blood
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lab practical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
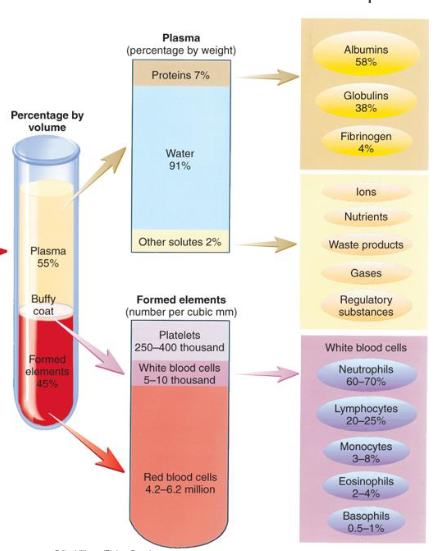
composition of blood
plasma proteins
albumin, globulins, fibrnogen
electrolytes and ions
potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, hydrogen, hydroxide, & bicarbonate
nutrients
glucose, cholesterol, amino acids, fatty acids, triglycerides & regulatory proteins
vitamins & enzymes
waste products
urea, uric acid, creatinine, ammonia salts
gases
O2, CO2, and inert nitrogen
cannot react with anything
albumin
provides colloid osmotic pressure in the plasma
prevents water loss in capillaries
globulins
mainly immunoglobulins
antibodies that are released during an immune response
fibrinogen
responsible for blood clotting
erythropoietin (EPO)
a glycoprotein hormone secreted by interstitial fibroblast cells of the kidneys in response to low oxygen levels
formed elements are erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
blood is a __
suspension; a substance in which formed elements or large particles if acted upon will settle
i.e. centrifuge
erythrocytes or RBCS do not have __
nuclei
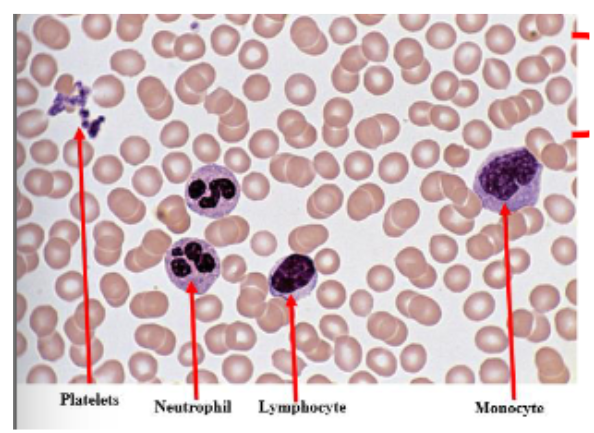
identify a blood smear
from left to right: platelets, neutrophils, lymphocyte, monocyte
hematopoiesis
blood formation
erythropoiesis
RBC formation
the bone marrow of all the bones produces RBCS until age __
5
function of erythrocytes
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
neutrophils
phagocytize pathogens or debris
eosinophil
kill parasitic worms; slightly phagocytic; complex role in allergy and asthma
basophil
release histamine and other mediators of inflammation; contain heparin, an anticoagulant
lymphocyte
mount immune response by direct cell attack or via antibody production
monocyte
develop into macrophages in tissues and phagocytize pathogens or debris
platelets
seal small tears in blood vessels; instrumental in blood clotting
decomposition of oxygen
98.5% attached to hemoglobin
1.5% dissolved in plasma

decomposition of carbon dioxide
7% dissolved in plasma
23% in combination with hemoglobin
70% transported as bicarbonate ions
combination of H2O & CO2 under pressure makes carbonic acid, which is unstable
carbonic anhydrase (an enzyme) increases the rate of the reaction to form bicarbonate ions
makes it possible for fluid in plasma to transport large amounts of CO2 in form of bicarbonate ions from tissues to lungs → reconverted to CO2 → expelled as a waste product
hematocrit
ratio of the volume of RBC to the total volume of blood
transfusion
transfer of blood or blood components from one individual to another
infusion
introduction of fluid other than blood
antibodies (agglutinins)
can bind to RBC antigens, resulting in either agglutination or hemolysis
agglutination
clumping
caused by antibodies
hemolysis
rupture
caused by antibodies
type A blood
has type A surface antigens
has anti-B antibodies in plasma
type B blood
has type B surface antigens
has anti-A antibodies in plasma
type AB blood
has both type A and type B surface antigens
has neither anti-A nor anti-B antibodies
type O blood
has neither type A nor type B surface antigens
has both anti-A and anti-B plasma antibodies
Rh factor
named after Rhesus monkeys
relates to the presence of a particular protein in the blood
people can be Rh+ or Rh-