HISTEM W16/17 Tooth Development and Eruption
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Which week of fetal development does primary dentition and permanent dentition begin?
Week 6 = Primary dentition development begins → 20 teeth
Week 10 = Permanent dentition development begins → 32 teeth
any missing or supernumerary teeth are determined at this time.
T or F - the first teeth for both primary and permanent teeth begin to develop in the maxillary anterior region first and then mandibular anterior region. The development progresses posteriorly from the anterior region.
FALSE → develops first in the MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION and then maxillary anterior region.
Why does teeth development progress posteriorly from the anterior region?
It allows time for both jaws to grow and accommodate more teeth as development continues.
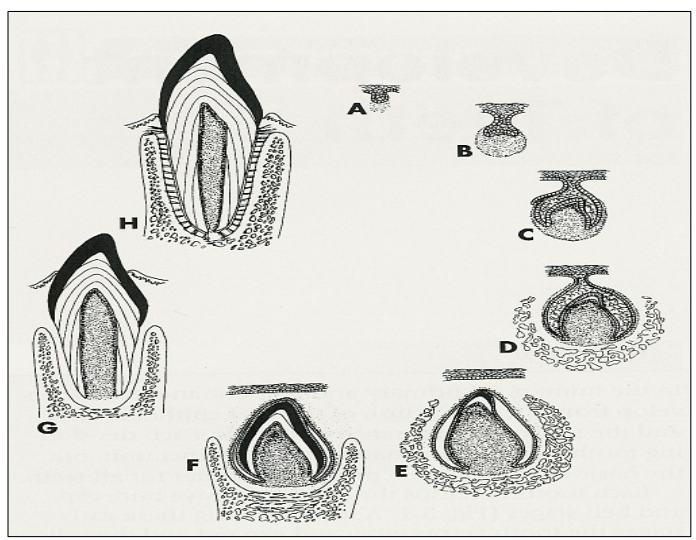
Label the stages of tooth development.
A = tooth bud
B = Cap
C = Bell
D = dentinogensis
E = amelogenesis
F = crown formation
G = root formation and tooth eruption
H = functional tooth.
REVIEW: What are the 5 stages pf developmental processes?
Induction
Proliferation
Differentiation
Morphogenesis
Maturation
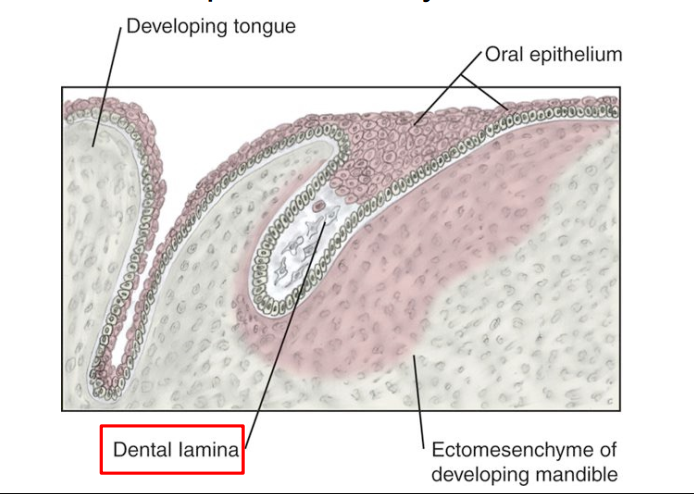
Describe the Initiation stage (6-7th week) of Odontogensis.
Initiation Stage (6th–7th week) → physiological process:
First stage of tooth development (odontogenesis).
Stomodeum is lined by ectoderm
Outer ectoderm gives rise to Oral epithelium
Oral epithelium grows downward/deeper into the underlying ectomesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme is INDUCED to produce the dental lamina
Key event: Inductive interaction between oral epithelium and ectomesenchyme begins tooth formation.
Clinical relevance: Disturbances here may cause anodontia (missing teeth) or supernumerary teeth (extra teeth).
What happens if there is a lack of initiation during teeth development?
Causes absence of a single tooth or multiple teeth
Hypodontia - more common; less than normal teeth
commonly occurs to Perm MxLI, M3, MdPM2
Anodontia - missing all teeth
**Abnormal initiation = extra teeth; supernumerary teeth/hyperdontia
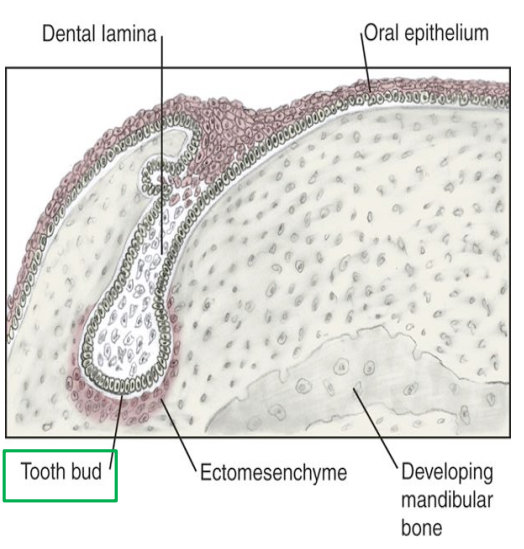
Describe the Proliferation stage (8th week) of odontogenesis.
Proliferation Stage AKA Bud Stage (8th week):
Second stage of odontogenesis.
Dental lamina proliferates into tooth buds (oval masses) that penetrate into ectomesenchyme
future tooth germ
*each dental arch should have 10 buds (primary teeth)
What is successional (secondary) lamina? When is it initiated?
Precursor tissue for the formation of tooth buds of permanent teeth
Initiated between 10th week and 10th month after birth.
Perm molars → 20th week in utero for M1; 5th year of life for M3
Successional lamina is lingual to the dental lamina of primary teeth.
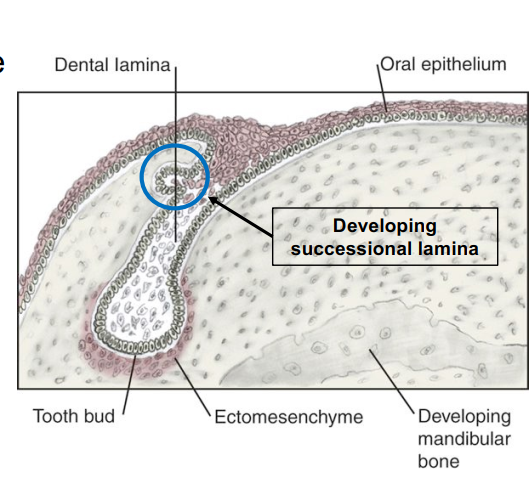
Closer look at secondary lamina and tooth buds of permanent teeth.
