PARTICLE MODEL OF MATTER (ORIGINAL)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not edited to only have the stuff we need for eoys
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is density?
the mass per unit volume (1m^3 or 1cm^3) of a substance
Equation for density?
mass/volume (m/v)
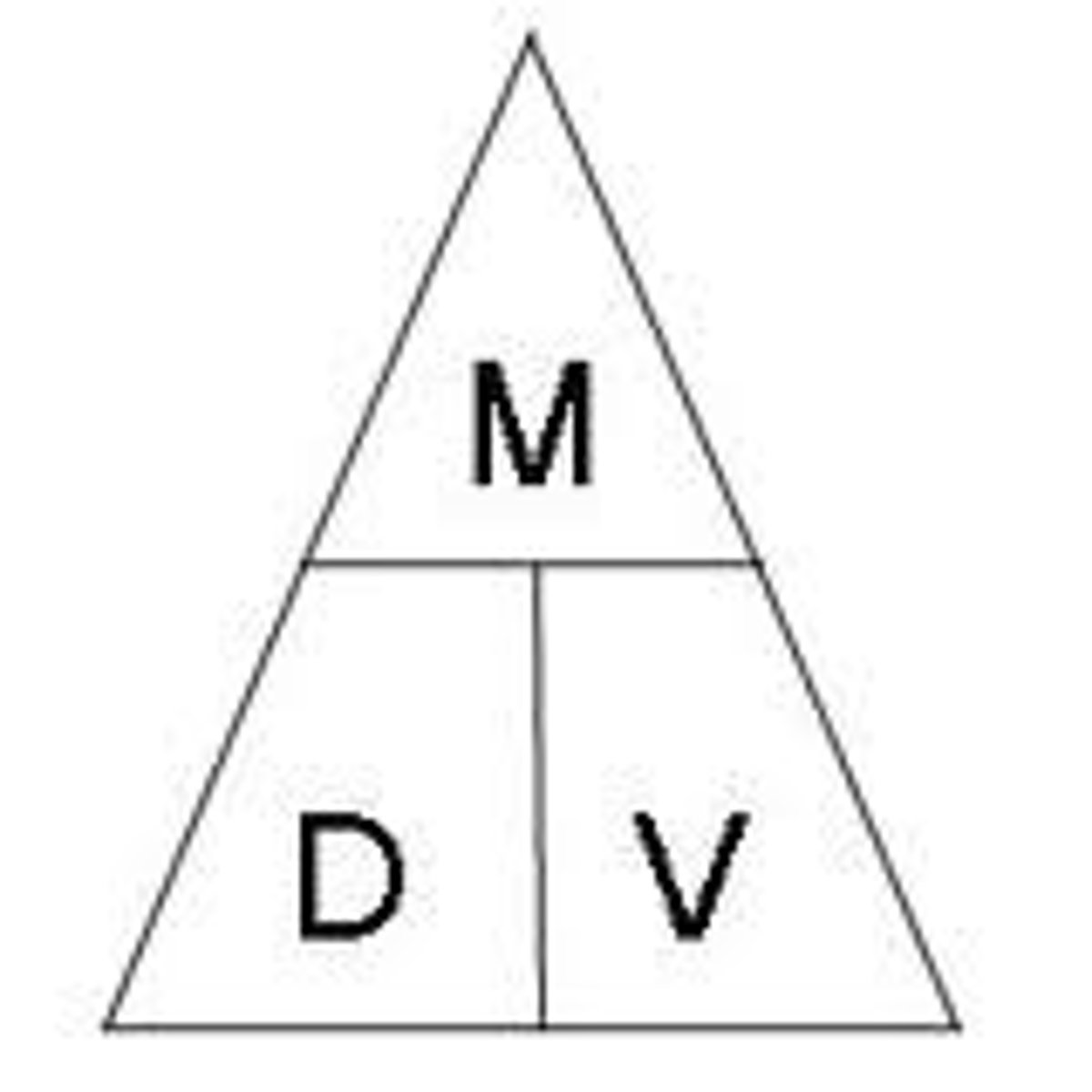
Equation for volume?
