Biosci 221 Exam 3
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Infectious disease & Survey of bacteria
Last updated 12:42 AM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
What are normal microbiota (resident flora) and their benefits?
Normal flora is found in all areas of the human body exposed to the environment (one exception is the lungs), but internal organs and body fluids are considered sterile in a healthy individual
* They prevent colonization by pathogens by competing for attachment & nutrients
* In other words… __they are preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms__
* Some synthesize vitamins that are absorbed as nutrients by the host
* They prevent colonization by pathogens by competing for attachment & nutrients
* In other words… __they are preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms__
* Some synthesize vitamins that are absorbed as nutrients by the host
2
New cards
General understanding of the resident flora of various anatomical areas (not specific names of bacteria) and how they may function to protect or to be opportunistic pathogens
(https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/Manchester_Community_College_(MCC)/Remix_of_Openstax%3AMicrobiology_by_Parker_Schneegurt_et_al/12%3A_Microbial_Interactions_Flora_Pathogenicity_and_Epidemiology/12.01%3A_Normal_Microbiota_of_the_Body)
* __Skin__
* derive nutrition from skin cells and secretions such as sweat and sebum
* inhibit transient-microbe colonization by producing antimicrobial substances and outcompeting other microbes that land on the surface of the skin
* This helps to protect the skin from pathogenic infection
* __GI tract__
* aid in digestion and contribute to the production of feces, the waste excreted from the digestive tract, and flatus, the gas produced from microbial fermentation of undigested food
* can synthesize vitamins
* __Urogenital system__
* (vaginal microbiota) defend against vaginal infections and sexually transmitted infections by occupying cellular binding sites and competing for nutrients.
* __Skin__
* derive nutrition from skin cells and secretions such as sweat and sebum
* inhibit transient-microbe colonization by producing antimicrobial substances and outcompeting other microbes that land on the surface of the skin
* This helps to protect the skin from pathogenic infection
* __GI tract__
* aid in digestion and contribute to the production of feces, the waste excreted from the digestive tract, and flatus, the gas produced from microbial fermentation of undigested food
* can synthesize vitamins
* __Urogenital system__
* (vaginal microbiota) defend against vaginal infections and sexually transmitted infections by occupying cellular binding sites and competing for nutrients.
3
New cards
Infection
occurs when a pathogen or parasite enters and begins to grow on the host
* Most infections do cause signs or symptoms and go unnoticed
* **Signs** can be observed by examination (*objective* marker of disease)
* Ex. Fluid-filled rash, Fever of 102°F
* **Symptoms** are experienced by the person (*subjective* indicator of disease)
* Ex. Pain, Fatigue
* Disease occurs when the patient develops symptoms
* Most infections do cause signs or symptoms and go unnoticed
* **Signs** can be observed by examination (*objective* marker of disease)
* Ex. Fluid-filled rash, Fever of 102°F
* **Symptoms** are experienced by the person (*subjective* indicator of disease)
* Ex. Pain, Fatigue
* Disease occurs when the patient develops symptoms
4
New cards
pathogen (primary (frank pathogen) versus opportunistic) (COPs)
* A **pathogen** is any bacterium, virus, fungus, protozoan, or worm (helminth) that causes disease in humans
* **Primary pathogens** are likely to cause disease after infection in a healthy host
* Rapidly reproduce/increase in number
* Moderate to high virulence
* **Opportunistic pathogens** are less likely to cause disease in a healthy host; they often affect immune-compromised hosts
* Low virulence
* Part of microbiota, transient microbes
* **Colonizing opportunistic pathogens (COPs)** are microbes that asymptomatically colonize the human body and, when the conditions are right, can cause infections
* Persist indefinitely and transmit w/o detection
* **Primary pathogens** are likely to cause disease after infection in a healthy host
* Rapidly reproduce/increase in number
* Moderate to high virulence
* **Opportunistic pathogens** are less likely to cause disease in a healthy host; they often affect immune-compromised hosts
* Low virulence
* Part of microbiota, transient microbes
* **Colonizing opportunistic pathogens (COPs)** are microbes that asymptomatically colonize the human body and, when the conditions are right, can cause infections
* Persist indefinitely and transmit w/o detection
5
New cards
Virulence
the degree of pathogenicity; describes the level of harm by a pathogen following infection
* **Pathogenicity** is the ability of the organism to cause disease
* Increased virulence, increased death\*
* **Pathogenicity** is the ability of the organism to cause disease
* Increased virulence, increased death\*
6
New cards
Infectious dose (ID)
the amount of a pathogen that's required to establish an infection
* ID50 refers to the dose or number of organisms that will infect 50% of an experimental group of hosts within a specified time.
* ID50 refers to the dose or number of organisms that will infect 50% of an experimental group of hosts within a specified time.
7
New cards
Lethal dose (LD)
the amount of a pathogen following injection that's required for death
* LD50 refers to the dose or number of organisms that will kill 50% of an experimental group of hosts within a specified time.
