A&P Bone Tissue
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
bone remodeling
the building of new bone tissue and breaking down of old bone tissue
effects of microgravity
loss of 1-2% of bone mass per month especially in the pelvis, backbone, and lower limbs
bone
consists of osseous tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, adipose tissue, blood, and nervous tissue
osteology
the study of bone structure and the treatment of bone disorders
skeletal system
consists of the framework of bones and their cartilages
tendons
connects muscle to bone
bone tissue weight
18% of the human body
mineral storage in bone
calcium and phosphorus
red bone marrow
A highly vascularized connective tissue located in microscopic spaces between trabeculae of spongy bone tissue
hemopoiesis / hematopoiesis
Blood cell production, which occurs in red bone marrow after birth
what does red bone marrow produce
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
what is red bone marrow composed of
developing blood cells, adipocytes, fibroblasts, and macrophages within a network of reticular fibers
yellow bone marrow
consists of adipose cells, which store triglycerides
long bone
a bone with a greater length than width
diaphysis
the long cylindrical portion of the bone. “body” or “shaft”
epiphyses
the ends of a long bone
metaphyses
regions between the diaphysis and epiphyses. contains a growth plate, hyaline cartilage or the epiphyseal line
epiphyseal line
a line of bone that forms once bone ceases to grow in length, replaces cartilage
articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articulation (joint) with another bone. reduces friction and absorbs shock. limited repair
periosteum
The membrane that covers bone and consists of connective tissue, osteoprogenitor cells, and osteoblasts; is essential for bone growth, repair, and nutrition. RICH IN SENSORY NERVES.
perforating fibers
Thick bundles of collagen that extend from the periosteum into the bone extracellular matrix to attach the periosteum to the underlying bone
medullary cavity / marrow cavity
The space within the body of a bone that contains yellow bone marrow. Also called the marrow cavity.
endosteum
thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity and internal spaces of spongy bone.
functions of bone tissue
support, protection, assists in movement, stores minerals and fats, produces blood cells
extracellular matrix composition
15% water, 30% collagen fibers, 55% crystallized mineral salts
calcification
crystallization of tissue because of the deposition of mineral salts (hydroxyapatite). initiated by osteoblasts
what provides bone its tensile strength
collagen fibers
osteoprogenitor cells
Stem cell derived from mesenchyme that has mitotic potential and the ability to differentiate into an osteoblast. found along the inner osteogenic layer of the periosteum, in the endosteum, and in the canals within bone that contain blood vessels
osteoblasts
bone-building cells. secretes collagen and organic components for bone deposition, initates calcification.
osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain daily metabolism.
osteoclasts
A large, multinuclear cell that resorbs (destroys) bone matrix. releases lysosomal enzymes that digest minerals and proteins in the extracellular bone matrix.
compact bone tissue
contains few spaces; strongest type of bone tissue. found beneath the periosteum and makes up bulk of diaphysis
osteon
The basic unit of structure in adult compact bone, consisting of a central canal with its concentrically arranged bone lamellae, bone lacunae, osteocytes, and bone canaliculi. Also called a haversian system.
osteonic canal
A circular channel running longitudinally in the center of an osteon (haversian system) of mature compact bone, containing blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves. also called a haversian canal
concentric bone lamellae
circular plates of mineralized extracellular matrix of increasing diameter, surrounding a small network of blood vessels and nerves located in the osteonic canal. similar to rings of a tree
bone lacunae
spaces between concentric bone lamellae that contain osteocytes
bone canaliculi
Small channel or canal, as in bones, where it connects lacunae.
interstitial bone lamellae
fragments of older osteons that have been partially destroyed during bone rebuilding or growth.
perforating / volkmann’s canals
transverse small passageways that blood vessels and nerves from the periosteum penetrate into compact bone
spongy bone tissue
Bone tissue that consists of an irregular latticework of thin plates of bone called bone trabeculae; spaces between bone trabeculae of some bones are filled with red bone marrow; found inside short, flat, and irregular bones and in the epiphyses (ends) of long bones. Also called cancellous or trabecular bone tissue.