weight x length x height
How to calculate the density of a cuboid
measure weight, height and length
calculate the volume
find the mass of the object using a weighing scale
calculate the density
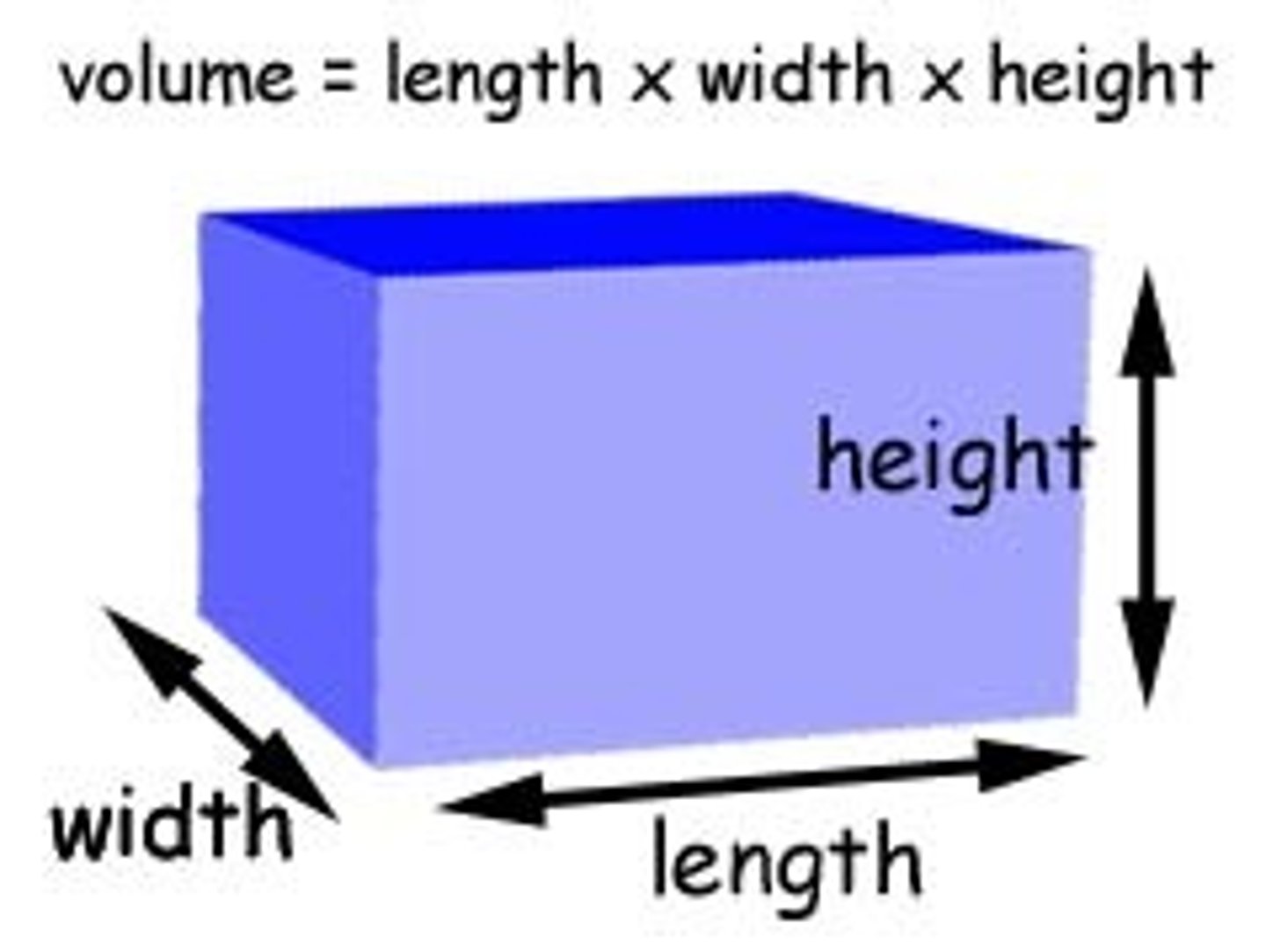
How to calculate the density of a liquid
weigh the measuring cylinder on a weighing scale
use a measuring cylinder to find the volume of a liquid
using a weighing scale calculate the mass
subtract the mass presented by the weighing scale by the mass of the measuring cylinder to get the mass of the liquid