* used as an indicator of a substance’s relative toxicity
* Thus, a substance with a high LD50 would have a low toxicity (less virulence), while a substance with a low LD50 would have a high toxicity (high virulence)
* LD50 refers to the dose or number of organisms that will kill 50% of an experimental group of hosts within a specified time.
* used as an indicator of a substance’s relative toxicity
* Thus, a substance with a high LD50 would have a low toxicity (less virulence), while a substance with a low LD50 would have a high toxicity (high virulence)
8
New cards
Infectious Disease
a disease caused by a pathogen and may or may not be communicable or contagious to another
* In other words, they are caused by an infectious agent, they cause an infection but don’t have to be transmissible
* In other words, they are caused by an infectious agent, they cause an infection but don’t have to be transmissible
9
New cards
Communicable Disease
a disease caused by an infectious agent that is transmissible to another person
10
New cards
**Characteristics of virulence** (what about the cell itself, or molecules it produces, allow it to cause damage)
Aspects of the pathogen that contribute to virulence:
* **adhesion**
* **invasion**, the entry of a pathogen into a living cell, where it then lives
* **invasiveness**, the ability of a bacterial pathogen to spread rapidly through tissues, can produce enzymes that degrade host tissue
* **toxigenicity**, capacity to produce toxins at the site of multiplication
* **adhesion**
* **invasion**, the entry of a pathogen into a living cell, where it then lives
* **invasiveness**, the ability of a bacterial pathogen to spread rapidly through tissues, can produce enzymes that degrade host tissue
* **toxigenicity**, capacity to produce toxins at the site of multiplication
11
New cards
Reservoirs and Sources - human, animal, inanimate(fomite, food, water, soil)
* **Reservoir** = an animal (including humans) or an environment (soil, water, etc.) that normally harbors the pathogen
* **Source** - where you specifically acquired the pathogen
* Sometimes source and reservoir are the same or different
* **Source** - where you specifically acquired the pathogen
* Sometimes source and reservoir are the same or different
12
New cards
Carriers - Asymptomatic - Passive, Incubatory, Convalescent, Chronic
* **Asymptomatic carrier** harbors the potential disease agent but does not have the disease
* May also be considered healthy carriers - no history of having the infection
* **Passive carriers** are those who never experience symptoms despite being infected.
* **Active carriers** = actively sick with the infection
* **Convalescent carriers** = recovering from the illness
* **Incubatory carriers** = still in the incubation stage of the infection
* **Chronic carriers** = those who continue to harbor a pathogen for months or even years after their initial infection
* May also be considered healthy carriers - no history of having the infection
* **Passive carriers** are those who never experience symptoms despite being infected.
* **Active carriers** = actively sick with the infection
* **Convalescent carriers** = recovering from the illness
* **Incubatory carriers** = still in the incubation stage of the infection
* **Chronic carriers** = those who continue to harbor a pathogen for months or even years after their initial infection
13
New cards
Animals: zoonosis and vectors
* **Zoonotic diseases** are infections of animals that can be transmitted to humans
* Pathogens may or may not cause the animal reservoir to have a disease
* Transmission may be direct or indirect “spillover” to humans
* The majority of emerging diseases are zoonotic in origin
* A **vector** is a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal.
* Pathogens may or may not cause the animal reservoir to have a disease
* Transmission may be direct or indirect “spillover” to humans
* The majority of emerging diseases are zoonotic in origin
* A **vector** is a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal.
