Specialised Cells
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Plant, Bacterial and Animal cells are typical cells, most cells are specialised for a particular function, so…
their function can vary
Multicellular organisms
Contains lots of different types of cells (i.e. cells with different structures)
Specialised cells
Cells which have developed certain characteristics (known as adaptations) in order to perform particular functions
Cells specialise by undergoing differentiation:
A process by which cells develop the structure and characteristics needed to be able to carry out their functions
Egg cells and Sperm cells are specialised for…
reproduction
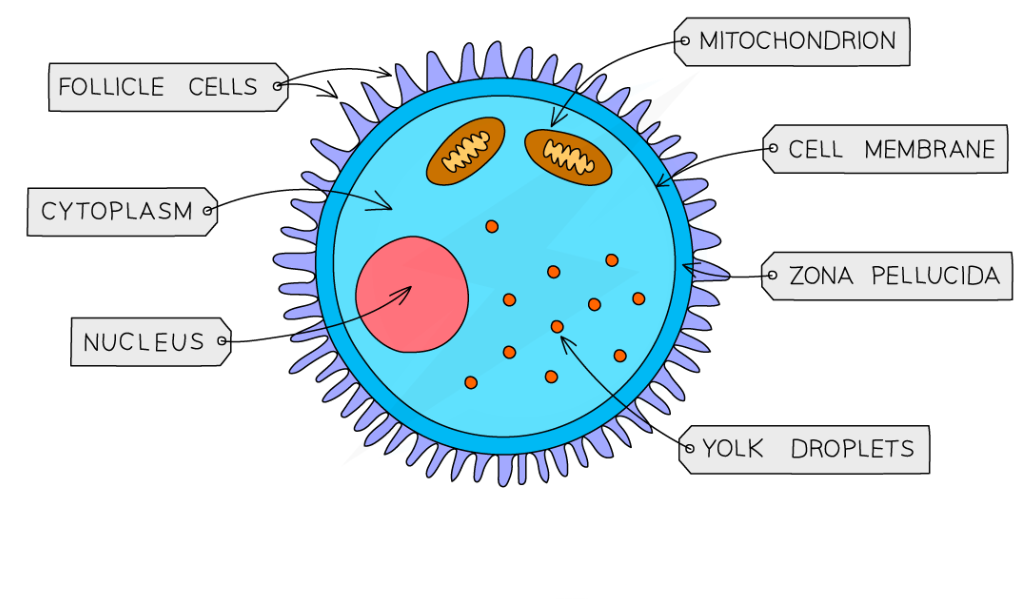
Egg cells
Its main function is to carry the female DNA and to nourish the developing embryo in the early stages
How its adapted to its function:
Contains nutrients in the cytoplasm to feed the embryo
Haploid nucleus
Straight after fertilisation, its membrane changes structure to stop any sperm getting in. This makes sure the offspring end up with the right amount of DNA