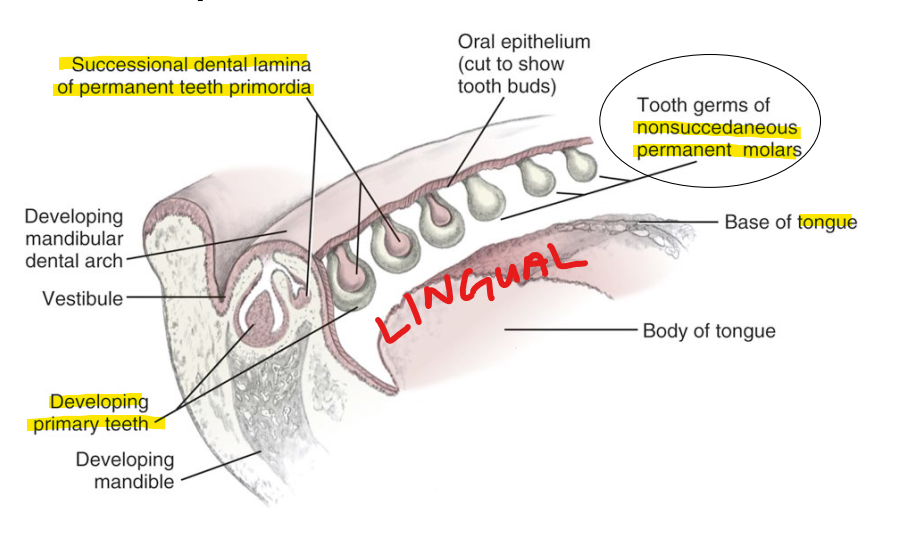
What can happen if there are developmental disturbances during the Profliferation stage of Odontogenesis (Bud stage)?
Macrodontia
Microdontia
Distomolar → extra molar behind 8’s
Peg Molar → smaller than normal tooth “peg shaped”
Tooth buds for all _____ teeth arise from successional (secondary) lamina EXCEPT ?
Tooth buds for all permanent teeth EXCEPT molars
The tooth buds for permanent molars arise from _____?
the posterior extension of the dental lamina distal to the dental lamina of primary teeth.
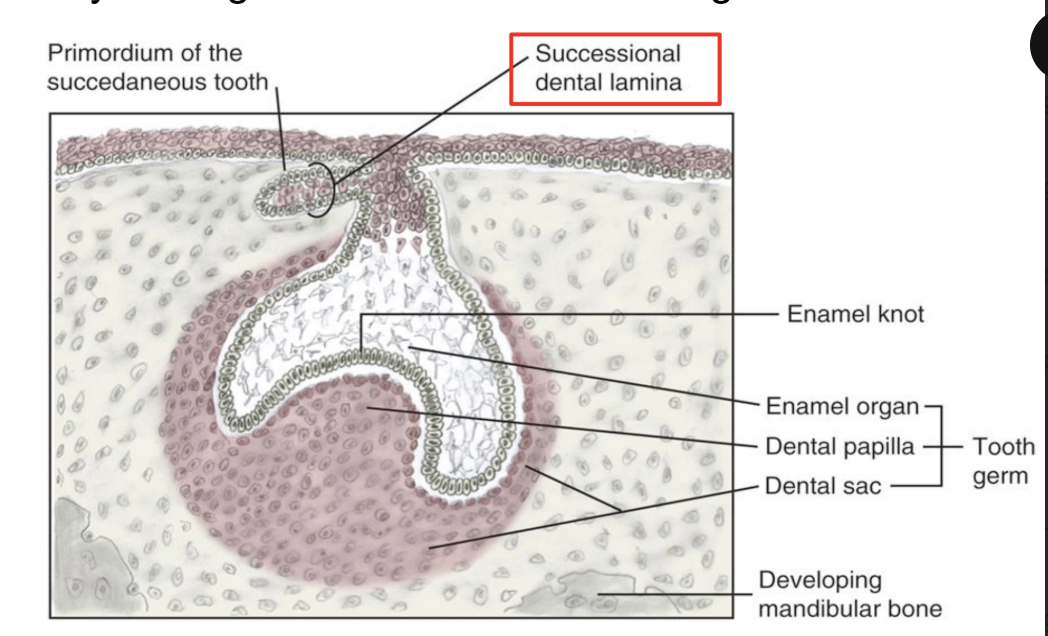
Describe the third stage of odontogenesis (9-10th week of development)
Third stage: Cap Stage
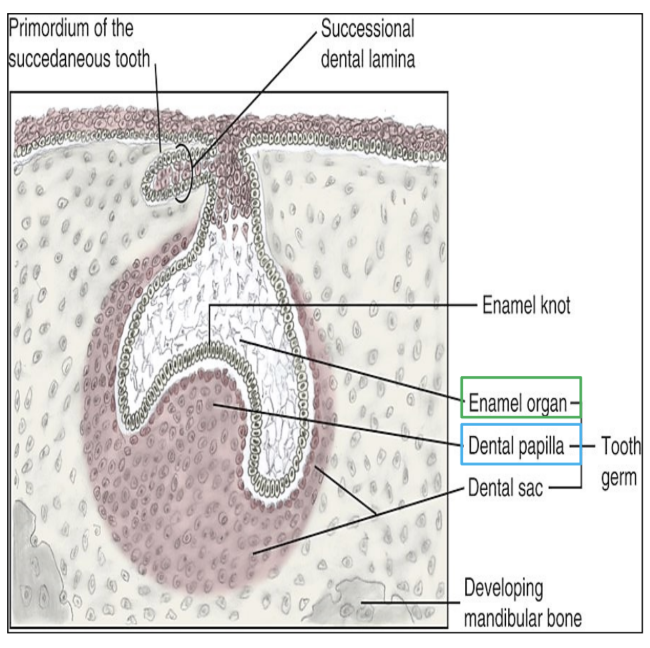
Proliferation and differentiation of cells to form tooth germ (primordium) of a primary tooth.