calculate the density using volume / mass
How do you calculate the mass of the liquid using a weighing scale?
the empty container - the container with the liquid
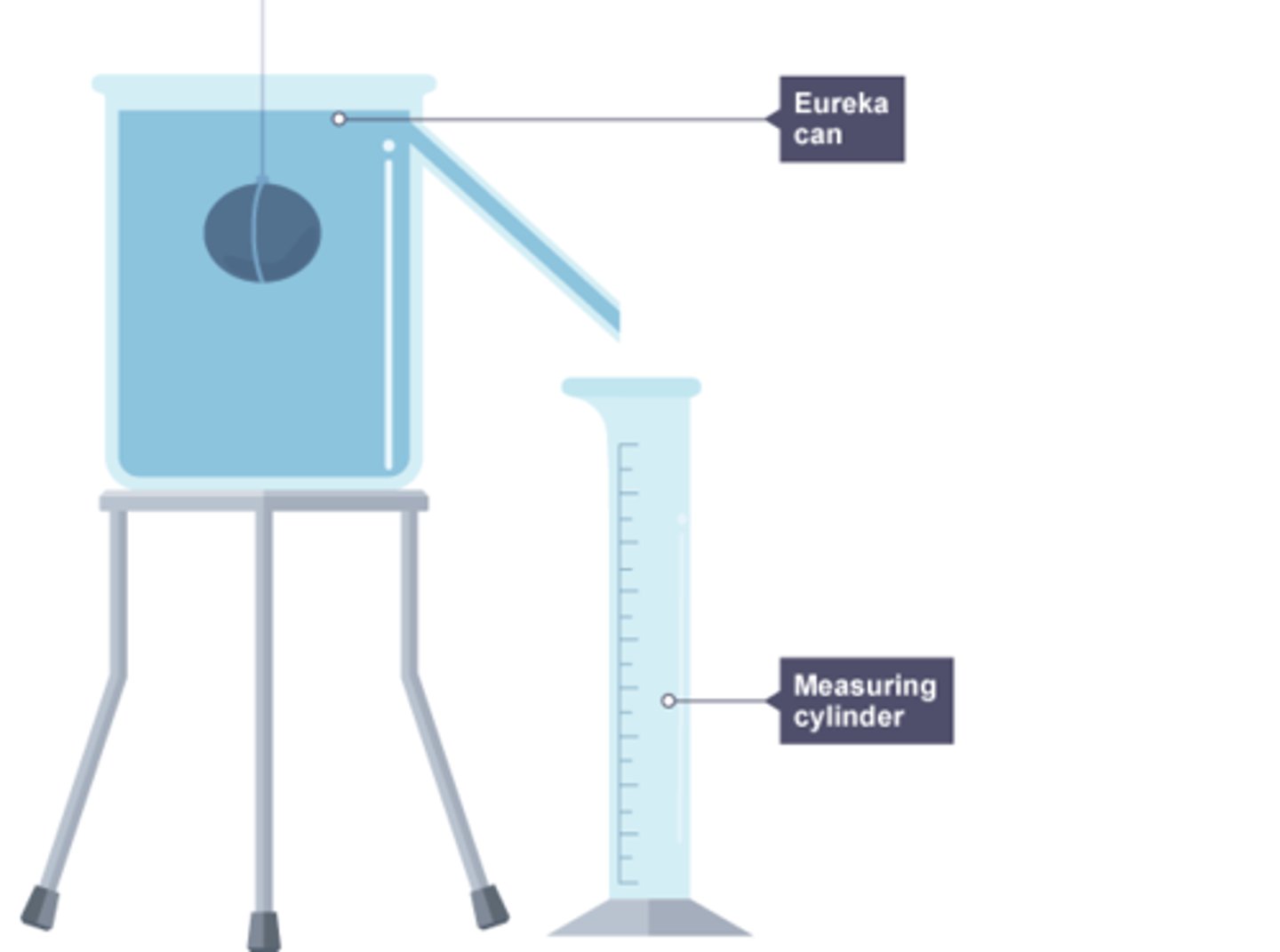
How to calculate the density of an irregular solid
measure the mass of the object using a weighing scale
fill the displacement can until the water is level with the bottom of the pipe
place a measuring cylinder under the pipe
submerge the shape in the can and wait until no more water runs out
measure the volume of the displaced water using the measuring cylinder
