Exam 2 Bio 314
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
E
Which characteristic describes the tails of phospholipids?
A. amphipathic
B. coated with sugars
C. hydrophilic
D. stiff
E. hydrophobic
A
Which term correctly describes the entire phospholipid molecule?
A. amphipathic
B. apathetic
C. hydrophilic
D. hydropathic
E. hydrophobic
C
Why do phospholipids form bilayers in water?
A. The hydrophobic head shuns water, while the hydrophilic tail is attracted to water.
B. The hydrophobic tail is attracted to water, while the hydrophilic head shuns water.
C. The hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tail shuns water.
D. The hydrophilic head is insoluble in water.
E. The hydrophobic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophilic tail shuns water.
C
How does the inclusion of cholesterol affect animal cell membranes?
A. It tends to make the lipid bilayer more fluid.
B. It has little effect on the properties of the lipid bilayer.
C. It tends to make the lipid bilayer less fluid.
D. It makes the lipid bilayer more permeable.
E. It makes the lipid bilayer wider.
A
One of the grand challenges in biology is understanding how the first cells formed on Earth. Since all cells are bound by a cell membrane, origin of life researchers are interested in modeling what the first membranes may have been like. What types of molecules might these researchers consider to be the original building blocks of cell membranes?
A. amphipathic molecules
B. hydrophilic molecules
C. hydrophobic molecules
D. carbohydrate molecules
E
Porin proteins—which form large, water-filled pores in mitochondrial and bacterial outer membranes—fold into β-barrel structures. The amino acids that face the outside of the barrel have what kind of side chains?
A. charged
B. polar
C. amphipathic
D. hydrophilic
E. hydrophobic
B
The shape of a cell and the mechanical properties of its plasma membrane are determined by a meshwork of fibrous proteins called what?
A. lamellipodium
B. cell cortex
C. glycocalyx
D. basal lamina
E. tight junction
C
On what side of the plasma membrane are the carbohydrate chains of glycoproteins, proteoglycans, and glycolipids located?
A. the cytosolic side
B. both sides
C. the extracellular side
D. the underside
E. the inside
C
What is a functionally specialized region of a cell membrane, typically characterized by the presence of specific proteins, called?
A. carbohydrate layer
B. cell cortex
C. membrane domain
D. glycocalyx
E. sphingomyelin domain
D
Multipass transmembrane proteins can form pores across the lipid bilayer. The structure of one such channel is shown in the diagram.
In this figure, what do the areas shown in red represent?
A. the hydrophobic side chains of the transmembrane α helices
B. the hydrophobic lipid tails of the bilayer
C. the hydrophobic side chains of the transmembrane β barrel
D. the hydrophilic side chains of the transmembrane α helices
E. the amphipathic side chains of the transmembrane α helices
F. the hydrophilic side chains of the transmembrane β barrel
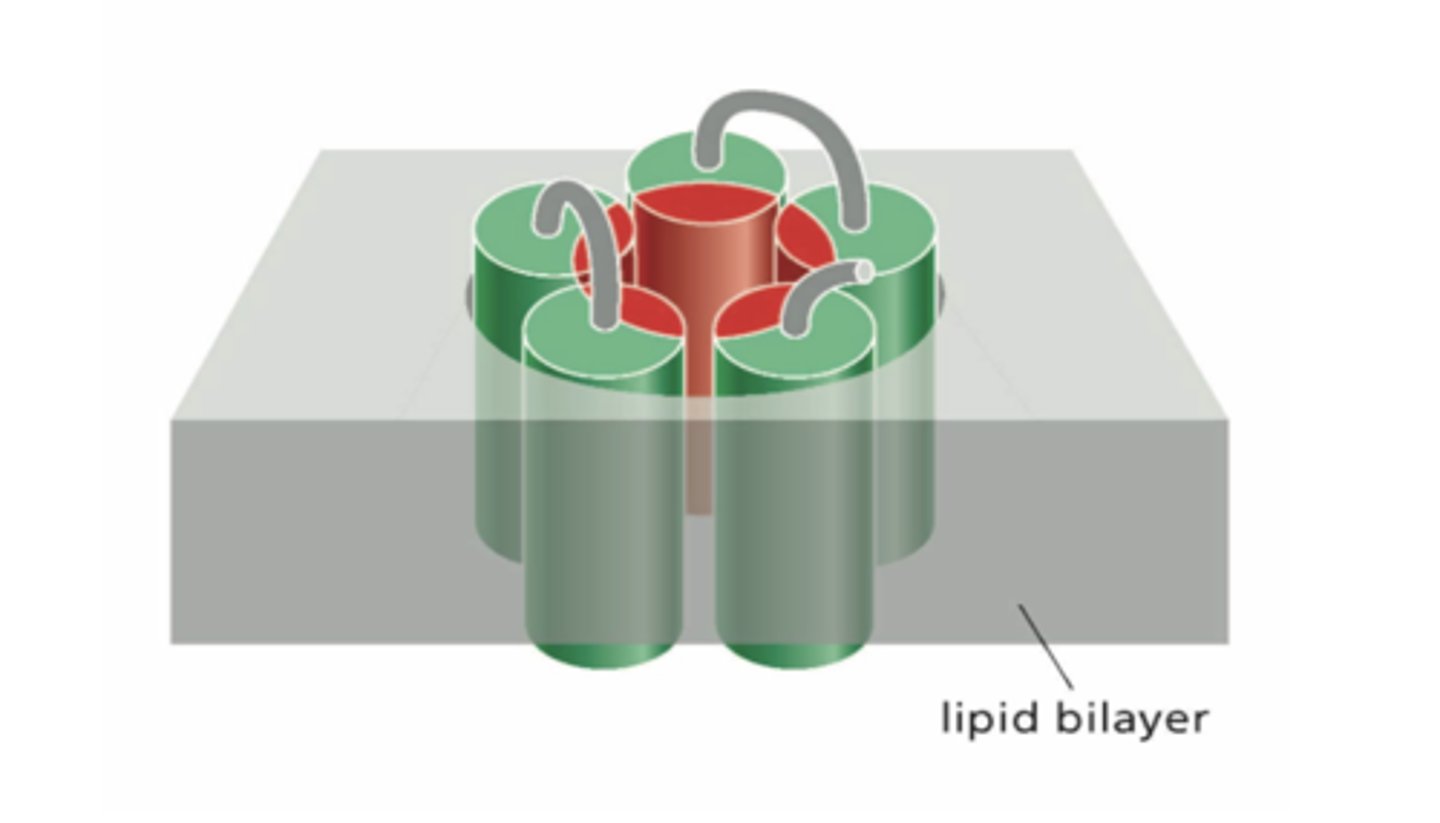
C
What would you predict about the properties of the helix in membrane-associated proteins?
A. Hydrophobic
B. Hydrophilic
C. Amphipathic
C
Based on what you know about beta-sheets, would you expect amino acid side chains in a poly peptide that will form a beta barrel to be
A. All hydrophobic
B. Hydrophobic and uncharged
C. Alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic
D. Alternating positively and negatively charged
B
If the solution concentration inside the cell is 400 mM and the solute concentration outside of the cell is 800 mM, which direction will water move by osmosis?
A. Into the cell
B. Out of the cell
C. The water will not move
B
Lipid bilayers are highly impermeable to which molecule(s)?
A. oxygen
B. Na+ and Cl-
C. carbon dioxide
D. water
E. steroid hormones
D
What is the voltage difference across a membrane of a cell called?
