BIOL 302 - Cell and Molecular Biology Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/186
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
1
New cards
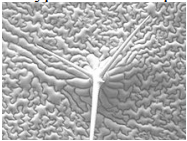
Type of microscope used to collect this image:
a. light microscope
b. scanning electron microscope
c. transmission electron microscope
d. fluorescence microscope
e. confocal microscope
a. light microscope
b. scanning electron microscope
c. transmission electron microscope
d. fluorescence microscope
e. confocal microscope
b. scanning electron microscope
2
New cards
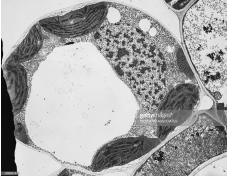
What type of cell is most likely shown below?
a. red blood cell
b. muscle cell
c. plant mesophyll cell
d. nerve cell
e. macrophage
a. red blood cell
b. muscle cell
c. plant mesophyll cell
d. nerve cell
e. macrophage
c. plant mesophyll cell
3
New cards
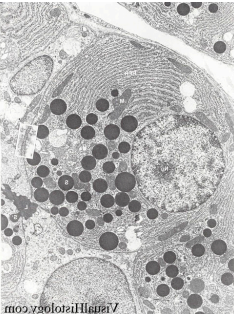
What is the function of this cell?
a. energy generation
b. photosynthesis
c. secretion
d. movement
e. support
a. energy generation
b. photosynthesis
c. secretion
d. movement
e. support
c. secretions
4
New cards
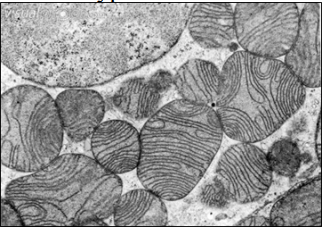
What type of cell is most likely shown below?
a. red blood cell
b. muscle cell
c. plant mesophyll cell
d. nerve cell
e. macrophage
a. red blood cell
b. muscle cell
c. plant mesophyll cell
d. nerve cell
e. macrophage
b. muscle cell
5
New cards
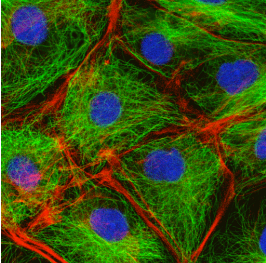
What part of the cell is labeled in blue?
a. nucleus
b. ER
c. mitochondria
d. Golgi
e. cytoskeleton
a. nucleus
b. ER
c. mitochondria
d. Golgi
e. cytoskeleton
a. nucleus
6
New cards
Which of the following molecules would not form hydrogen bonds?
a. CH3OH
b. CH3OCH3
c. CH3COOH
d. NH3
e. H2O
a. CH3OH
b. CH3OCH3
c. CH3COOH
d. NH3
e. H2O
b. CH3OCH3
7
New cards
Which of these reactions is most likely to take place spontaneously?
a. carbon dioxide being fixed into sugars
b. a glycogen molecule breaking into several sugar molecules
c. nucleotides forming a chain of nucleic acid
d. glucose molecules combining to make starch
a. carbon dioxide being fixed into sugars
b. a glycogen molecule breaking into several sugar molecules
c. nucleotides forming a chain of nucleic acid
d. glucose molecules combining to make starch
b. a glycogen molecule breaking into several sugar molecules
8
New cards
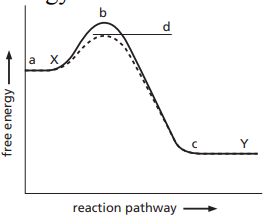
8\. In the free energy diagram for the reaction X → Y, ________ represents the change in free energy for the reaction. This diagram shows a __________ reaction.
a. a-c, spontaneous
b. c-b, non-spontaneous
c. b-a, spontaneous
d. a-b, non-spontaneous
e. c-a, spontaneous
a. a-c, spontaneous
b. c-b, non-spontaneous
c. b-a, spontaneous
d. a-b, non-spontaneous
e. c-a, spontaneous
e. c-a, spontaneous
9
New cards
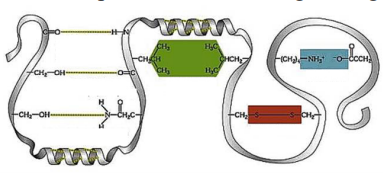
9\. Type of interaction highlighted with green hexagon.