calculate the density
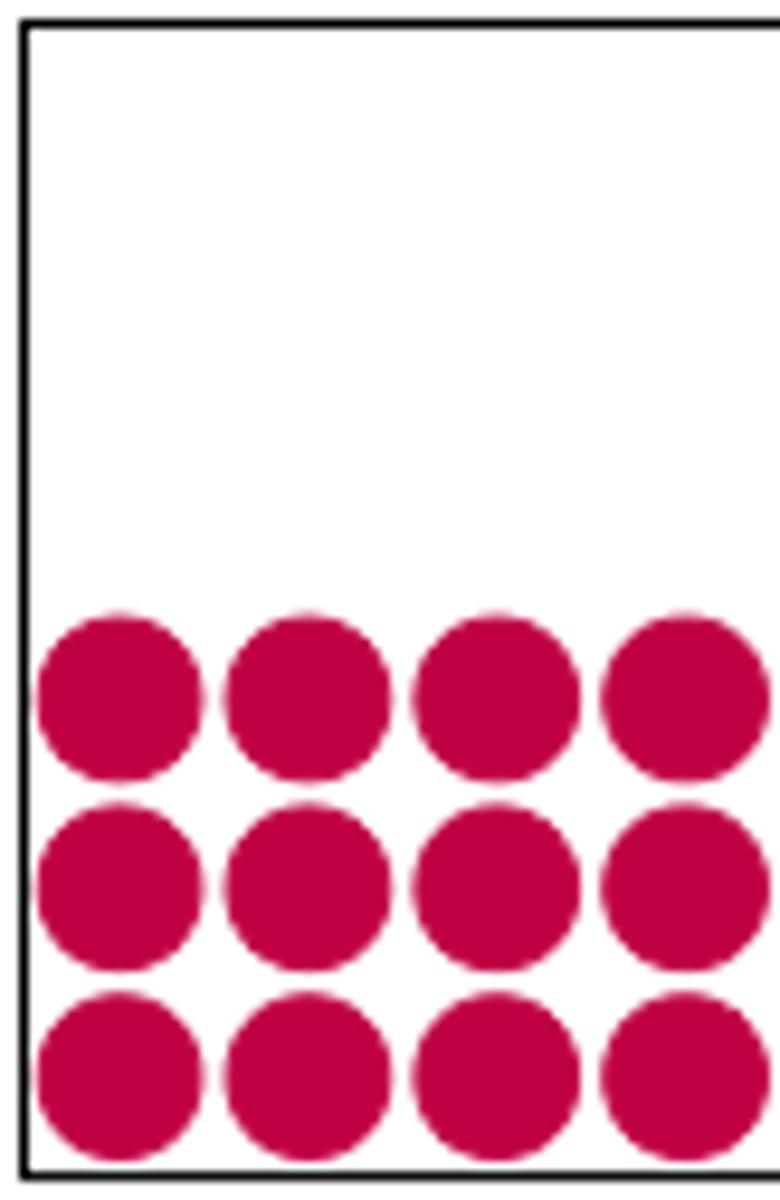
Describe a solid particle diagram / solid particle arrangement
particles are in a regular fixed pattern
particles vibrate on the spot
particles are very close together
very strong forces/bonds

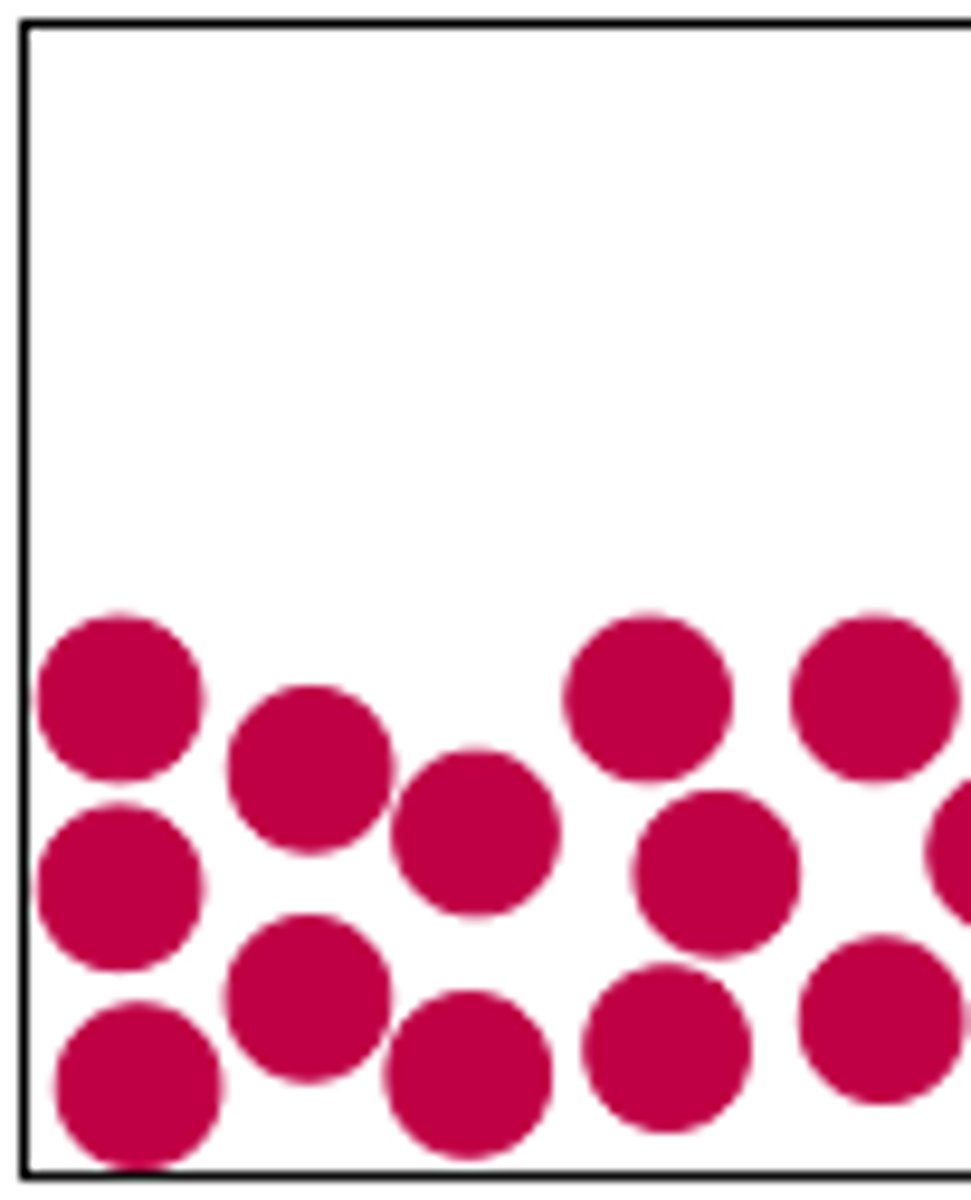
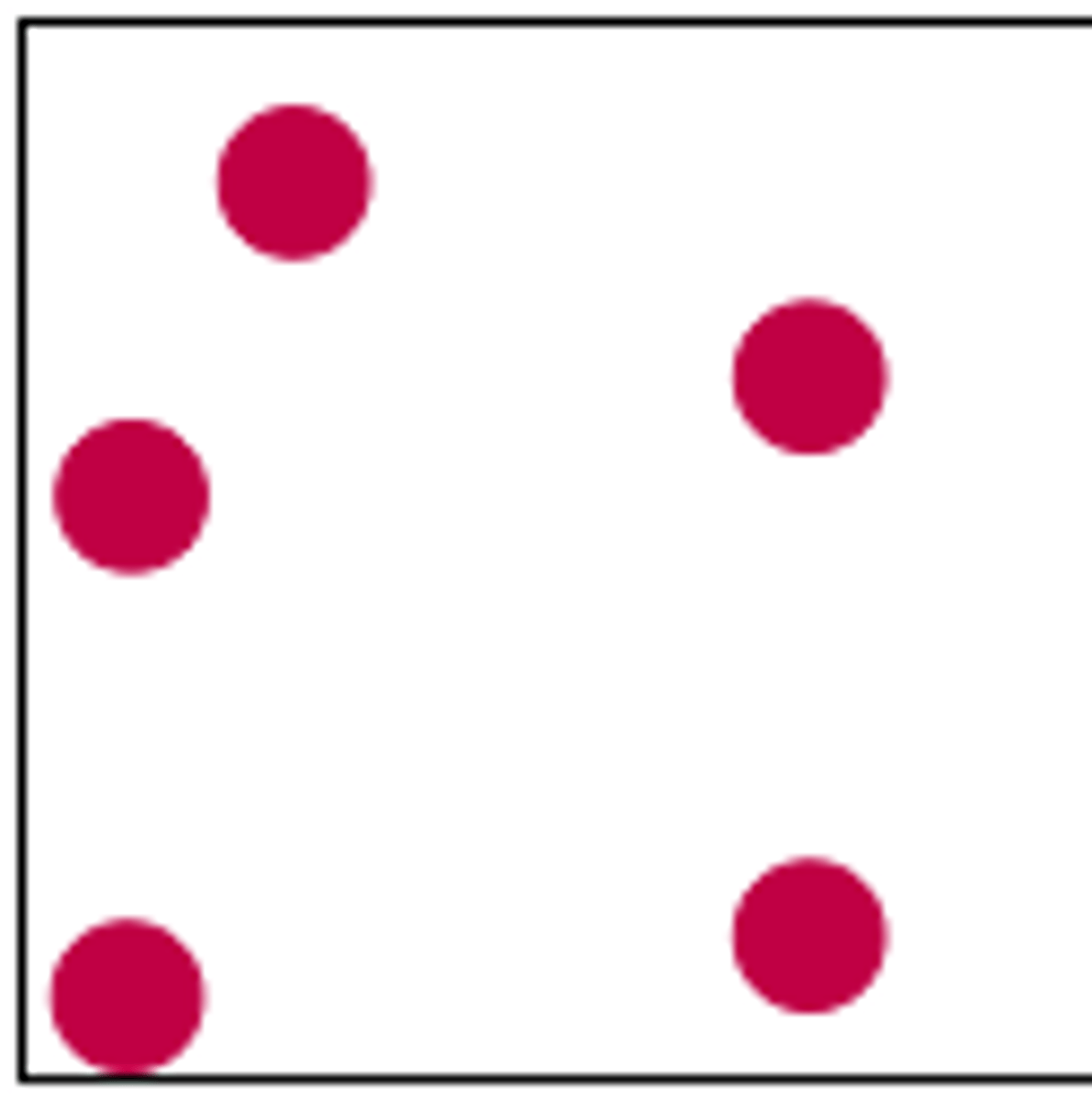
liquid particle diagram
particles are in a random pattern
particles slide
particles are close together
weak forces/bonds

gas particle diagram
particles have no pattern
particles move freely and in random directions