further developing into enamel organ, dental papilla, dental sac
Enamel Organ → formation of tooth bud in a cap shaped with deep central depresion
Dental papilla → condensed mass of ectomesenchyme within the concavity of the enamel organ
Dental sac → condensed mass of ectomesenchyme surrounding outside of the enamel organ
The predominant physiological process is MORPHOGENESIS:
Morphogenesis = formation of a CAP SHAPED attached to the dental lamina
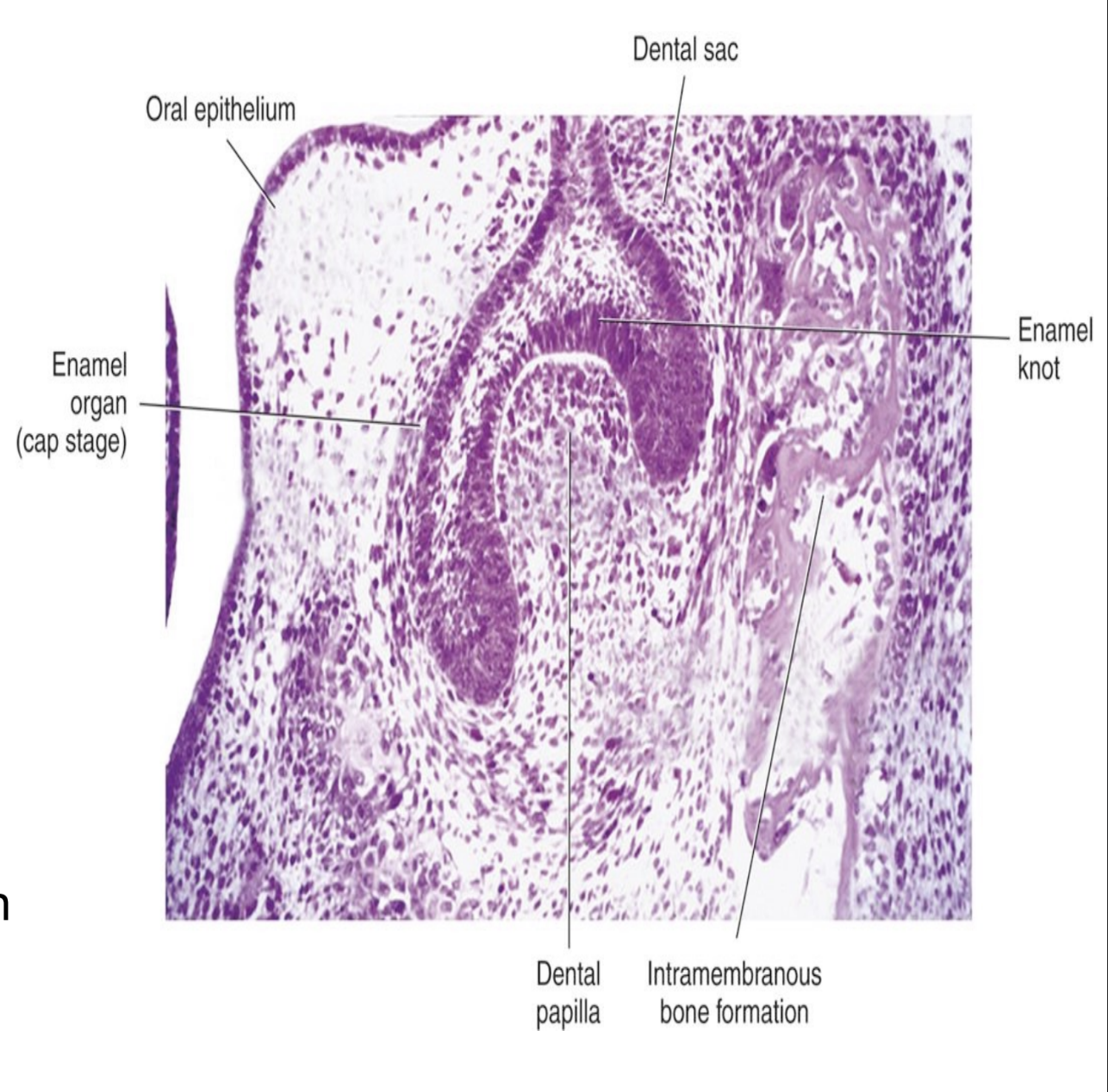
What are the 3 components of the tooth germ? What do each of the components develop into?
enamel organ (with enamel knot) → enamel, crown
dental papilla → dentin and pulp
dental sac → cementum, PDL, alveolar bone
The basement membrane between the enamel organ and dental papilla develops into the future ____.
site for the future DEJ (dentoenamel junction)
What dental abnormalities happen if there are disturbances during Cap Stage? (4)
Dens in dente → enamel organ invaginates into dental papilla
