enzymes (chap 4) -olevel pure bio
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
what are enzymes
proteins that function as biological catalysts
speed up the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed to start a reaction
remain chemically unchanged at the end of a reaction
what is a catalyst
a substance that can speed up a chemical reaction without itself being changed at the end of the reaction
what are the characteristics of enzymes
enzymes speed up chemical reactions -it lowers the activation energy needed to start a reaction
enzymes are specific in nature - only substrates with a shape complementary to the active site of the enzyme can bind with the enzyme and cause a chemical reaction
enzymes are only required in minute quantities and remain chemically unchanged after a reaction - enzymes can be used over and over again so only a small amount of an enzyme can catalyse the reaction for a large amount of substrate
enzymes are affected by temperature
enzymes are affected by pH - they are denatured by pH that is too far from the optimum pH
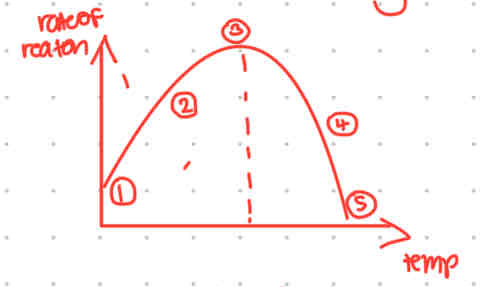
pls explain this temperature graph and label each part yk
enzyme is less active at lower temperatures as kinetic energy of molecules is low, so enzymes and substrates move more slowly and the rate of substrate colliding with enzyme is low.
as the temperature increases, kinetic energy increases and there’s a higher chance of substrate colliding into enzyme molecules, so rate is increased
this is the optimum temperature where the enzyme is most active
increasing temperature above the optimum causes the active site of the enzyme to denature and lose its shape and hence its shape is no longer complementary to the shape of substrate molecules
all enzymes are denatured and enzyme substrate reactions can no longer occur
explain the lock and key hypothesis
the enzyme is the lock and the substrate is the key
the shape of the enzyme active site is complementary to the substrate
when a substrate is bonded to the active site of an enzyme, an enzyme-substrate complex is formed
chemical reactions take place at the active site to convert the substrate into the product
the product separates from the enzyme
the enzyme remains unchanged and is free to combine with ore substrate molecules.