Cerebral Cortex
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
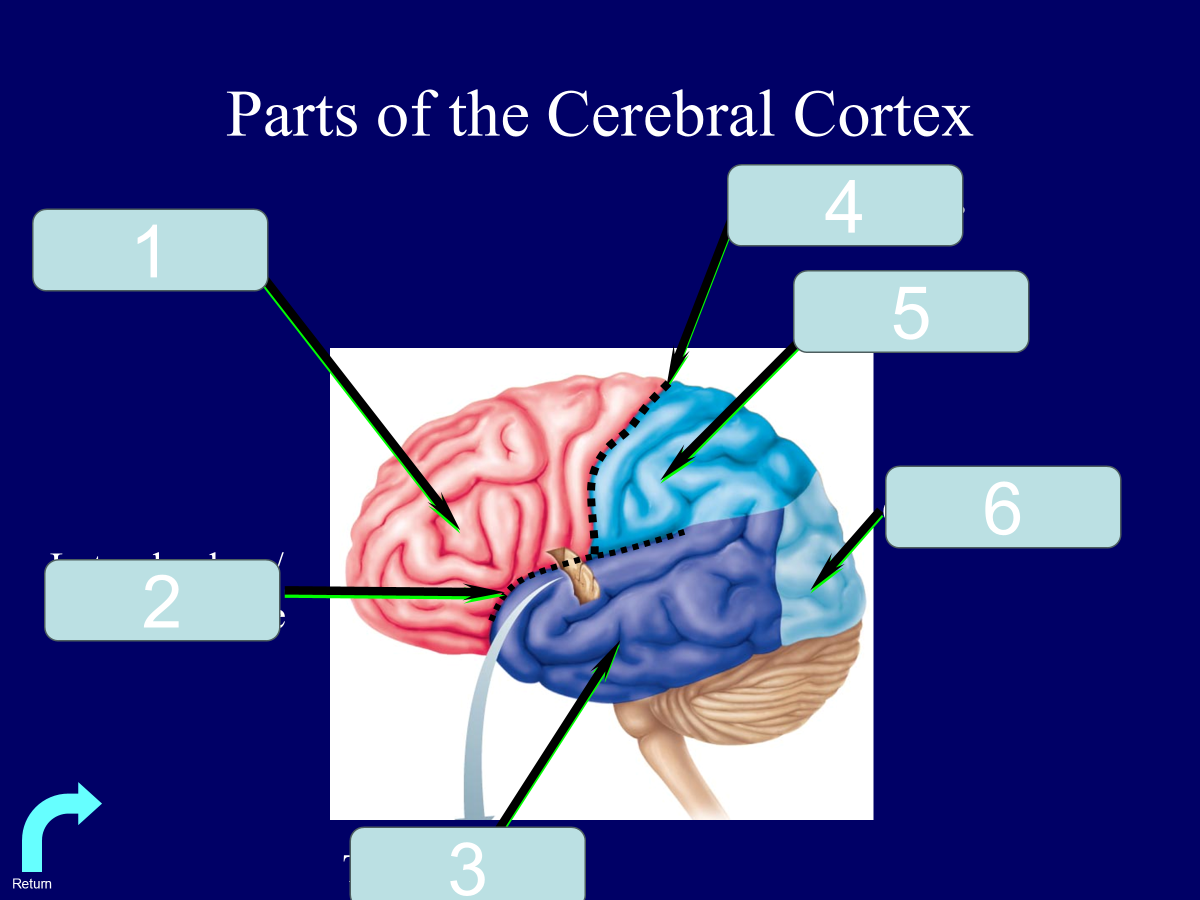
frontal lobe
lateral sulcus/sylvian fissure
temporal lobe
central sulcus
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
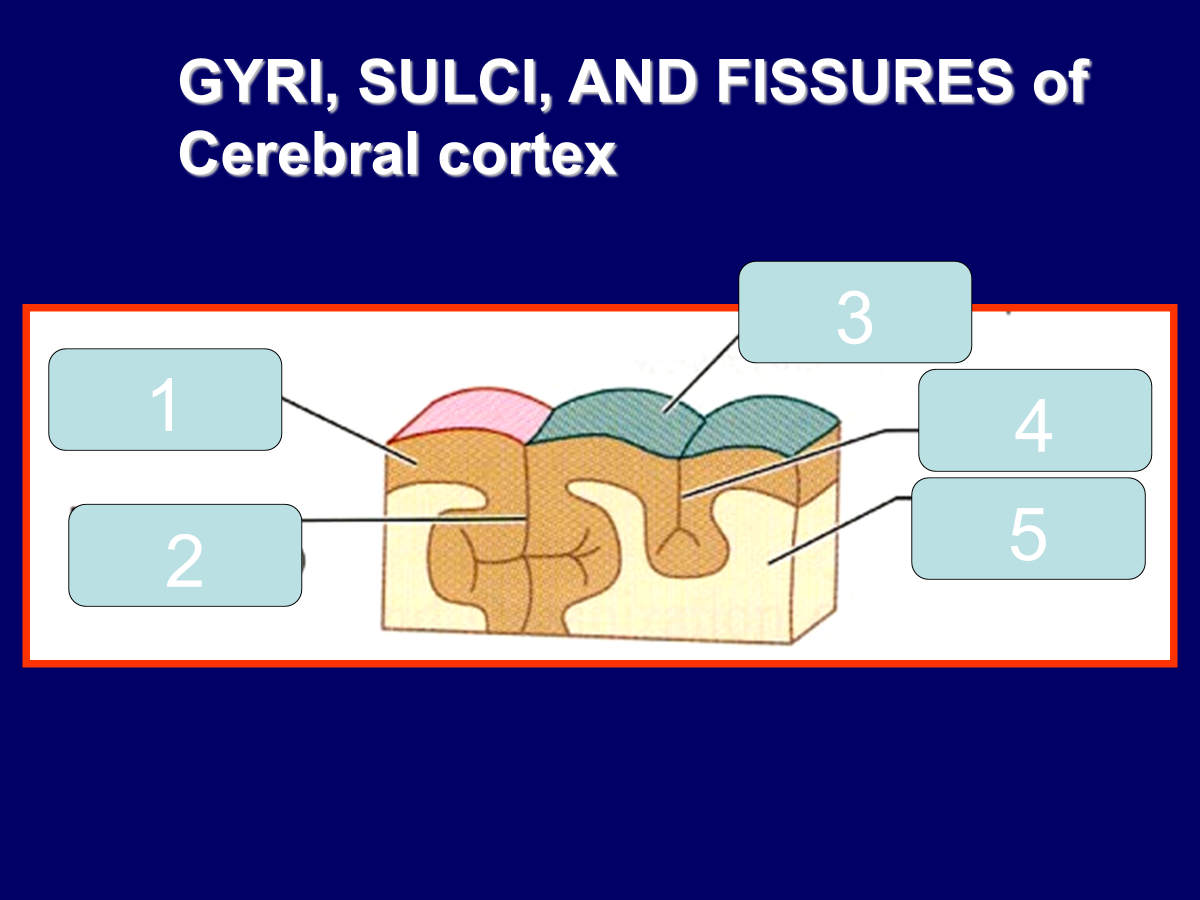
cortex (gray matter)
fissure (a deep sulcus)
gyrus
sulcus
white matter
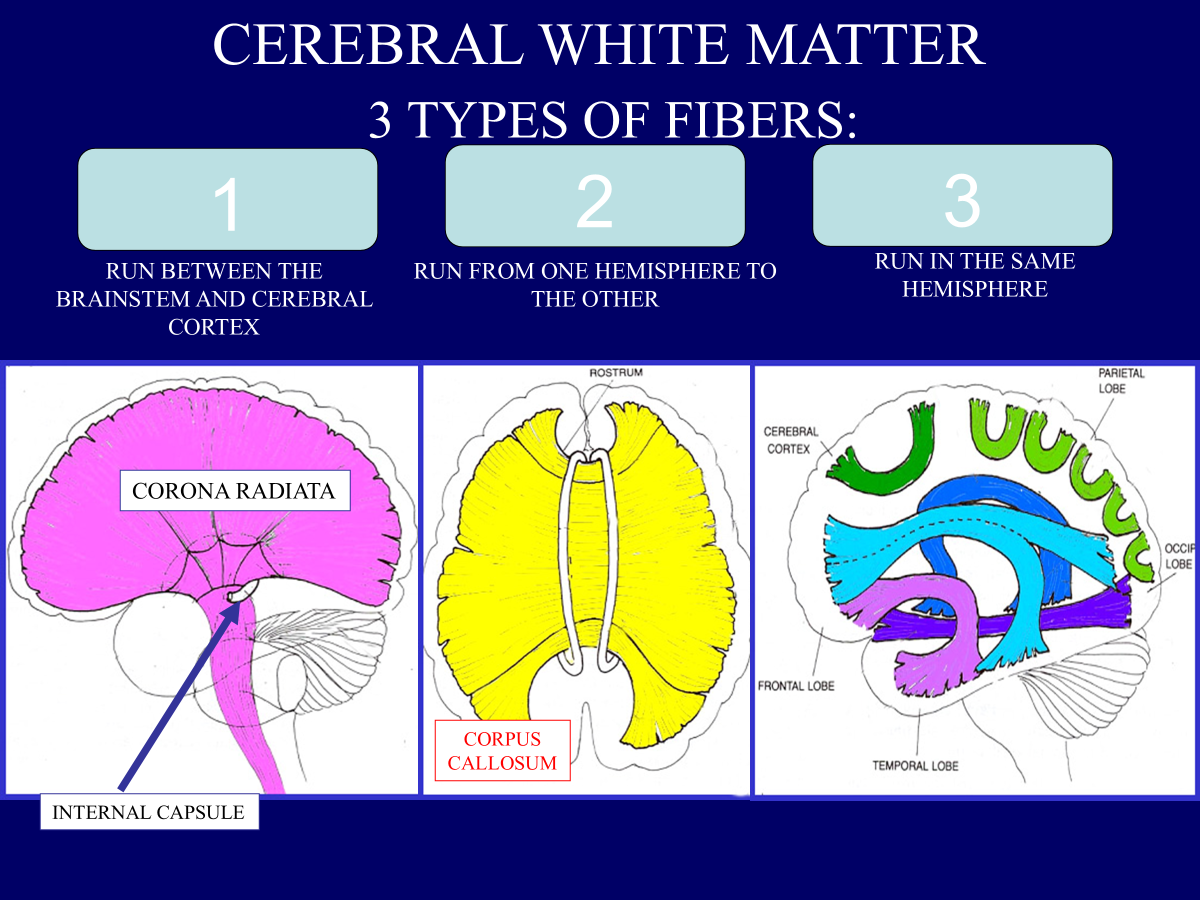
projection
commissural
association
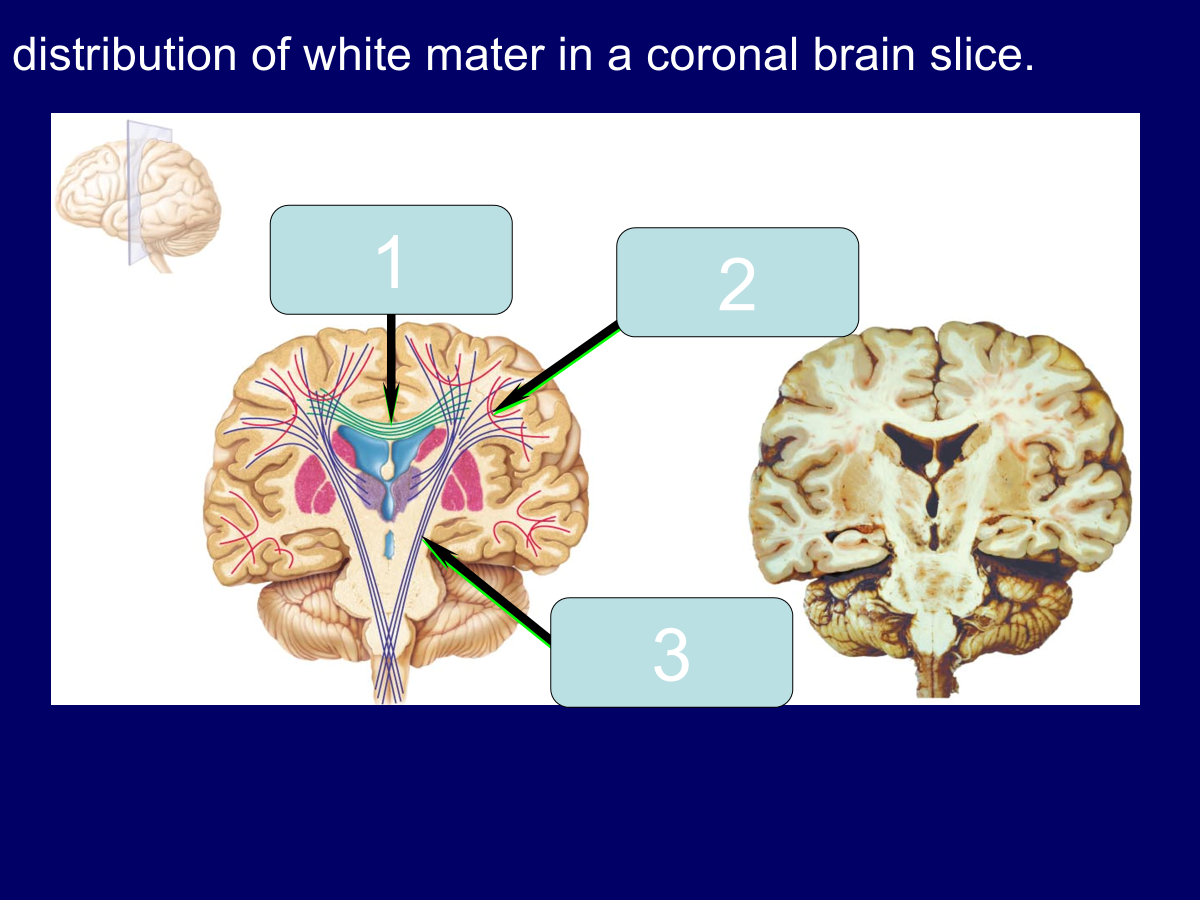
commissural fibers
association fibers
projection fibers
