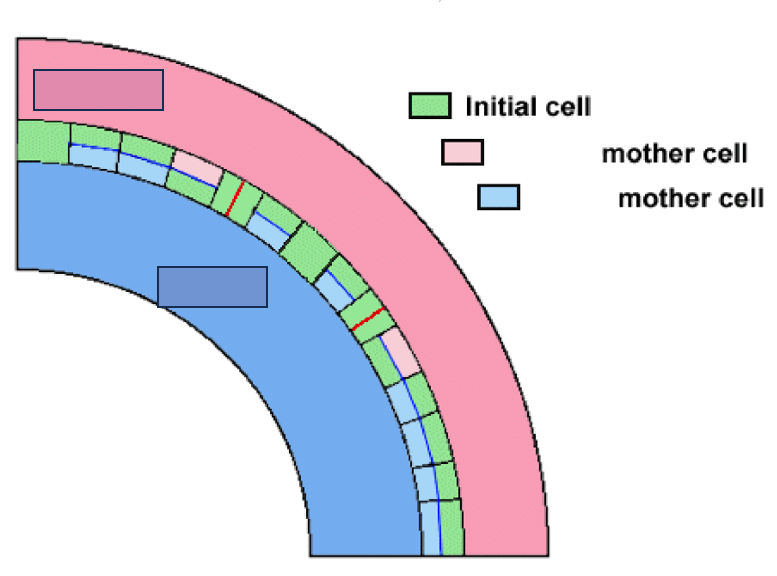
Phloem
What mother cell is portrayed through the light pink boxes?
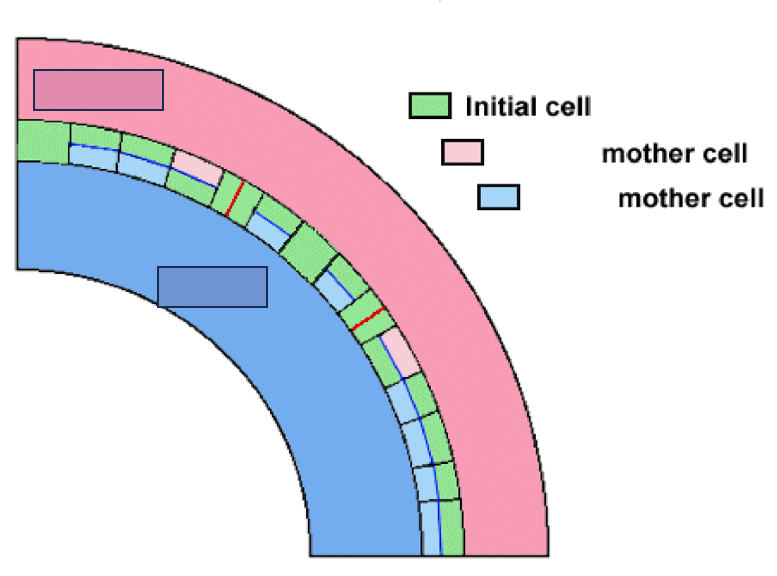
Xylem
What mother cell is portrayed through the light blue boxes?
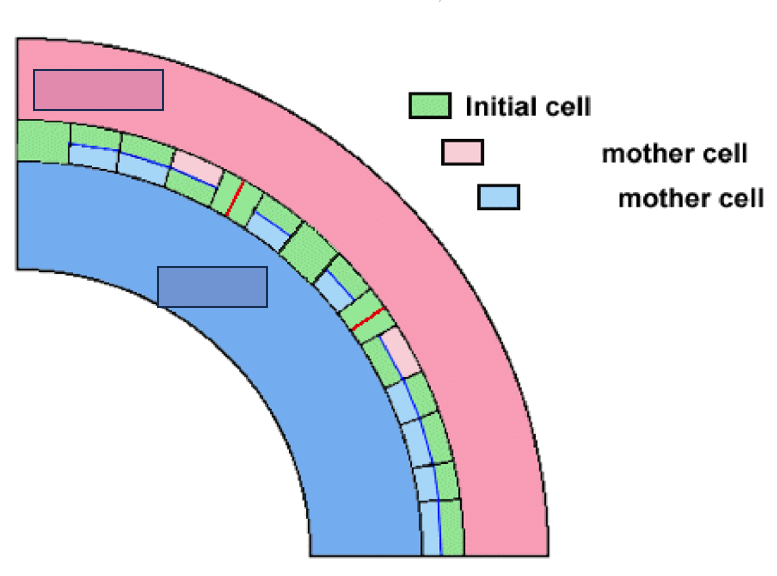
outward, inward
In reference to the figure presented, the vascular cambium and procambium are positioned in such a way that phloem develops _______ and xylem _________.