A. potential balance
B. electrical current
C. gradient establishment
D. membrane potential
D
The movement of an ion against its concentration gradient is called what?
A. osmosis
B. passive transport
C. facilitated diffusion
D. active transport
B
What determines the direction that glucose is transported across the membrane, through a glucose transporter?
A. a molecule's size
B. concentration gradient
C. a molecule's charge
D. membrane potential
C
Glucose enters the cell by which process?
A. osmosis
B. active transport
C. facilitated diffusion
D. simple diffusion
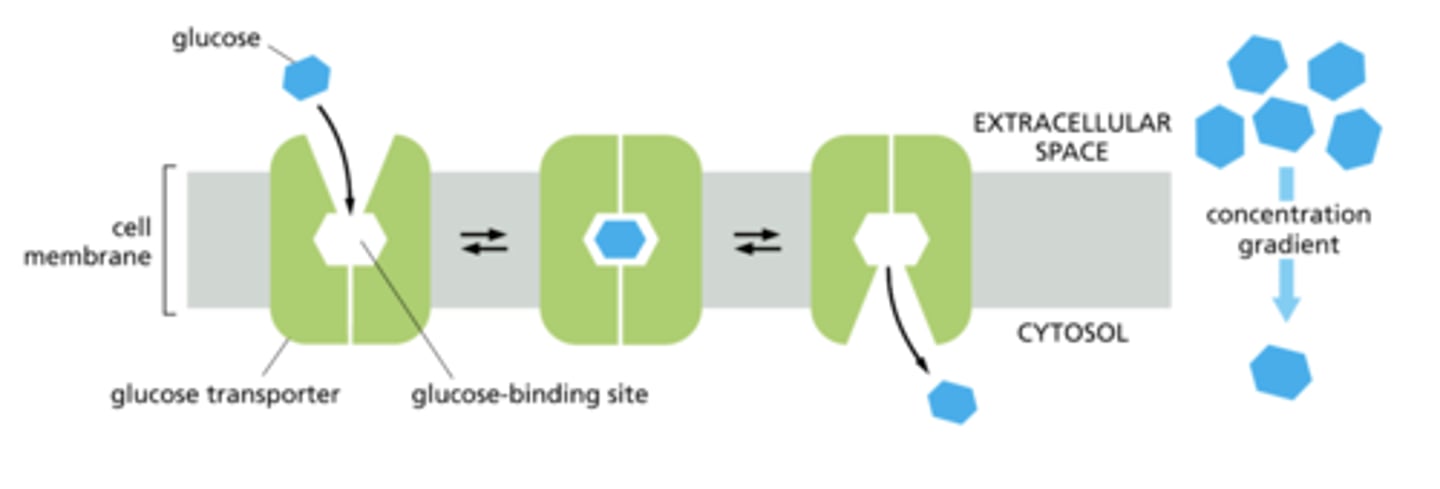
B- symport
C- antiport
A- uniport
Within the image of membrane transport proteins, identify the correct type of transport by dragging the labels to their targets.
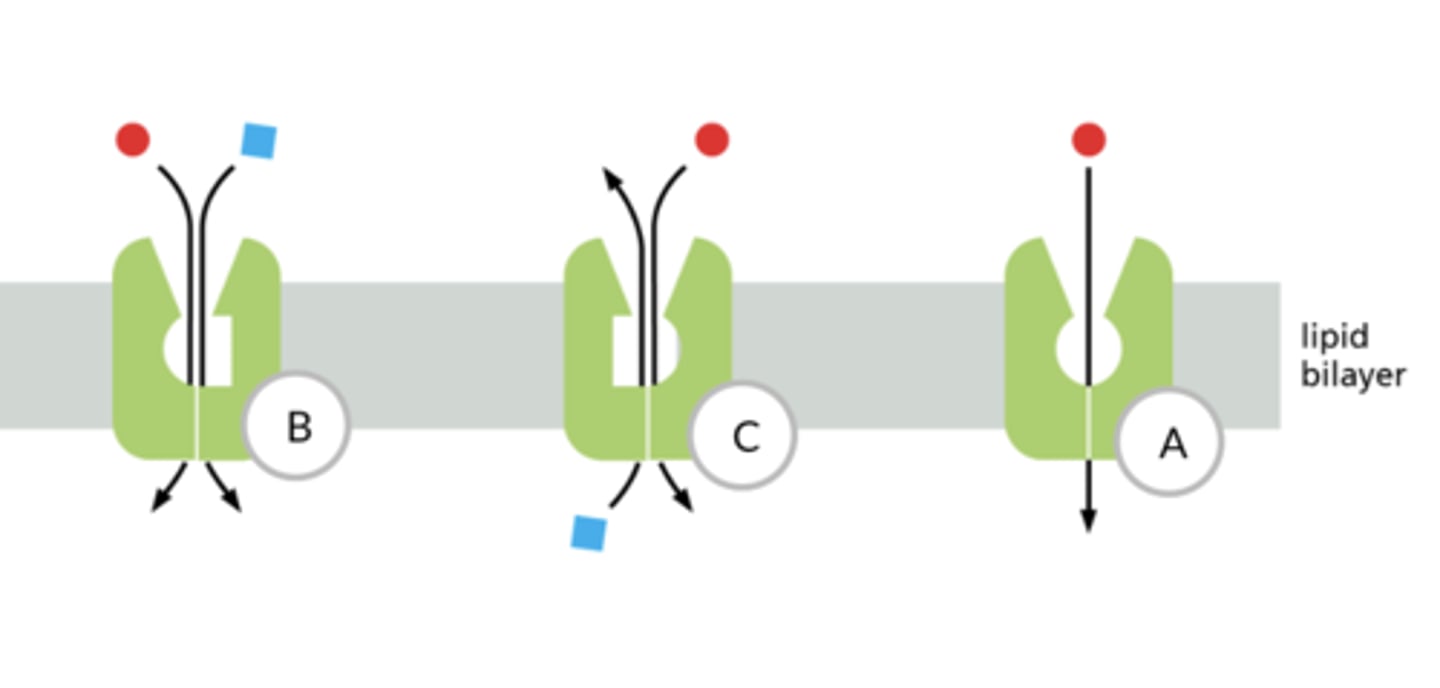
B
What is typically true of ion channels?
A. They are open all the time.
B. They are gated.
C. They hydrolyze ATP.
D. They are nonselective.
E. They operate by active transport.
B
For voltage-gated channels, a change in the membrane potential has what effect on the channel?
A. It makes the channel more sensitive to the binding of neurotransmitters.
B. It alters the probability that the channel will be found in its open conformation.
C. It changes which ions can pass through the channel.
D. It changes the width of the channel opening.
E. It either opens the channel or closes it, depending on the voltage.
E
To pass through the pore of an ion channel, what must be true of an ion?