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
c. hydrophobic interaction
10
New cards
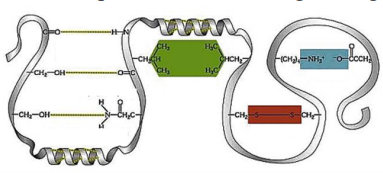
10\. Type of interaction highlighted with blue rectangle.
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
b. electrostatic attraction
11
New cards
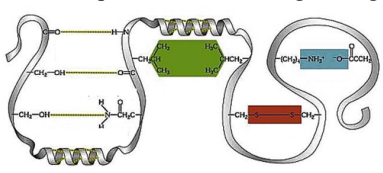
11\. Type of interaction highlighted with yellow dotted lines.
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
a. hydrogen bond
b. electrostatic attraction
c. hydrophobic interaction
d. peptide bond
e. disulfide bond
a. hydrogen bond
12
New cards
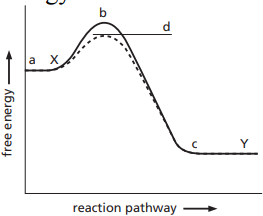
The solid line in the energy diagram represents changes in free energy as the reactant is converted to product under standard conditions. The dashed line shows changes observed when the same reaction takes place in the presence of an enzyme. Which answer below indicates how the presence of an enzyme affects the activation energy of the reaction (catalyzed versus uncatalyzed)?
a. d – c versus b – c
b. d – a versus b – a
c. a + d versus a + b
d. d – c versus b – a
e. none of the above
a. d – c versus b – c
b. d – a versus b – a
c. a + d versus a + b
d. d – c versus b – a
e. none of the above
b. d – a versus b – a
13
New cards
Organelle that is involved in synthesis of secreted proteins.
a. nucleus
b. endoplasmic reticulum
c. lysosome
d. golgi apparatus
e. mitochondria
a. nucleus
b. endoplasmic reticulum
c. lysosome
d. golgi apparatus
e. mitochondria
b. endoplasmic reticulum
14
New cards
Organelle that is involved in degradation of old unneeded proteins.
a. nucleus
b. endoplasmic reticulum
c. lysosome
d. Golgi apparatus
e. mitochondria
a. nucleus
b. endoplasmic reticulum
c. lysosome
d. Golgi apparatus
e. mitochondria
c. lysosome
15
New cards
Cell component which does not contain DNA.
a. nucleus
b. Golgi apparatus
c. chloroplast
d. mitochondria
a. nucleus
b. Golgi apparatus
c. chloroplast
d. mitochondria
b. Golgi apparatus
16
New cards
Cell component that consists of protein filaments that give a cell shape.
a. ribosomes
b. cytoskeleton
c. vesicles
d. plasma membrane
e. peroxisome
a. ribosomes
b. cytoskeleton
c. vesicles
d. plasma membrane
e. peroxisome
b. cytoskeleton
17
New cards
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
Cytosol
18
New cards
What substrates does glycolysis use?
1 glucose
2 ATP
2 NAD+
2 ATP
2 NAD+
19
New cards
What does glycolysis produce?
2 pyruvate
2 ATP
2 NADH (cytosol)
2 ATP
2 NADH (cytosol)
20
New cards
Does glycolysis require oxygen?
no
21
New cards
Where in the cell is pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA?
mitochondrial matrix
22
New cards
What substrates are used to convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
2 pyruvate
2 NAD+
2 NAD+
23
New cards
What does the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA produce?
2 acetyl CoA
2 CO2
2 NADH (matrix)
2 CO2
2 NADH (matrix)
24
New cards
Does the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA require oxygen?
no
25
New cards
Where does the citric acid cycle occur in the cell?
mitochondrial matrix
26
New cards
What substrates are needed during the citric acid cycle?