Gemination → single tooth diving into 2; large single rooted tooth shared pulp cavity
Fusion → union of 2 adjacent tooth germs = broader tooth; separate roots
Tubercles → extra cusps, enamel extensions
Describe what happens during the fourth stage of Odontogenesis.
4th stage (11-12th week of dev.) = Bell Stage = Differentiation phase
Dental papilla further invaginates into the enamel organ creating bell shape
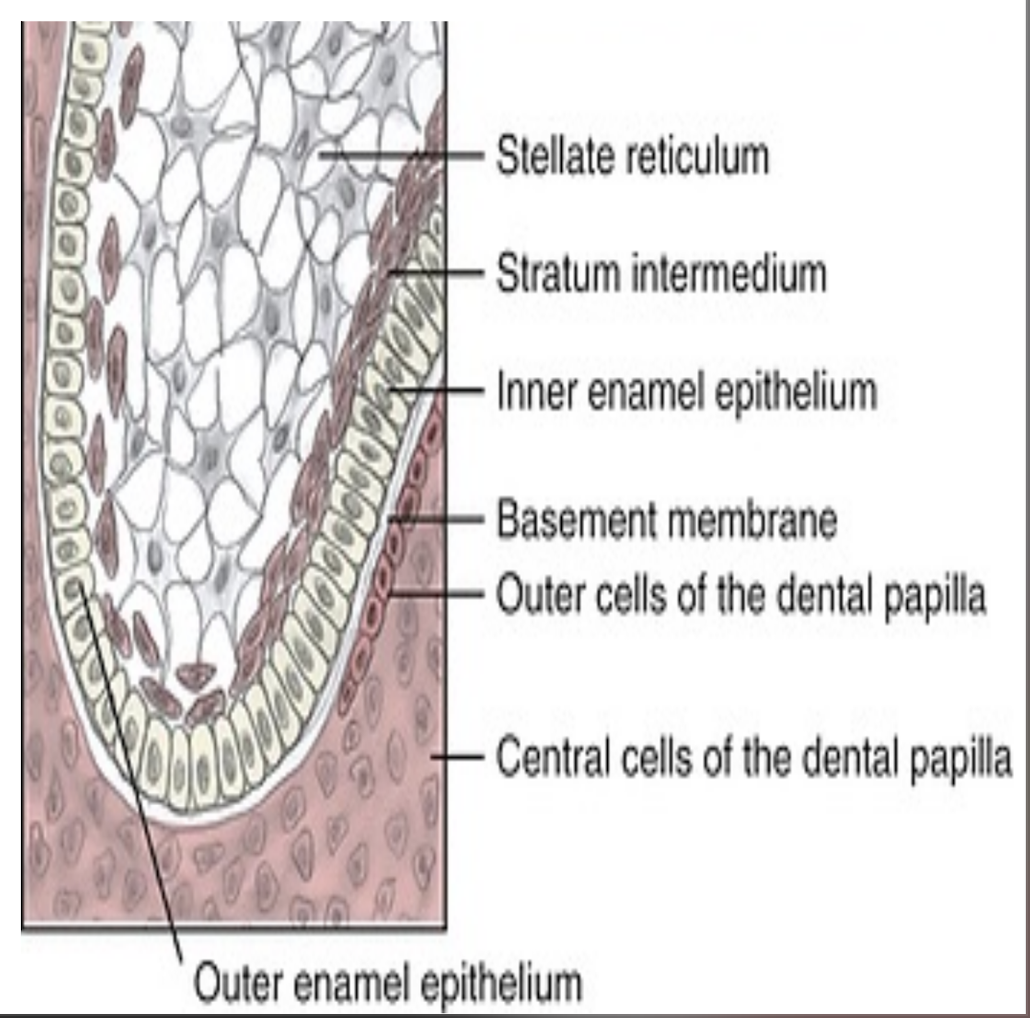
Enamel organ cells DIFFERENTIATE into 4 layers:
Outer enamel epithelium
Stellate Reticulum
Stratum Intermedium
Inner enamel epithelium
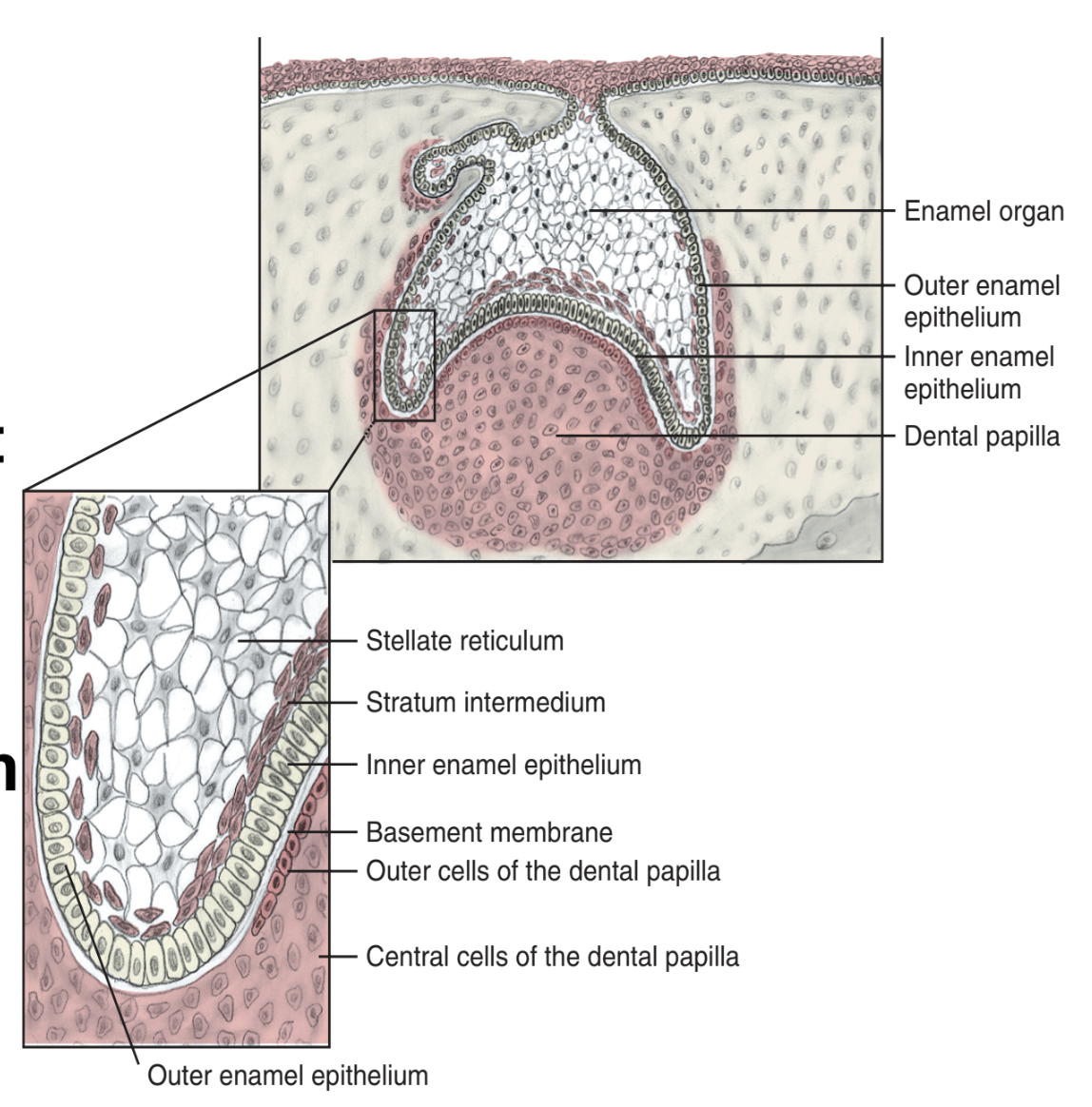
Describe Outer Enamel Epithelium (OEE) and its function.
Outer enamel epithelium (OEE) are the outer CUBOIDAL cells of the enamel organ
fx: protective barrier of the enamel organ during enamel production
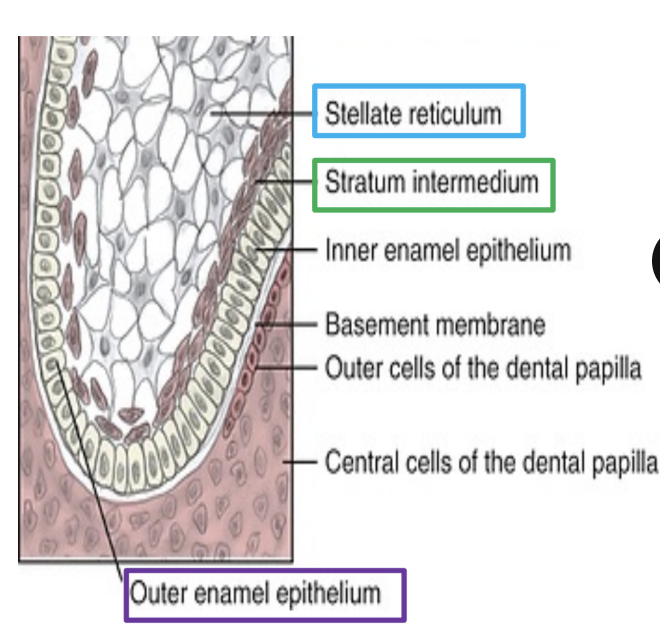
The ____ and ____ are betewen the outer and inner enamel epithelium. These layers support enamel production.