14
New cards
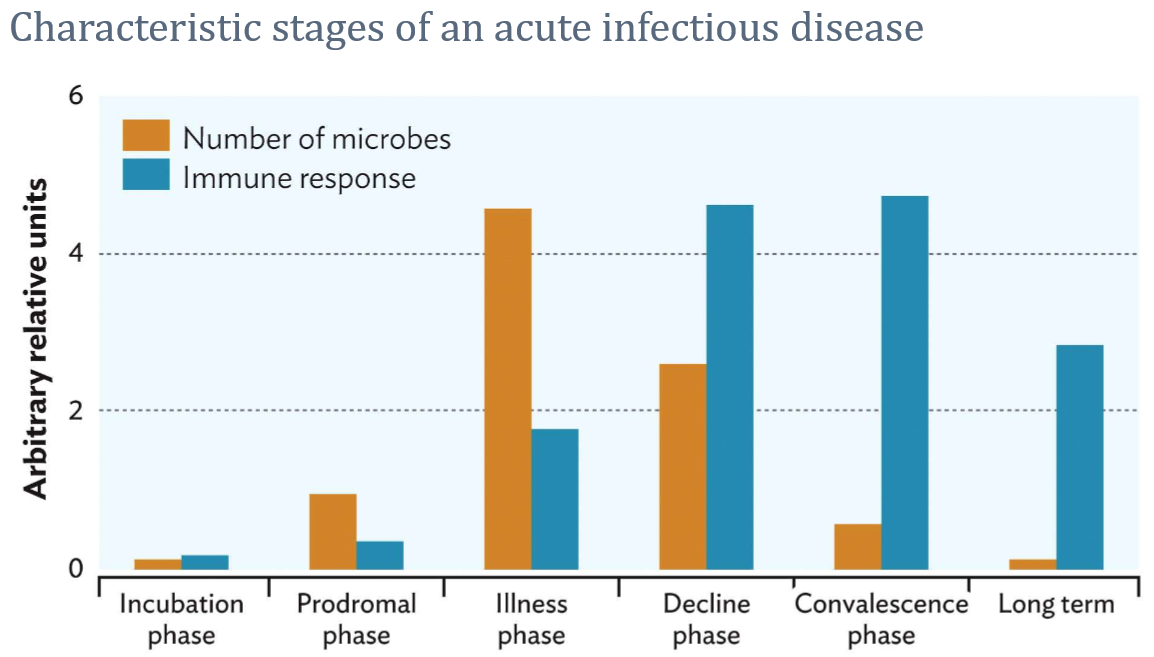
Cycle - Incubation, Prodromal, Invasion (Illness), Convalescence, and comparison between no. of organisms and symptoms
* **Incubation** = This refers to the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, and from when symptoms and signs are first apparent
* **Prodromal** = In this phase, the numbers of infectious agents start increasing and the immune system starts reacting to them
* It is characterized by early symptoms that might indicate the start of a disease before specific symptoms occur
* **Invasion** = is characterized by active replication or multiplication of the pathogen and its numbers peak exponentially, quite often in a very short period of time.
* includes the time when a person shows apparent symptoms of an infectious disease
* Symptoms are very pronounced, both specific to the organ affected as well as in general due to the strong reaction of the immune system
* **Convalescence** = the patient recovers gradually and returns to normal
* may continue to be a source of infection even if feeling better
* Depending on the severity of the infection, some people may have permanent damage even after the infection resolves.
* **Prodromal** = In this phase, the numbers of infectious agents start increasing and the immune system starts reacting to them
* It is characterized by early symptoms that might indicate the start of a disease before specific symptoms occur
* **Invasion** = is characterized by active replication or multiplication of the pathogen and its numbers peak exponentially, quite often in a very short period of time.
* includes the time when a person shows apparent symptoms of an infectious disease
* Symptoms are very pronounced, both specific to the organ affected as well as in general due to the strong reaction of the immune system
* **Convalescence** = the patient recovers gradually and returns to normal
* may continue to be a source of infection even if feeling better
* Depending on the severity of the infection, some people may have permanent damage even after the infection resolves.
15
New cards
Types of Infections - Local, systemic, mixed, primary and secondary, acute and chronic, asymptomatic
* **Local infection** = an infection that affects only one body part or organ
* **Systemic infection** = affects the entire body
* **Mixed infection** = infected with more than one strain of the same species of bacteria
* **Primary infection** = when you are initially exposed to a pathogen?
* **Secondary infection** = one that occurs when a different infection, known as a primary infection, has made a person more susceptible to disease
* occurs either after or because of another infection
* **Acute infection** = symptoms develop and resolve rapidly (i.e. the common cold)
* **Chronic infection** = involves symptoms that develop gradually and resolve slowly
* **Asymptomatic infection** = where a disease or infection does not lead to any (noticeable) symptoms
* **Systemic infection** = affects the entire body
* **Mixed infection** = infected with more than one strain of the same species of bacteria
* **Primary infection** = when you are initially exposed to a pathogen?
