B3.1 gas exchange
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
gas exchange function in plants and mammal
obtain gases for metabolism
release waste products
respiration
photosynthesis
gas exchange occurs
diffusion - gases travel from high to low concentration to reach diffusion
structure to facilitate gas exchange (4)
large SA:V (branches+foldings)
permeability of O2 and CO2
thin tissue layer minimise diffusion distance
moist layer for gases to dissolve
how is concentration gradient maintained (3)
Dense capillary network around gas exchange surfaces
Continuous blood flow
Ventilation
With air for lungs
With water for gills
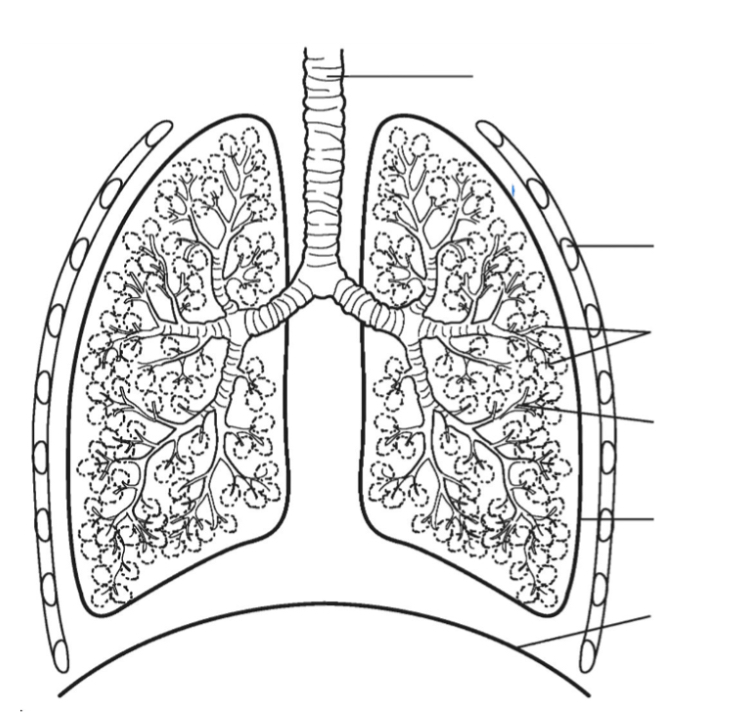
Lungs
trachea
bronchus
bronchiole
alveoli
lungs
ribs
intercostal muscle
diaphragm
definition for ventilation + gas exchange + cellular respiration
Ventilation : exchange of air between atmosphere and lungs - breathing
Gas exchange : exchange of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and bloodstream - passive diffusion
Cellular Respiration : release of ATP from organic molecules
exchange on ventilation rate
increase rate exercise > increase cellular respiration > increases uptake of oxygen > increase ATP - breath in faster
By product of cellular respiration increases: Co2 > blood gets acidified > proteins like RBC denatures > dont carry oxygen > dies.
To avoid Co2 accumulation - breath out faster > ventilation rate faster
respiratory system (5)
air travels from nose&mouth - pharynx - trachea
air divides into two bronchi
right : 2 lobes, left : 3 lobes
bronchi - many bronchiole ( increases SA)
bronchiole - airsacs: alveoli ( gas exchange w bloodstream occurs)