stellate reticulum and stratum intermedium
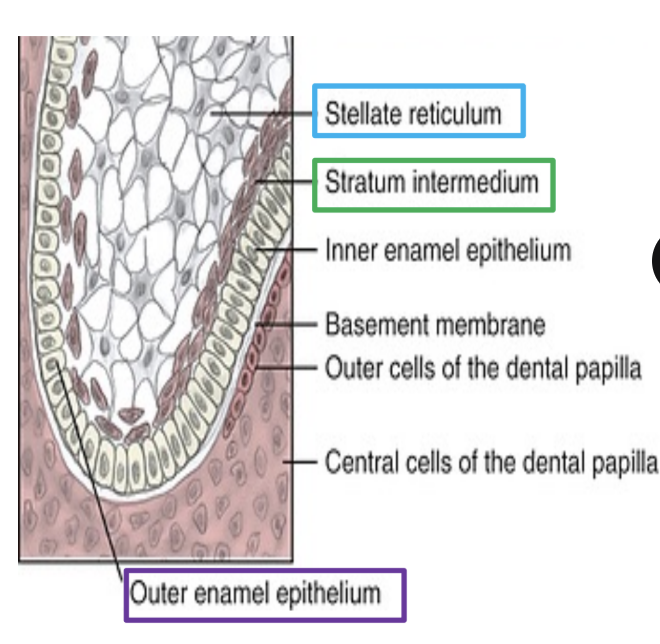
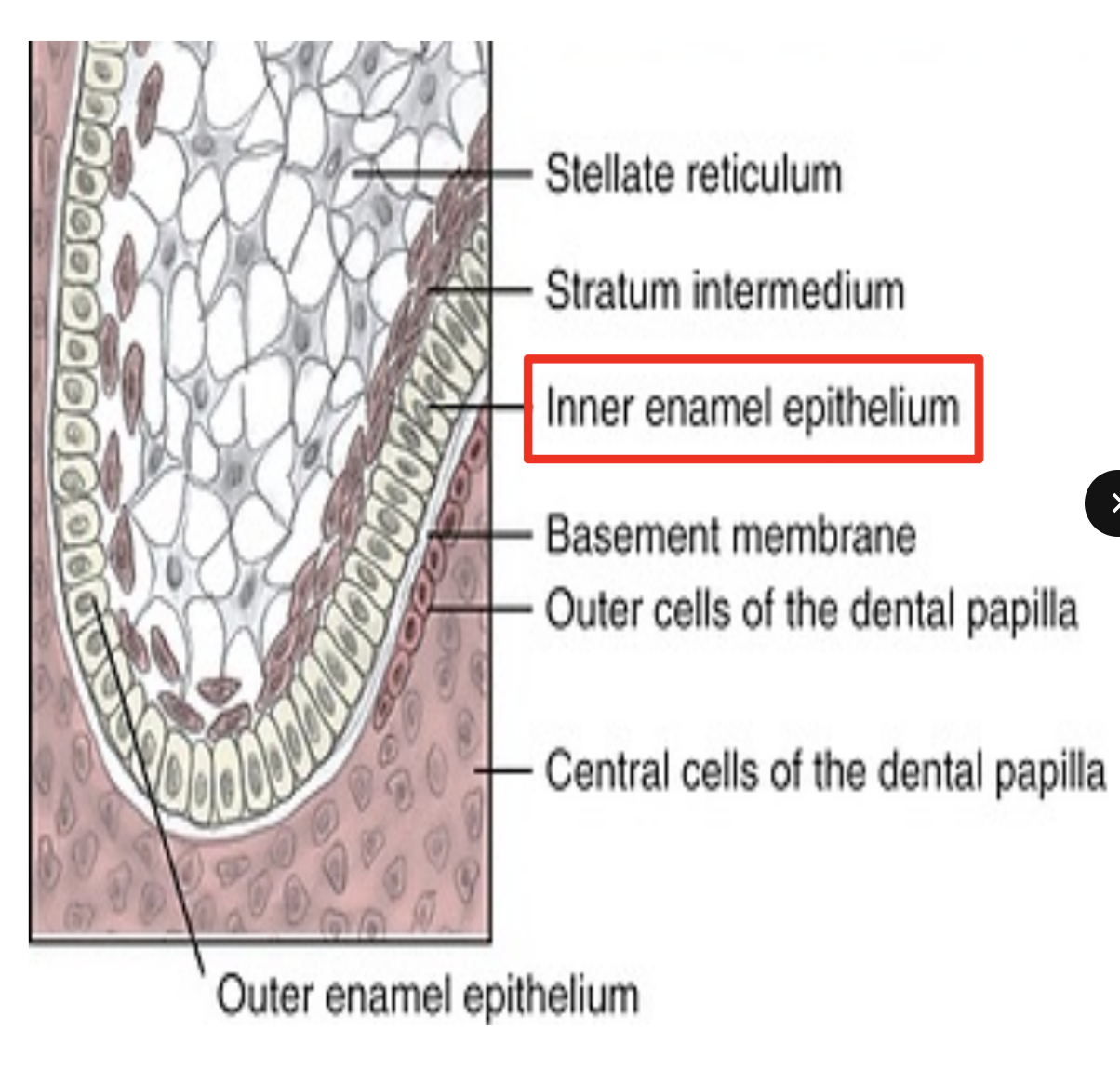
Describe inner enamel epithelium (IEE) and its function.
IEE are tall COLUMNAR cells of the enamel organ
fx: acts as basal margin of enamel organ and gives rise to Hertwig’s Epithelial root sheath (HERS)
HERS induces dental papilla cells to differentiate into odontoblasts to form root dentin
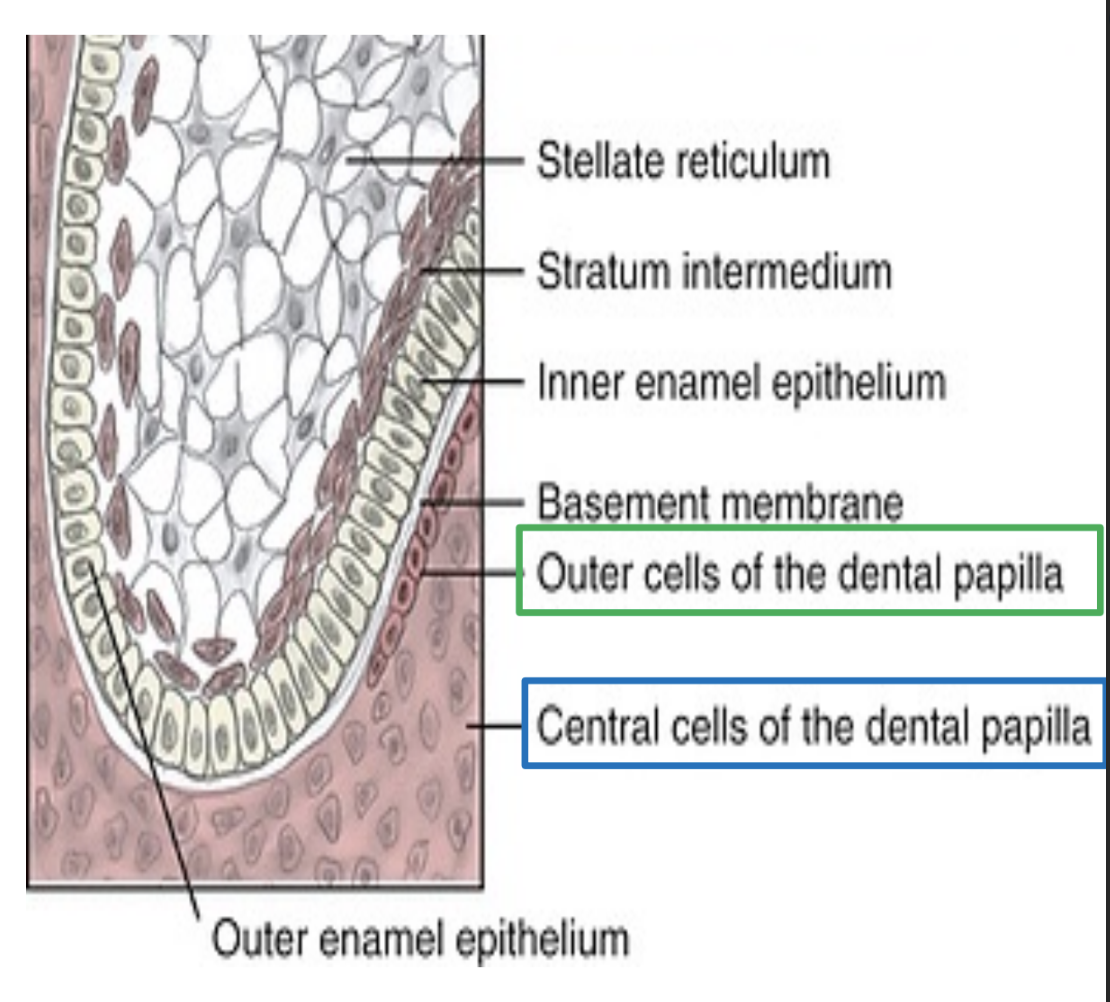
During the 4th stage of Odontogenesis (Bell Stage), Dental papilla also undergoes differentiation. Describe process.