* **Secondary infection** = one that occurs when a different infection, known as a primary infection, has made a person more susceptible to disease
* occurs either after or because of another infection
* **Acute infection** = symptoms develop and resolve rapidly (i.e. the common cold)
* **Chronic infection** = involves symptoms that develop gradually and resolve slowly
* **Asymptomatic infection** = where a disease or infection does not lead to any (noticeable) symptoms
16
New cards
Sequelae
Pathological consequences that may develop after a disease resolves
17
New cards
Types of Direct and Indirect Transmission, paying particular attention to respiratory droplets, aerosols, droplet nuclei
* **Direct contact transmission** = organisms may spread directly from person to person
* Touching, kissing, sex, droplets from direct sneezing or coughing (this occurs when someone is sneezing or coughing in your personal space; IF they cough or sneeze and it lingers in the air until someone enters the space OR the secretions dry up and then become airborne later - that is INDIRECT transmission)
* **Indirect transmission** = pathogens may spread indirectly through an intermediary, which may be living or nonliving
* __Airborne transmission__ (droplet nuclei, aerosols)
* __Fomites__ (inanimate objects)
* __Vehicles__ (food, water, or air)
* Vectors (ticks, mosquitoes, flies)
* Touching, kissing, sex, droplets from direct sneezing or coughing (this occurs when someone is sneezing or coughing in your personal space; IF they cough or sneeze and it lingers in the air until someone enters the space OR the secretions dry up and then become airborne later - that is INDIRECT transmission)
* **Indirect transmission** = pathogens may spread indirectly through an intermediary, which may be living or nonliving
* __Airborne transmission__ (droplet nuclei, aerosols)
* __Fomites__ (inanimate objects)
* __Vehicles__ (food, water, or air)
* Vectors (ticks, mosquitoes, flies)
18
New cards
Adherence and colonization (list a few characteristics that influence)(also associated with virulence)
* **Adhesins** enable the microbiota to attach to host cells
* Like cell surface layers or appendages that aid in attachment (virulence factor)
* **Colonization** refers to the ability of the microbe to say attached to the surface and replicate, despite the host defenses
* Like cell surface layers or appendages that aid in attachment (virulence factor)
* **Colonization** refers to the ability of the microbe to say attached to the surface and replicate, despite the host defenses
19
New cards
Toxin production - Endotoxins and Exotoxins and comparisons between the 2
* **Endotoxin** = toxin that is not secreted but released after the cell is damaged
* Composed of LPS
* Target organs are damaged; the heart, muscles, blood cells, and intestinal tract show dysfunctions
* General physiological effects (fever, malaise, diarrhea, aches, shock)
* Weakly immunogenic/antigenic
* Usually heat stable
* **Exotoxin** = toxin molecule (protein) secreted by a living bacterial cell into the infected tissue
* Usually G+ bacteria
* Strong specificity for a target cell
* Very specific in their action (entero-, neuro-, cyto- toxin)
* Strongly antigenic
* Can produce toxoids or antitoxins
* Very toxic in small amounts
* Usually heat labile
* Composed of LPS
* Target organs are damaged; the heart, muscles, blood cells, and intestinal tract show dysfunctions
* General physiological effects (fever, malaise, diarrhea, aches, shock)
* Weakly immunogenic/antigenic
* Usually heat stable
* **Exotoxin** = toxin molecule (protein) secreted by a living bacterial cell into the infected tissue
* Usually G+ bacteria
* Strong specificity for a target cell
* Very specific in their action (entero-, neuro-, cyto- toxin)
* Strongly antigenic
* Can produce toxoids or antitoxins
* Very toxic in small amounts
* Usually heat labile
20
New cards
(From one host to the next:) Portals of entry/exit
* **Fecal-oral**: portal is the mucosa of the GI tract
* **Skin**: portal is the skin epithelium
* **Respiratory**: portal is the mucosa of the respiratory tract
* **Urogenital**: portal is the mucosa of the genital and urinary tract
* **Parenteral**: portal is through breaks in the skin
* **Entry via the eye**: portal is conjunctiva (mucous membranes on the eyeball and inner eyelid)
* **Skin**: portal is the skin epithelium
* **Respiratory**: portal is the mucosa of the respiratory tract
* **Urogenital**: portal is the mucosa of the genital and urinary tract
* **Parenteral**: portal is through breaks in the skin
* **Entry via the eye**: portal is conjunctiva (mucous membranes on the eyeball and inner eyelid)
21
New cards
Communicable verses Non-communicable
* **Communicable** = infectious disease
* **Non-communicable** = chronic disease; not passed from person to person
* **Non-communicable** = chronic disease; not passed from person to person
22
New cards
Prevalence
Refers to the total number of cases and reflects the length of the illness, recovery, and deaths
23
New cards
Incidence
The rate of new cases that occur during a specified time period (usually expressed in relation to a population number such as 1000, 10000, or 100000)
24
New cards
morbidity and mortality rates
* **Morbidity** is the rate of illness due to a disease
* **Mortality** is the rate of death due to a disease
* **Mortality** is the rate of death due to a disease