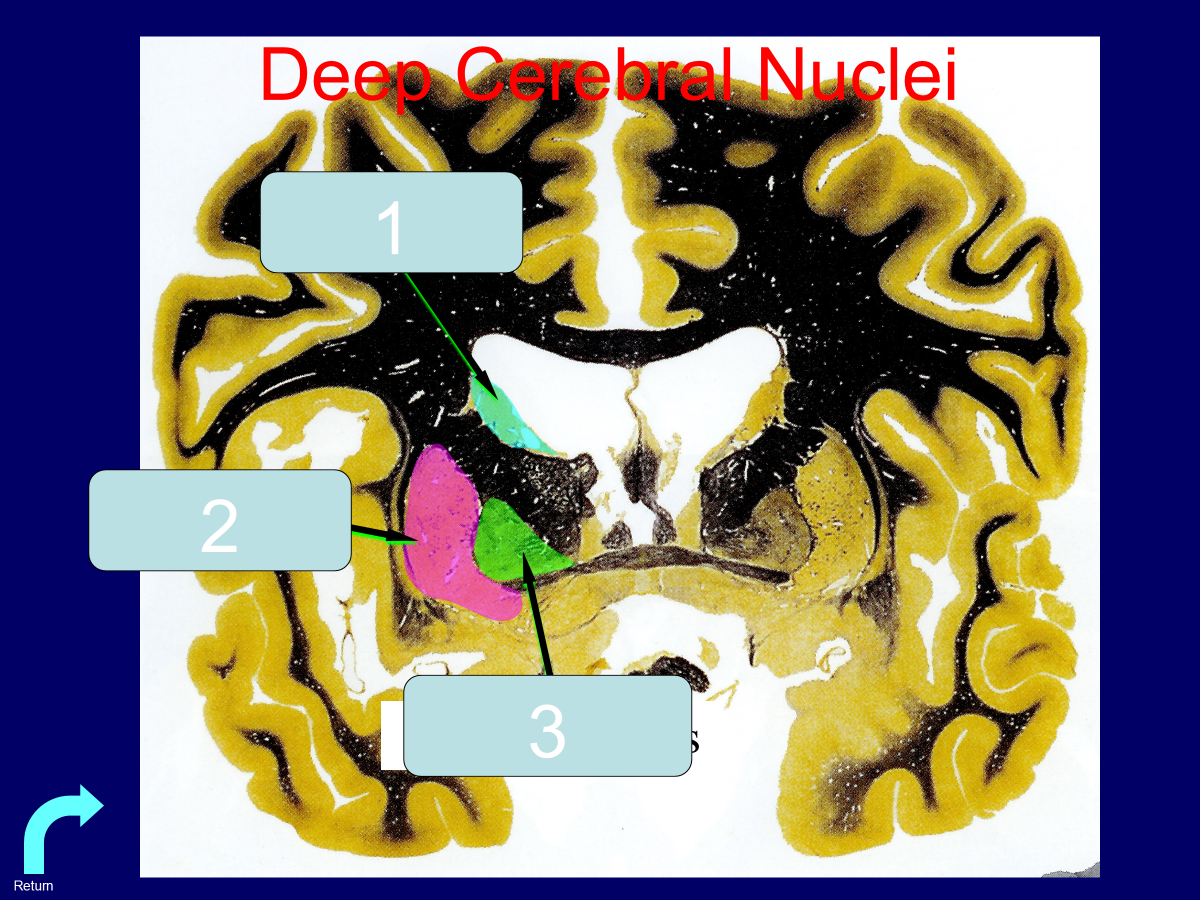
caudate
putamen
globus pallidus
The _______________ facilitates cognitive behavior (allows you to move the way you want to move)
The caudate nucleus facilitates cognitive behavior (allows you to move the way you want to move)
The Basal ganglia/Deep brain nuclei operate on the principle of disinhibition which is releasing inhibitory stimulation. Release of inhibition on the thalamus allows for motor behavior whereas inhibition prevents motor behavior. Students only need to know that the basal ganglia facilitates movement through these loops