particles are far apart
negligible forces/bonds
What does negligible mean?
too small to be significant
Special properties of a solid?
densest
keeps it shape
particles vibrate faster when hotter
can't be compressed
Special properties of a liquid?
relatively dense
can flow
can't be compressed
Special properties of a gas?
least dense
can be compressed
What are the changes of state?
sublimation, deposition, melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation
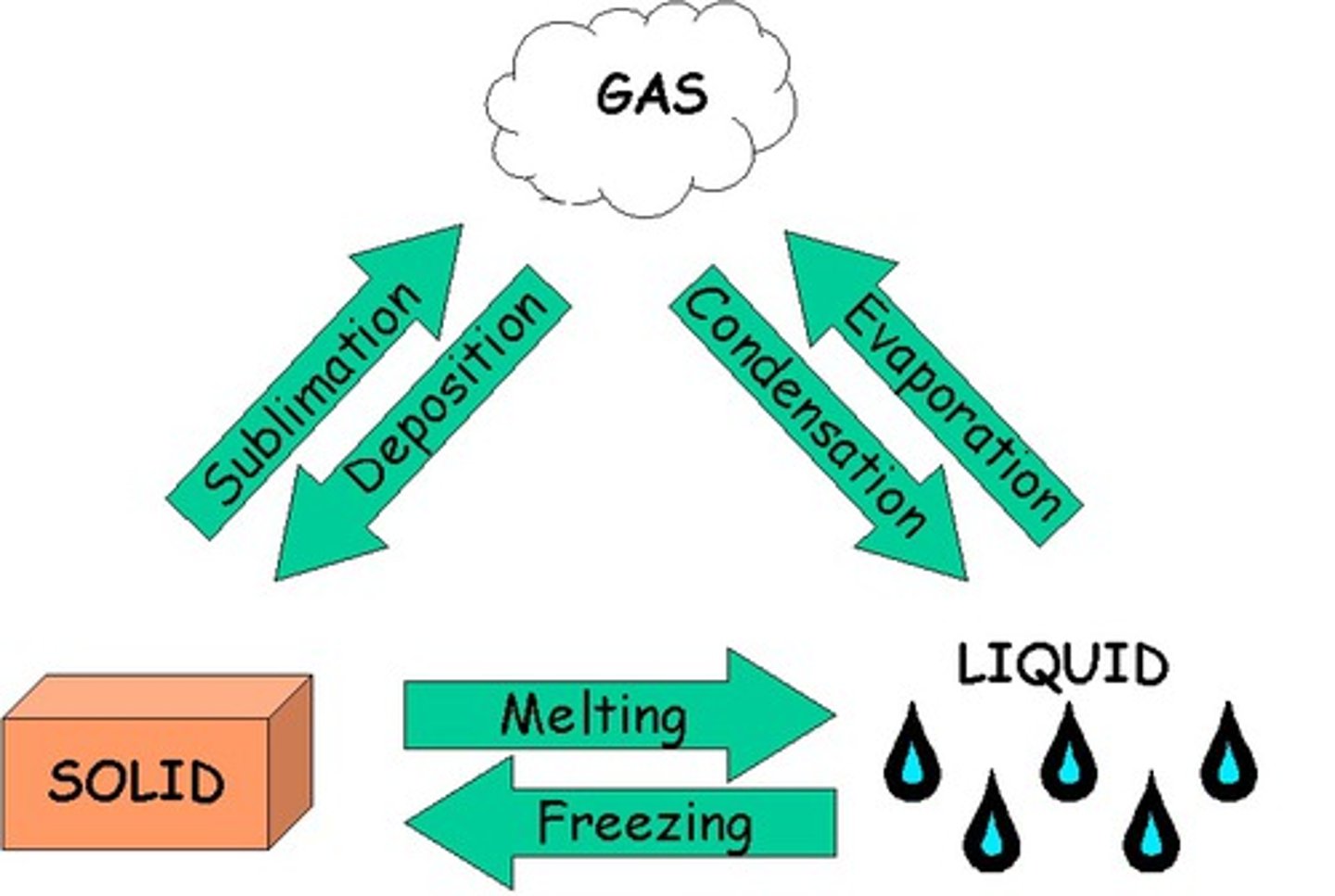
What is sublimation?