“hot spots” in bone scans
increased metabolism. can be a sign of bone cancer, abnormal healing of fractures, abnormal bone growth
“cold spots” in bone scans
decreased metabolism. can be a sign of degenerative bone disease, decalcified bone, fractures, bone infections, pagets disease, rheumatoid arthritis
periosteal arteries
small arteries accompanied by nerves that enter the diaphysis through perforating canals into osteonic canals
nutrient artery
large artery near the center of the diaphysis. passes through the nutrient canal. once into the medullary cavity, it splits into proximal and distal branches towards the ends of the bones
nutrient foramen
a hole in the diaphysis for the nutrient artery to enter
nutrient canal
small canal in the compact bone of the diaphysis
metaphyseal arteries
enters through the metaphyses of a long bone and supplies the red and yellow blood marrow and spongy bone tissue along with the nutrient artery
epiphyseal arteries
enters the epiphyses of a long boneand supplies the red and yellow bone marrow and spongy bone there
ossification or osteogenesis
process of bone formation
intramembranous ossification
bone forms directly within mesenchyme (in fetus) simpler. flat bones of skull, facial bones, mandible, medial part of clavicle
endochondral ossification
bone forms within hyaline cartilage that develops from mesenchyme (in fetus)
steps of intramembranous ossification
development of the ossification center, calcification, formation of bone trabeculae, development of the periosteum
steps of endochondral ossification
development of the cartilage model, growth of cartilage model, development of primary ossification center, medullary cavity development, development of secondary ossification center, formation of articular cartilage and growth plate
cartilage model
hyaline cartilage formed by mesenchyme in fetus development. covered by the perichondrium
perichondrium
membrane that covers cartilage. turns into periosteum if the cartilage turns to bone
interstitial growth
growth from within that causes increase of length
appositional growth
growth from outside, growth in thickness
hypertrophy
increase in size
primary ossification center growth
growth inwards
secondary ossification center growth
growth outwards
zone of resting cartilage
site of small scattered chondrocytes. do not function in bone growth in length
zone of proliferating cartilage
site of medium chondrocytes stacked like coins.
zone of hypertrophic cartilage
site of large, maturing chondrocytes in columns
zone of calcified cartilage
site of mostly dead chondrocytes, only a few cells thick. calcification happens here
factors affecting bone growth and remodeling
minerals, vitamins, hormones
fracture
any break in a bone
stress fracture
a series of microscopic fissures in bone that forms without any evidence of injury to other tissues
reactive phase
blood vessel clotting (fracture hematoma) around site of fracture, swelling and inflammation occur. several weeks
reparative phase 2a
fibrious cartilage callus formation. fibroblasts produce collagen fibers. about 3 weeks
reparative phase 2b
bony callus formation. fibrious cartilage converted to spongy bone. 3-4 months
bone remodeling phase
compact bone replaces spongy bone around fracture site
open (compound) fracture
The broken ends of the bone protrude through the skin. Conversely, a closed (simple) fracture does not break the skin.
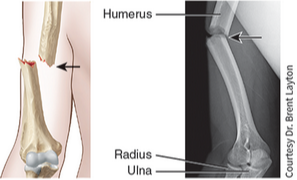
comminuted (crumbled) fracture
The bone is splintered, crushed, or broken into pieces at the site of impact, and smaller bone fragments lie between the two main fragments.
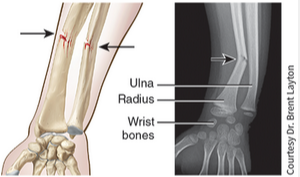
greenstick fracture
A partial fracture in which one side of the bone is broken and the other side bends, similar to the way a green twig breaks on one side while the other side stays whole, but bends; occurs only in children, whose bones are not fully ossified and contain more organic material than inorganic material.
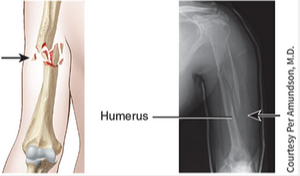
impacted fracture
One end of the fractured bone is forcefully driven into the interior of the other.