2 acetyl CoA
6 NAD+
2 FAD
6 NAD+
2 FAD
27
New cards
What is produced by the citric acid cycle?
4 CO2
6 NADH (matrix)
2 FADH2 (matrix)
2 GTP
6 NADH (matrix)
2 FADH2 (matrix)
2 GTP
28
New cards
Does the citric acid cycle require oxygen?
Yes but not directly;
needed to regenerate NAD+ and FAD
needed to regenerate NAD+ and FAD
29
New cards
Where is the electron transport chain located?
inner mitochondrial membrane
30
New cards
What substrates are in the electron transport chain?
10 NADH (2 from cytosol; 8 from mitochondrial matrix)
2 FADH2
Oxygen
2 FADH2
Oxygen
31
New cards
What are the products of the electron transport chain?
10 NAD+
2 FAD
H2O
26 ATP
2 FAD
H2O
26 ATP
32
New cards
Is oxygen required in the electron transport chain?
yes
33
New cards
Calculate the total yield of ATP from one glucose molecule.
total yield of ATP=30
2 ATP from glycolysis = 2 ATP
2 NADH from glycolysis (cytosol) x 1.5 = 3 ATP
8 NADH from prod. of acetyl CoA and citric acid cycle (mitochondrial matrix) x 2.5 = 20 ATP
2 FADH2 from citric acid cycle (mitochondrial matrix) x 1.5 = 3 ATP
2 GTP from citric acid cycle is converted to 2 ATP = 2 ATP
2 ATP from glycolysis = 2 ATP
2 NADH from glycolysis (cytosol) x 1.5 = 3 ATP
8 NADH from prod. of acetyl CoA and citric acid cycle (mitochondrial matrix) x 2.5 = 20 ATP
2 FADH2 from citric acid cycle (mitochondrial matrix) x 1.5 = 3 ATP
2 GTP from citric acid cycle is converted to 2 ATP = 2 ATP
34
New cards
In aerobic respiration carbohydrates are ultimately broken down into ________.
a. acetyl-CoA
b. CO2
c. O2
d. H2O
e. heat
a. acetyl-CoA
b. CO2
c. O2
d. H2O
e. heat
b. CO2
35
New cards
Most ATP in eukaryotic cells is produced in the __________.
a. mitochondria
b. nucleus
c. cytoplasm
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum
e. peroxisome
a. mitochondria
b. nucleus
c. cytoplasm
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum
e. peroxisome
a. mitochondria
36
New cards
Most ATP produced in aerobic respiration occurs by _________.
a. glycolysis
b. the formation of acetyl-CoA
c. the citric acid cycle
d. oxidative phosphorylation
a. glycolysis
b. the formation of acetyl-CoA
c. the citric acid cycle
d. oxidative phosphorylation
d. oxidative phosphorylation
37
New cards
In glycolysis, the activation of glucose is accomplished by ______.
a. NADH
b. coenzyme A
c. ATP
d. CO2
e. O2
a. NADH
b. coenzyme A
c. ATP
d. CO2
e. O2
c. ATP
38
New cards
The final electron acceptor in cellular respiration is _______.
a. pyruvate
b. CO2
c. O2
d. H2O
e. NAD+
a. pyruvate
b. CO2
c. O2
d. H2O
e. NAD+
c. O2 (oxygen)
39
New cards
Which stage of cellular respiration requires ATP?
a. glycolysis
b. citric acid cycle
c. electron transport chain
d. none of the above
a. glycolysis
b. citric acid cycle
c. electron transport chain
d. none of the above
a. glycolysis
40
New cards
As protons flow through ______, energy is released and exploited to combine ADP and inorganic phosphate to form ATP.
a. the electron transport chain
b. the outer mitochondrial membrane
c. cytochrome oxidase
d. ATP synthase
e. NADH
a. the electron transport chain
b. the outer mitochondrial membrane
c. cytochrome oxidase
d. ATP synthase
e. NADH
d. ATP synthase
41
New cards
10\. Cyanide poisoning can be deadly. What is a plausible reason for why taking barbiturates is not toxic if it also inhibits part of the electron transport chain?