Basal nuclei → involved with movement
___________ is an hypokinetic disorder (inhibition)
Parkinson’s disease is an hypokinetic disorder (inhibition)
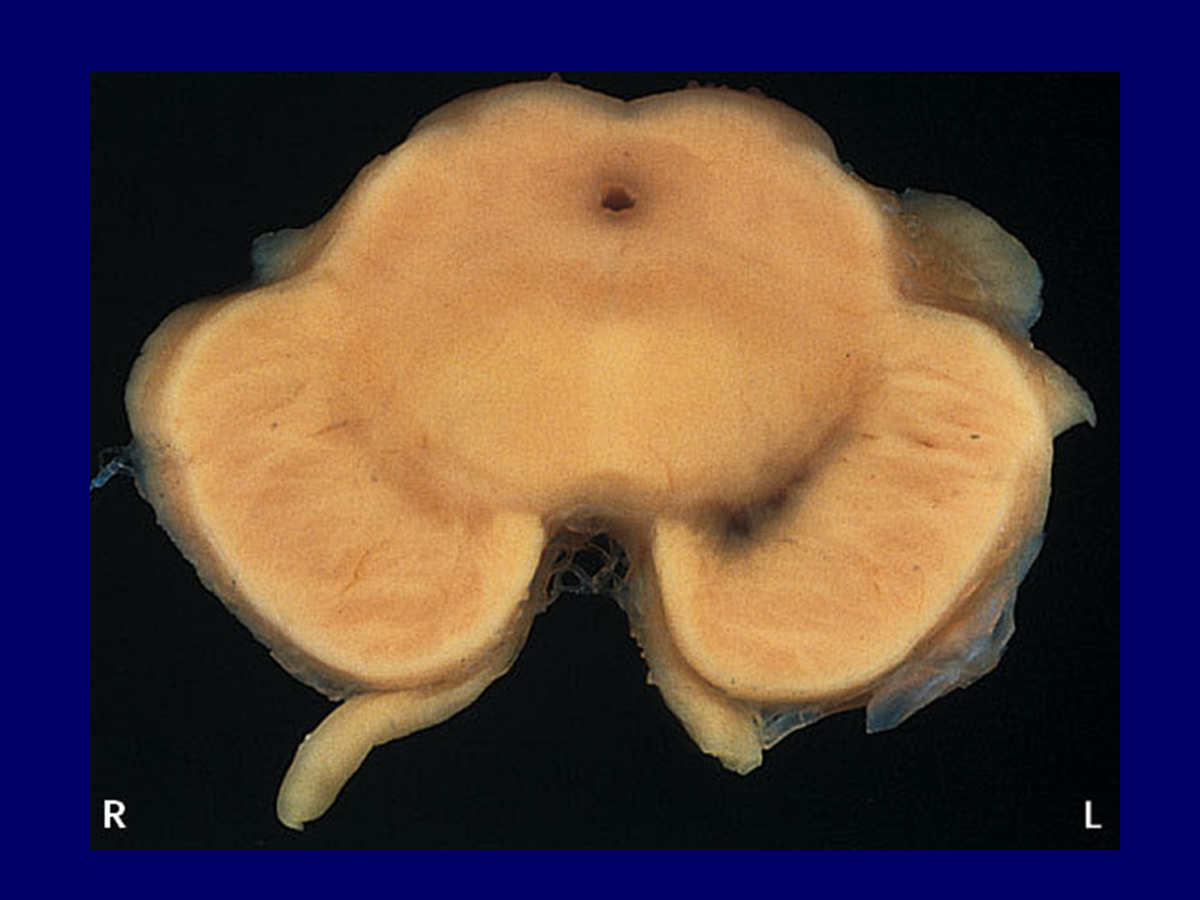
what is the blackened area? What is the significance in regards to Parkinson’s disease?
The blackened area in this cross section of the midbrain is a source of dopaminergic neurons that project to the basal ganglia. When these neurons die, behavior is inhibited.
