2.5 economic growth
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
why is economics growth an important objective
increase econ growth - increase GDP - increase income - increase living standards
main causes for economic growth
AD - increase AD - increase Real GDP
AS - increase AS - increase productive capacity
factors that would increase AD therefore cause econ growth
Consumption
Investment
Govt expenditure
Net exports
what can cause an increase in AS
supply side policies
technological advances
relative productivity
changes in education + skills
2 types of econ growth
Short run growth (actual growth)
Long run growth (potential growth)
actual growth
the year-on-year increase in a country's real Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which reflects the economy's actual performance
features of actual growth
caused by increase in AD
can also be caused by increase in SRAS
can be achieved through changes in Govt policy
measured by increases in Real GDP
potential growth
Growth caused by the expansion of the economy’s productive capacity - Long run growth
features of potential growth
caused by increase in LRAS
UK long run growth estimated between 2-2.5%
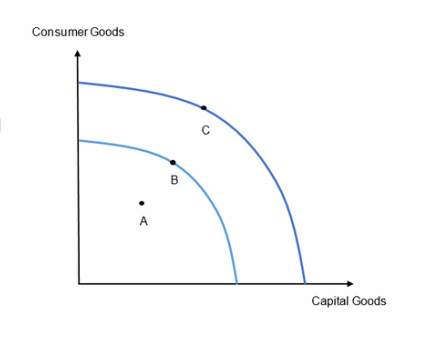
actual growth vs potential growth on a PPF
A-B - actual growth
B-C - potential growth
the importance of international trade for economic growth
increase in exports - increase AD
increase in net x(-m) - increase actual growth
increase x - should help trade balance (current account)
increase x - multiplier effect
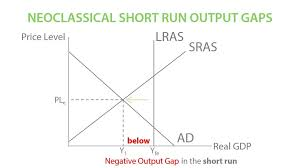
output gaps
whene there is a difference between actual vs potential growth
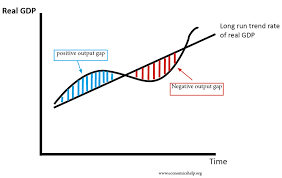
positive output gap
decreasing unemployment - increasing demand for resources
increase costs - increase inflation
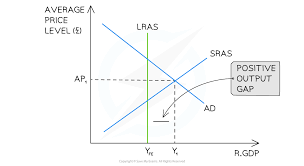
negative output gaps
occurs when actual growth< potential growth
increasing unemployment - decreasing AD
inflation likely to fall due to decrease AD (D.pull pressure) + decreasing costs
trade cycle
periodic fluctuations in economic activity, typically encompassing periods of expansion, followed by periods of contraction (recession), and then recovery
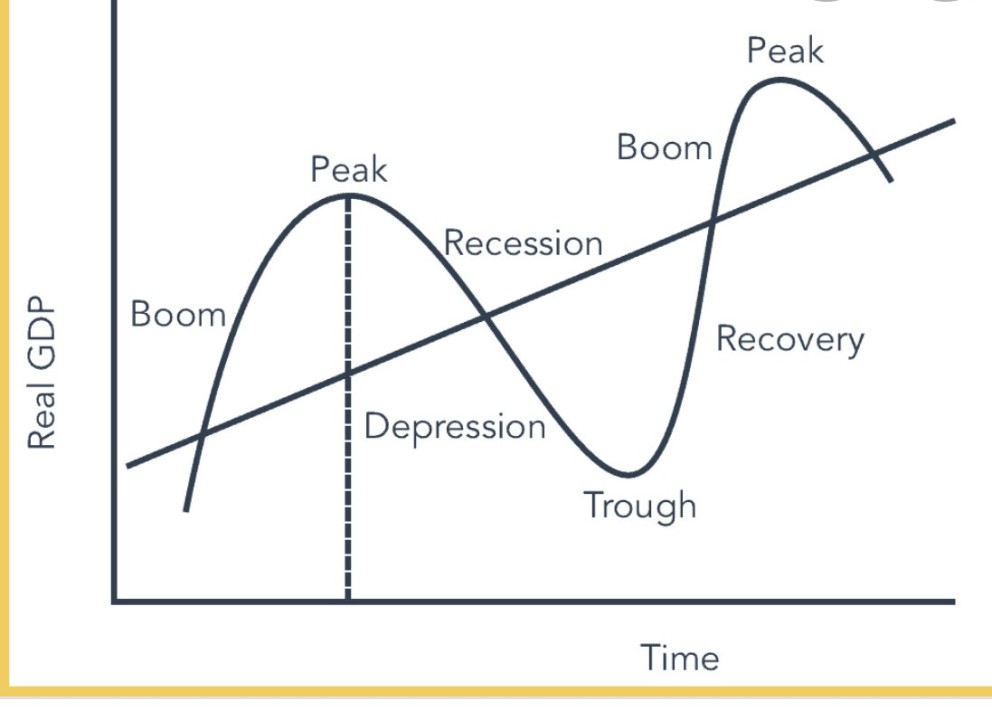
boom
the period where actual growth is above trend leading to a “peak”
recession
the period where actual growth falls (negative) for 2 successive quarters
characteristics of boom
above trend of economic growth
unemployment pull - low labour market - “skill shortages”
inflation rises
high business/consumer confidence
why are there skill shortages in a boom
low labour supply - where employers need certain skills but there is a low availbality of them
characteristics of a recession
low/falling econ growth
unemployment high
inflation pull is low (possible deflation)
low business and consumer confidence
benefits of econ growth
increase income
increase bus. confidence
increase emplyment
increase tax revenue
increase tax and decrease Govt spending - improve fiscal situation for Govt
costs of econ growth
increase negative externalities
increase inflation - costs of living
likely increase in wealth inequality
increase resource depletion and degradation - increase external costs
increase income - increase imports - worsen current account
impact of econ growth on consumers
increase in prices of houses and shares - leads to a positive wealth effect
improved technology could lead to lower prices or higher quality goods
may lead to increased happiness
could lead to increased externalities
may lead to inflation
impact of econ growth on firms
increase investment
increase business confidence
improved technology - lower costs
higher profits
firms that sell inferior goods may lose out
changing technologies may cause some markets to disappear e.g. DVD rental stores