Male Reproductive System 15
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Gonads
Produce gametes (haploids) and is primary organ.
Testis
Male gonad and produces gametes (spermatozoa). Produce testosterone
Ovary
Female gonad
Ova
Female gametes
Epididymis, ductus deferens, and urethra
Accessory ducts for storage, maturation, and transportation of sperm
Penis/scrotum
External genitalia
Organs
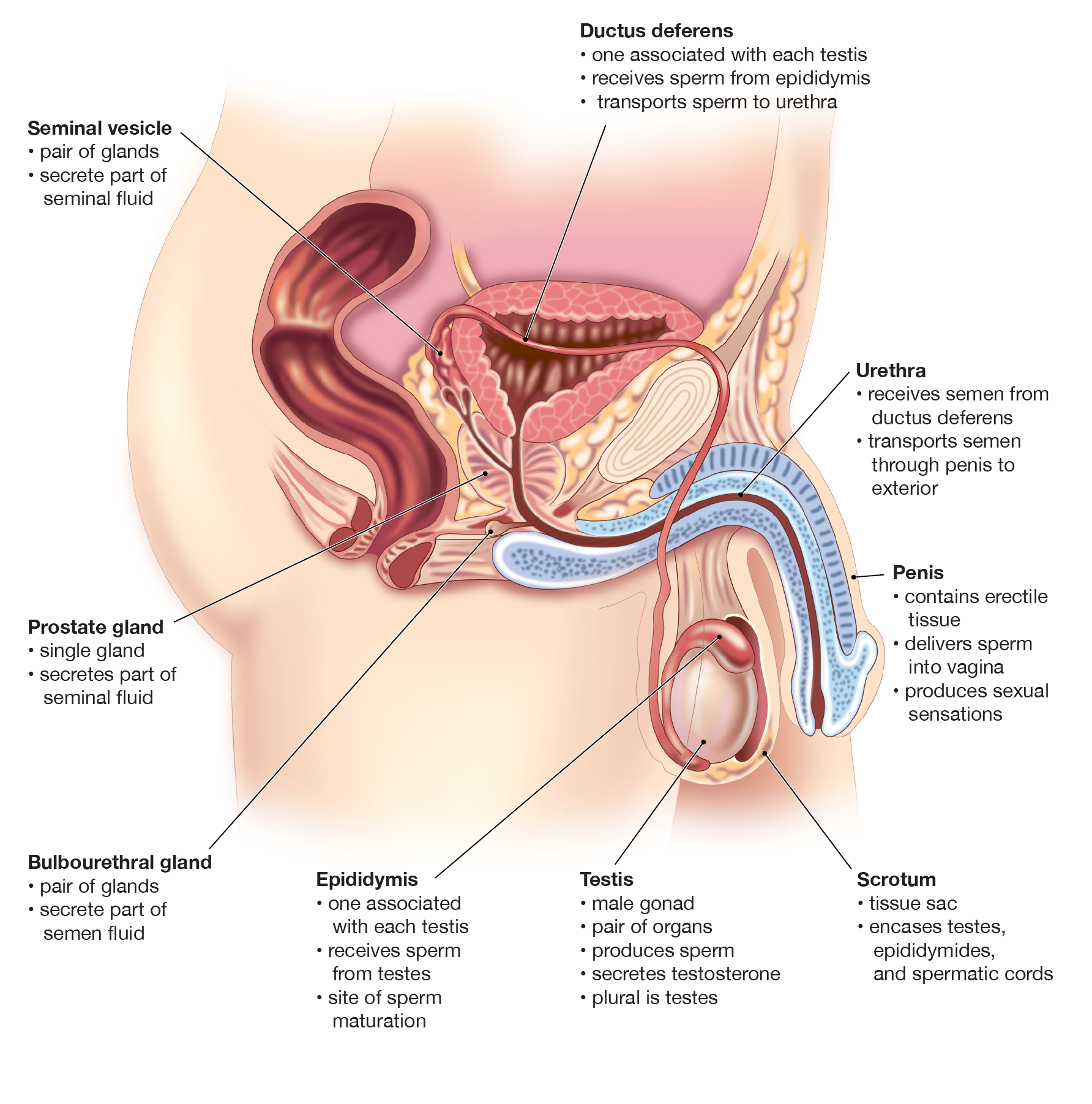
Ductus deferens
Transports sperm from scrotum through pelvic cavity to urethra
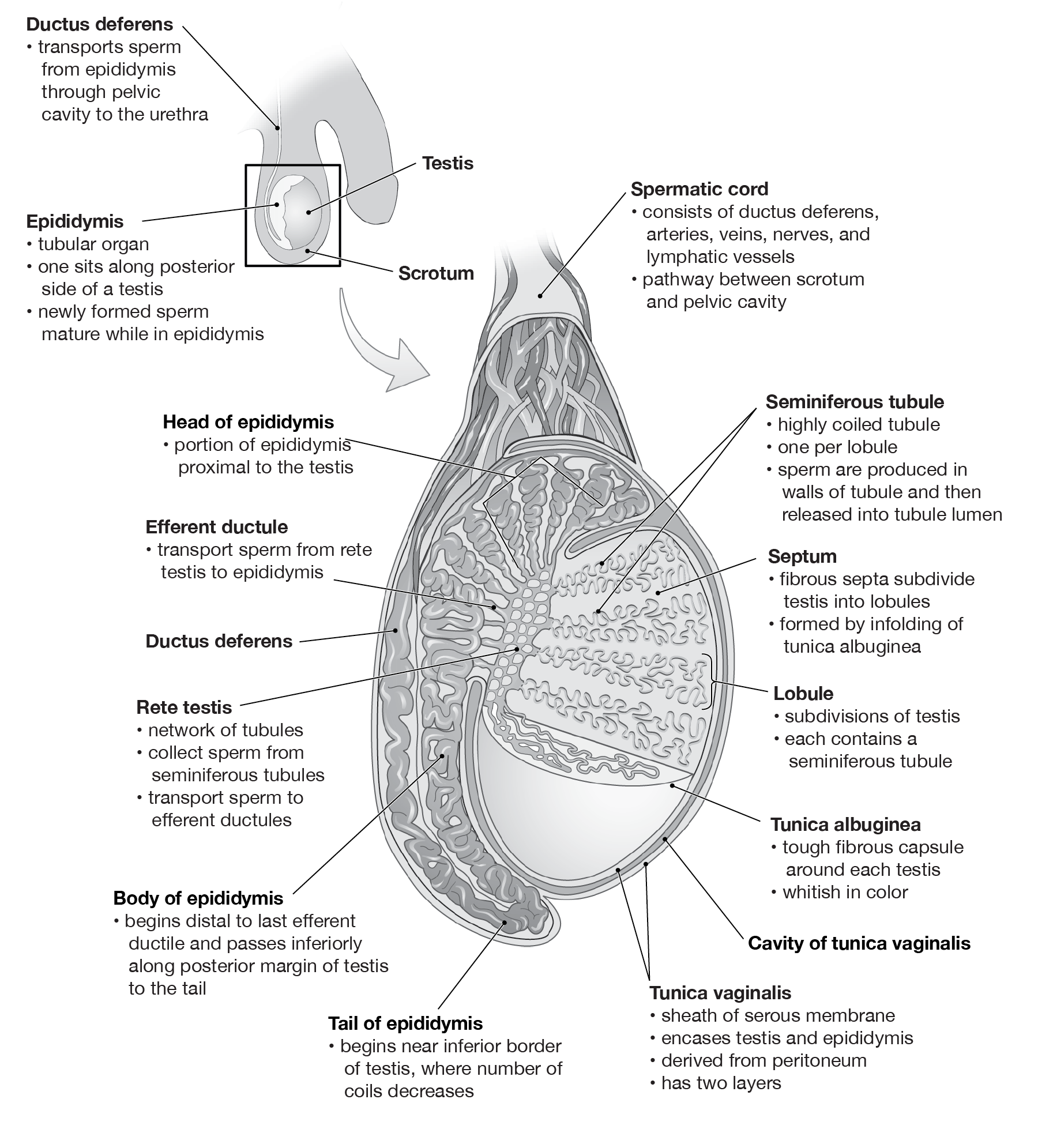
Structure of testis
Function of testis
Sperm production and secrete testosterone
Sperm production
Spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Diploid stem cell [spermatogonium] divides via mitosis to produce type A and B. Type A repeats cell division. Type B produces spermatocytes that undergo meiosis 1 producing secondary that undergo meiosis 2 to produce haploid gametes (spermatids)
Spermiogenesis
Converts spermatid into spermatozoan (sperm)
Testosterone secretion
Performed by interstitial cells located in seminiferous tubules
Testosterone targets
Stimulation of trellis cells to promote Spermatogenesis; stimulate bone and muscle growth; secondary sexual characteristics; libido; accessory glands
Cross section of seminiferous tubule