structure of alveolus
thin epithelial layer ( one cell thick ) > minimuze diffusion distances
surrounded by rich capillaries layer > increase capacity for ge with blood
spherical in shape > maximize SA for ge
internal surface - covered with surfactant > dissolved gas better able to diffuse in bloodstream + reduce surface tention
where is pneumocytes
(alveolar cells) - line the alveoli , comprise the majority of inner surface of lungs
what is alveoli made out of
type 1 + type 2 pneumocytes
type 2 pneumocytes
secrete alveolar fluid → contain surfactant
how surfactant works
Alveoli is moist, water attracts to together due to cohesion , risk of alvelio collasping
Type 2 pneunocytes secret surfactant, reduce surface tension
adaptations for lungs(4)
surfactant - decrease pressure
short diameter of bronchiole - slow air flow increases efficiency
many alveoli attached at the end - increase SA for gas exchange
extensive capillaries around alveoli - short diffusion distance
ventilation in antagonistic muscle
Inhalation
external intercostal muscle contracts → ribcage move out and up
diaphagram contracts and flattens
volume increase in thorax, decrease pressure
air flows into the lungs
exhalation
internal intercostal muscle contracts → ribcage moves in and down
Abdominals contract. pushes diaphragm up into dome shape
volume decrease in thorax, Increase pressure
air flows out the lung
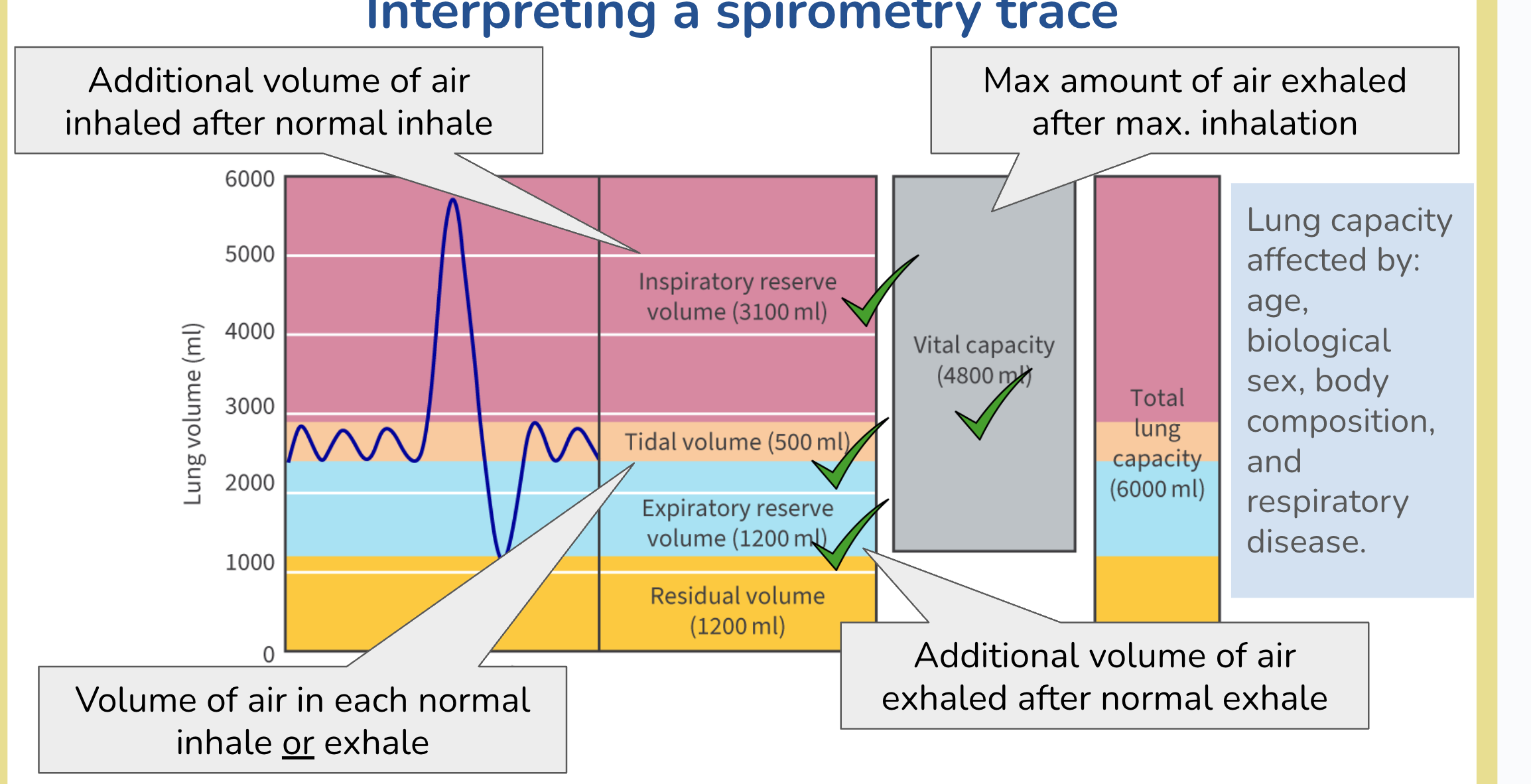
measure lung volume
spirometry
spirometry trace
gas exchange in leaf
stomata
guard cells control opening and closing of stomata
adaptations of leaf
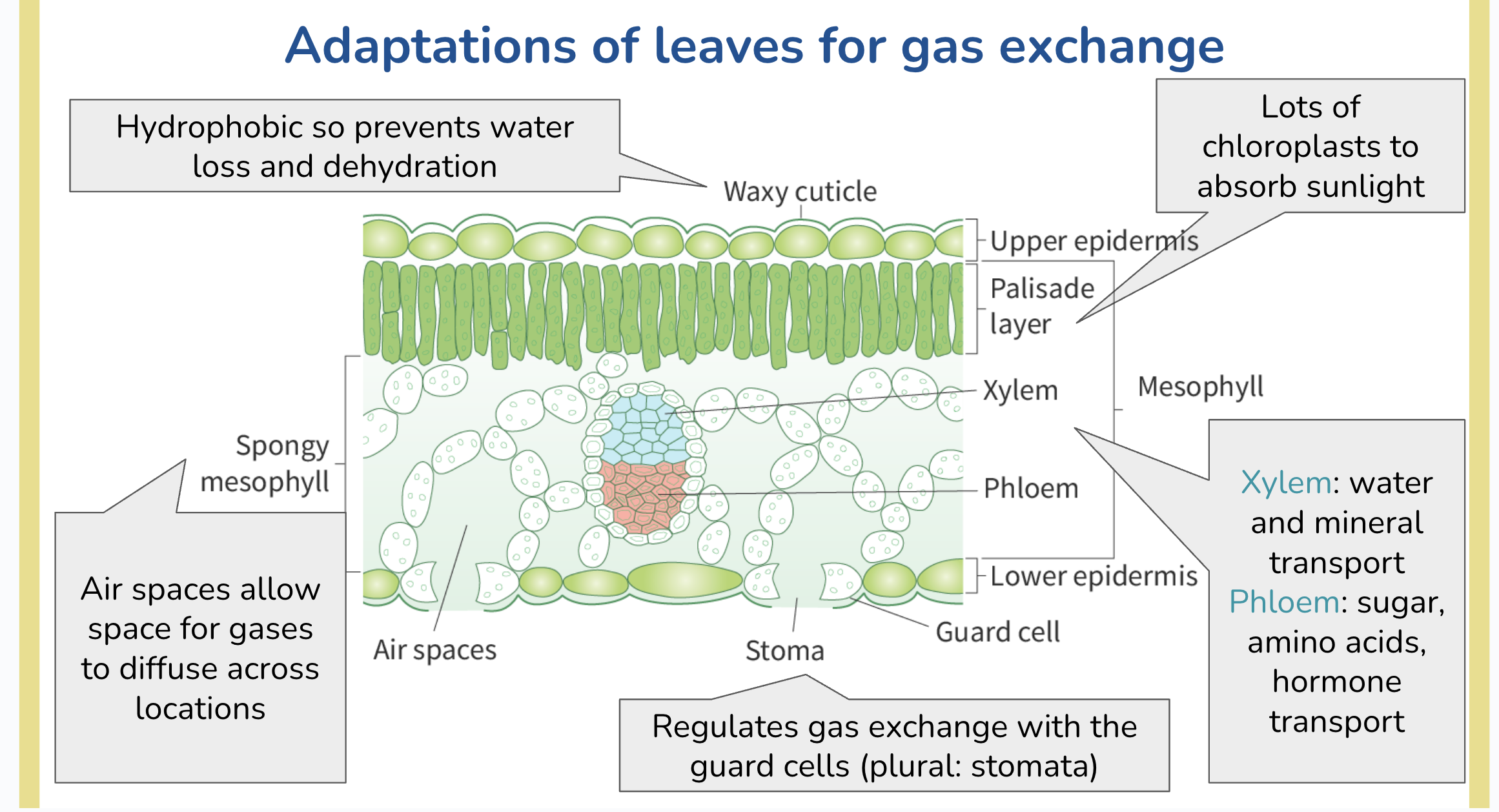