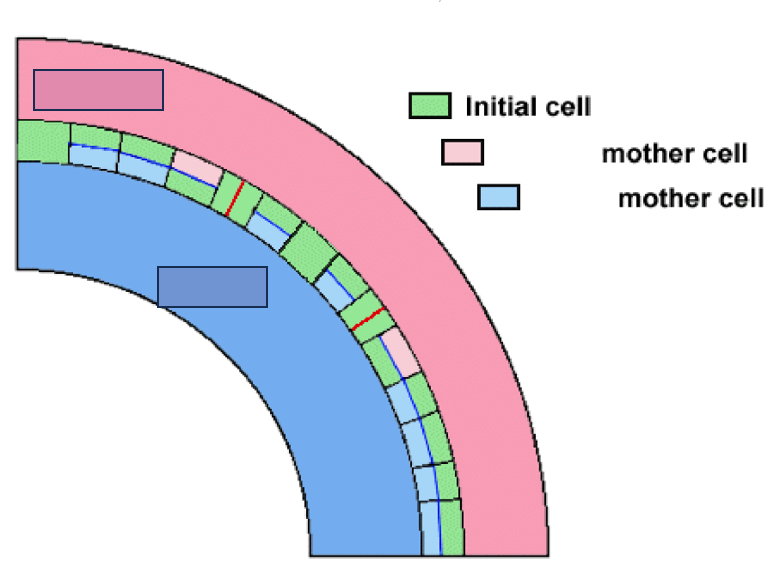
mother cells, initial cells
According to the figure, cells which are produced periclinally become ____________ while those produced anticlinally become what?
meristem
One of its characteristics is being constantly mitotically active.
specialized, meristematic cell
Parent cells divide into two— one becomes _______ and the other will continue to function as a __________.