A. It must avoid contact with the channel wall.
B. It must be positively charged.
C. It must interact with non polar groups in the selectivity filter.
D. It must surround itself with water molecules.
E. It must interact with polar groups in the narrowest part of the channel.
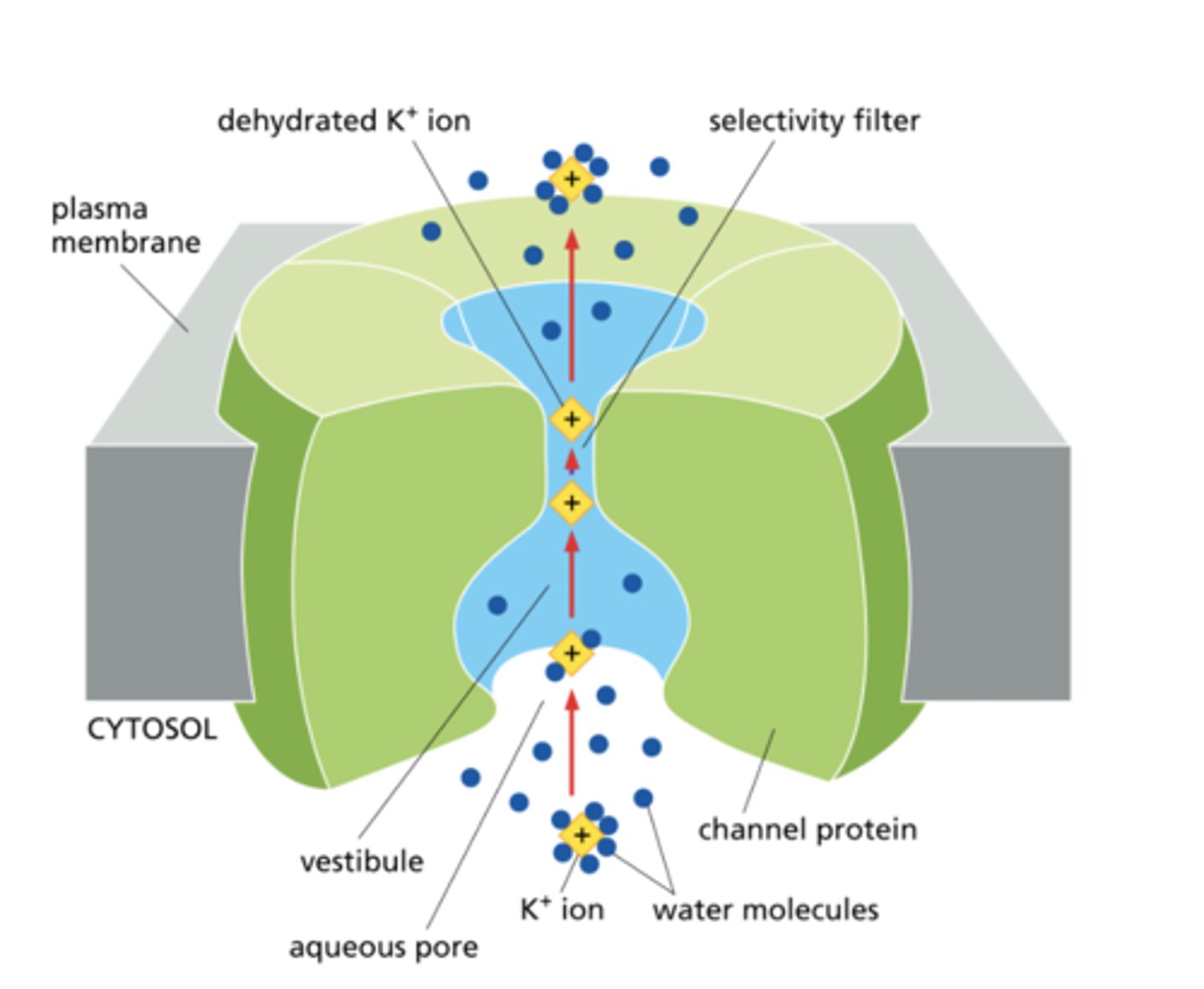
E
When a neuron has been stimulated by a signal, the change in membrane potential first spreads locally to adjoining regions of the plasma membrane by what means?
A. action potential
B. opening of voltage-gated ion channels
C. opening of ligand-gated ion channels
D. active transport
E. passive spread
C
Which correctly describes molecules that can most easily diffuse across a lipid bilayer?
A. Any charged polar molecule including amino acids or glucose
B. Small uncharged molecules such as CO2 and small ions such as H+
C. Small uncharged molecules such as O2, and small uncharged polar molecules such as H2O
D. Amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids, and charged polar molecules such as ethanol
E. Any of these molecules can freely diffuse across a bilayer, it just depends on a concentration gradient
C
If the solute concentration inside the cell is 200 mM and the solute concentration outside of the cell is also 200mM, which direction will water move by osmosis?
A. Into the cell
B. Out of the cell
C. There will not be net movement of water
D
Amino acids are taken up by animal cells using a support in the plasma membrane. What is the most likely ion whose electrochemical gradient drives the import?
A. K+
B. Cl-
C. PO4^3-
D. Na+
E. Ca^2+
A
Considering the graph below, with the letters labeling different aspects of membrane potential within a neuron, which statement is most correct?
A. 'A' represents resting potential where electrochemical equilibrium is achieved largely through the action of potassium leak channels
B. 'B' represents threshold potential, where voltage gated sodium channels open.
C. 'C' represents the action potential, where voltage gated sodium channels are open and the membrane rapidly depolarizes
D. 'A' represents repolarization, where potassium channels are open and sodium channels are inactivated
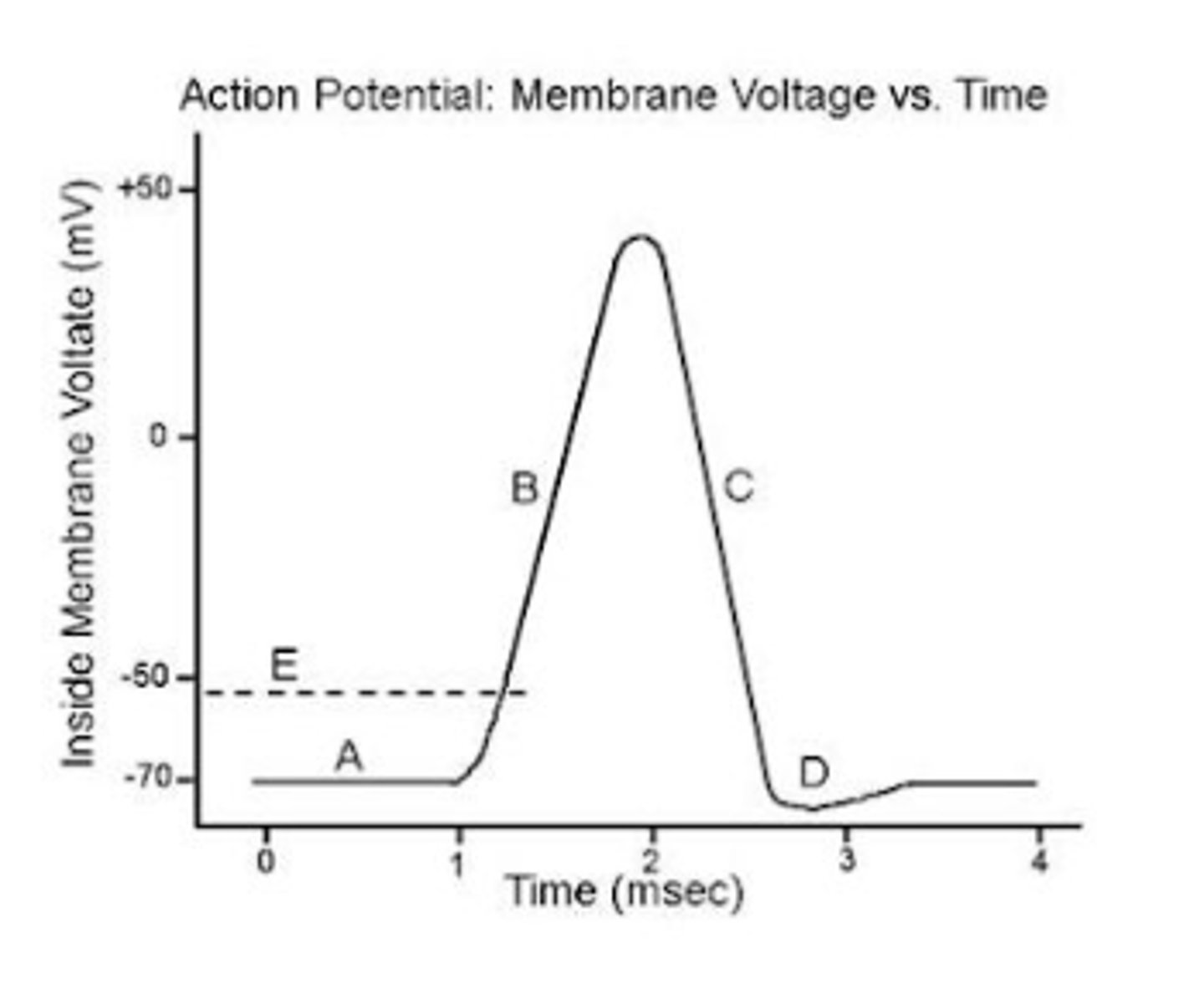
A
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) from the pufferfish is a potent neurotoxin. The figure shows patch-clamp results from membranes of a normal (control) axon and on treated with TTX. Which of the following mechanisms would be consistent with these effects of the toxin?