Dental papillae differentiates into outer cells and central cells of dental papilla.
Outer cells differentiate into Odontoblasts
Central cells differentiate into the Primordium of the pulp
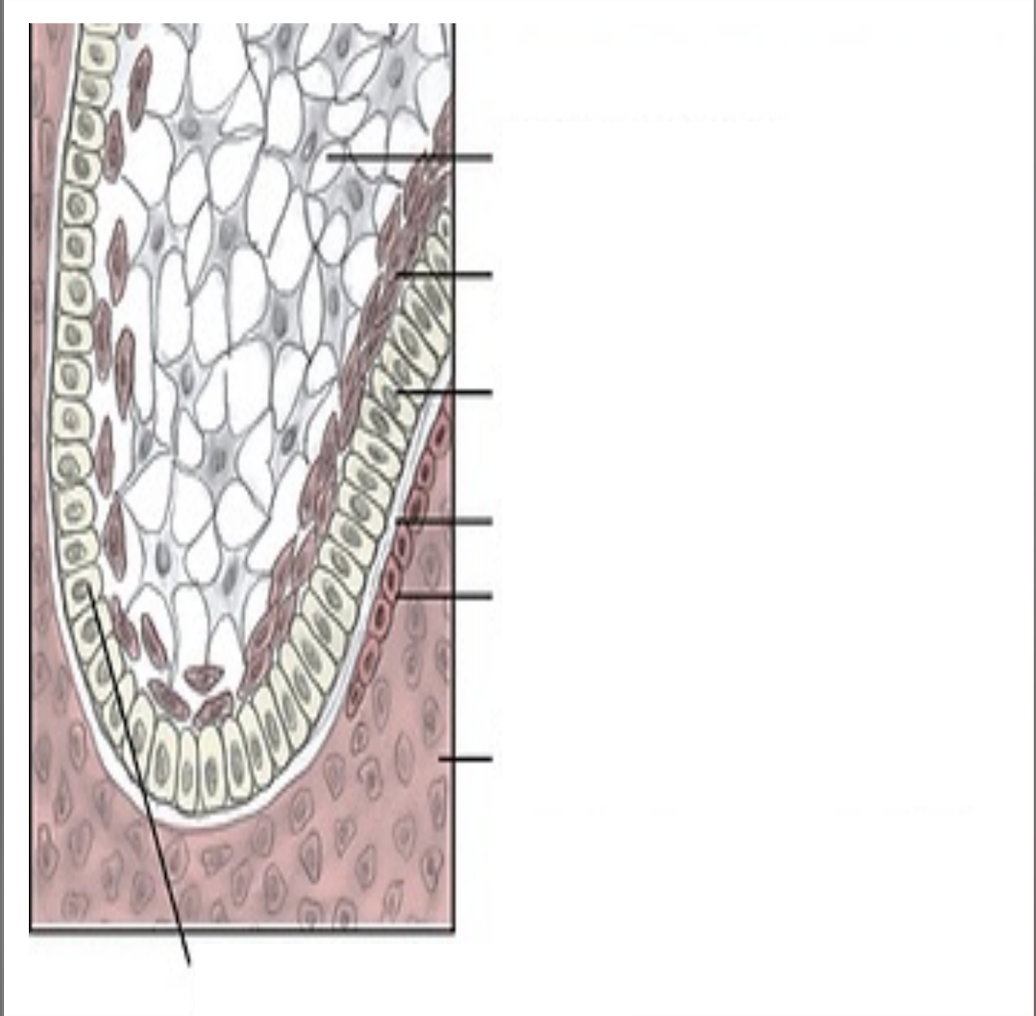
Label this image.
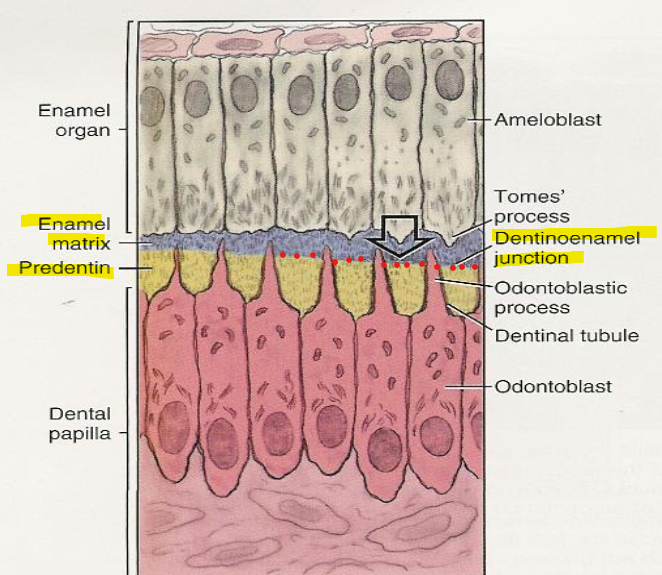
What happens during the Appositional stage of Odontogensis?
Enamel, dentin, and cementum are secreted in successive layers.
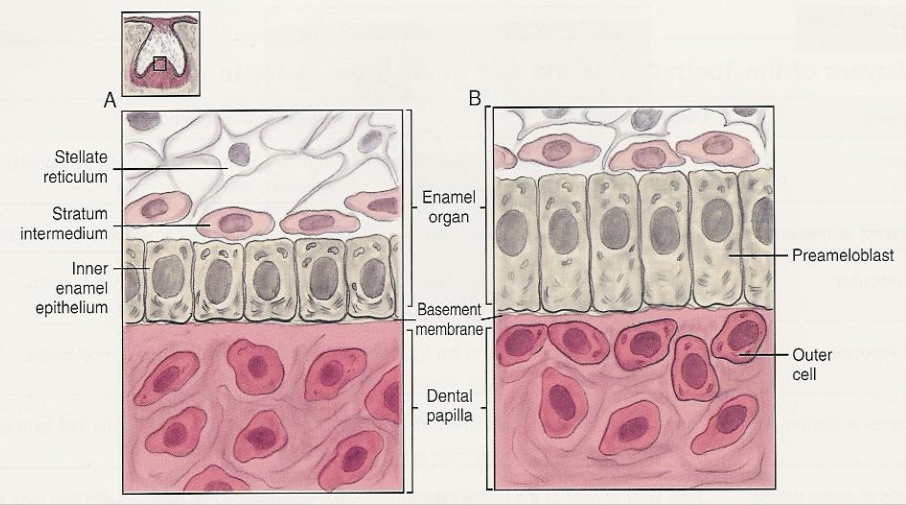
After the first layer of ______ is formed. ____ begins to form enamel.