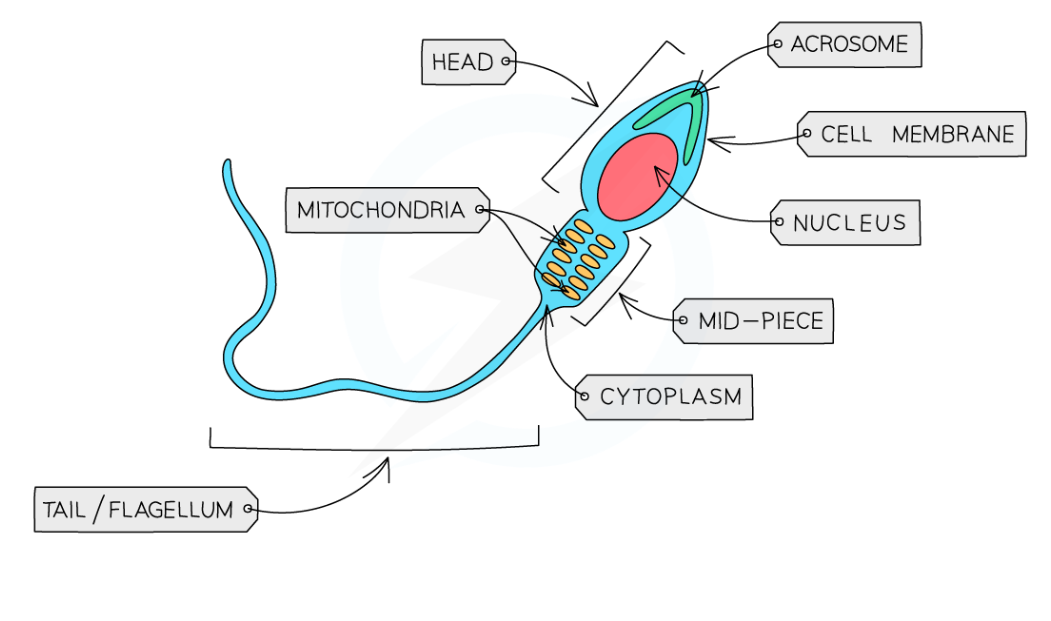
Sperm cells -
Transports the male’s DNA to the female’s egg
How its adapted to its function:
Has a long tail so it can swim to the egg
Has a lot of mitochondria in the middle section to provide the energy (from respiration) needed to swim this distance
Has an acrosome at the front of the ‘head’ containing enzymes that help the sperm penetrate the egg's outer layers during fertilization
Contains a haploid nucleus
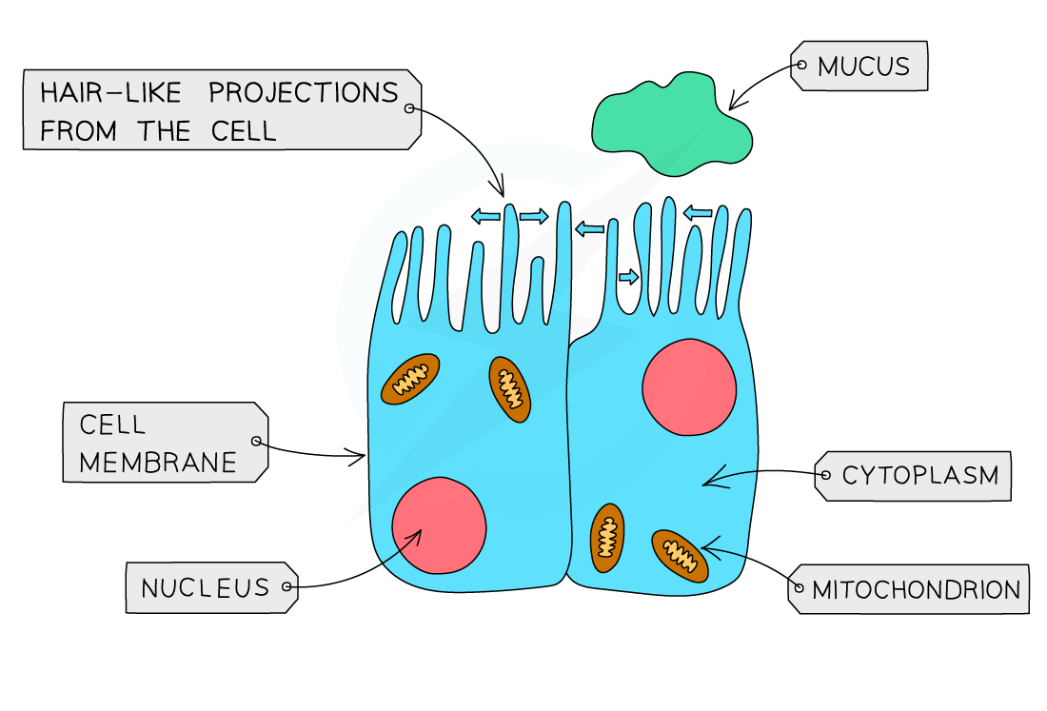
Ciliated Epithelial Cells
Specialised for moving materials
Lines the surfaces of organs
Some of them have cilia (hair-like structures) on the top surface of the cell
Its function is to move substances - the cilia beat to move substances in one direction, along the surface of the tissue
e.g. the lining of the airways contains lots of this to help move mucus (and all the particles from the air it has trapped) up to the throat so it can be swallowed and doesn’t reach the lungs