________________ is a hyperkinetic disoder (always a genetic condition), where there is lack of inhibition from the deep cerebral nuclei and there is unrestricted movement (caused by a degernation of the corpus stratum and cerebral cortext)
Huntington’s disease is a hyperkinetic disoder (always a genetic condition), where there is lack of inhibition from the deep cerebral nuclei and there is unrestricted movement (caused by a degernation of the corpus stratum and cerebral cortext)
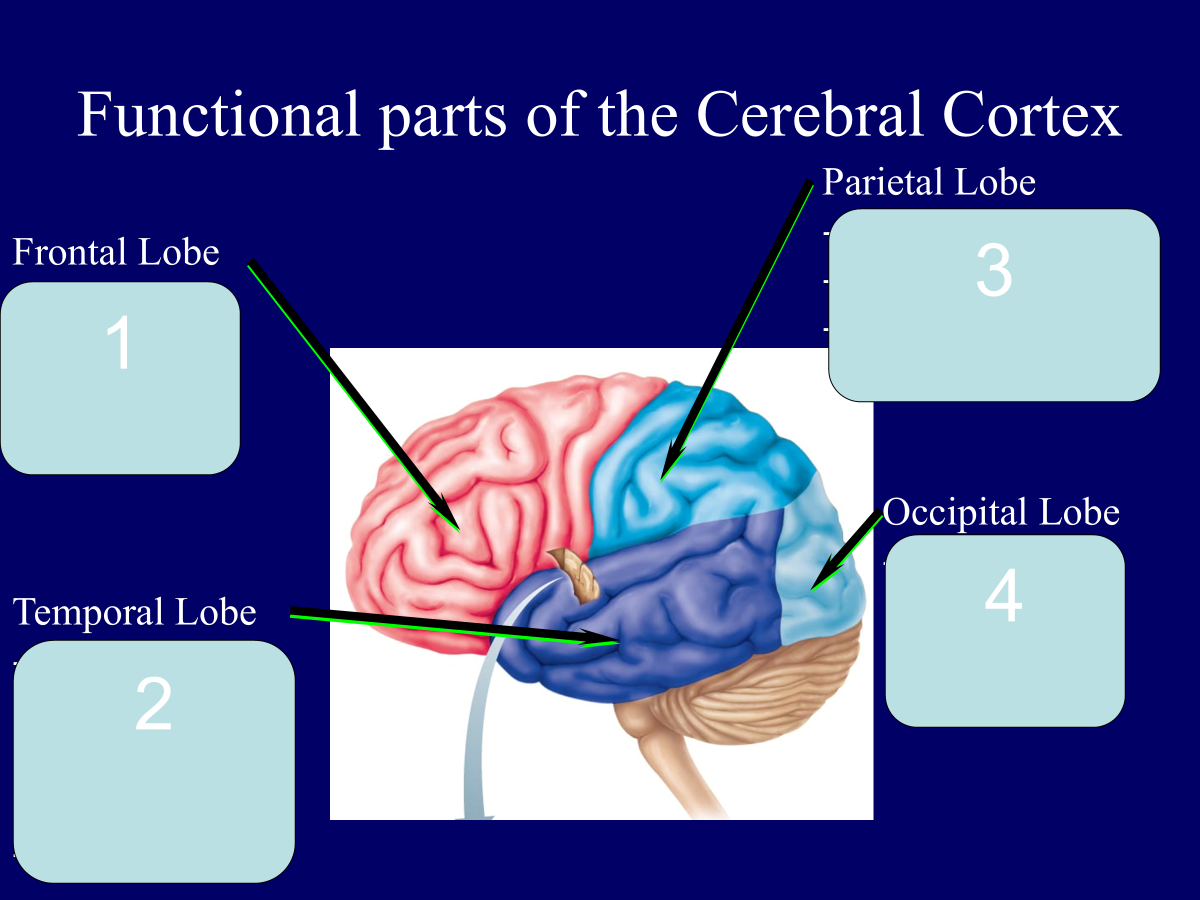
(frontal lobe) planning; personality; goals; movement
(temporal lobe) memory; understanding; language; form of objects; emotions
(parietal lobe) awareness; sensation; location of objects
(occipital lobe) vision
The cerebral cortex is organized into ____________
The cerebral cortex is organized into columns.
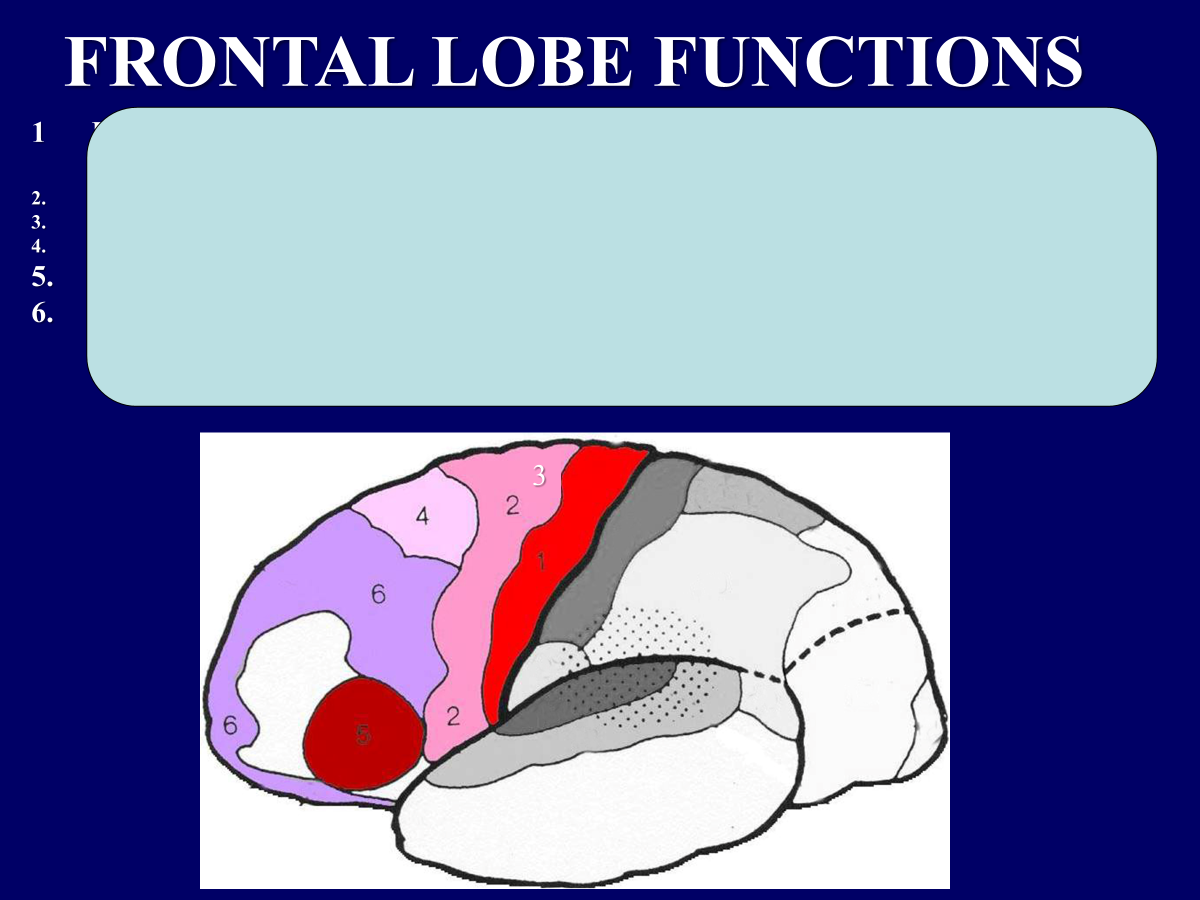