A. The toxin binds to and blocks axonal voltage-gated sodium channels
B. The toxin binds to and activates axonal voltage-gated sodium channels.
C. The toxin binds to and blocks axonal voltage-gated potassium channels
D. The toxin binds to and activates axonal voltage-gated potassium channels
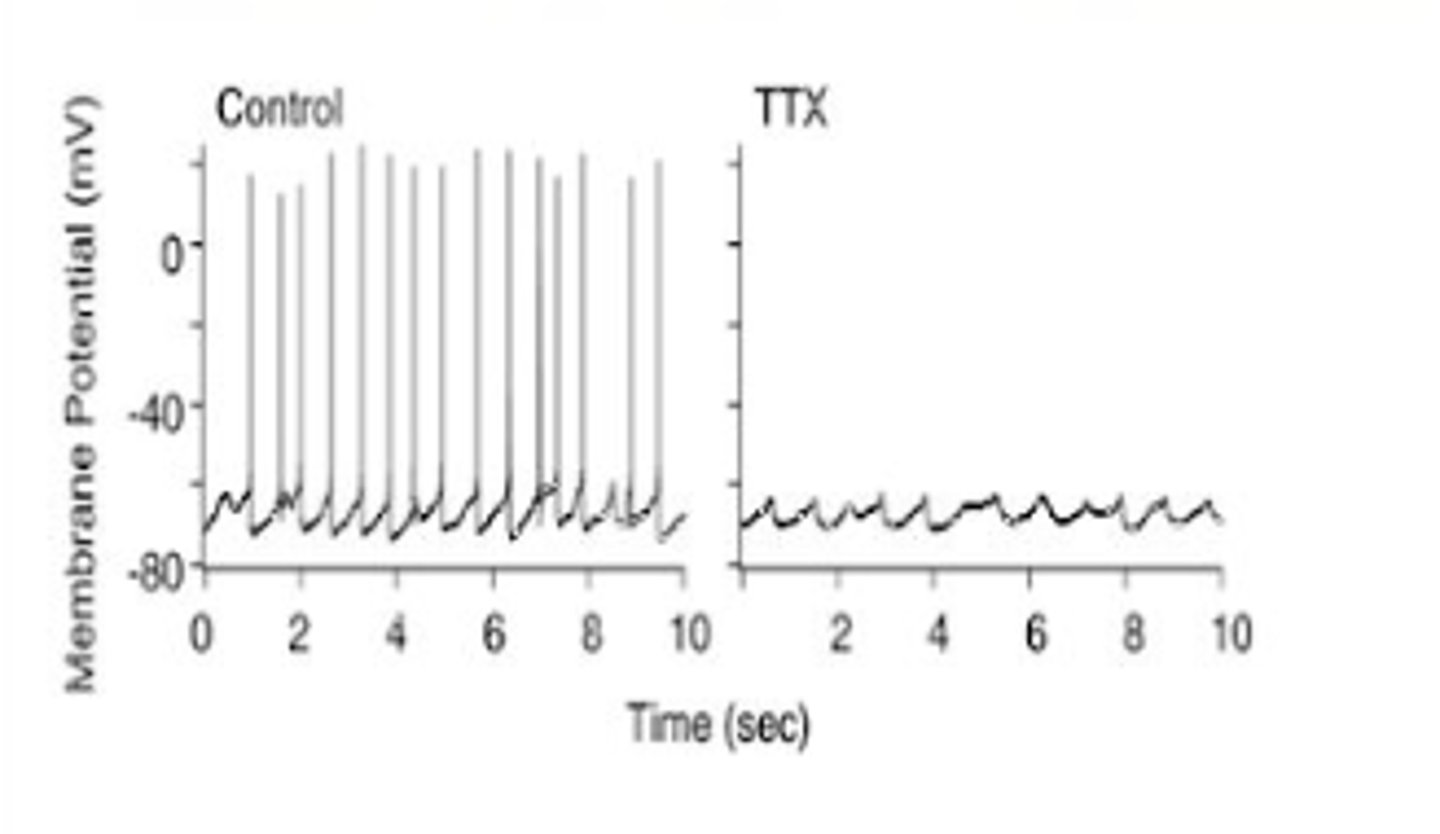
C
Which of the following organelles is thought to gave arisen by the engulfment of a bacterium by a primitive eukaryotic cell?
A. Nucleus
B. Lysosome
C. Mitochondrion
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
A
The unfolded protein response:
A. In the ER can trigger cell death
B. Helps distinguish endocytosed cargoes destined for the lysosome
C. Is caused by the highly acidic environment inside the lysosome
D. Is a mechanism to ensure proper folding of proteins that are translocated across membranes as unfolded proteins
B
Rab GTPase proteins on vesicle membranes are important:
A. for removing the protein coats to reduce naked vesicles
B. for vesicle recognition by cytoskeleton motor proteins and target membrane tether proteins
C. for providing the energy that drives vesicle fusion at target membranes.
D. for removing chaperones from cargo proteins during vesicle fusion
E. for all these processes
D
Which of the following statements is true about active transport?
A. Active transport cannot be performed by transporters
B. Active transport is required for movement of molecules down a concentration gradient
C. Active transport is required only for the transport of molecules- small molecules can diffuse across membranes passively
D. Energy from one ion gradient can be used to drive transport of a different ion against its gradient
A
What advantage is there in transporting a molecule via a transporter rather than an ion channel?