solid to gas
What is deposition?
gas to solid
What is melting?
solid to liquid
What is freezing or solidifying?
liquid to solid
What is condensation
gas to liquid
What is evaporation or boiling?
liquid to gas
Difference between evaporation and boiling?
boiling is when a liquid becomes a gas at the boiling point and evaporation is when a liquid becomes a gas below the boiling point with only the surface particles changing shape
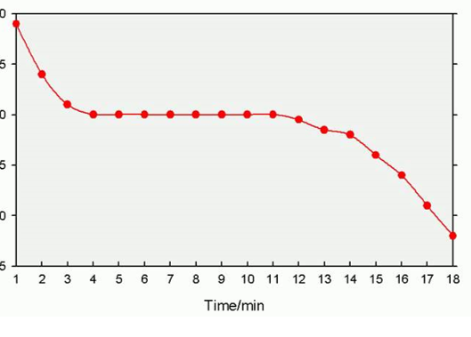
Describe the cooling stearic acid experiment
clamp the test tube of stearic acid
record the temperature every 2 minutes
What should we not do in a cooling stearic acid experiment?
don’t clamp too tightly otherwise the test tube will break
do not move the thermometer once in the stearic acid so it will be a more accurate reading
What happens to the particles during the stearic acid experiment
they organise into neat rows
What is internal energy?
energy stored by the particles that make up the system
Equation for internal energy?
sum of kinetic energy of particles + sum of the potential energy of the particles (the sum of all the energy in the particles)
What is potential energy?
the energy stored in the bonds/intermolecular forces when changing state (the energy of their bonds and arragngement)
What is kinetic energy?
energy of the particles motion
When does the kinetic energy of the particles change?
when the temperature changes
How to calculate your pressure on the ground?
draw the outline of your shoe and calculate the area of the sole
use the scale to measure your weight in Newtons