25
New cards
Endemic
**Endemic** disease is one that is always present in a community at a low rate, often in an animal reservoir
* Ex. plague, Lyme disease
* Ex. plague, Lyme disease
26
New cards
Epidemic
**Epidemic** disease is one in which the number of cases increases in a community in a short time
* Ex. outbreaks
* Ex. outbreaks
27
New cards
Pandemic
**Pandemic** disease is an endemic that spreads worldwide
* Ex. influenza, HIV, covid-19
* Ex. influenza, HIV, covid-19
28
New cards
*Enterococcus faecalis* and VREs
* *E. faecalis* is the most abundant GPC in the human intestinal tract and is frequently used as an indicator organism in colder environments (i.e. water, frozen foods, brackish, and saltwater)
* **VRE**, or Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci, are responsible for many serious HAIs
* Identified as a Serious Threat by CDC
* **VRE**, or Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci, are responsible for many serious HAIs
* Identified as a Serious Threat by CDC
29
New cards
*Staphylococcus aureus*
* Troublesome hospital pathogen and common foodborne illness
* Possess enzymes that coat the bacteria and protect it from the immune system and antibiotics (virulence factor)
* __Exotoxins__ damage the host tissue and weaken host defenses (i.e. Toxis shock syndrome toxin (TSST), exfoliative toxin, enterotoxin)
* **Skin infections**
* Folliculitis (superficial)
* Boil or furuncle (deep)
* Carbuncles are boils joined together
* Impetigo (collection of multiple infective lesions)
* Nonbullous
* Bullous
* **Food poisoning**
* Methicillin-resistant *S. aureus* (**MRSA**)
* Was an HAI but is now no longer confined to a hospital
* Possess enzymes that coat the bacteria and protect it from the immune system and antibiotics (virulence factor)
* __Exotoxins__ damage the host tissue and weaken host defenses (i.e. Toxis shock syndrome toxin (TSST), exfoliative toxin, enterotoxin)
* **Skin infections**
* Folliculitis (superficial)
* Boil or furuncle (deep)
* Carbuncles are boils joined together
* Impetigo (collection of multiple infective lesions)
* Nonbullous
* Bullous
* **Food poisoning**
* Methicillin-resistant *S. aureus* (**MRSA**)
* Was an HAI but is now no longer confined to a hospital
30
New cards
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
* **Necrotizing fasciitis** = “flesh-eating,” extremely rapid spread, life-threatening infection that frequently arises from superficial wounds and in healthy individuals with no medical history, can also be associated with compromised individuals
* bacteria produce enzymes that cause necrosis of fat and fascia that surrounds muscles and organs, making treatment extremely difficult
* __Natural reservoirs__ = human nasopharynx and parts of the skin
* Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxins (**SPEs**)
* Can produce high levels of inflammation and lead to shock
* **Hemolysin**
* Lyses RBCs
* **Erysipelas**
* Acute infection (swollen lymph nodes, fever, systemic symptoms)
* Rash (may be on the face)(“butterfly” appearance)
* **Cellulitis**
* Uncomplicated, non-necrotizing inflammation of the dermis related to acute infection
* __Symptoms__: localized pain, swelling, tenderness, erythema, and warmth
* **Streptococcal pharyngitis**
* Also known as __strep throat__
* Contagious; spreads through person-to-person contact and indirect contact with items contaminated by secretions
* __Symptoms__: high fever, sore throat, and tender, enlarged lymph nodes
* Some strains of *S. pyogenes* produce exotoxins
* Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxins (**SPEs**) can cause fever and scarlet fever (red rash)
* “strawberry tongue”
* **Post-streptococcal sequelae**:
* Acute rheumatic fever (ARF)
* Glomerulonephritis (kidney disease)
* bacteria produce enzymes that cause necrosis of fat and fascia that surrounds muscles and organs, making treatment extremely difficult
* __Natural reservoirs__ = human nasopharynx and parts of the skin
* Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxins (**SPEs**)
* Can produce high levels of inflammation and lead to shock
* **Hemolysin**
* Lyses RBCs
* **Erysipelas**
* Acute infection (swollen lymph nodes, fever, systemic symptoms)
* Rash (may be on the face)(“butterfly” appearance)
* **Cellulitis**
* Uncomplicated, non-necrotizing inflammation of the dermis related to acute infection
* __Symptoms__: localized pain, swelling, tenderness, erythema, and warmth
* **Streptococcal pharyngitis**
* Also known as __strep throat__
* Contagious; spreads through person-to-person contact and indirect contact with items contaminated by secretions
* __Symptoms__: high fever, sore throat, and tender, enlarged lymph nodes
* Some strains of *S. pyogenes* produce exotoxins
* Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxins (**SPEs**) can cause fever and scarlet fever (red rash)
* “strawberry tongue”
* **Post-streptococcal sequelae**:
* Acute rheumatic fever (ARF)
* Glomerulonephritis (kidney disease)
31
New cards
*Bacillus cereus*
* Common airborne and dust borne
* Resistant to usual methods of disinfection and antisepsis (b/c of endospores)
* Spores survive cooking and reheating
* Resistant to usual methods of disinfection and antisepsis (b/c of endospores)
* Spores survive cooking and reheating
32
New cards
*Clostridium botulinum*
* Rare but severe intoxication usually from home-canned food