A. Transporters can perform active transport, channel proteins can only perform passive transport
B. Channels are much more specific than transporters
C. Transport through a transporter is faster than by a channel
D. Transport through transporters can be controlled via channels cannot, they are always open
B
Transporters review: which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Transporters can transport molecules against their concentration gradients by coupling transport to an energy source
B. Transporters cannot transport ions against their electrochemical gradient, as this is energetically unfavorable
C. Transporters are highly specific as they have a binding site for the molecule being transported
D. The Na+ K+ pump uses ATP to drive transport of Na+ and K+
A
Some signal sequences are bipartite (splits into 2 parts). SMAD4 is a transcription factor normal found in the nucleus, whereas GFP protein goes to the cytosol. Imagine you identify a predicted sorting signal and when you remove it you see that SMAD4 is now found in the cytosol. But when you add that sequence to GFP, GFP does not enter the nucleus but remains cytosolic. This tells you that this sequence is
A. Necessary for targeting to the nucleus but not sufficient.
B. Sufficient for targeting to the nucleus but not necessary.
C. Both necessary and sufficient for targeting to the nucleus.
D. Neither necessary nor sufficient for targeting to the nucleus.
B
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the transport of molecules into the nucleus?
A. the nuclear localization signal (NLS) is not removed after transport
B. does not require energy, as the ΔG is negative
C. fully folded and assembled proteins can be transported
D. proteins are bound by soluble nuclear import receptors in the cytosol
E. macromolecular complexed can be transported through nuclear pores
D
SNARE proteins on transport vesicles:
A. Form a protein coat so the vesicle can bud
B. Pinch off the vesicle from the membrane
C. Attach the vesicle to a cytoskeleton motor protein for movement to its target
D. Bind other SNARE proteins on the target organelle membrane
B
What is one difference between constitutive pinocytosis and receptor mediated endocytosisis?
A. Pinocytosis uses larges vesicles, receptor-mediated endocytosis uses small vesicles.
B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis takes up specific molecules, pinocytosis indiscriminately takes up molecules randomly.
C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis uses clathrin-coated vesicles, pinocytosis uses names vesicles.
D. Receptor-mediated endocytosis only takes up proteins, pinocytosis only takes up fluid.
E. All of these are true
E
Which of the following is UNTRUE about ion channels?
A. They exist in open and closed conformations
B. They are selective for one type of ion
C. Their activities can be measured by the patch clamp technique
D. They are transmembrane proteins
E. Their specific binding pocked is alternately exposed to each side of the membrane
C
Animal cells rely on an electrochemical gradient (potential) across the plasma membrane. The most important factor in establishing this gradient is
A. A Na+/Cl- anti porter that uses the chloride concentration gradient to drive sodium export out of the cell.
B. Na+ leak channels that allow the membrane to achieve a Nernst equilibrium
C. A Na+/K+ ATPase transporter that pumps sodium ions out of the cell.
D. Na+/glucose symporters that use glucose to produce Na+ gradients
B
After generation of an action potential in a nerve cell, how does the membrane repolarize again?
A. Opening of sodium channels and clossing of voltage-gated potassium channels
B. Inactivation of sodium channels and opening of voltage-gated potassium channels
C. Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
D. Release of neurotransmitter into the cell
A
Which of the following best explains why action potentials are only propagated in one direction along an axon?
A. Na+ channels become inactivated for a brief period after an action potential
B. K+ channels have a higher activation threshold than Na+ channels
C. There is a delay before K+ channels open after initiating an action potential
D. K+ leak channels delay the membrane from depolarizing after an action potential
A
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the transport of molecules into the nucleus?
A. Transport takes place through the TOM complex
B. The nuclear localization signal (NLS) is not removed after transport
C. Fully folded and assembled proteins can be transported
D. Macromolecular complexes can be transported through nuclear pores
E. Proteins are bound by soluble nuclear import receptors in the cytosol
C
Chaperones are required during mitochondrial protein import because
A. They form the part of the TOM translocation complex that binds the signal sequence
B. They join the TOM and TIM complexes to allow translocation through both membranes into the matrix
C. They assist in protein folding after import into the matrix
D. They phosphorylate the mitochondria import receptor.
C
Uptake of glucose from the gut occurs by
A. Receptor mediated endocytosis
B. Phagocytosis
C. A Na+ symporter
D. Osmosis
C
Newly synthesized proteins are modified in the endoplasmic reticulum by N-glycosylation. During this process:
A. Oligosaccharides are transferred to proteins through disulfide linkages
B. Oligosaccharides are assembled by the addition of sugar residues one by one to the protein
C. Oligosaccharides are covalently linked to the polypeptide chain
D. Oligosaccharides are added only to proteins destined for lysosomes, not to proteins that will be secreted
C
Plant cells must transport Na+ out of the cytosol to keep Na+ low because high cytosolic Na+ is toxic. The figure depicts a plant cell where the number of ion symbols per compartment represents relative ion concentration. Given the information provided, which of the following would be a viable option form removing Na+ ions from the cytosol
A. Na+/ H+ symport into the vavuole
B. Na+/ H+ symport across the plasma membrane
C. Na+/ H+ anti port across the plasma membrane
D. Coupled Na+ transport from the vacuole to outside the cell
E. Gated Na+ channels in either the plasma membrane or the vacuolar membrane
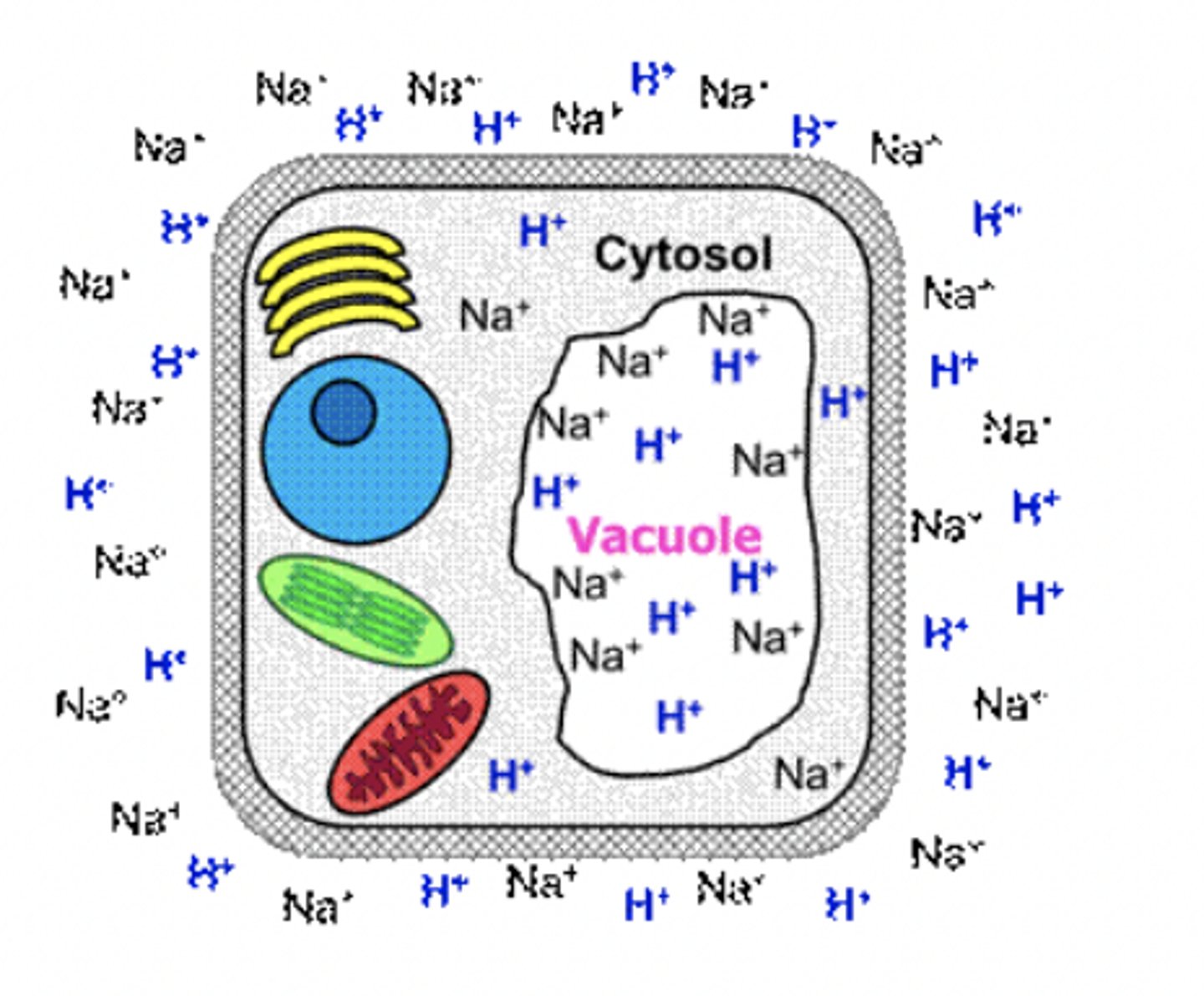
C
After diffusion of a neurotransmitter across a synaptic cleft, how is the neurotransmitter typically perceived by the post-synaptic cell?