PRIMARY SOMATOMOTOR CORTEX [PRECENTRAL GYRUS]; PRECISE MOTOR MOVEMENTS
SUPPLEMENTARY MOTOR CORTEX: GROSS STEREOTYPED MOTOR MOVEMENTS
PREMOTOR AREA: ASSOCIATION AREA; COORDINATION OF LEARNED MOTOR RESPONSES
4.FRONTAL EYE FIELDS: EYE MOVEMENTS
5.BROCA’S AREA: MOTOR SPEECH [LEFT HEMISPHERE, USUALLY]
6.PREFRONTAL CORTEX: INTELLIGENCE, PERSONALITY, JUDGEMENT,
FORESIGHT
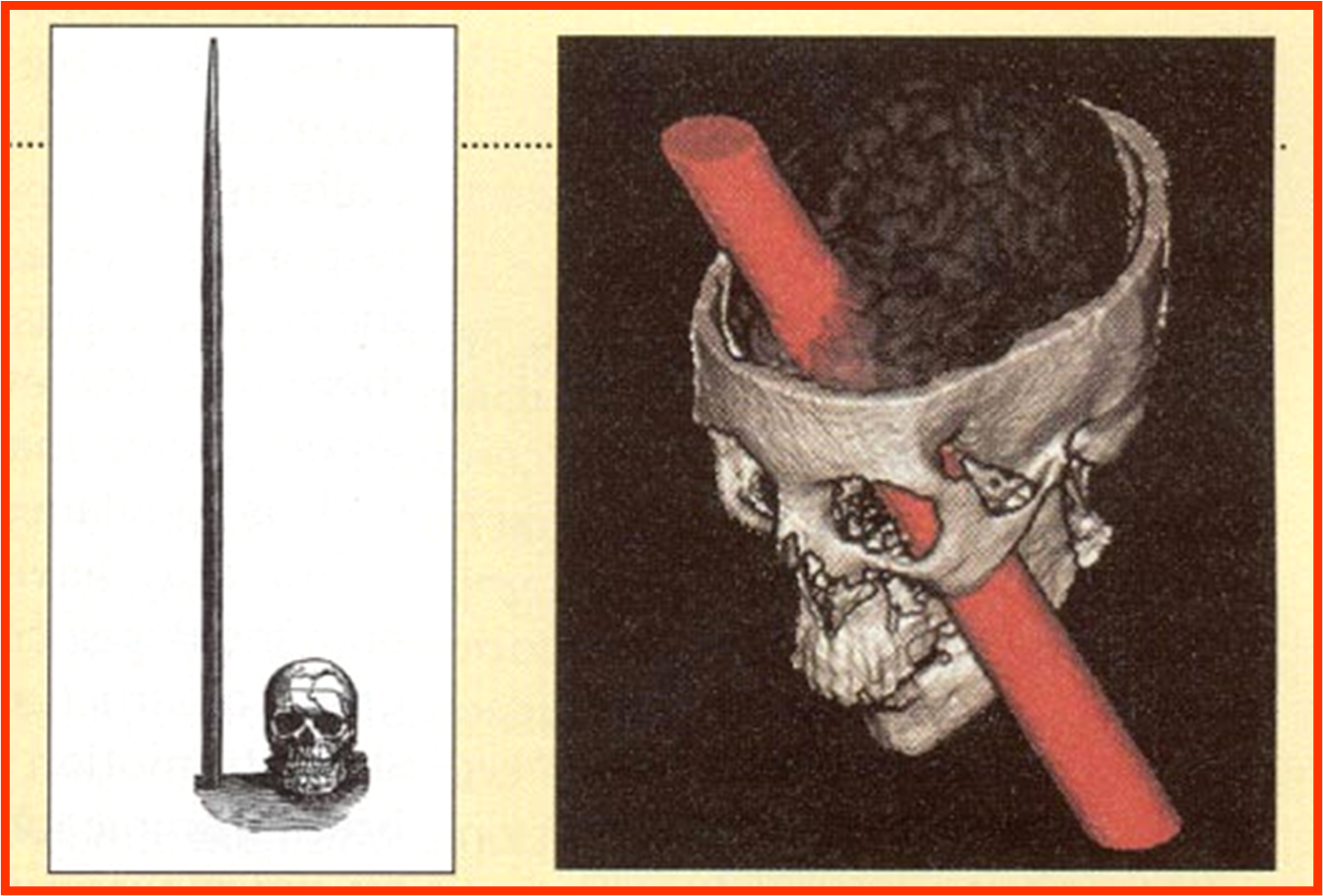
A railroad worker, named Phineas Gage, had a metal spike pierce his orbit and obliterate his left eye and the anterior part of his frontal lobes from a demolition explosion. Phineas’s personality completely changed from before the injury. He more aggressive and had difficulty with doing his job as a railroad worker
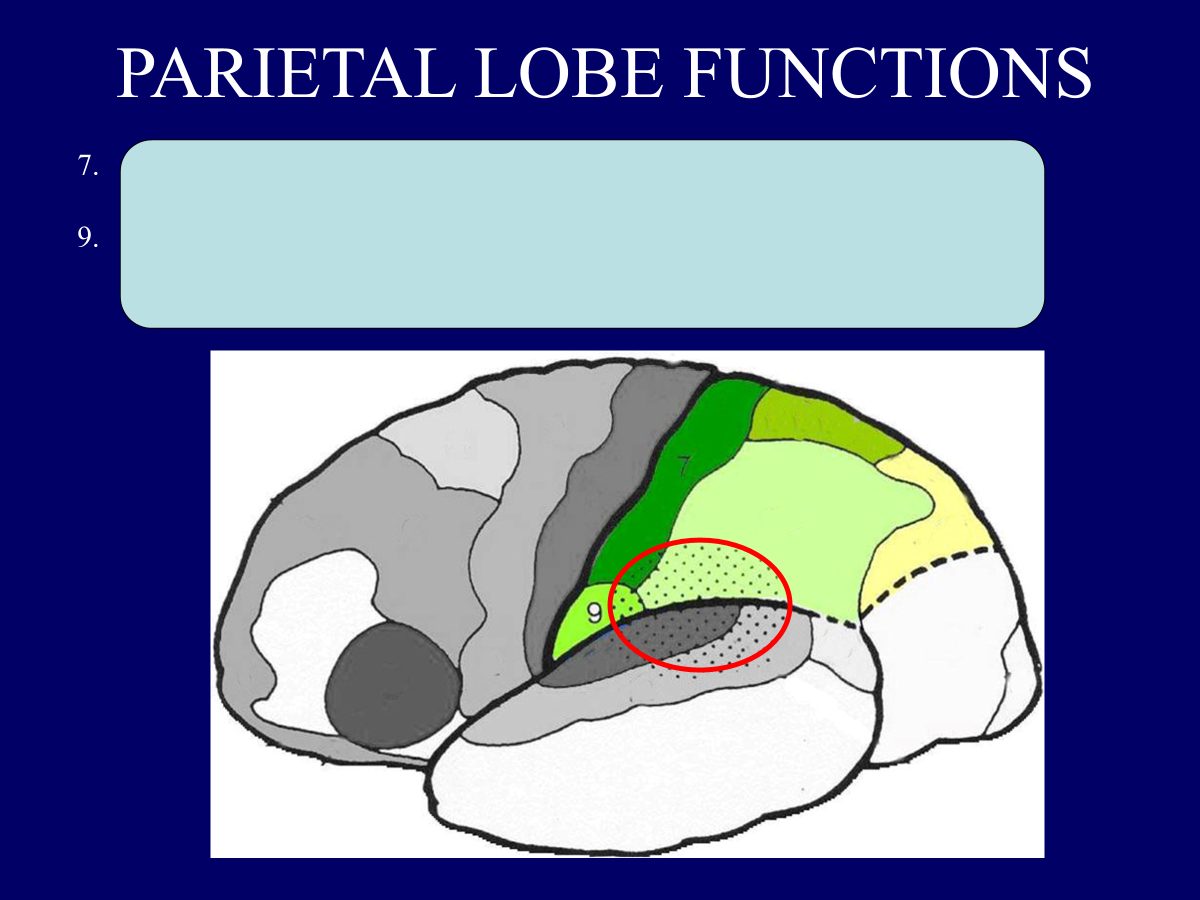
7.PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX [POSTCENTRAL GYRUS]: GENERAL SENSATIONS/PRECISE LOCALIZATION.