a. NADH can still donate electrons at Complex II with barbiturate inhibition of the electron transport chain.
b. FADH2 can still donate electrons at Complex II with barbiturate poisoning.
c. Cyanide inhibition of Complex IV also inhibits ATP synthase.
d. Electrons from NADH can still flow downstream of Complex I with barbiturate inhibition of the electron transport chain.
a. NADH can still donate electrons at Complex II with barbiturate inhibition of the electron transport chain.
b. FADH2 can still donate electrons at Complex II with barbiturate poisoning.
c. Cyanide inhibition of Complex IV also inhibits ATP synthase.
d. Electrons from NADH can still flow downstream of Complex I with barbiturate inhibition of the electron transport chain.
b. FADH2 can still donate electrons at Complex II with barbiturate poisoning.
42
New cards
All of the following will decrease the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain except _________.
a. cyanide
b. increased levels of NADH
c. increased levels of ATP
d. carbon monoxide
a. cyanide
b. increased levels of NADH
c. increased levels of ATP
d. carbon monoxide
b. increased levels of NADH
43
New cards
An inhibitor of Complex II would cause all of the following except ______________.
a. an unchanged proton concentration in the inter-membrane space
b. potential damage to cells from reactive oxygen species (build-up of O2)
c. a build-up of FADH2
d. impaired oxidative phosphorylation
a. an unchanged proton concentration in the inter-membrane space
b. potential damage to cells from reactive oxygen species (build-up of O2)
c. a build-up of FADH2
d. impaired oxidative phosphorylation
a. an unchanged proton concentration in the inter-membrane space
44
New cards
Why is more ATP produced per molecule of NADH than FADH2?
a. NADH donates its electrons at Complex I.
b. NADH is in its reduced form and FADH2 is in its oxidized form.
c. FADH2 donates its electrons at Complex IV.
d. More NADH is produced in the citric acid cycle than FADH2
a. NADH donates its electrons at Complex I.
b. NADH is in its reduced form and FADH2 is in its oxidized form.
c. FADH2 donates its electrons at Complex IV.
d. More NADH is produced in the citric acid cycle than FADH2
a. NADH donates its electrons at Complex I.
45
New cards
Which of the following statements about cellular respiration is true?
a. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle occur in the same cellular compartment.
b. More ATP is generated by glycolysis than by oxidative phosphorylation.
c. The protein complexes of the electron transport chain are located in the plasma membrane.
d. The citric acid cycle does not use O2 but cannot proceed without it.
e. Respiration occurs in animals but not plants.
a. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle occur in the same cellular compartment.
b. More ATP is generated by glycolysis than by oxidative phosphorylation.
c. The protein complexes of the electron transport chain are located in the plasma membrane.
d. The citric acid cycle does not use O2 but cannot proceed without it.
e. Respiration occurs in animals but not plants.
d. The citric acid cycle does not use O2 but cannot proceed without it.
46
New cards
If a cell lacks mitochondria, how much ATP would be produced per breakdown of one glucose molecule?
a. 2
b. 4
c. none
d. 30
e. 28
a. 2
b. 4
c. none
d. 30
e. 28
a. 2
47
New cards
A nucleosome core particle is made up of ____________.
a. the core histones and RNA
b. the core histones and DNA
c. histone H1 and DNA
d. histone H1 and RNA
a. the core histones and RNA
b. the core histones and DNA
c. histone H1 and DNA
d. histone H1 and RNA
b. the core histones and DNA
48
New cards
Why is it important for histones to be positively charged?
a. so they can bind to each other
b. so they can bind to DNA
c. so they can bind to RNA
d. both a and b
a. so they can bind to each other
b. so they can bind to DNA
c. so they can bind to RNA
d. both a and b
b. so they can bind to DNA
49
New cards
How many different types of histones are in a nucleosome core particle?