**Image is IEE differentiating into PREAMELOBLASTS
First layer of predentin is formed → Ameloblasts begin to form enamel.
T or F - First enamel that is deposited is on the surface of dentin establishes the CEJ.
F - it establishes the DEJ.
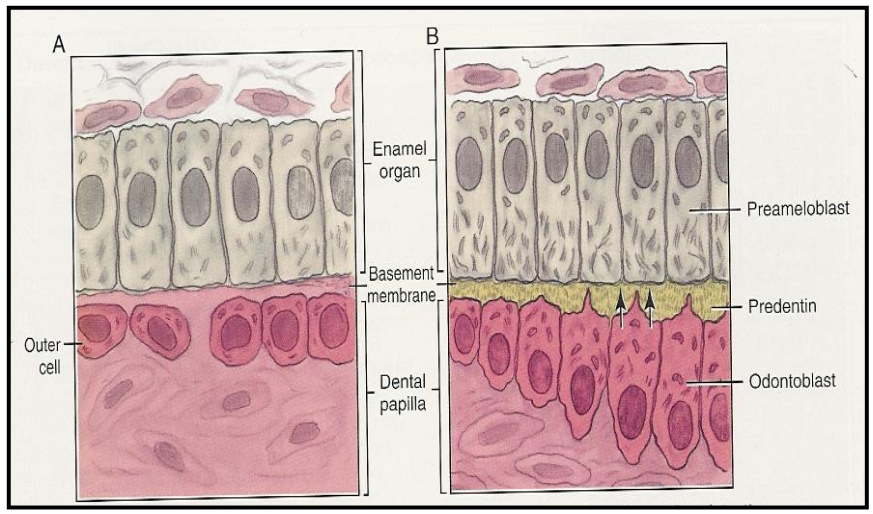
Dentinogenesis → Outer cells of the dental papilla differentiating into Odontoblasts
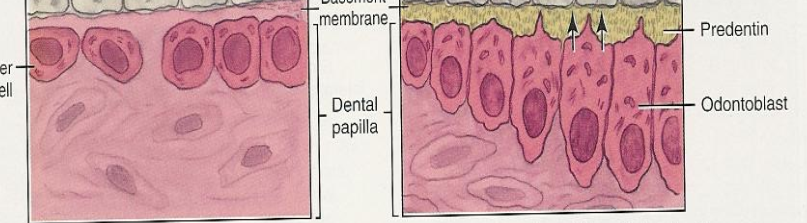
What is the Reduced Enamel Epithelium (REE)?
REE is a thin membrane on the entire surface of the crown that acts to protect the enamel until the tooth is ready to erupt.
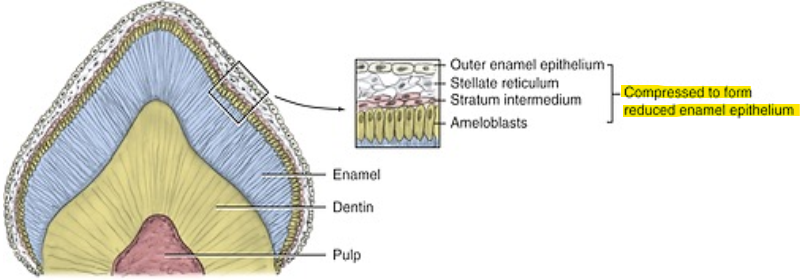
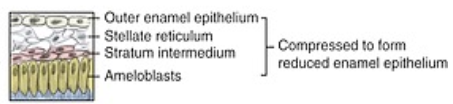
What layers of the developing tooth is compressed to form the REE?
Outer enamel epithelium, Stratum reticulum, stratum intermedium, Ameloblasts
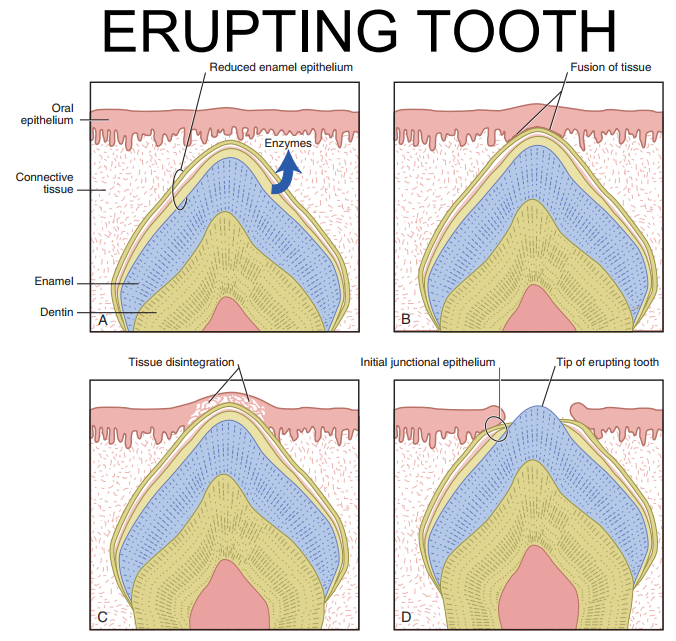
T or F - As the tooth erupts, IEE fuses with the epithelial lining and forms the epithelial attachment.
F - it is the REE that fuses with the enamel epithelium.
What happens during the final stage of Odontogenesis?
Maturation → dental tissue types fully mineralize.
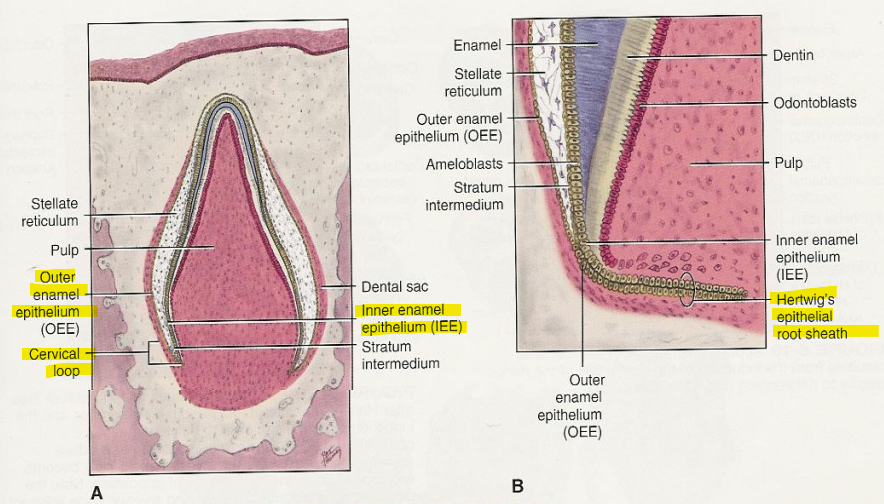
What is the Cervical loop?
Cervical loop: The junction where the inner enamel epithelium (IEE) meets the outer enamel epithelium (OEE) at the cervical end of the enamel organ. → merging of the innermost and outermost layer of the enamel organ in a “cervical loop” and it grows down as a double row of cells (HERS)
During root formation, the cervical loop elongates apically to form the Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (HERS).