9.PRIMARY GUSTATORY AREA: TASTE INTERPRETATION.
WERNICKE’S AREA (DOTTED): SPEECH INTERPRETATION

This is an example of ________________, where the patient is completely unaware of objects and events in half of his or her surrounding space, as a result of damage to the parietal association cortex.
This is an example of neglect syndrome, where the patient is completely unaware of objects and events in half of his or her surrounding space, as a result of damage to the parietal association cortex.
Damage to the ___________ causes deficits in spatial relationships of objects (Patients may be able to locate the objects; however, they cannot organize and order them in the proper orientation.)
Damage to the parietal lobe causes deficits in spatial relationships of objects (Patients may be able to locate the objects; however, they cannot organize and order them in the proper orientation)
The ______ and ______ have the majority of neurons dedicated to them.
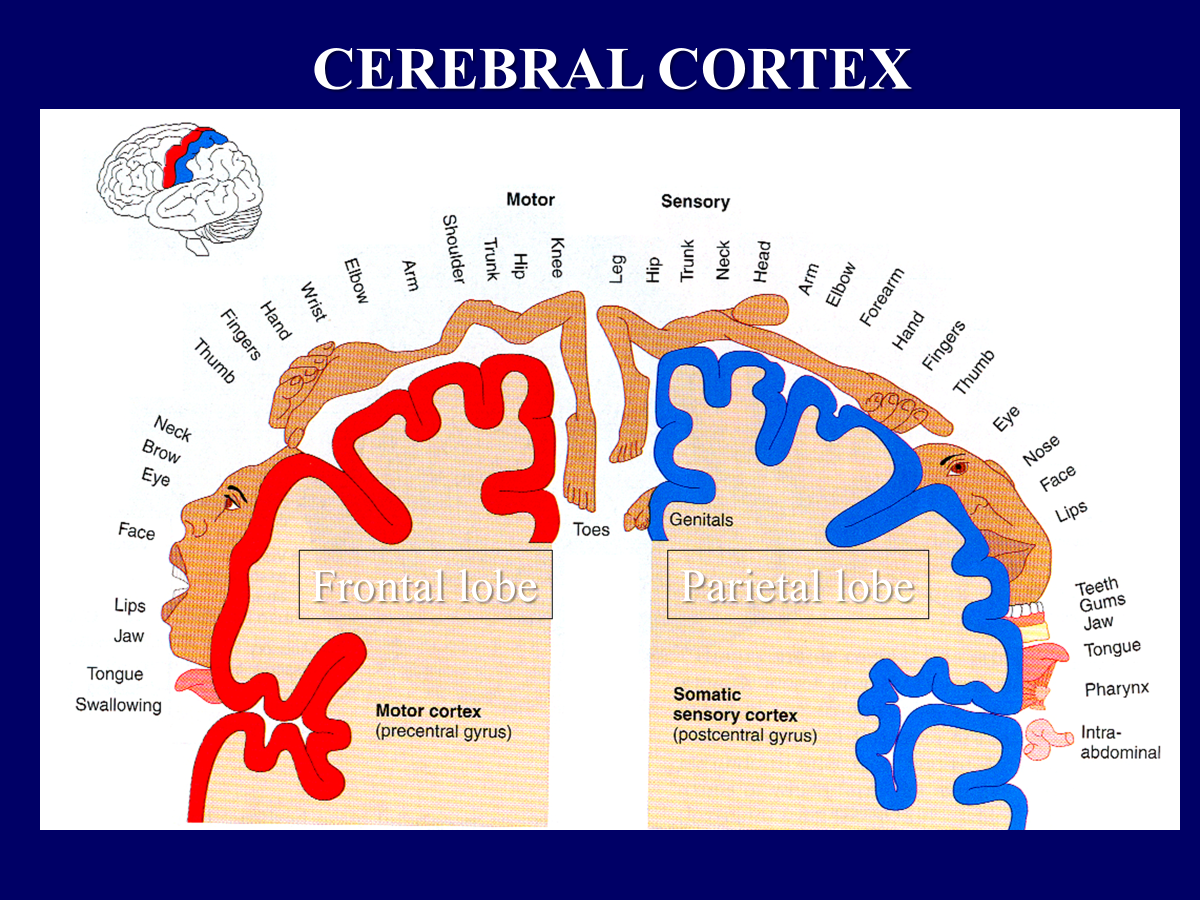
The face and hands have the majority of neurons dedicated to them.
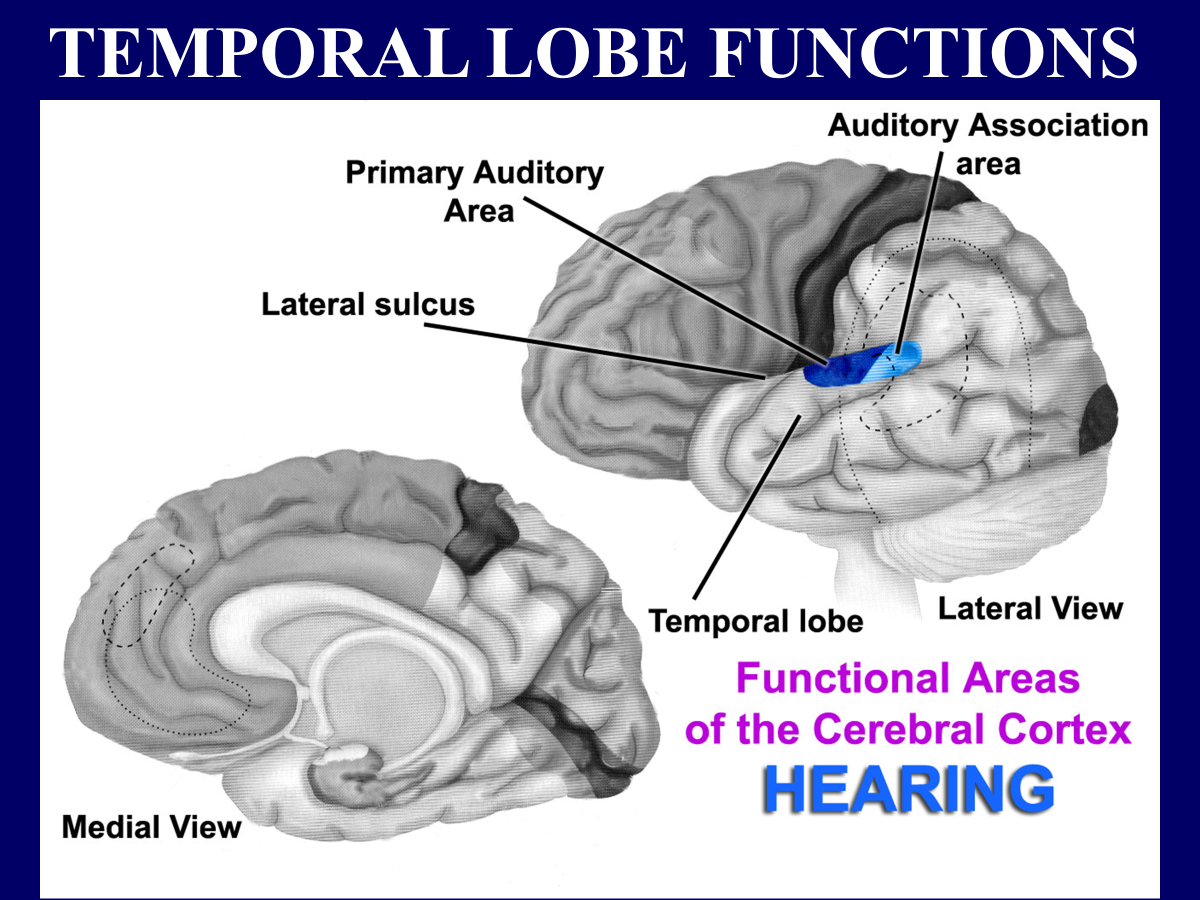
Temporal Lobe functions
lateral → hearing
medial → olfaction
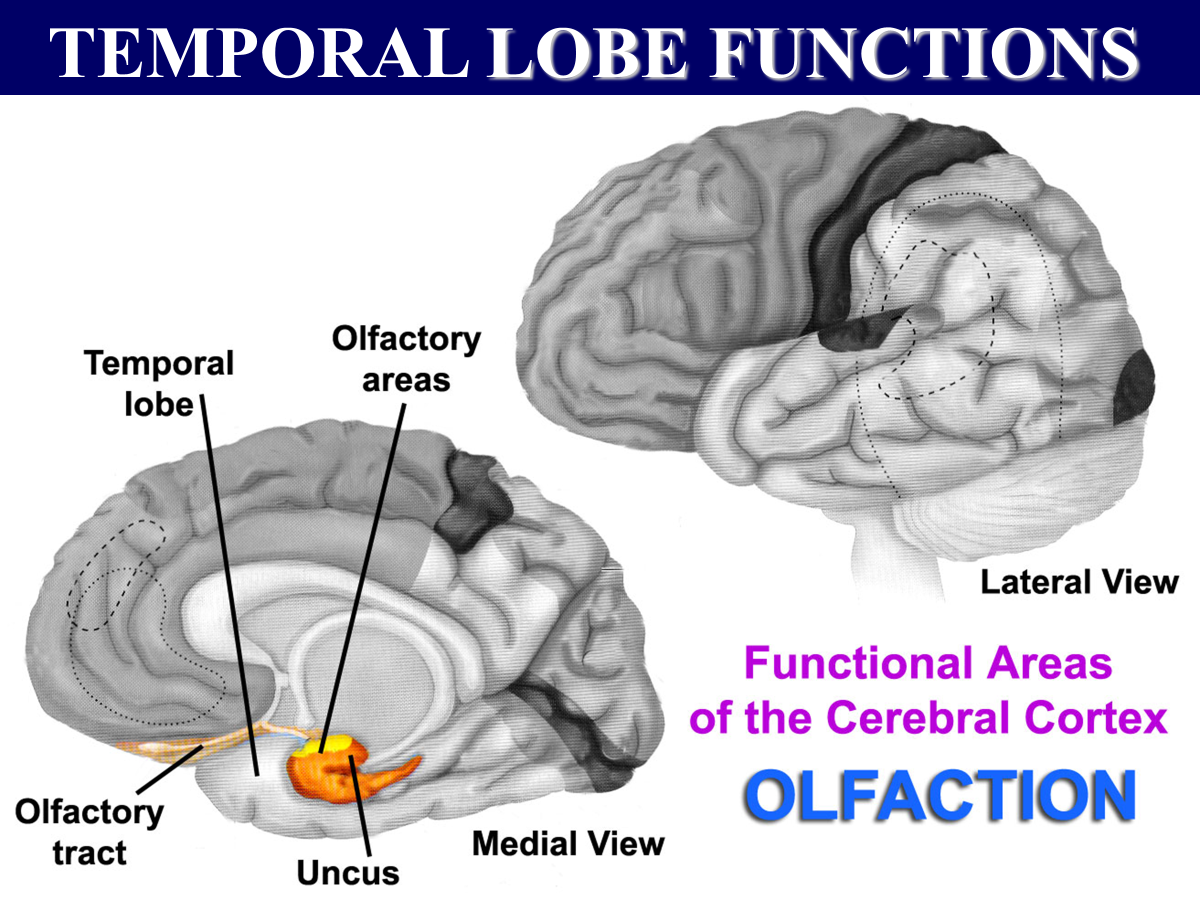
CN _____ is the only nerve that goes directly into the cerebral cortex
CN I is the only nerve that goes directly into the cerebral cortex
Damage to the _______ (lobe #5) in the cortex can cause a loss of desire for addictive behaviors.
Damage to the insula (lobe #5) in the cortex can cause a loss of desire for additve behaviors.
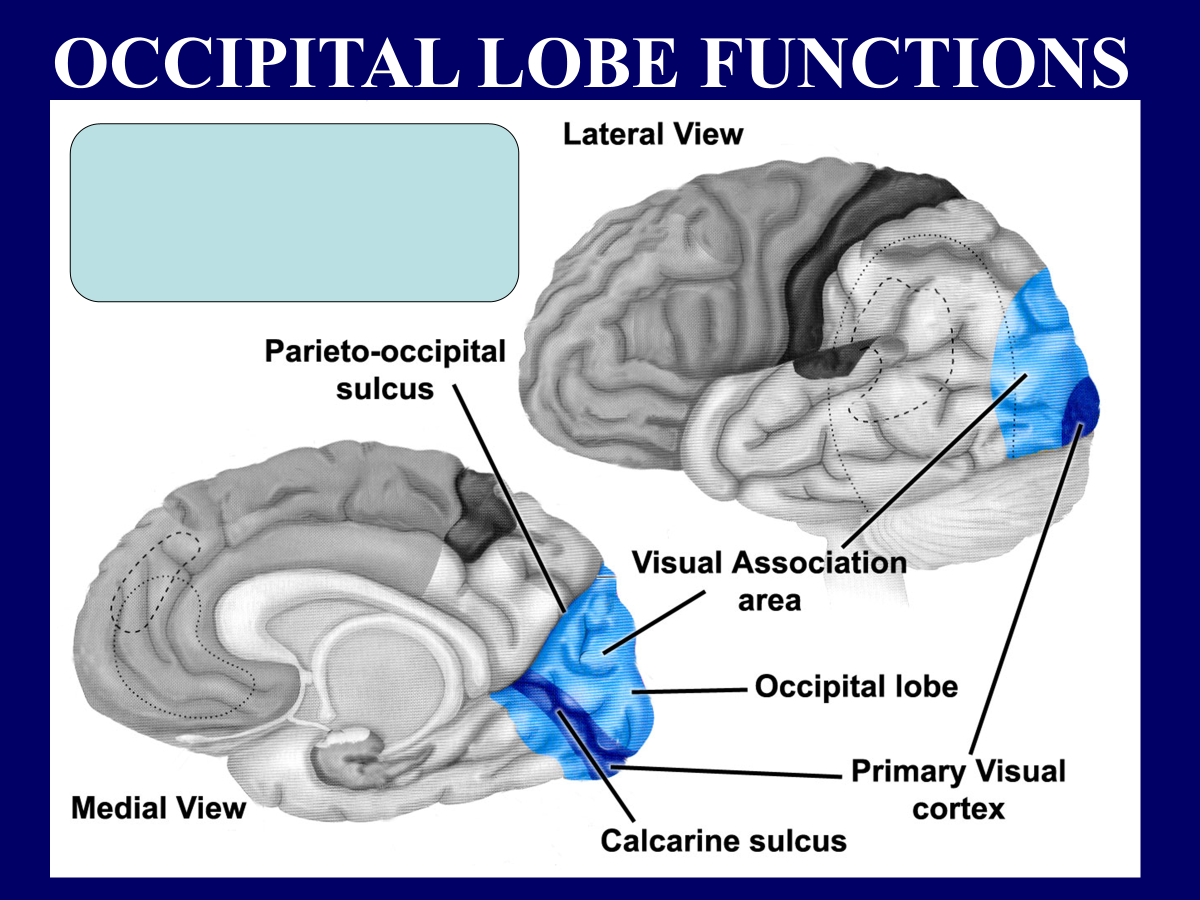
Vision → occipital lobe function
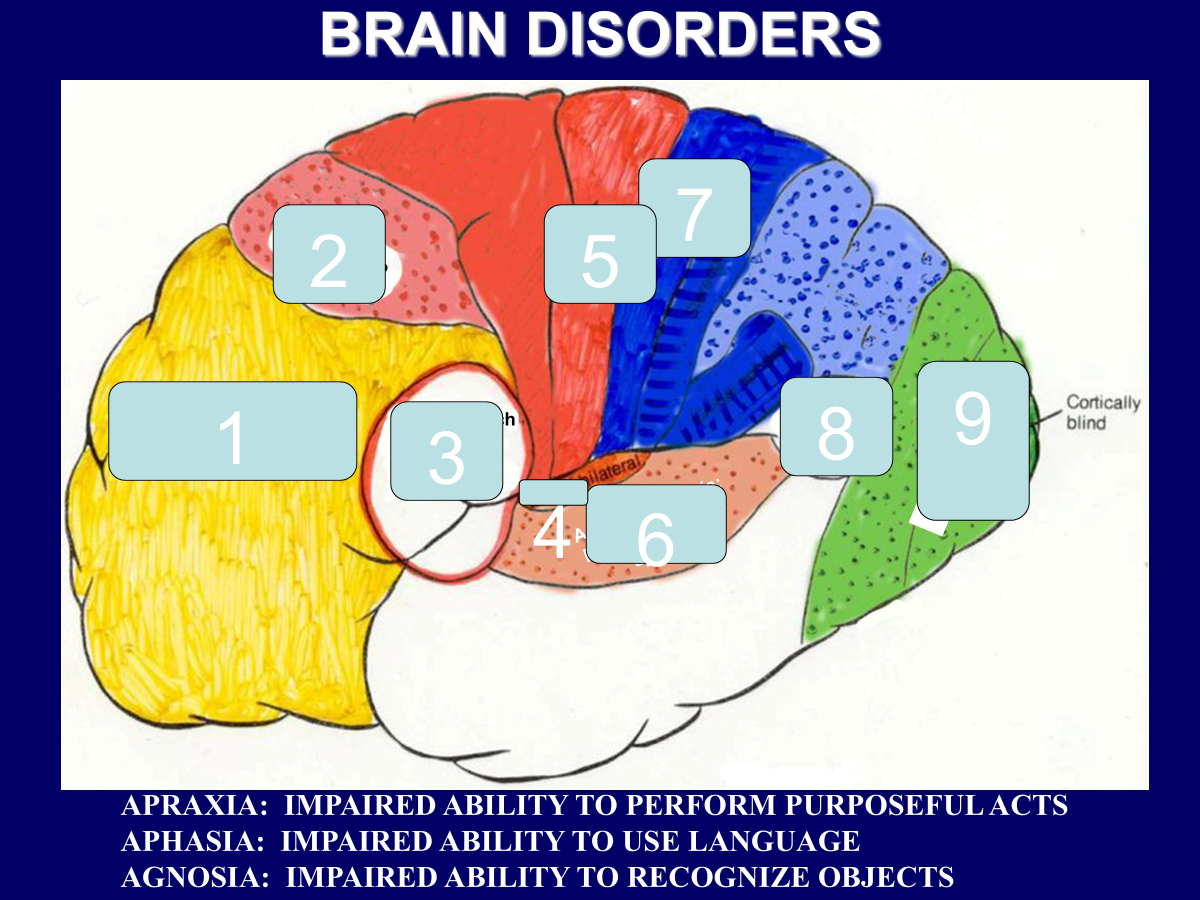