smaller
Upon the development of the secondary vascular tissues, the pith becomes __________.
continuous
For as long as the cells of the vascular cambium are alive, the development of secondary xylem and phloem is _____________.
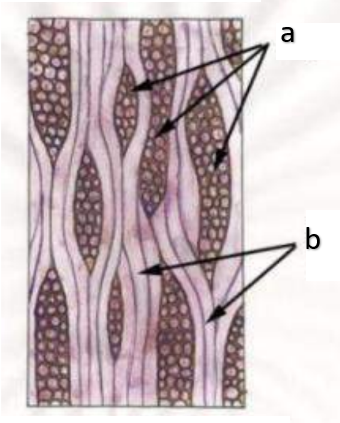
tangential section of vascular cambium
What is shown in the image presented?
ray initials
a
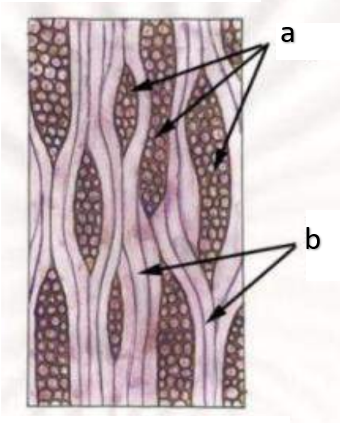
ray initials
may give rise to upright, procumbent, tile, and square cells parenchyma cells
ray initial
a
upright cell
b
procumbent cell
c
tile cell
d
square cell
e
fusiform initials
b
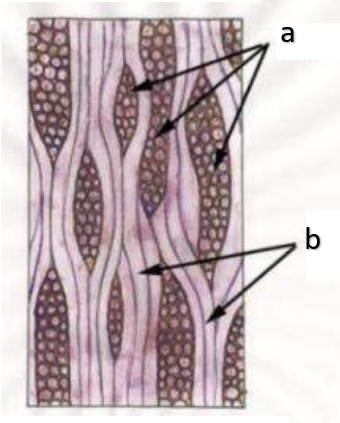
secondary xylem
technical term for wood
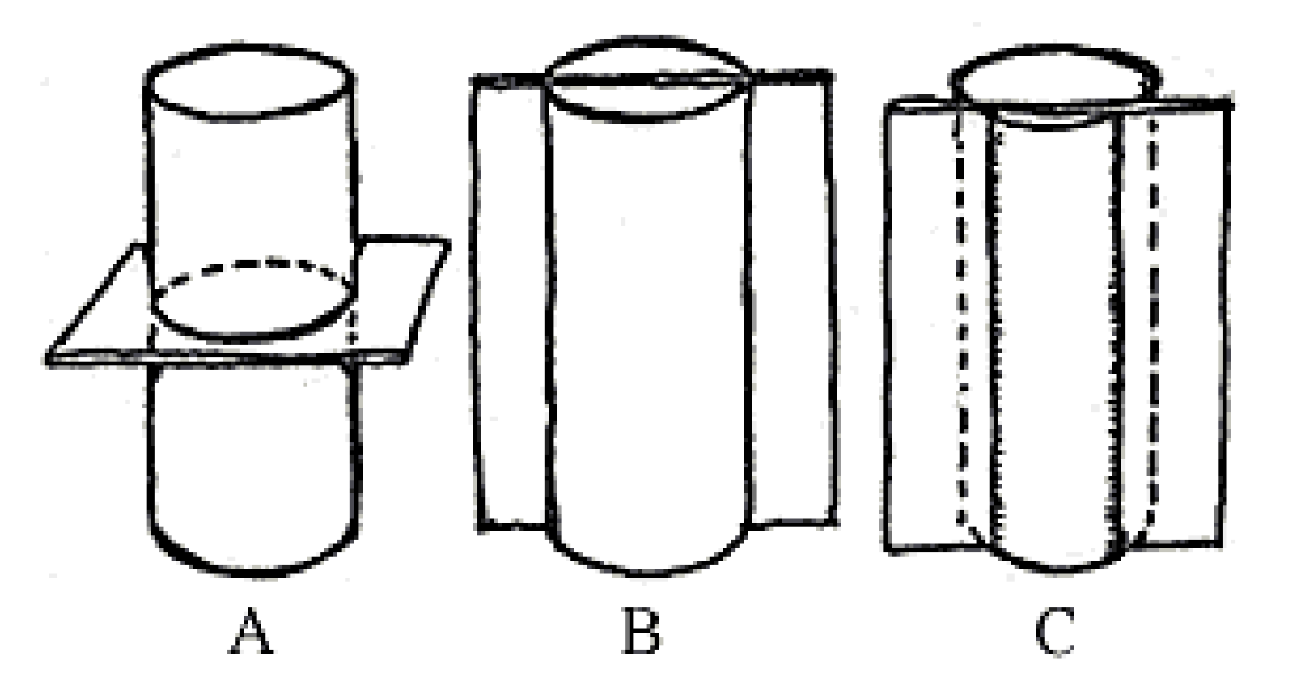
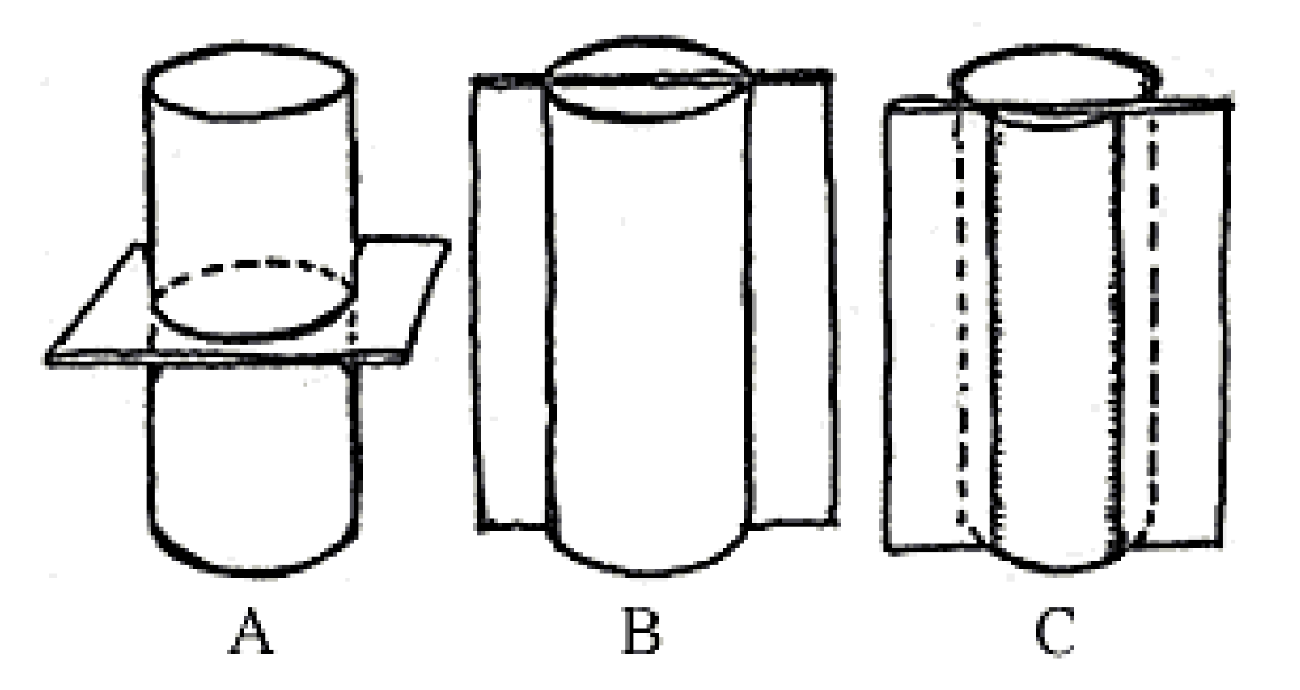