calculate the pressure
Equation for pressure?
force/area (f/a)
What is pressure?
the amount of force applied on a unit area (1m^2 or 1cm^2)
What is the correlation between area and pressure?
the smaller the area the larger the pressure
What is the correlation between force and pressure?
the larger the force the greater the pressure
how to increase pressure of a gas
pump in more gas
decrease the space
increase the temperature
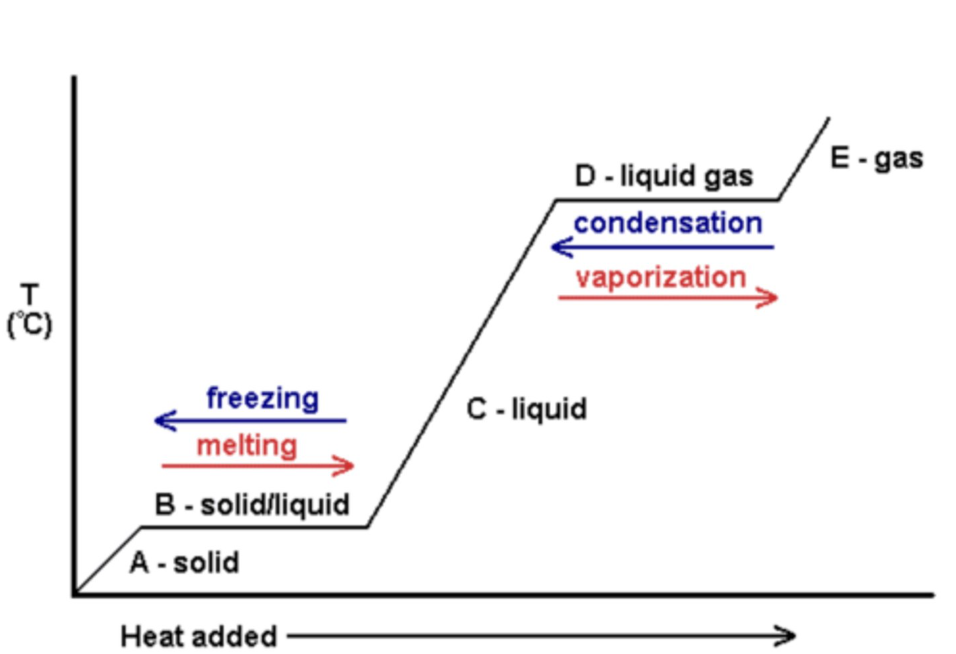
what happens to the energy and particles in a temperature time graph when it's a solid, liquid, gas (section a, c, e)
kinetic energy increases/decreases
the energy makes the particles move faster
internal energy increases/decreases
the particles move slightly apart
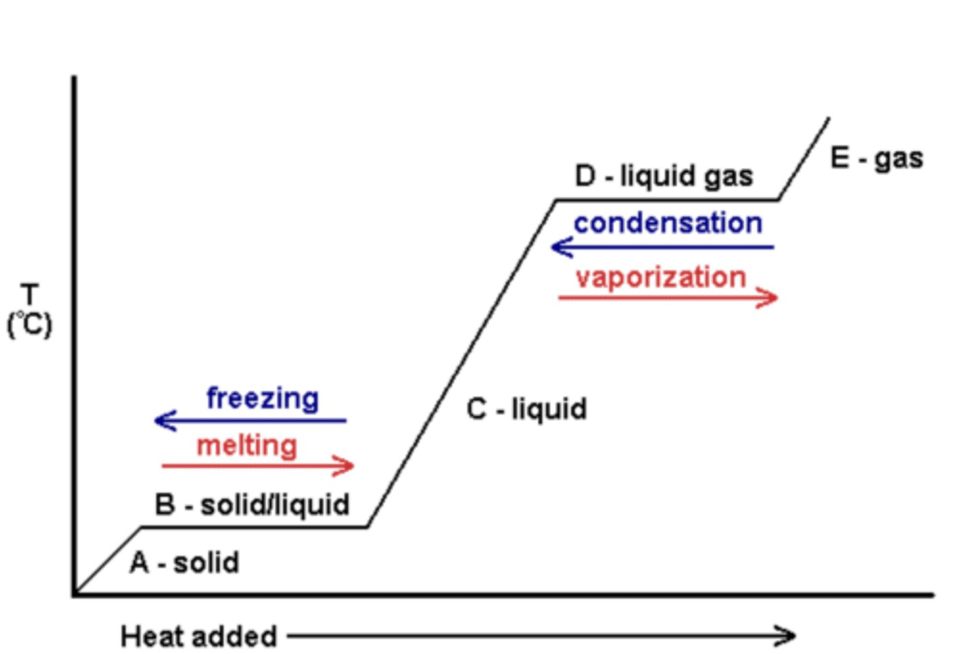
what happens to the energy and particles in a temperature time graph when it's changing state (section b, d)
potential energy increase/decrease
the energy is used to break the bonds/forces between particles
internal energy increases/decreases
the particles move slightly apart
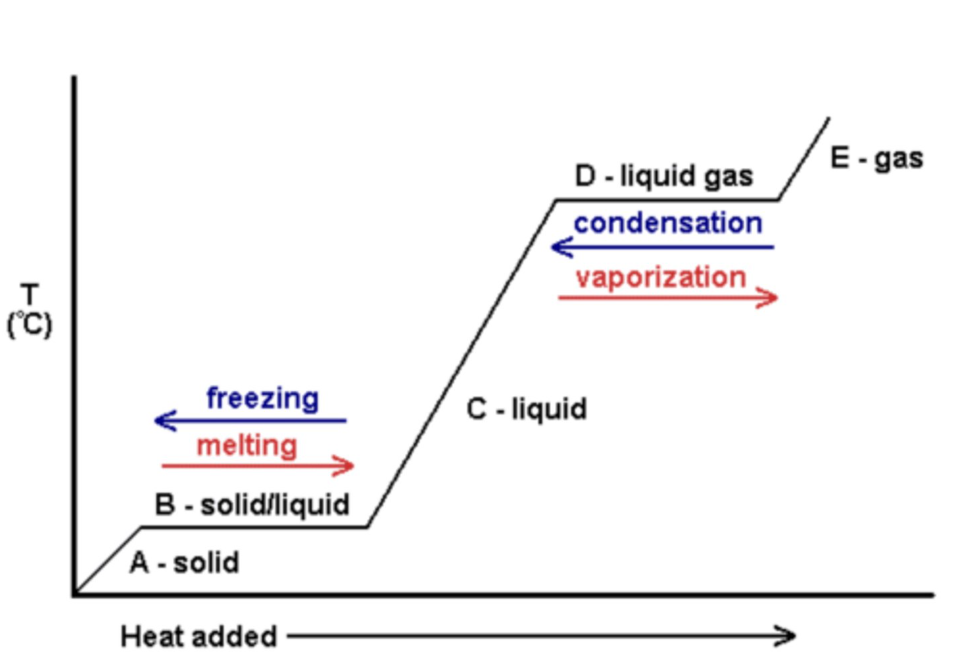
what happens to the substance/temperature in a temperature time graph when it's a solid, liquid, gas (section a, c, e)
the temperature changes rises/decreases until the boiling or melting point and the state is either solid liquid or gas
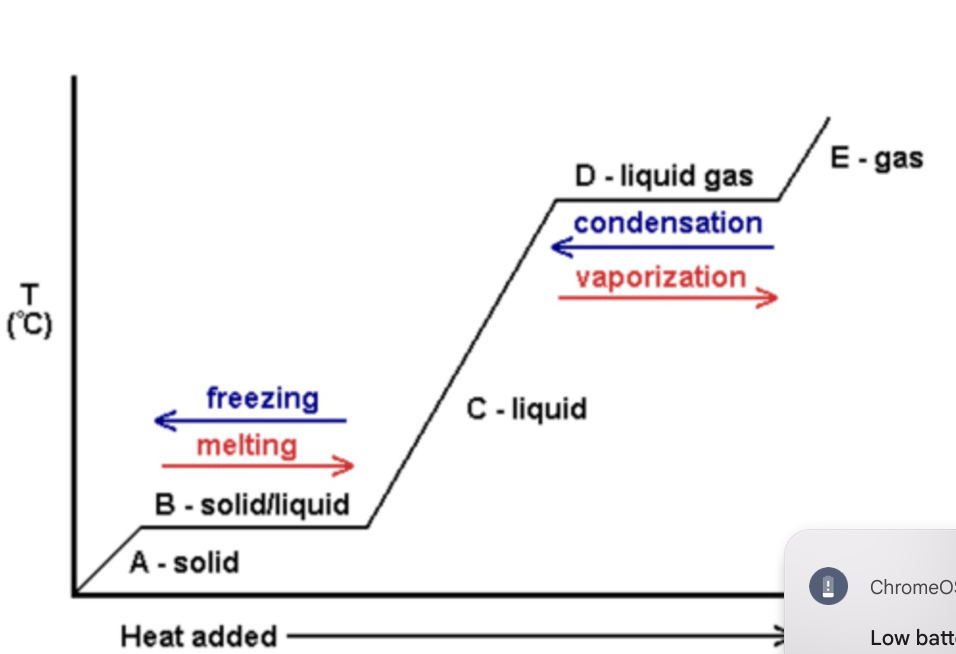
what happens to the substance/temperature in a temperature time graph when its changing state (sections b, d)
the temperature is steady and the state changes
What is the resolution in physics?