waxy cuticle - hydrophobic - prevents water loss
palisade layer/mesophyll - photosynthesis, lots of chloroplast
spongy mesophyll - lots of air spaces for gas exchange
xylem&pholem
stoma + guard cells - gas moves in and out
transpiration
movement of water from roots to leaves
Water vapour diffuse out the leaf via stoma, creating a negative pressure gradient → water drawn out of xylem through cell wall by capillary action, generate tension → draw water up xylem vessel from roots to leaf
Transpiration facilitates:
Temperature regulation
Absorption of water and minerals from soil
factors affecting transpiraton
increase transpiration
light - more light, more transpiration
temperature- more heat, more evaporation, more transpiration
decrease transpiration
humidity: more humid, higher concentration of water vapour outside the plant ( low concentration gradient) slower transpiration
hemoglobin (location, function , structure)
Location: RBC
Function : transport O2 to respiring tissue, transport byproduct Co2 to lungs
Structure: quaternary, conjugated protein - 4 polypeptide with heme group
hemoglobin and oxygen
coorporative binding
structure changes - affinity for oxygen ^
fetal hemoglobin higher affinity than adult hemoglobin, why?
more efficient delivery of O2 from placenta to fetus
Co2 binds xx to hemoglobin
allosterically
change the shape - less affinity for O2
how does Bohr Shift illustrates when there is ^ in Co2
increase Co2, increase carbonic acid , decrese pH
hemoglobin change shape, decrease affinity to oxygen
O2 dissociation curve shifts right, O2 is released more readily to respiring tissues