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
e. five
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
e. five
d. four
50
New cards
Which of the following statements is false?
a. Changes in chromatin structure are associated with changes in gene expression.
b. Nucleosomes serve to compact DNA inside the nucleus.
c. The first level of chromatin compaction is the "beads on a string" from.
d. The most compacted form of chromatin is a mitotic chromosome.
e. Heterochromatin is the least compacted form of an interphase chromosome.
a. Changes in chromatin structure are associated with changes in gene expression.
b. Nucleosomes serve to compact DNA inside the nucleus.
c. The first level of chromatin compaction is the "beads on a string" from.
d. The most compacted form of chromatin is a mitotic chromosome.
e. Heterochromatin is the least compacted form of an interphase chromosome.
e. Heterochromatin is the least compacted form of an interphase chromosome.
51
New cards
Which of the following statements about chromatin is true?
a. Chromatin that involves histones is present in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
b. Nucleosomes consist of DNA wrapped around proteins known as chromatin remodeling proteins.
c. Chromatin never gets further compacted than the 30nm chromatin fiber.
d. Patterns of methylation or acetylation of histones can regulate gene expression.
a. Chromatin that involves histones is present in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
b. Nucleosomes consist of DNA wrapped around proteins known as chromatin remodeling proteins.
c. Chromatin never gets further compacted than the 30nm chromatin fiber.
d. Patterns of methylation or acetylation of histones can regulate gene expression.
d. Patterns of methylation or acetylation of histones can regulate gene expression.
52
New cards
Which of the following correctly describes eukaryotic histones in a nucleosome structure?
a. A core histone heptamer plus a linker histone
b. A core histone octamer plus a linker histone
c. A core histone plus a linker histone octamer
d. A core histone octamer plus 2 linker histones
e. A core histone nonamer
a. A core histone heptamer plus a linker histone
b. A core histone octamer plus a linker histone
c. A core histone plus a linker histone octamer
d. A core histone octamer plus 2 linker histones
e. A core histone nonamer
b. A core histone octamer plus a linker histone
53
New cards
Which level of protein structure is stabilized primarily by hydrogen bonding?
a. Tertiary structure
b. Secondary structure
c. Primary structure
d. Quaternary structure
a. Tertiary structure
b. Secondary structure
c. Primary structure
d. Quaternary structure
b. secondary structure
54
New cards
What functional group is created when amino acids are joined together?
a. ketone
b. carboxylic acid
c. amide
d. ester
a. ketone
b. carboxylic acid
c. amide
d. ester
c. amide
55
New cards
Which of the following contributes to the primary structure of a protein?
a. Hydrophobic interactions
b. Peptide bonding between amino acids
c. Hydrogen bonding between R groups
d. Hydrogen bonding between an amine and carbonyl group
a. Hydrophobic interactions
b. Peptide bonding between amino acids
c. Hydrogen bonding between R groups
d. Hydrogen bonding between an amine and carbonyl group
b. Peptide bonding between amino acids
56
New cards
You are given the amino acid sequence Ala-Gly-His-Tyr. This is an example of which level of protein structure?
a. Secondary
b. Primary
c. Tertiary
d. Quaternary
a. Secondary
b. Primary
c. Tertiary
d. Quaternary
b. primary
57
New cards
The term "denaturation," when used in conjunction with proteins or nucleic acids, refers to a change in structural characteristics primarily due to __________.
a. changes in primary structure
b. the disruption of noncovalent bonds
c. the disruption of covalent bonds
d. none of the above
a. changes in primary structure
b. the disruption of noncovalent bonds
c. the disruption of covalent bonds
d. none of the above
b. the disruption of noncovalent bonds
58
New cards
Proteins that covalently add an acetyl group to the tail of the core histones and alters chromatin structure are a type of _____________.
a. helicase
b. histone modifying enzyme
c. chromatin remodeling proteins
d. protease
a. helicase
b. histone modifying enzyme
c. chromatin remodeling proteins
d. protease
b. histone modifying enzyme
59
New cards
A nucleosome core particle is composed of:
a. two copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 147 bp of DNA
b. two copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 1470 bp of DNA
c. four copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 147 bp of DNA
d. four copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 1470 bp of DNA
a. two copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 147 bp of DNA
b. two copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 1470 bp of DNA
c. four copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 147 bp of DNA
d. four copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 1470 bp of DNA
a. two copies each of histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 and 147 bp of DNA
60
New cards
True or False
Okazaki fragments are short segments of newly synthesized DNA.