* __Botulism__ = intoxication associated with inadequate food preservation
* Foodborne pathogen
* Spore-forming
* Associated with vegetables and honey
* Botulinum toxin can cause paralysis; considered the most potent acute toxin known
* Infant botulism & wound botulism
* __Botulism__ = intoxication associated with inadequate food preservation
* Foodborne pathogen
* Spore-forming
* Associated with vegetables and honey
* Botulinum toxin can cause paralysis; considered the most potent acute toxin known
* Infant botulism & wound botulism
33
New cards
*Clostridium perfringens*
* **Clostridial myonecrosis:** muscle tissue is affected
* Extremely serious, life-threatening disease
* True __saprophyte__, growing only on dead tissue
* Produces toxins
* *C. perfringens* enterotoxin (**CPE**) produced by some strains can lead to gastrointestinal disease
* **Gastroenteritis**
* Spores contaminate food that has not been cooked thoroughly
* Mild, intestinal illness; 2nd most common form of food poisoning worldwide
* Associated with “thick” foods - meats w/gravy, casseroles, stews
* Extremely serious, life-threatening disease
* True __saprophyte__, growing only on dead tissue
* Produces toxins
* *C. perfringens* enterotoxin (**CPE**) produced by some strains can lead to gastrointestinal disease
* **Gastroenteritis**
* Spores contaminate food that has not been cooked thoroughly
* Mild, intestinal illness; 2nd most common form of food poisoning worldwide
* Associated with “thick” foods - meats w/gravy, casseroles, stews
34
New cards
*Clostridioides difficile*
* **Antibiotic-associated colitis/Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC)**
* Urgent threat
* Caused by chronic antibiotic use
* Nosocomial infection
* Toxin production
* G+, endospore forming
* Urgent threat
* Caused by chronic antibiotic use
* Nosocomial infection
* Toxin production
* G+, endospore forming
35
New cards
*Listeria monocytogenes*
* G+ non-spore-forming coccobacilli
* Associated with animals and animal products
* Causes mild gastroenteritis to more severe cases of meningitis, fetal demise
* 3rd leading cause of fatalities of food born illness
* Foodborne pathogen → causes diarrhea and fever
* Associated with animals and animal products
* Causes mild gastroenteritis to more severe cases of meningitis, fetal demise
* 3rd leading cause of fatalities of food born illness
* Foodborne pathogen → causes diarrhea and fever
36
New cards
*Streptomyces*
* Phylum actinobacteria
* Actinomycetes
* Form mycelia with branching filaments
* *Streptomyces* - source of most currently used antibiotics
* Abundant in soil
* Actinomycetes
* Form mycelia with branching filaments
* *Streptomyces* - source of most currently used antibiotics
* Abundant in soil
37
New cards
*Bifidobacterium bifidus*
* Pioneer colonizer of the human intestinal tract
* Associated with vaginal births and breastfeeding
* Responsible for many of the significant benefits of breastmilk
* Probiotic agent
* Associated with vaginal births and breastfeeding
* Responsible for many of the significant benefits of breastmilk
* Probiotic agent
38
New cards
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis* (tuberculosis)
* Acid-fast
* Cases are on the rise in developed nations due to HIV and a growing indigent population
* Multidrug resistant (**MDR**) tuberculosis
* highly infectious
* produces rapid onset and fatal disease among patients with HIV
* Spread from person to person (no animal reservoir)
* Cases are on the rise in developed nations due to HIV and a growing indigent population
* Multidrug resistant (**MDR**) tuberculosis
* highly infectious
* produces rapid onset and fatal disease among patients with HIV
* Spread from person to person (no animal reservoir)
39
New cards
*Mycobacterium leprae* (leprosy)
* Hansen’s bacillus/Disease
* Strict parasite
* Causes **leprosy**, a chronic disease that begins in the skin and mucous membranes and progresses into nerves
* Endemic regions throughout the world
* Not highly virulent
* Strict parasite
* Causes **leprosy**, a chronic disease that begins in the skin and mucous membranes and progresses into nerves
* Endemic regions throughout the world
* Not highly virulent
40
New cards
*Bartonella henselae*
* Cat-scratch disease
* A lymphatic infection associated with a clawing injury by cats
* A lymphatic infection associated with a clawing injury by cats
41
New cards
*Rickettsia rickettsia*
* Rocky Mountain spotted fever
* Zoonosis carried by dog and wood ticks (and lice)
* First symptoms are fever, chills, headache, and a distinct spotted rash
* May damage the heart and CNS
* fatality rates are 20% if not treated
* Zoonosis carried by dog and wood ticks (and lice)
* First symptoms are fever, chills, headache, and a distinct spotted rash
* May damage the heart and CNS
* fatality rates are 20% if not treated
42
New cards
*Burkholderia cepacia*
active in biodegradation of a variety of substances; opportunistic agent in the respiratory tract, urinary tract, and occasionally skin infections; drug-resistant, numerous outbreaks in consumer products
43
New cards
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
* **Gonorrhea** (“the clap”)
* Pelvic inflammatory disease
* infection spreads to uterus and fallopian tubes
* Opthalmia neonatorum
* eye infection
* Most women do not exhibit symptoms but most men do
* Pelvic inflammatory disease