A. Binding to a voltage-gated ion channel
B. Binding to the Na+/K+ pump
C. Binding to a transmitter-gated ion channel
D. Binding to a mechanically-gated ion channel
D
A neurotransmitter than opened ligand-gated chloride (Cl-) channels in a postsynaptic neuron would be
A. Excitatory because the postsynaptic membrane would depolarize
B. Inhibitory because the postsynaptic membrane would depolarize
C. Excitatory because the postsynaptic membrane would hyper polarize
D. Inhibitory because the postsynaptic membrane would hyper polarize
C
Newly synthesized proteins that are targeted to the ER
A. Are recognized as mRNAs that then associate with specialized ribosomes
B. Are maintained in unfolded conformation by chaperones in the cytosol until they can be fed through the translocator
C. Are bound by a signal recognition particle (protein) shortly after translation is initiated by a cytosolic ribosome.
D. Are trafficked to the ER in membrane vesicles
A
Which of the following statements is true about endocytosis
A. Clathrin-coated vesicles internalize material from the plasma membrane
B. Proteins are transported directly across the plasma membrane into the cytosol through a channel in the membrane
C. It can be used to internalize molecules from the plasma membrane for degradation in the Golgi
D. Only molecules that mind membrane receptors are internalized
A
A yeast mutant is defective in the secretion of proteins. If the mutant accumulates secretory proteins in the ER, which process is the mutated gene most likely necessary for?
A. Transport from the ER to the Golgi
B. Transport from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum
C. Transport from the ER to the plasm membrane
D. Transport from the ER to the endosome
E. Transport from the endosome to the ER
A
What combination of factors could produce an ER membrane protein with the topology shown?
A. A cleavable N-terminal signal sequence, followed by a STOP, followed by an internal START.
B. An internal START signal, followed by a STOP
C. A cleavable N-terminal signal sequence, following by a STOP
D. A cleavable N-terminal signal sequence and an internal START signal
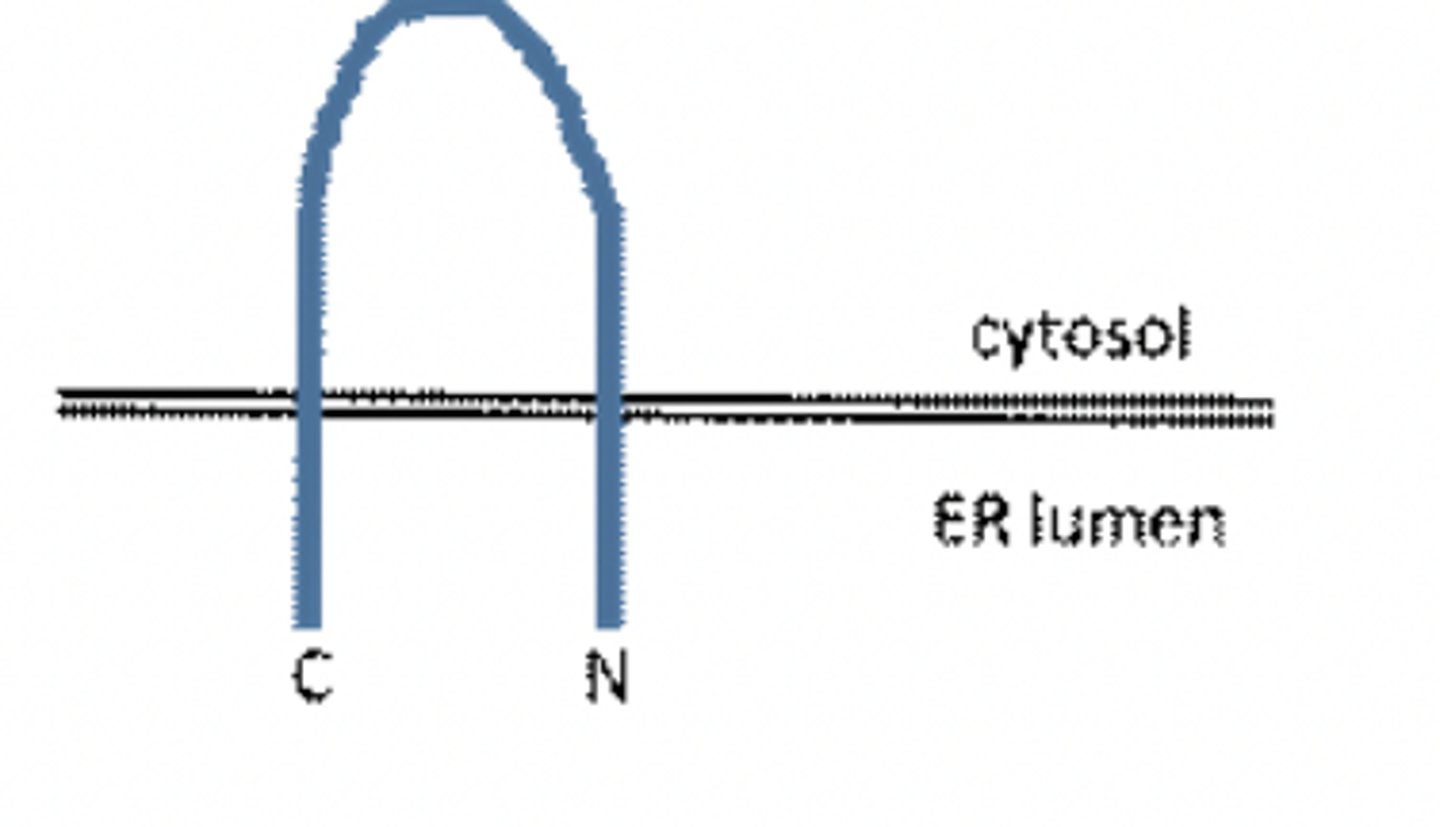
B
Clathrin, found in coats on transport vesicles
A. Provides specificity in sorting cargo proteins
B. Can deform the membrane to form a bud
C. Is required for the fusion of ER-derived vesicles with the Golgi
D. Is the type of cargo receptor protein
E. Is required to guide vesicles to their target membranes
D
Which of the following are possible fates of a plasma membrane receptor protein after it is endocytosed?
