Dance Midterm HKIN 342 TWU
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Musical Theatre/Broadway Jazz
A form first seen in the 1920s on Broadway (new york) and in film; influenced by ballroom, ballet, tap and even early modern. Involves singing/ lip- syncing and dancing.Broadway Jazz truly evolved from earlier forms of Musical Theatre; dancing and singing, used to tell a story,
Swing
An American social dance that originated alongside Jazz music in Harlem, New York City. It has many forms/styles: Shag, Lindy Hop, Charleston, West Coast Swing, East Coast Swing that evolved in the 1920s and 30s and continued into the 40s and 50s
How does swing dancing work
physical social form of dance involving partners where the male is known as the “lead” and the female is known as the “follow”. The East Coast basic step consists of two 2 beat steps and a “rock step” (also known for its Slow, Slow, Quick, Quick rhythm) and is characteristic of this style.
Jazz
Originated in 1930s-1950s; was heavily influenced by the vernacular dances of the Africans when brought to the Americas on slave ships and has roots in Caribbean and Latin American traditional dance. It developed alongside Jazz music in New Orleans.
what are the key elements of jazz
key elements include syncopated rhythm, isolations, improvisation, a low center of gravity and a high level of energy. always developed in parallel to popular music.
Lyrical Jazz
A combination of Jazz and ballet. An expressive way to dance with movements based on music and lyrics to create imagery and communicate a message or story.
Liturgical
A form of lyrical dance, expressive and meant as a form of worship and spiritual connection for the dancer and audience to God.
Tap
Emerged in the 1920s and developed alongside Jazz music. A style of American theatrical dance, distinguished by percussive footwork, that marks out precise rhythmic patterns on the floor; focussing on the development of rhythmic ability and its relation to musicality and sequencing.
What are tap dance inspirations
Irish solo step dance, English clog dance, Spanish Flamenco, and African dance movements. Shoes eventually became a hard soled leather shoe with metal plates.
Ballet
includes traditional steps, positions, and body carriage. While also providing a technical foundation and understanding of dance positions and proper placement while developing overall coordination and a sense of poise and grace.
Ballet origins
Originated in Italian Renaissance courts and was brought to France by Catherine de' Medici in the 16th Century. Often involves a classic story line and utilizes simple gestures and characterization.
Contemporary Ballet
maintains elements of traditional ballet (lower body) and incorporates the stylistic movements of other genres such as modern.
Modern
There are very broad parameters within this style of dance. Viewed as a rebellion against ballet. Focusses on self-expression and individualism; it embraces abstractionism, performance art, contact improvisation, release technique, and improvisation.
LABAN MOVEMENT ANALYSIS
Rudolph Laban (1879-1958) - the developed LMA based on:
Theory used mainly in dance& gymnastics
2 types of movement: functional & expressive
F & E help to appreciate the nature of movement, objectives and context
LABAN MOVEMENT ANALYSIS (LMA) aims to:
Structure learning tasks
Observe& analyze movement
Communicate an accepted terminology/ vocabulary
Evaluate content & develop a curriculum
Dance Elements of LMA (4)
body
effort/dynamics
shape
space
Body
INITIATION of movement starting from specific body parts- which body parts are moving