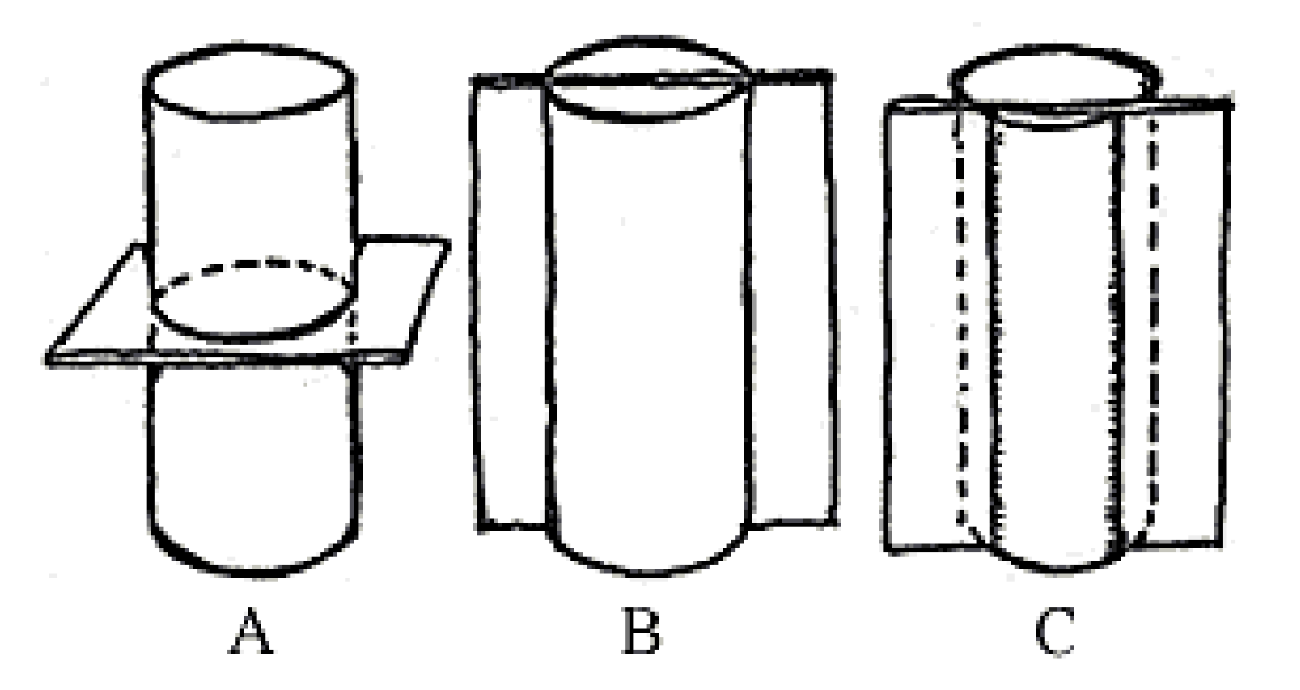
transverse section or cross section
A
radial longitudinal section (RLS)
B
tangential longitudinal section (TLS)
C
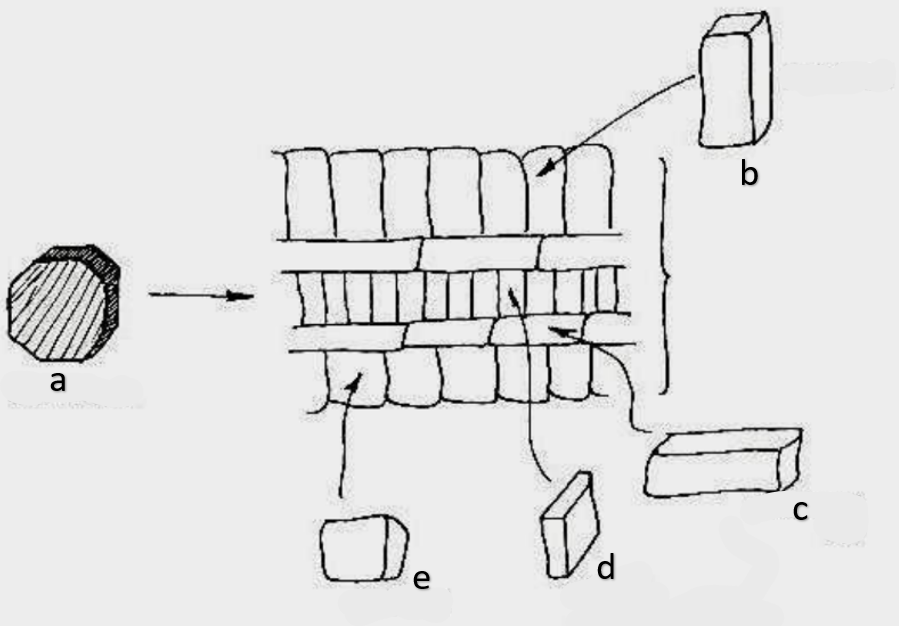
initials
meristematic cell; origin
fusiform initials
elongated in tangential section; taper; give rise to tracheary elements (vessels and tracheids)
ray initials