* infection spreads to uterus and fallopian tubes
* Opthalmia neonatorum
* eye infection
* Most women do not exhibit symptoms but most men do
44
New cards
*Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli* 0157:H7 - STECs
* Escherichia coli - commensal
* live in intestines
* *Escherichia coli* 0157:H7 - pathogen
* causes a severe intestinal infection
* most common strain to cause illness in people
* Shiga Toxin-Producing *E. coli* (**STECs**)
* causes bloody diarrhea (similar to that caused by *Shigella*)
* live in intestines
* *Escherichia coli* 0157:H7 - pathogen
* causes a severe intestinal infection
* most common strain to cause illness in people
* Shiga Toxin-Producing *E. coli* (**STECs**)
* causes bloody diarrhea (similar to that caused by *Shigella*)
45
New cards
*CREs -* Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteraceae
* Untreatable and hard-to-treat infections from CRE bacteria are on the rise in patients in medical facilities
* Have become resistant to nearly all antibiotics we have today
* Almost half of the hospital patients who get bloodstream infections from CRE bacteria die from the infection
* Have become resistant to nearly all antibiotics we have today
* Almost half of the hospital patients who get bloodstream infections from CRE bacteria die from the infection
46
New cards
*Legionella pneumophila*
* Legionnaire’s disease
* Intracellular pathogen
* Contaminates various water sources, ranging from lakes to the hot water and air-conditioning distribution systems of large buildings
* Transmission via inhalation of contaminated water droplets
* Causes atypical pneumonia
* Fatality rate 3-30%
* Intracellular pathogen
* Contaminates various water sources, ranging from lakes to the hot water and air-conditioning distribution systems of large buildings
* Transmission via inhalation of contaminated water droplets
* Causes atypical pneumonia
* Fatality rate 3-30%
47
New cards
*Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
* Commonly grows in the soil as a decomposer, but in humans, it can infect surgical wounds or form biofilms in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients
* MDR
* Very common HAI
* Most common cause of hospital-acquired pneumonia
* Cause of endocarditis, meningitis, UTIs, abscesses, corneal disease
* Opportunistic pathogen
* MDR
* Very common HAI
* Most common cause of hospital-acquired pneumonia
* Cause of endocarditis, meningitis, UTIs, abscesses, corneal disease
* Opportunistic pathogen
48
New cards
*Salmonella enterica*
* **Salmonellosis**
* **Typhoid fever**
* No animal reservoir
* Associated with food preparation
* Fecal-oral route
* Intermittent fevers and diarrhea
* **Enterocolitis**
* Associated with animal contact
* **Typhoid fever**
* No animal reservoir
* Associated with food preparation
* Fecal-oral route
* Intermittent fevers and diarrhea
* **Enterocolitis**
* Associated with animal contact
49
New cards
*Shigella* spp.
* **Shigellosis**
* Bloody diarrhea
* Produces Shiga toxin
* Low infective dose
* Also called bacillary dysentery
* Similar pathogenesis to STEC
* No animal reservoir; fecal-oral route via food or water
* Bloody diarrhea
* Produces Shiga toxin
* Low infective dose
* Also called bacillary dysentery
* Similar pathogenesis to STEC
* No animal reservoir; fecal-oral route via food or water
50
New cards
*Yersinia pestis*
Causes a deadly disease (plague) that can be transmitted from animals to humans by an infected flea
* bubonic plague
* organisms moves from site to lymph nodes
* not transmissible
* septicemic plague
* pathogen enters bloodstream
* not transmissable
* pneumonic plague
* pathogen infects lungs
* transmissable, easily spread
* bubonic plague
* organisms moves from site to lymph nodes
* not transmissible
* septicemic plague
* pathogen enters bloodstream
* not transmissable
* pneumonic plague
* pathogen infects lungs
* transmissable, easily spread
51
New cards
*Campylobacter jejuni*
^^(I did not see anything on *C. jejuni* specifically\*)^^
52
New cards
*Vibrio cholerae*
* Fecal-oral route (contaminated water)
* “Rice water stools”
* Noninvasive → does not cause fever or bloody stools
* Cholera toxin
* Secretory diarrhea
* “Rice water stools”
* Noninvasive → does not cause fever or bloody stools
* Cholera toxin
* Secretory diarrhea
53
New cards
*Vibrio parahaemolyticus*
gastroenteritis from raw seafood; symptoms similar to cholera
54
New cards
*Vibrio vulnificus*
gastroenteritis from raw oysters; serious complications in persons with diabetes or liver disease. Associated with __necrotizing fasciitis__ from swimming in ocean water with an open wound
55
New cards
*Bdellovibrio*
* Predatory bacteria
* Has the ability to parasitize and kill other G- bacteria
* Has the ability to parasitize and kill other G- bacteria
56
New cards
*Treponema pallidum*
* spirochete
* “Great imitator”
* primary syphilis
* __chancre__: painless inflammatory reaction
* latency
* “Great imitator”
* primary syphilis
* __chancre__: painless inflammatory reaction
* latency
57
New cards
*Leptospira interrogans*
* causes **leptospirosis**, a zoonosis
* bacteria shed in urine; infection occurs by contact with contaminated urine; targets kidneys, liver, brain, eyes
* sudden high fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, conjunctivitis, and vomiting
* long term infections may affect the kidneys and liver
* 50-60 cases a year in the U.S.