CONNECTION of different body parts to each other-which body parts are connected
SEQUENCING of movement between body parts- which parts are influenced by others
PATTERNS of body organization-general statements about body organization
Effort/dynamics
EFFORT= Space, weight and time
SPACE: direct/indirect
WEIGHT: strong/light
TIME: sudden/sustained
FLOW= the continuousness of or “ongoingness” of motions (it is difficult to remove flow)
FLOW: bound (lacking flow)/ free (a sense of continuousness)
Shape
the way the body changes shape during movement
FORMS- static shapes- wall-like, ball-like, pin-like
MODES OF SHAPE CHANGE- - the way the body is interacting with and the relationship the body has to the environment
SHAPE QUALITIES-describes whether the body is OPENING (growing larger with extension) or CLOSING (growing smaller with more flexion)
SHAPE FLOW SUPPORT- the absence or presence of torso movement (specifically in changing shape to support movements of the rest of the body)
Space
GENERAL SPACE
FLOOR PATHWAYS & AIR PATHWAYS ( while travelling)
EXTENSIONS- where/what space a movement pattern uses UpStage (US)-DownStage (DS)-Stage Right (SR)-Stage Left (SL)
CLASS SPACE- where? A gym, a stage, a room, outside
SPACE BETWEEN PEOPLE
LEVELS- low, medium, high
PERSONAL SPACE (KINESPHERE)
DIRECTIONS- of the body or body parts
LEVELS – of body parts used
EXTENSIONS- of limbs used
LEVELS- patterns made with body parts
Dance movement purpose and fundamentals
To provide a variety of movement experiences
To enable children to move efficiently and effectively
To develop a sense of rhythm
Creativity should be a part of all dance & rhythm activities
Allow the scope of the activity to determine the degree of freedom
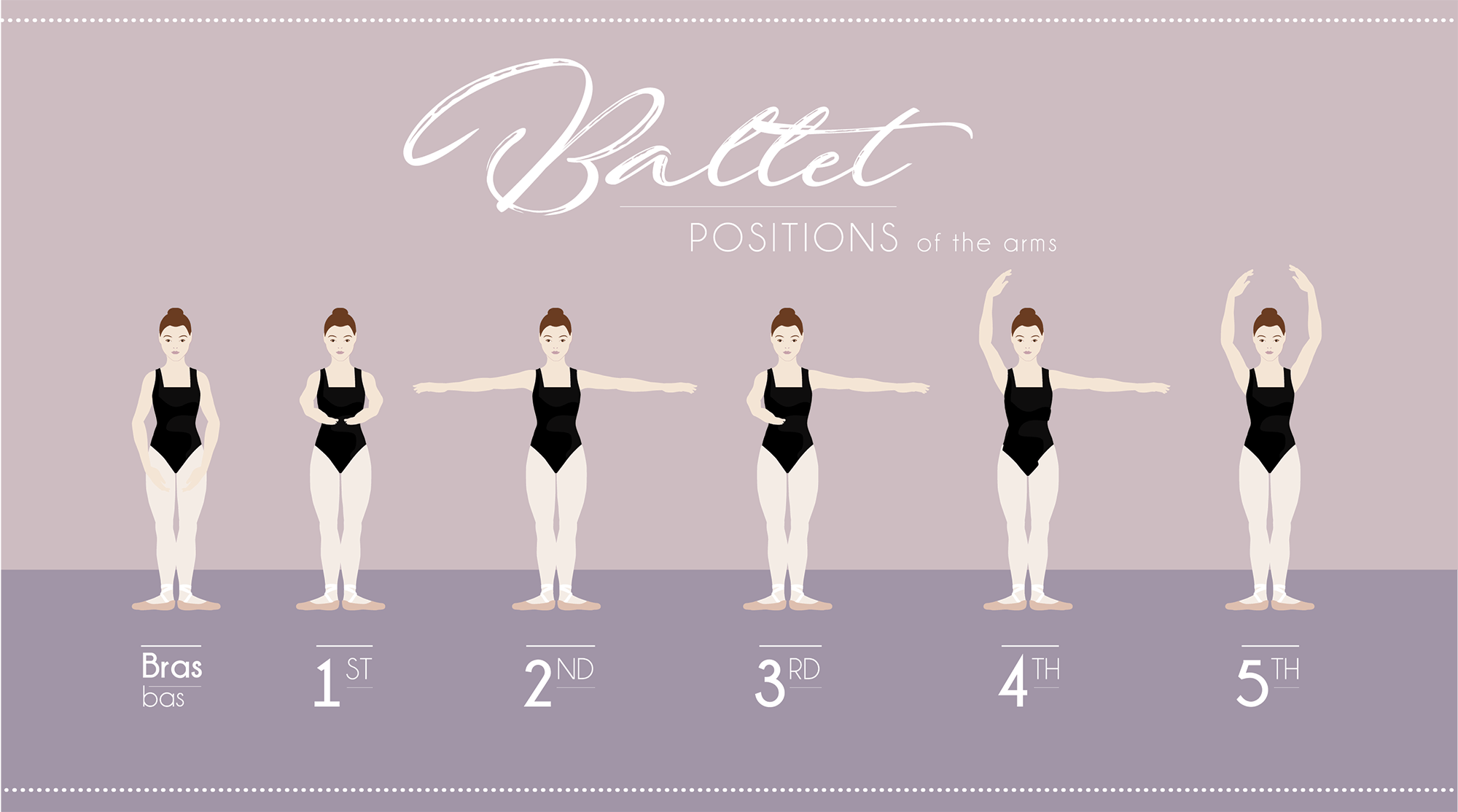
Ballet positions —> Arms
Ballet positions —> feet

Basic Movement Principles: Balancing
arabesque, passe, tendu
Basic Movement Principles:Turning
pirouette, chaine turns, fouettes
Basic Movement Principles: Locomotion
(Travelling): pas de bouree, chasse, jete
Basic Movement Principles: Jumping
jete, leap, pas de chat
Dance & the Christian Perspective
Dance is worship. God is pleased with whatever form of dance (no matter how small or great) it is. He is pleased with our worship.
RHYTHM
the basis of music and dance
Expressive movements are made with or without music
Body movements tend to be rhythmic (heartbeat, rocking)
Tempo
speed of the music; can be constant or show acceleration or deceleration
Beat
the underlying pulse of the music and is always continuous (even if not heard)
Meter
the organization of beats into regular reoccurring pattern of measures or bars
ex. 4/4, 2/4, 3/4, 6/8, 9/12
Accent
notes or beats in a rhythmic pattern that receives more force than others
Intensity
loud, soft, light, heavy
Phrase
a natural grouping of measures, coherent segments that make up a melody
Teaching progressions
listen and move to the music
teach part 1 of the dance without and with music
teach part 2 without and with music
do part 1 & 2 together without and with music
repeat the additional parts, adding to the last section
put the entire dance together without music
identify trouble spots
reviews and refine
practice without teacher
preform
Phrase
is to dance as a sentence is to a book
is considered the smallest and simplest unit of form
has a beginning, a middle and end
is made up of individual movements that share common elements of intent
Motif
When a phrase is manipulated or changed, commonly used dance improvisational technique
Repetion
simply repeat the exact movement