Okazaki fragments are short segments of newly synthesized DNA.
True
61
New cards
True or False
Okazaki fragments are formed as part of synthesis of the leading strand of DNA.
Okazaki fragments are formed as part of synthesis of the leading strand of DNA.
False, synthesis of the lagging strand of DNA.
62
New cards
True or False
Okazaki fragments have a short stretch of RNA at their 5' end.
Okazaki fragments have a short stretch of RNA at their 5' end.
True, primase initiates each Okazaki fragment with an RNA primer
63
New cards
True or False
Okazaki fragments account for the overall synthesis of one DNA strand in a 3' to 5' direction.
Okazaki fragments account for the overall synthesis of one DNA strand in a 3' to 5' direction.
True, Each Okazaki fragment is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction but the overall growth of the lagging strand occurs in the 3' to 5' direction
64
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to open up the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases
Uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to open up the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases
helicase
65
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Coats DNA that is single-stranded
Coats DNA that is single-stranded
single-strand binding protein
66
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Initiates DNA synthesis by synthesizing an RNA primer
Initiates DNA synthesis by synthesizing an RNA primer
primase
67
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Adds nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand using a parental strand as a template
Adds nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand using a parental strand as a template
DNA polymeras
68
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Holds DNA polymerase onto the DNA template strand
Holds DNA polymerase onto the DNA template strand
sliding clamp
69
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Attaches sliding clamp to the DNA
Attaches sliding clamp to the DNA
clamp loader
70
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Removes the RNA primer from newly synthesized DNA strands
Removes the RNA primer from newly synthesized DNA strands
nuclease
71
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the previous Okazaki fragment; this fills in the gap in the DNA left by the nuclease
Adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the previous Okazaki fragment; this fills in the gap in the DNA left by the nuclease
DNA repair polymerase
72
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Joins DNA fragments together by forming a phosphodiester bond between the 3' OH of one DNA fragment and the 5' phosphate of the adjacent DNA fragment
Joins DNA fragments together by forming a phosphodiester bond between the 3' OH of one DNA fragment and the 5' phosphate of the adjacent DNA fragment
DNA ligase
73
New cards
Which enzyme performs this function during DNA replication?
Nicks the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA to relieve the tension in DNA created during DNA replication
Nicks the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA to relieve the tension in DNA created during DNA replication
DNA topoisomerase
74
New cards
True or False
DNA replication in eukaryotes is a bidirectional process.
DNA replication in eukaryotes is a bidirectional process.
True, at each replication origin there are two replication forks that move in opposite directions away from the origin
75
New cards
True or False
DNA replication is a semiconservative process.
DNA replication is a semiconservative process.
True, each product of replication consists of one old DNA strand and one newly synthesized DNA strand
76
New cards
True or False
The replication fork is symmetric
The replication fork is symmetric
False, the replication fork is asymmetric meaning that one newly synthesized strand grows overall at its 3' end and one newly synthesized strand grows overall at its 5' end
77
New cards
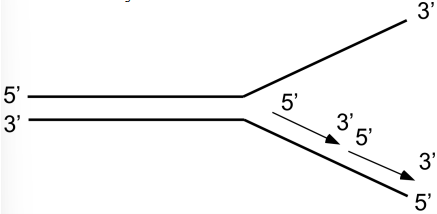
Which Okazaki fragment will be synthesized first?