A. Recycling from endosomes back to the plasma membrane
B. Trancytosis to another region of the plasma membrane (in polarized cells)
C. Degradation in lysosomes/vacuoles
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
E
Which statement about cysteine disulfide bonds is FALSE?
A. They stabilize the structure of proteins
B. They can occur either within a peptide chain or between different peptide chains
C. Their formation is catalyzed primarily in the ER
D. They are particularly important for many secreted proteins
E. They are non covalent bonds
C
Which of the following does not describe activities in the Golgi during the trafficking of a secretory protein?
A. Carbohydrate chains on glycoproteins are sequentially modified as the protein transits through the cisternae.
B. Proteins are sorted to different specialized vesicles, including secretory vesicles.
C. Signal recognition particles deliver secretory proteins from the ER to the Golgi.
D. Protein coated transport vesicles bud off each cisterns and deliver cargo to the next cisterna
B
Which of the following statements about lysosomes is FALSE?
A. An acidic pH is maintained within lysosomes, which is necessary for the activity of lysosomal enzymes
B. The reason lysosomal proteins are glycosylated is that this prevents them from digesting other cellular proteins
C. Many macromolecules taken up by endocytosis are sorted in the endosome, then trafficked to the lysosome where they are digested
D. Large bodies, such as bacteria in phagosomes, are broken down by the lysosome
C
The emerging concept in cell biology of phase condensation is important because
A. It allows lipids to coalesce into membranes
B. It can decrease the activation energy of enzymatic reactions
C. It can help drive processes by concentration reactants or subunits
D. It helps drive the formation of secretory vesicles
E. All of these are true
D
Compare and contrast protein import into the nucleus versus the mitochondrion. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A. The signal sequence is typically removed from mitochondrial proteins but not from nuclear proteins
B. Nuclear import receptors are soluble in the cytosol while mitochondrial import receptors are associated with TOM in the mitochondrial membrane.
C. Nuclear proteins are translocated into the nucleus in fully folded conformation while mitochondrial proteins are unfolded and bound by chaperones.
D. Import into mitochondria requires energy while nuclear import is by passive transport.
C
Which of the following DOES NOT contribute to the sorting of cargo proteins into specific vesicles targeted to different destinations within a cell?
A. specific interactions between cargoes and cargo receptors
B. specific interactions between cargo receptors and adaptin proteins
C. specific interactions between adaptins and coat proteins such as clathrin
D. all of these contribute to protein sorting
E
Which of the following molecules would you expect to be able to rapidly diffuse directly across a lipid bilayer?
A. Glucose
B. Na+3
C. ATP4
D. Cl-5.
E. None of the above
True
Many ion channels are gated, opening in response to voltage, ligand binding or mechanical forces. True or False
B
Which of the following statements is true?
A. Channel proteins can perform both active and passive transport
B. Channels can switch between open and closed forms
True
Facilitated diffusion (passive transport) is mediated by integral membrane proteins. True or False
A
Patch-clamp analysis can be used to:
A. To measure the current through an ion channel
B. To purify chloroplasts for protein import studies
C. To analyze the energy requirements for protein transport
D. To generate mutants in proteins of the secretory pathway
E. All of the above
All are true
- exist in open and closed conformations
- selective for one type of ion
- activities can be measured by the patch clamp technique
- transmembrane proteins
Which of the following is true about ion channels?
Necessary for targeting to mitochondria
Imagine you are studying the transport of proteins into mitochondria. You engineer a mitochondrial protein to remove its predicted sorting signal and see that it is now found in the cytosol. This tells you that the sorting signal is:
C
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Nuclear pores can transport both RNA and protein molecules
B. Small molecules can freely diffuse through nuclear pores
C. Transport of proteins into the nucleus does not require energy
D. Receptor proteins recognize proteins with a nuclear localization signal and transport them into the nucleus
ER lumen
Imagine you are studying a protein with multiple transmembrane regions that is inserted into the ER membrane. The proteins has a typical cleavable N-terminal ER signal sequence. Which side of the membrane would you expect the N-terminus to be?
C
Which one of the following is true?
A. Proteins transport into mitochondria requires energy, protein transport into the nucleus does not
B. A receptor is required for protein transport into mitochondria but not into the nucleus
C. Proteins have to be unfolded for transport into mitochondria, whereas folded proteins can be transported into the nucleus
A
The outer membrane of the nucleus is continuous with the membrane of which other organelle?
A. endoplasmic reticulum
B. Golgi apparatus
C. mitochondrion
D. peroxisome
E. endosome
A
Which of these strategies do prokaryotic cells use to isolate and organize their chemical reactions?
A. aggregating proteins into multi-component complexes that form biochemical subcompartments with distinct functions
B. confining the proteins required for different metabolic processes within the plasma membrane
C. None; these strategies are used only by eukaryotic cells.
D. confining proteins required for different metabolic processes within different membrane-enclosed compartments
E. None; prokaryotes do not regulate their metabolic processes.
E
Most mitochondrial and chloroplast proteins are made within which part of the cell?
A. mitochondrion or chloroplast itself
B. Golgi apparatus
C. endoplasmic reticulum
D. peroxisome
E. cytosol
D
Proteins destined for the Golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes, and even the cell surface must pass through which organelle?
A. nucleus
B. peroxisome
C. mitochondrion
D. ER
C
The movement of materials from the plasma membrane, through endosomes, and then to lysosomes describes which type of pathway?
A. endosomal pathway
B. exocytic pathway
C. endocytic pathway
D. endolytic pathway
E. secretory pathway
B
Which proteins play a central role in the fusion of a vesicle with a target membrane?
A. tethering proteins
B. SNAREs
C. clathrin
D. Rab proteins
E. adaptin
B
Through which of the following do proteins travel from one cisterna to the next in the Golgi apparatus?
A. transporters in the cisternal membranes
B. transport vesicles that bud from one cisterna and fuse with the next
C. pores in the cisternal membranes
D. bridges that link the cisternae
E. membranes via osmosis
B
What is true of protein glycosylation in the ER?
A. Sugar residues are added one at a time by a series of enzymes attached to the ER membrane.
B. Oligosaccharides are added by an enzyme that has its active site on the lumenal side of the ER membrane.
C. A block of sugar residues is added to the N-terminal signal sequence, creating a common, N-linked oligosaccharide.
D. Only proteins bearing a dolichol residue become glycosylated.
E. Only proteins phosphorylated on an asparagine residue become glycosylated.
E
Phagocytosis is a process by which cells do which of the following?
A. secrete hormones and neurotransmitters
B. digest their own worn-out organelles
C. engage in receptor-mediated endocytosis
D. ingest extracellular fluid and macromolecules
E. consume large particles, such as microbes and cell debris
C
Which of the following is true of lysosomes?
A. Most of the lysosomal membrane proteins have glycosylated regions on the cytosolic side of the membrane.
B. Lysosomes contain around 40 types of hydrolytic enzymes, which are optimally active at pH 7.2.
C. An ATP-driven H+ pump in the lysosomal membrane maintains the organelle's pH.
D. Lysosomes have a pH that is higher than that of the cytosol.
E. The products of digestion in lysosomes leave the lysosome by transport vesicles.
ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
What is the main function of mitochondria?