isodiametric (almost equal in diameter) in tangential section; give rise to ray parenchyma and axial parenchyma
axial parenchyma
vertical arrangement
ray parenchyma
horizontal arrangement
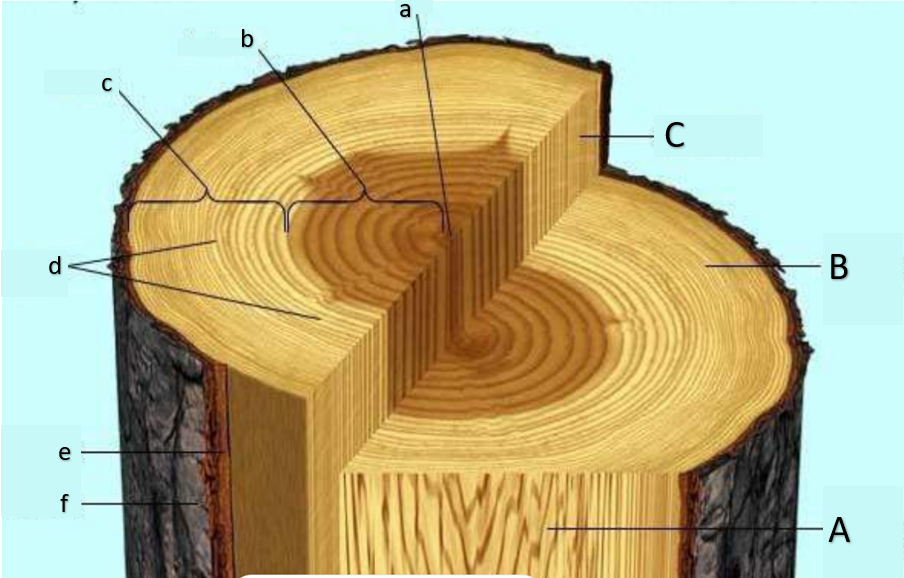
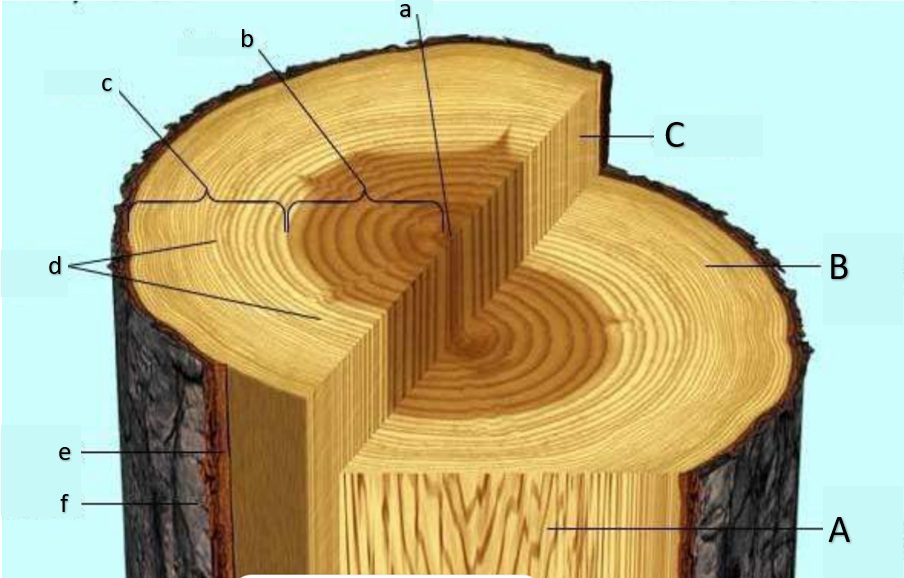
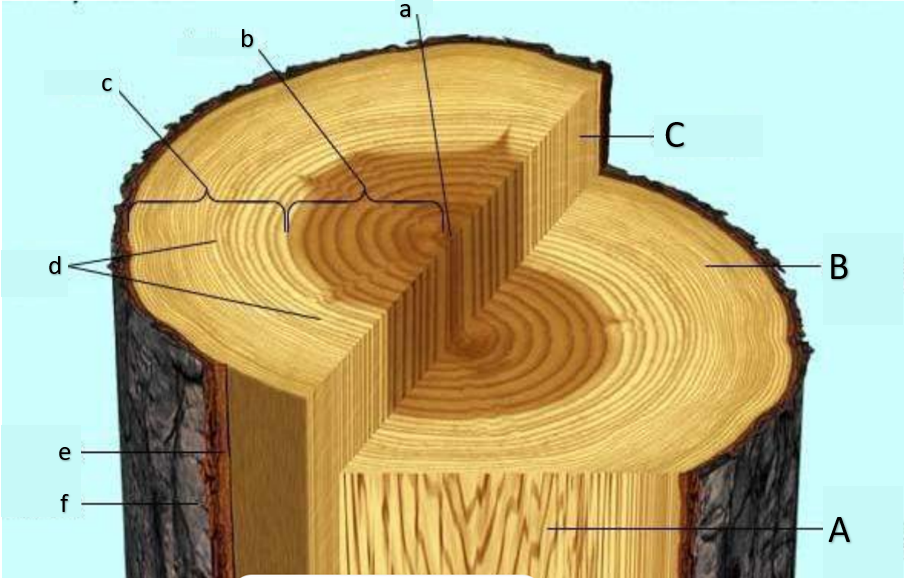
pith
a
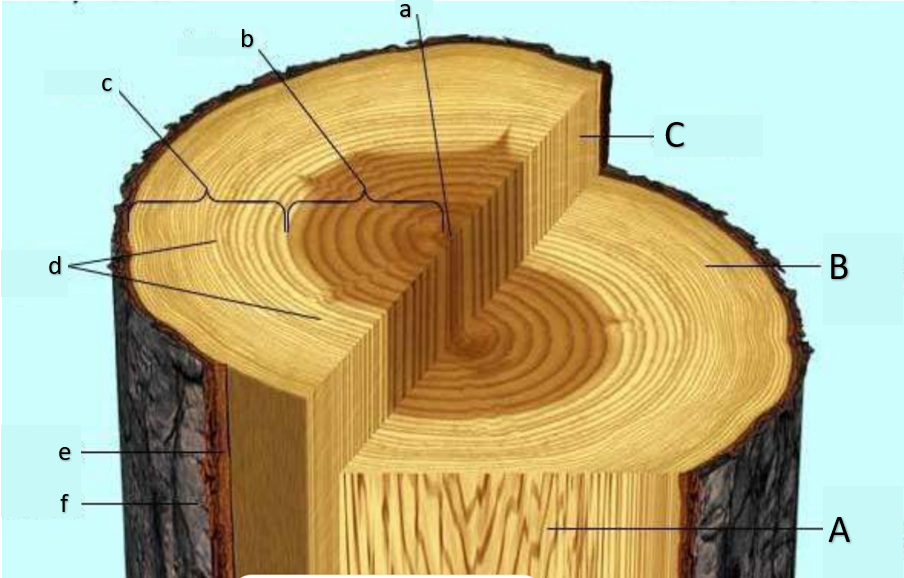
heartwood
b
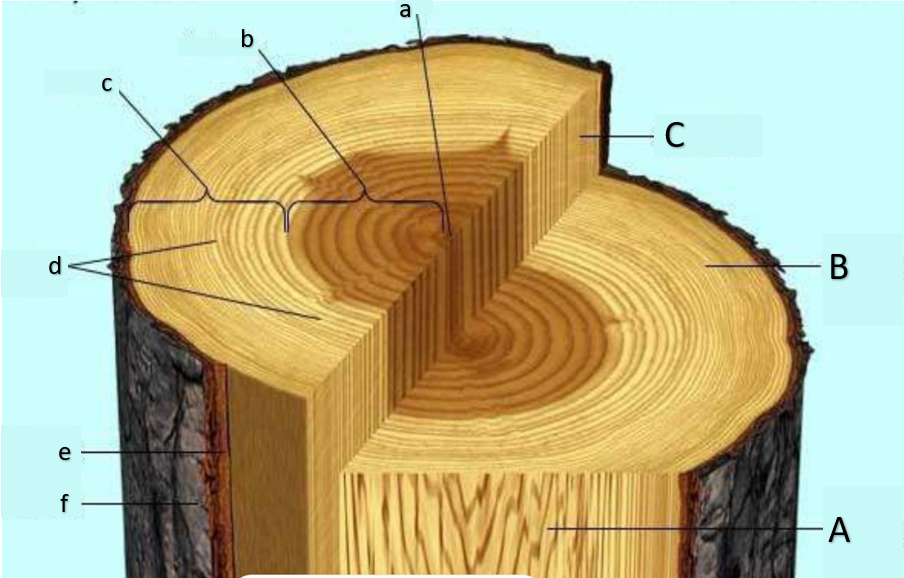