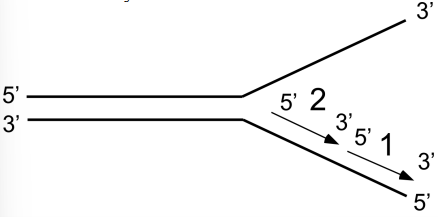
78
New cards
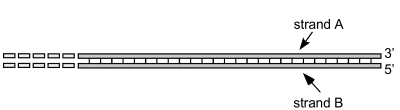
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____Replication of this strand involves several primer molecules.
_____Replication of this strand involves several primer molecules.
__A__ Replication of this strand involves several primer molecules.
79
New cards
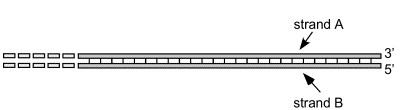
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____Replication of this strand involves a single primer molecule.
_____Replication of this strand involves a single primer molecule.
___B___ Replication of this strand involves a single primer molecule
80
New cards
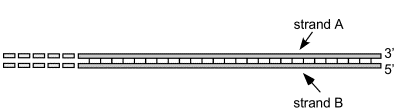
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____Okazaki fragments are synthesized using this strand as a template.
_____Okazaki fragments are synthesized using this strand as a template.
__A__ Okazaki fragments are synthesized using this strand as a template
81
New cards
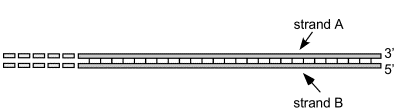
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____ This strand is for the leading strand template.
_____ This strand is for the leading strand template.
__B__ This strand is the leading strand template.
82
New cards
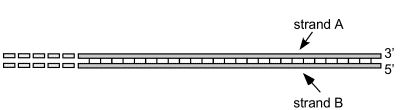
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____ This strand is the lagging strand template.
_____ This strand is the lagging strand template.
__A__ This strand is the lagging strand template
83
New cards
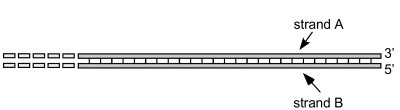
Associate each statement below with one or both of the strands. Fill in A, B or A+B to indicate strand A, strand B or both strands.
_____ The regular DNA replication machinery of the cell cannot prevent the shortening of this strand during successive replication cycles.
_____ The regular DNA replication machinery of the cell cannot prevent the shortening of this strand during successive replication cycles.
__A__ The regular DNA replication machinery of the cell cannot prevent the shortening of this strand during successive replication cycles.
84
New cards
What is the role of telomerase RNA in telomere lengthening?
a. it acts as a template
b. it acts as a primer
c. both a and b
a. it acts as a template
b. it acts as a primer
c. both a and b
a. it acts as a template
85
New cards
What kind of enzyme is telomerase?
a. DNA polymerase
b. RNA polymerase
c. Topoisomerase
d. Reverse transcriptase
a. DNA polymerase
b. RNA polymerase
c. Topoisomerase
d. Reverse transcriptase
d. Reverse transcriptase
86
New cards
The low error rate of DNA replication results from _________.
a. the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase
b. DNA mismatch repair
c. the ability of primase to fix errors made by DNA polymerase
d. both a and b
e. both b and c
a. the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase
b. DNA mismatch repair
c. the ability of primase to fix errors made by DNA polymerase
d. both a and b
e. both b and c
d. both a and b
87
New cards
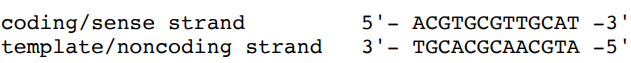
Given the coding strand of a DNA molecule shown below, fill in the sequence of the template strand and write the RNA strand that is made from the template strand.