Function: Marks the transition from crown formation to root development, directing the shape and number of roots.
Once HERS forms and induces root dentin, it breaks down, allowing cementoblasts from the dental sac to form cementum.
T or F - Root formation begins after the first dentin has been laid down.
F - Root formation begins AFTER the Crown is COMPLETELY FORMED.
After the first layer of dentin is formed. ________ breaks apart. What are the remnants called?
Hertwigs epithelial root sheath breaks down.
Remnants are called epithelial rests of Malassez.
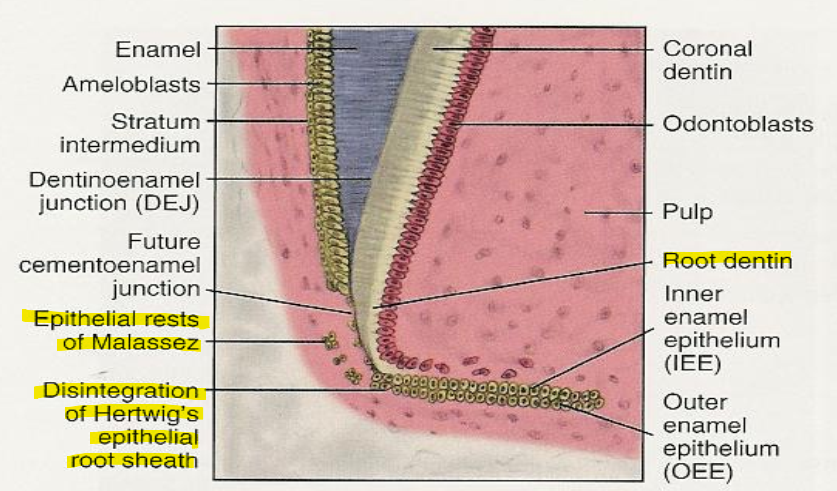
What are epithelial rests of Malassez (ERM)?
ERM - Small clusters of epithelial cells located within the periodontal ligament (PDL).
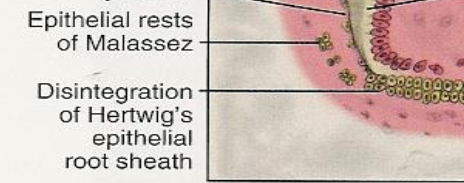
Arrange the following in the correct order of occurrence:
Deposition of Cementum
Formation of Dentin
Lengthening of the Root
Completion of the Crown
Completion of the crown
Formation of dentin (root dentin formation begins)
Lengthening of the root
Deposition of cementum
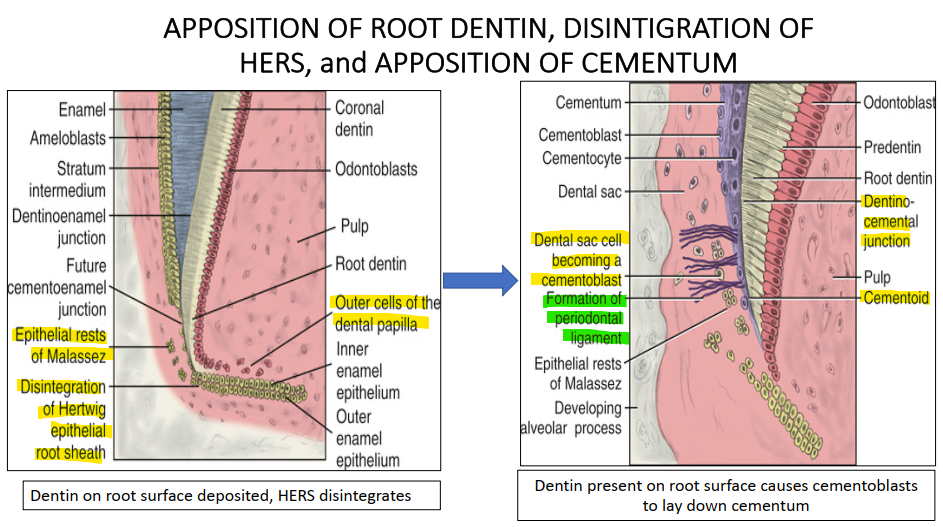
Cementoblasts differentiate from which cells?
Cells of the dental sac
As the cementoblasts cover root dentin with cementoid, what is form? What is also happening at the same time?
DCJ is formed (dentocemental junction)
AT THE SAME TIME, central cells of the dental papilla are condensing to form the pulp
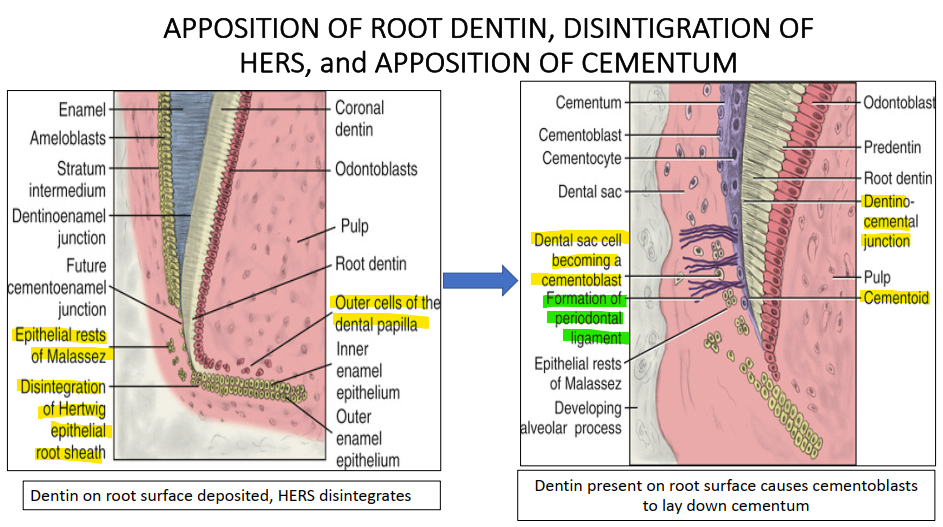
The periodontal ligament and alveolar bone develops from _____?
Remaining Ectomesenchyme from the dental sac forms the PDL
Some will mineralizes to form the tooth socket and alveolar bone
**process involves collagen fibres that make up the PDL.
What is Oligocontia?
The absence of 6 or more teeth
Anodontia, hypodontia, oligodontia, and hyperdontia are caused when there are disturbances to which stage of teeth development?
Initiation stage (Stage 1)
Microdontia and macrodontia occur when there are disturbances during _______ stage of tooth development.
Bud Stage (Stage 2)
Tubercle, Dens in dente, gemination and fusion are dental anomalies that occur when there has been disturbances during _____ stage of tooth development.
Cap stage ( stage 3)
Enamel pearl, enamel dysplasia, concrescence, dentinogenesis imperfecta, amelogenesis imperfecta and dilacerated roots are caused by disturbances during _______ stage of tooth developement.
Apposition and maturation stage (Stage 4 and 5)