sapwood
c
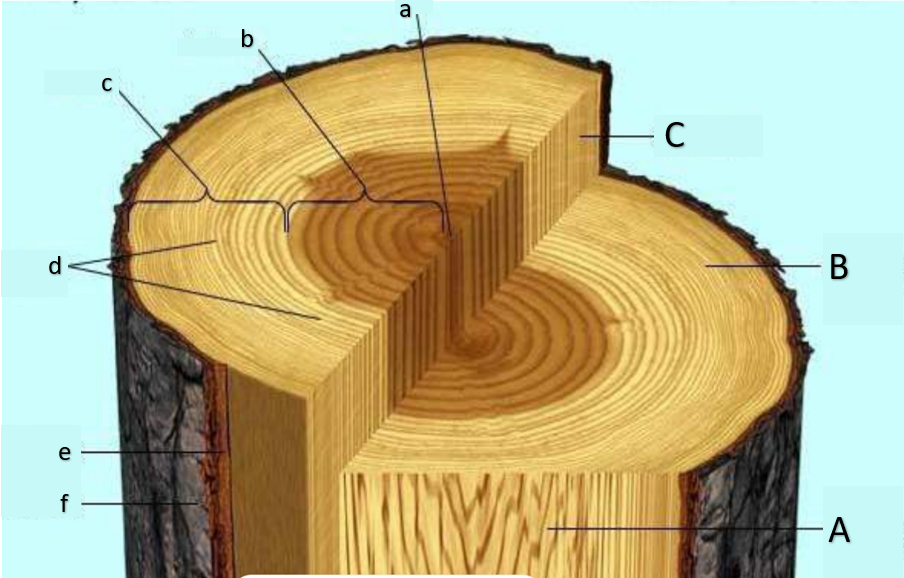
growth rings, annual rings
d
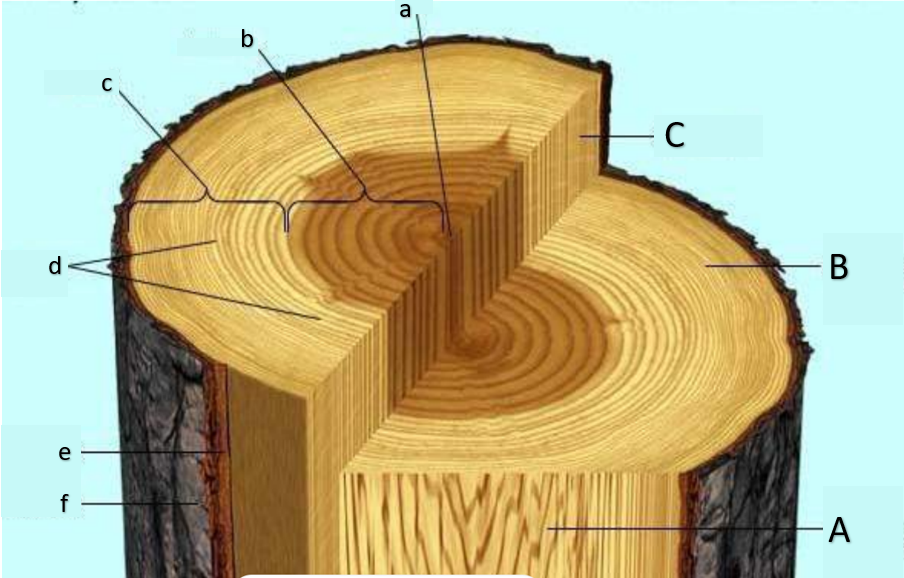
inner bark
e
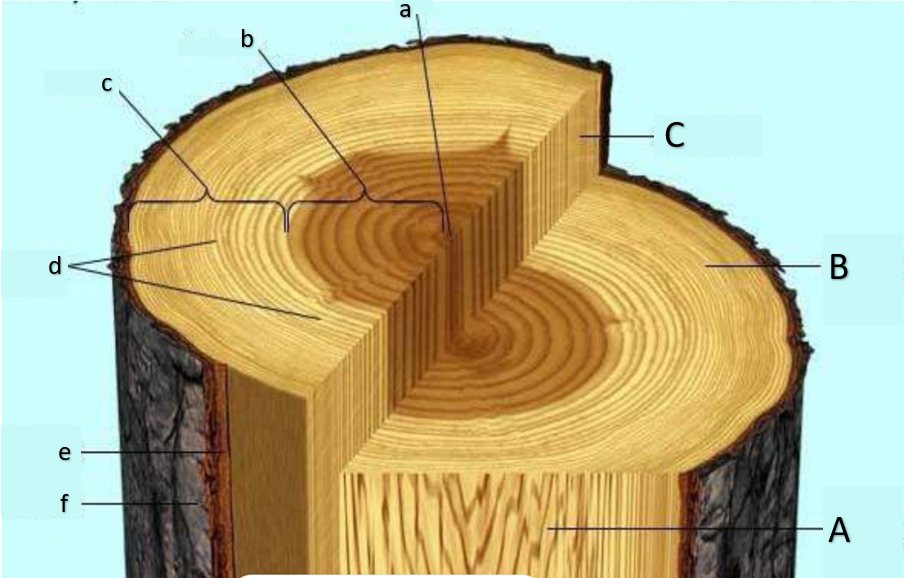
outer bark
f
tangential longitudinal section (TLS)
What is the type of sectioning in A?
transverse surface
What is the type of sectioning in B?
radial longitudinal section (RLS)
What is the type of sectioning in C?