\
\

88
New cards
Nitrogenous bases found in RNA.
a. adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
b. uracil, thymine, guanine, cytosine
c. adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
d. adenine, thymine, cytosine, uracil
e. adenine, guanine, thymine, uracil
a. adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
b. uracil, thymine, guanine, cytosine
c. adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
d. adenine, thymine, cytosine, uracil
e. adenine, guanine, thymine, uracil
c. adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
89
New cards
Which of the following statements about transcription is true?
a. It is the copying of both stands of DNA into complementary RNA molecules.
b. It is carried out on the entire sequence of a chromosome.
c. All genes are transcribed the same amount to produce equal numbers of mRNAs.
d. It produces a RNA molecule that is complementary to the sense strand of DNA.
e. It occurs in the 5' to 3' direction.
a. It is the copying of both stands of DNA into complementary RNA molecules.
b. It is carried out on the entire sequence of a chromosome.
c. All genes are transcribed the same amount to produce equal numbers of mRNAs.
d. It produces a RNA molecule that is complementary to the sense strand of DNA.
e. It occurs in the 5' to 3' direction.
e. It occurs in the 5' to 3' direction.
90
New cards
Which of the following are not noncoding RNAs?
a. mRNAs
b. tRNAs
c. rRNAs
d. miRNAs
a. mRNAs
b. tRNAs
c. rRNAs
d. miRNAs
a. mRNAs
91
New cards
Which of the following is true of RNA polymerase but not of DNA polymerase?
a. it has no proofreading ability
b. it synthesizes a nucleic acid in the 5' to 3' direction
c. it requires a primer
d. none of the above
a. it has no proofreading ability
b. it synthesizes a nucleic acid in the 5' to 3' direction
c. it requires a primer
d. none of the above
a. it has no proofreading ability
92
New cards
Cell structure that contains the genetic material of a eukaryotic cell.
a. nucleus
b. golgi apparatus
c. ribosome
d. peroxisome
e. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a. nucleus
b. golgi apparatus
c. ribosome
d. peroxisome
e. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a. nucleus
93
New cards
Type of electron microscopy that provides information on the surface features of cells.
a. transmission electron microscope
b. light microscopy
c. fluorescent microscopy
d. scanning electron microscopy
a. transmission electron microscope
b. light microscopy
c. fluorescent microscopy
d. scanning electron microscopy
d. scanning electron microscopy
94
New cards
Which of the following statements about spontaneous reactions is true?
a. Energy is absorbed
b. They are energetically unfavorable
c. Delta G is negative
d. They need to be coupled to nonspontaneous reactions to occur
a. Energy is absorbed
b. They are energetically unfavorable
c. Delta G is negative
d. They need to be coupled to nonspontaneous reactions to occur
c. Delta G is negative
95
New cards
Which of the following processes is an example of an anabolic pathway?
a. glycolysis
b. protein synthesis
c. DNA degradation
d. breakdown of fat
a. glycolysis
b. protein synthesis
c. DNA degradation
d. breakdown of fat
b. protein synthesis
96
New cards
Which of the following molecules is hydrophilic?
a. fats
b. CH4
c. alkanes
d. glucose
e. C2H4
a. fats
b. CH4
c. alkanes
d. glucose
e. C2H4
d. glucose
97
New cards
Organelle involved in protein modification and sorting.
a. peroxisome
b. chloroplast
c. nucleus
d. golgi apparatus
e. lysosome
a. peroxisome
b. chloroplast
c. nucleus
d. golgi apparatus
e. lysosome
d. golgi apparatus
98
New cards
Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells is false?
a. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles
b. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus
c. Prokaryotic cells are small and primitive
d. Many prokaryotic organisms consist of a single cell.
a. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles
b. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus
c. Prokaryotic cells are small and primitive
d. Many prokaryotic organisms consist of a single cell.
b. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleus
99
New cards
Which of the following statements about photosynthesis is false?
a. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light and dark reactions
b. ATP and NADPH are produced during the light reactions
c. ATP and NADPH are used in the dark reactions
d. Plants produce sugars during the light reactions
a. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light and dark reactions
b. ATP and NADPH are produced during the light reactions
c. ATP and NADPH are used in the dark reactions
d. Plants produce sugars during the light reactions
d. Plants produce sugars during the light reactions
100
New cards
Organelle that is involved in both protein synthesis and membrane synthesis.
a. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
b. golgi apparatus
c. lysosome
d. mitochondria
e. nucleus
a. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
b. golgi apparatus
c. lysosome
d. mitochondria
e. nucleus
a. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)