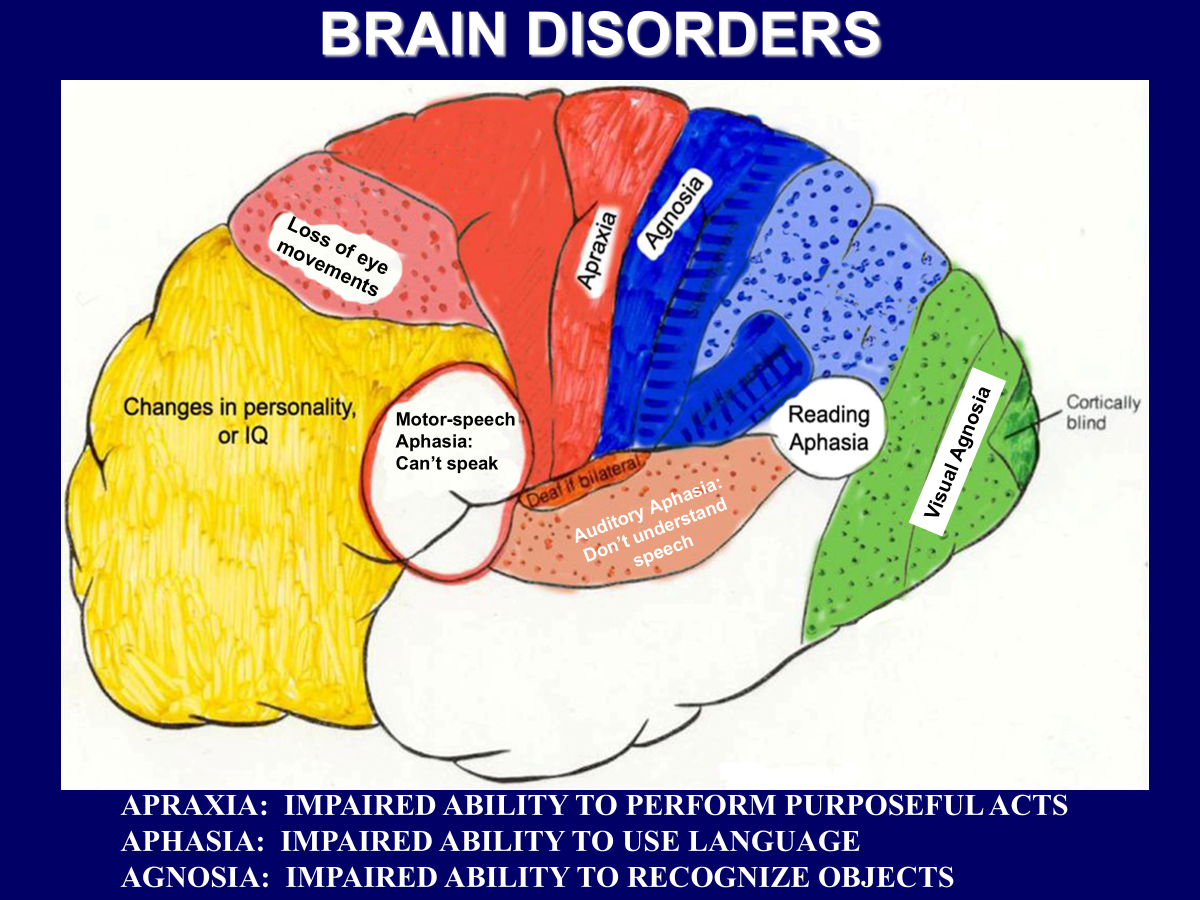
______________ → impaired ability to perform purposeful acts
______________ → impaired ability to use language
______________ → impaired ability to recognize objects
Apraxia → impaired ability to perform purposeful acts
Aphasia → impaired ability to use language
Agnosia → impaired ability to recognize objects
The 4 F’s of the Limbic System (The “emotional” brain) → amygdala (Provides an emotional response to environmental stimuli)
Fighting
Fleeing
Feeding
Flirting
The ___________ modulates states of consciousness and affects level of alterness, sleep, pain perception, muscle tone, integrates various sensory modalities
The Reticular Activating System (RAS) modulates states of consciousness and affects level of alterness, sleep, pain perception, muscle tone, integrates various sensory modalities