the smallest increment on an equipment
Example of resolution in physics?
1cm on a ruler
What is meniscus?
the bottom point in the curved upper surface of a liquid in a container
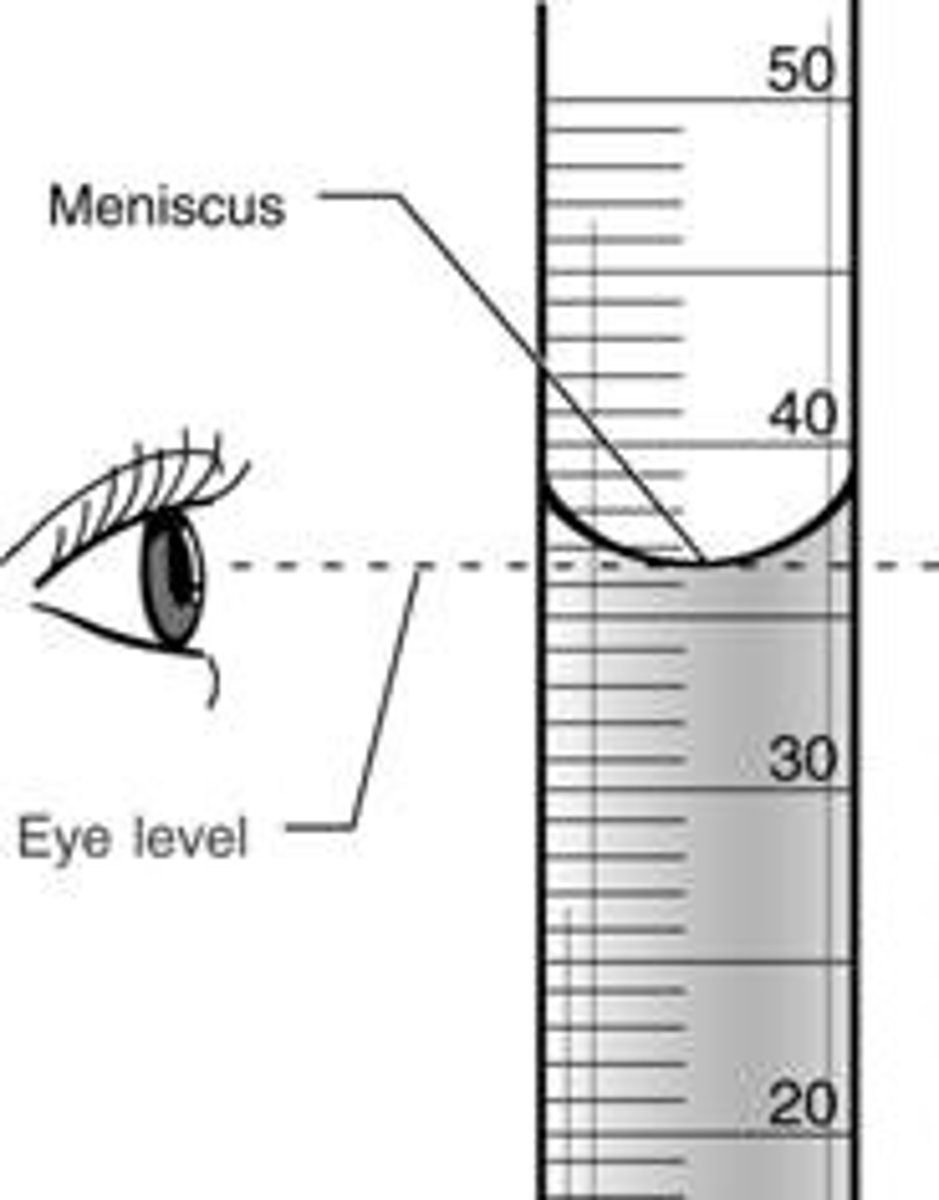
What is a parallax error?
when the volume of a liquid is read when the eye level is above or below the meniscus. It leads to inaccurate volumes being determined