* __increasing world wide__
* bacteria shed in urine; infection occurs by contact with contaminated urine; targets kidneys, liver, brain, eyes
* sudden high fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, conjunctivitis, and vomiting
* long term infections may affect the kidneys and liver
* 50-60 cases a year in the U.S.
* __increasing world wide__
58
New cards
*Borrelia burgdorferi*
* **Lyme disease**
* the most common vector-borne illness
* *B. burgdorferi*
* spirochete
* transmitted by tick bite
* linear chromosome
* complex life cycle
* the most common vector-borne illness
* *B. burgdorferi*
* spirochete
* transmitted by tick bite
* linear chromosome
* complex life cycle
59
New cards
*Bordetella pertussis*
^^(I did not see anything on *B. pertussis* specifically\*)^^
60
New cards
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
* persistent infection with *C. trachomatis* can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease
* most frequently reported sexually transmitted infectious disease
* 75% of infected women have no symptoms; most men are also asymptomatic
* __Chlamydia__ is the major cause of nongonococcal urethritis in the United States
* **Trachoma**
* caused by *C. trachomatis* serotypes A-C
* transmitted by hand-to-hand contact, contact with infected soaps and towels, and flies
* the __greatest single cause of preventable blindness__ throughout the world
* __neglected disease__
* most frequently reported sexually transmitted infectious disease
* 75% of infected women have no symptoms; most men are also asymptomatic
* __Chlamydia__ is the major cause of nongonococcal urethritis in the United States
* **Trachoma**
* caused by *C. trachomatis* serotypes A-C
* transmitted by hand-to-hand contact, contact with infected soaps and towels, and flies
* the __greatest single cause of preventable blindness__ throughout the world
* __neglected disease__
61
New cards
*Rhizobium*
* Intracellular Symbionts and Predators
* endosymbionts of plants that fix nitrogen
* endosymbionts of plants that fix nitrogen
62
New cards
*Bacteroides fragilis*
* *Bacteriodes* spp.
* major inhabitants of the human colon
* break down compounds that could be toxins
* produce polysaccharide A and other communication molecules to communicate with and direct the immune system
* removes side chains from bile acids
* can be opportunistic
* leading anaerobic HAI
* ^^(I did not see anything on *B. fragilis* specifically\*)^^
* major inhabitants of the human colon
* break down compounds that could be toxins
* produce polysaccharide A and other communication molecules to communicate with and direct the immune system
* removes side chains from bile acids
* can be opportunistic
* leading anaerobic HAI
* ^^(I did not see anything on *B. fragilis* specifically\*)^^
63
New cards
Cyanobacteria (Oxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria)
* oxygenic photoautotrophs = produce oxygen through photosynthesis
* __the only bacteria that produce oxygen__
* responsible for Earth’s atmosphere
* endosymbiosis leading to eukaryotic plants
* __the only bacteria that produce oxygen__
* responsible for Earth’s atmosphere
* endosymbiosis leading to eukaryotic plants
64
New cards
Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria
* Photosynthetic - __utilize different wavelengths__ of light than the cyanobacteria; __live in different depths__
* Contain photosynthetic pigment **bacteriochlorophyll**
* __Do not give off oxygen__ as a product of photosynthesis
* Contain photosynthetic pigment **bacteriochlorophyll**
* __Do not give off oxygen__ as a product of photosynthesis
65
New cards
*Caulobacter*
* Budding Appendaged Bacteria
* rods or cocci with an appendage
* lives in very low-nutrient environments
* __Strongest biological adhesive known__
* rods or cocci with an appendage
* lives in very low-nutrient environments
* __Strongest biological adhesive known__
66
New cards
Myxobacteria
* Gliding and Fruiting bacteria
* glide over moist surfaces and leave a slime trail
* produces **myxospores** that are resistant to desiccation, heat, and UV and can survive for several years (still not as resistant as endospores)
* glide over moist surfaces and leave a slime trail
* produces **myxospores** that are resistant to desiccation, heat, and UV and can survive for several years (still not as resistant as endospores)
67
New cards
*Deinococcus radiodurans*
* extraordinarily resistant to desiccation and radiation
* isolated from ground meat, feces, air, freshwater, and other sources, but natural habitat unknown
* isolated from ground meat, feces, air, freshwater, and other sources, but natural habitat unknown
68
New cards
Archaea groups - Know Methanogens or any of the others from the table that lists the 5 groups - know 1 and give 3 characteristics
Methanogenic archaea
* strict anaerobes
* capable of **methanogenesis**, an anaerobic respiration that generates methane as the final product of metabolism
* cells possess coenzyme M, factors 420 and 430, and methanopterin
* strict anaerobes
* capable of **methanogenesis**, an anaerobic respiration that generates methane as the final product of metabolism
* cells possess coenzyme M, factors 420 and 430, and methanopterin