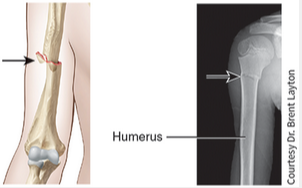
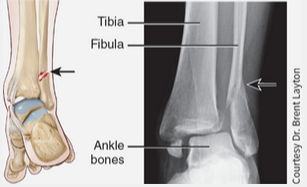
pott fracture
Fracture of the distal end of the fibula (lateral leg bone), with serious injury of the distal tibial articulation.
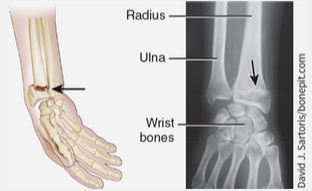
colles fracture
Fracture of the distal end of the lateral forearm bone (radius) in which the distal fragment is displaced posteriorly.
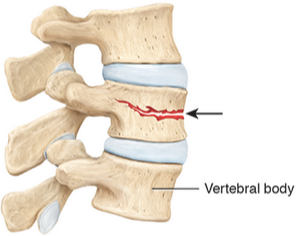
vertebral compression fracture
The vertebral body of one or more vertebrae fractures and becomes compressed into a wedge-shape. May be caused by injury, trauma, or more commonly in individuals with osteoporosis.
high-impact intermittent strains
more strongly influence bone deposition than lower-impact constant strains
demineralization
the loss of calcium and other minerals from bone extracellular matrix
demineralization in females
begins after age 30, accelerates after 45; 30% of calcium is lost by age 70. 8% bone mass lost every 10 years
demineralization in males
begins after age 60, 3% bone mass lost every 10 years.
calcium and phosphorus
makes bone extracellular matrix hard
magnesium
helps form bone extracellular matrix
fluoride
helps strengthen bone extracellular matrix
manganese
activates enzyme involved in synthesis of bone extracellular matrix
Vitamin A
Needed for the activity of osteoblasts during remodeling of bone; deficiency stunts bone growth; toxic in high doses
Vitamin C
Needed for synthesis of collagen, the main bone protein; deficiency leads to decreased collagen production, which slows down bone growth and delays repair of broken bones.
Vitamin D
Active form (calcitriol) is produced by the kidneys; helps build bone by increasing absorption of calcium from digestive canal into blood; deficiency causes faulty calcification and slows down bone growth; may reduce the risk of osteoporosis but is toxic if taken in high doses. People who have minimal exposure to ultraviolet rays or do not take vitamin D supplements may not have sufficient vitamin D to absorb calcium. This interferes with calcium metabolism.
Vitamins K and B12
Needed for synthesis of bone proteins; deficiency leads to abnormal protein production in bone extracellular matrix and decreased bone density.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland; promotes general growth of all body tissues, including bone, mainly by stimulating production of insulin-like growth factors.
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
Secreted by the liver, bones, and other tissues on stimulation by growth hormone; promotes normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts and by increasing the synthesis of proteins needed to build new bone.
Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4)
Secreted by thyroid gland; promote normal bone growth by stimulating osteoblasts.
Insulin
Secreted by the pancreas; promotes normal bone growth by increasing the synthesis of bone proteins.
Sex Hormones (estrogen and testosterone)
Secreted by the ovaries in women and by the testes in men; stimulate osteoblasts and promote the sudden “growth spurt” that occurs during the teenage years; shut down growth at the epiphyseal plates around age 18–21, causing lengthwise growth of bone to end; contribute to bone remodeling during adulthood by slowing bone resorption by osteoclasts and promoting bone deposition by osteoblasts.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Secreted by the parathyroid glands; promotes bone resorption by osteoclasts; enhances recovery of calcium ions from urine; promotes formation of the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol).
Calcitonin (CT)
Secreted by the thyroid gland; inhibits bone resorption by osteoclasts.
Exercise
Weight-bearing activities stimulate osteoblasts and, consequently, help build thicker, stronger bones and retard loss of bone mass that occurs as people age.
Aging
As the level of sex hormones diminishes during middle age to older adulthood, especially in women after menopause, bone resorption by osteoclasts outpaces bone deposition by osteoblasts, which leads to a decrease in bone mass and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
osteoporosis
Age‐related disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and increased susceptibility to fractures, often as a result of decreased levels of estrogens.