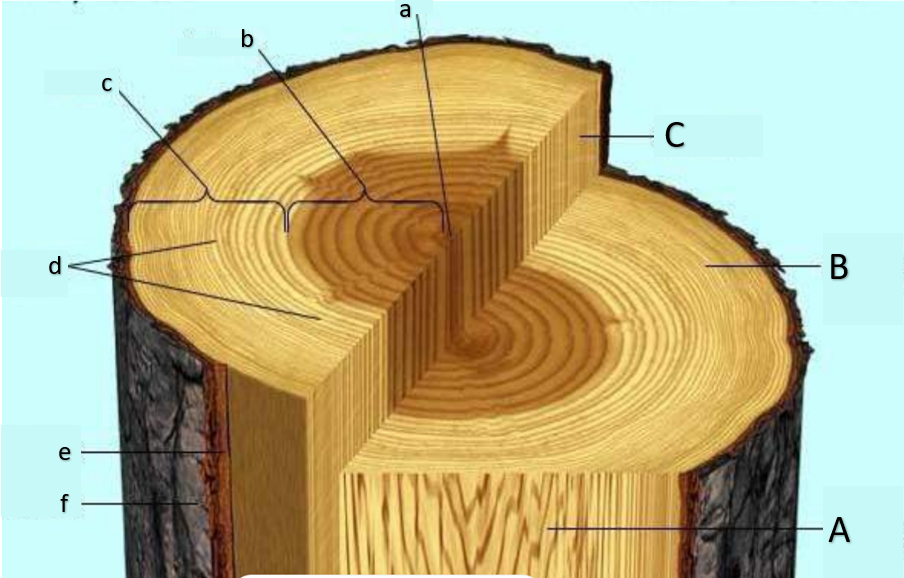
heartwood
water can no longer enter this part of the tree, causing it to run out of minerals and eventually die, losing its function of transport; main function is storage of organic substances, some of which imparting color
sapwood
functional in terms of transporting water and minerals; small pit due to occupation of secondary xylem;
outer bark
primarily made out of cork cells (dead cells)
inner bark
still considered bark; secondary phloem is present; functions at translocation; the plant will die if this is removed
translocation
transport of photosynthetic products (example: sugar)
girdling
severing the inner bark from the woody plant to keep them from growing further without cutting down the plant
absent
vessels are ________ in gymnosperms, with the exception of Gnetophyta.
tracheids
Conifers only have ______ in their xylem; it is said that around 90-95% of cells in their wood are represented by this, with the remaining 5-10% being ray parenchyma.
fibers
There are almost no _________ in conifer wood, hence why they are occasionally called soft wood.
tracheids and vessels or tracheary elements, parenchyma
Dicot wood (hard wood) includes different kinds of cells such as _________. These transport water and minerals and impart support and hardness to the plant due to presence of secondary cell wall. It also includes __________.
fibers
In addition to tracheary elements, dicot wood (hard wood) also includes _________. The absence of this is what causes conifer wood to be called soft wood, even if it isn’t actually soft.
transverse section and radial section
In reference to the image, in which sections are resin ducts highly prominent?
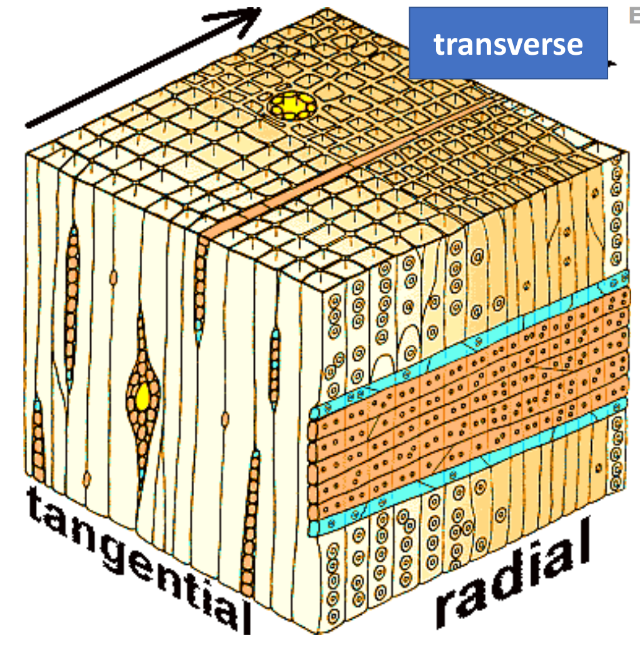
resin ducts
____________ are present in all parts of a conifer.
early wood or spring wood, resin duct
The thickness of tracheid’s cell walls may vary. They are thinner at the _________ and thicker when closer to the _________.