Mitochondrial import requires ATP hydrolysis by chaperones that unfold the protein during the import process
Which of the following statements about import of proteins into mitochondria is true?
B
If the solute concentration inside a cell is 300 mM and the solute concentration outside of the cell is 800 mM, which direction will water move by osmosis?
A. Into the cell
B. Out of the cell
C. The water will not move
C
Which of the following would you predict requires ATP?
A. Movement of water out of a cell that contains a lower solute concentration than the external medium
B. Diffusion of CO2 across a lipid bilayer
C. Active transport of Na+ out of a cell
D. Passive transport of glucose out of a cell
E. All of these require ATP
D
Cells can transport molecules against their concentration gradient by coupling transport to
A. ATP hydrolysis
B. input of light energy
C. transport of another molecule down its concentration gradient
D. all of the above
A
What advantage is there in transporting a molecule via a transporter rather than an ion channel?
A. Transporters can perform active transport, channel proteins can only perform passive transport
B. Channels are much more specific than transporters
C. Transport through a transporter is faster than by a channel
D. Transport through transporters can be controlled, transport via channels cannot, they are always open
B
Transporters can perform active transport only.
A. True
B. False
B
Ions will move through ion channels against their electrochemical gradient.
A. True
B. False
A
Patch-clamp analysis can be used
A. To measure current through an ion channel
B. To purify chloroplasts for protein import studies
C. To analyze the energy requirements for protein transport
D. To generate mutants in proteins of the secretory pathway
E. All of the above
B
Consider the graph below of membrane potential within a neuron.
If a stimulus causes the membrane of the neuron to depolarize to -45 mV, would an action potential be generated?
A. Yes
B. No
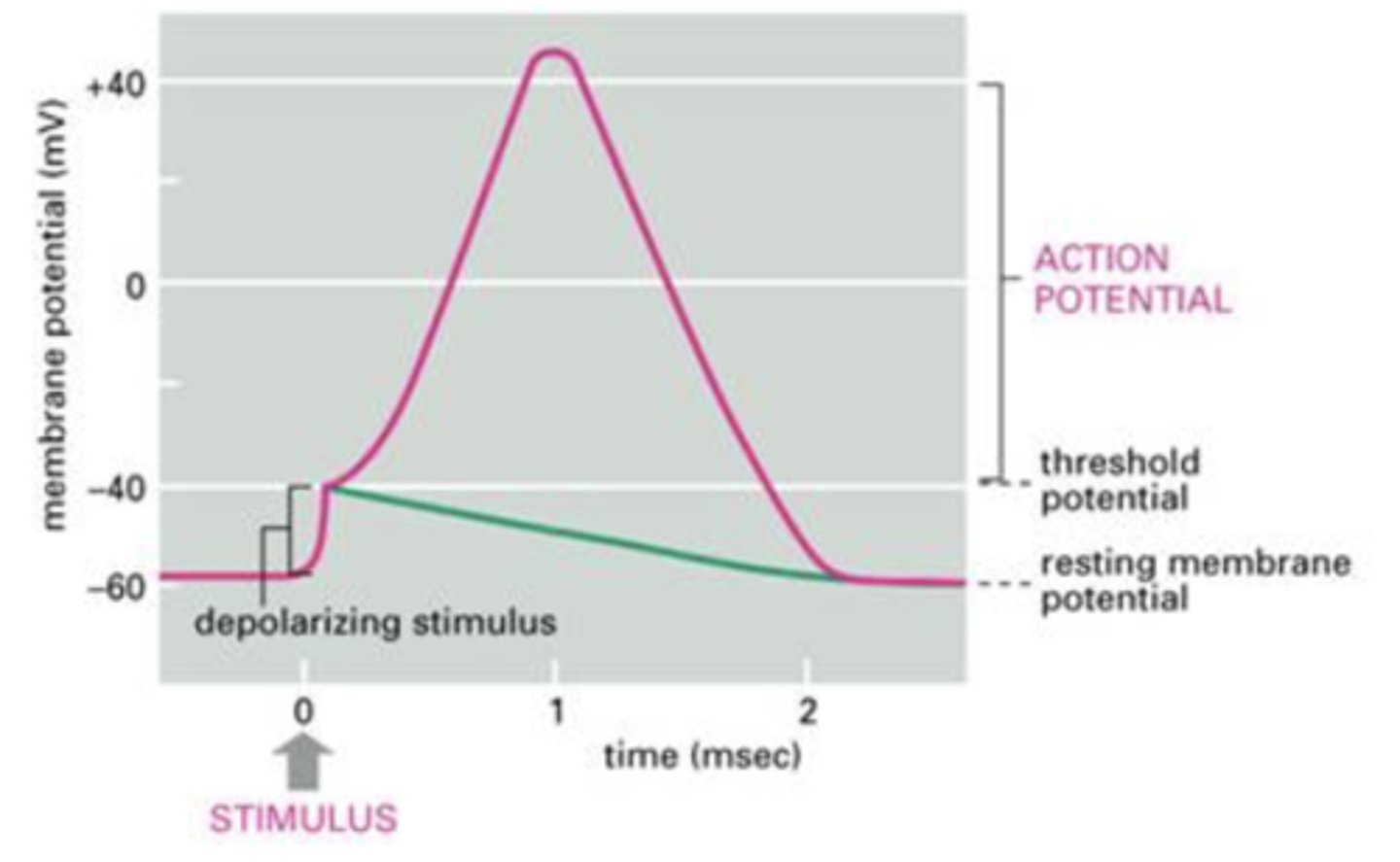
A
An action potential is generated in a nerve cell once the plasma membrane is
A. depolarized to the threshold potential
B. depolarized to the resting potential
C. repolarized to the threshold potential
D. repolarized to the resting potential
B
Most psychoactive drugs work by binding to voltage-gated ion channels and opening them.
A. True
B. False
E
Which of the following are found in animal cells but not in plant cells?
A. Mitochondria
B. Cell wall
C. Endosomes
D. Peroxisomes
E. none of the above
C
Which of the following organelles is thought to have arisen by the engulfment of a bacterium by a primitive eukaryotic cell?
A. nucleus
B. peroxisome
C. mitochondrion
D. vacuole
A
A major function of lysosomes is the degradation of proteins.
A. True
B. False
A
Transport of proteins into chloroplasts occurs via channels that are part of the TOC and TIC complexes.
A. True
B. False
A
Imagine you are studying the transport of proteins into peroxisomes. You engineer a peroxisomal protein to remove its predicted sorting signal and see that it is now found in the cytosol. This tells you that the sorting signal is
A. Necessary for targeting to peroxisomes
B. Sufficient for targeting to peroxisomes
C. Both necessary and sufficient for targeting to peroxisomes
A
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the transport of molecules into the nucleus?
A. transport takes place through the TOM complex
B. the nuclear localization signal (NLS) is not removed after transport
C. fully folded and assembled proteins can be transported
D. transport requires energy in the form of GTP
D
Which of the following is NOT a function of chaperone proteins during protein transport into mitochondria?
A. Bringing newly-synthesized proteins to mitochondria
B. Driving transport across the mitochondrial membrane
C. Folding the protein after transport into mitochondria
D. Phosphorylating the mitochondrial import receptor