Week 3: Social Aspects of Aging
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
Ageism
Systematic stereotyping of and discrimination against people because of their age.
2
New cards
Institutionalized ageism
our societal structure is based on the fact that everyone is young, failing to tend to the needs of older people
3
New cards
Internalized ageism
once labelled old and begin to be treated differently by society, an older persons self concept will be affected.
4
New cards
filial piety
Prominent in traditional Chinese culture
* emphasizes importance of caring for parents but extends to obeying them and honouring ones ancestors
* emphasizes importance of caring for parents but extends to obeying them and honouring ones ancestors
5
New cards
positive ageism
overemphasis on positive images of aging
(can stigmatize older persons who cannot meet this ideal)
(can stigmatize older persons who cannot meet this ideal)
6
New cards
Recap: Population is aging because of 3 demographic changes:
1. declining fertility rates
2. increasing life expectancy
3. immigration
7
New cards
there are more ____ _____ and better *____ _________* in aging friendly neighbourhoods
green space
street connectivity
street connectivity
8
New cards
Contextual vs. Compositional effects
composition:
➢ Making more of these built environment features because the neighbourhood is composed of more seniors
\
context:
➢ Older people move to the area with these features because it is healthier for them (context)
\
“people make the places OR places make people
* High demand from older individuals for built environment, therefore they will be built (compositional)
\
* Features already built (contextual) attracts older individuals
➢ Making more of these built environment features because the neighbourhood is composed of more seniors
\
context:
➢ Older people move to the area with these features because it is healthier for them (context)
\
“people make the places OR places make people
* High demand from older individuals for built environment, therefore they will be built (compositional)
\
* Features already built (contextual) attracts older individuals
9
New cards
Population age distribution is changing. This is __**not a crisis if:**__
1. we understand the trends
2. the society responds with evidence-based feasible policies
10
New cards
Policy - definition
A set of ^^ideas or a plan^^ of what to do ==in particular== situations that has been agreed to %%officially%% by
* a group of people,
* a business organization,
* a government,
* or a political party
* a group of people,
* a business organization,
* a government,
* or a political party
11
New cards
Policy only works if:
* targeted
* feasible
* evidence-based
* feasible
* evidence-based
12
New cards
Policy in context on population aging
**Situation:**
* more older adults and possibly dependency issues
\
**goal:**
* increasing the productivity of older adults
* healthy aging, social services, aging in place
\
**for good policy we need:**
* evidence of trajectories of aging and related issues
* more older adults and possibly dependency issues
\
**goal:**
* increasing the productivity of older adults
* healthy aging, social services, aging in place
\
**for good policy we need:**
* evidence of trajectories of aging and related issues
13
New cards
reasonable policies
By making older people productive (healthy aging, changes in labour regulations) this ratio doesn’t mean dependency anymore
so…
1. Address real issues
2. goal is clear
so…
1. Address real issues
2. goal is clear

14
New cards
Interaction between social factors throughout life
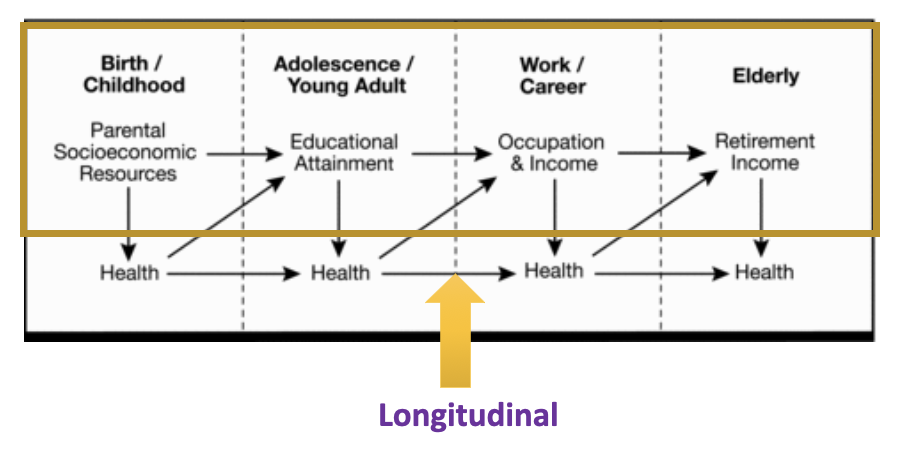
15
New cards
modernization theory
**The social status declines as people age**
due to lack of contribution?
* An inevitable result of aging or policies?
* Example of mandatory retirement at 65
* Older people themselves believe age is a limitation
due to lack of contribution?
* An inevitable result of aging or policies?
* Example of mandatory retirement at 65
* Older people themselves believe age is a limitation
16
New cards
intergenerational issues
Increasing life expectancy results in intergeneration competitions
* Can the job market be modified? \n
Change in family values/relations
* Shall care for older adults remain a responsibility of families?
* Can the job market be modified? \n
Change in family values/relations
* Shall care for older adults remain a responsibility of families?
17
New cards
Age relation
* older people themselves believe age is a limitation
* age organizes the society
* gives power and identity
* limits access to resources
* __intersects__ with other social factors
* age organizes the society
* gives power and identity
* limits access to resources
* __intersects__ with other social factors
18
New cards
Intersectionality
social factors as creators of ‘social location’
* age as a social factor
eg.
* being an @@older@@ %%women%% of ^^colour^^
= combines harms of marginalization
* impacts on health
* concomitant strengths, resilience, and power arising from combinations of social locations
* mobilize to improve health/ social status
* age as a social factor
eg.
* being an @@older@@ %%women%% of ^^colour^^
= combines harms of marginalization
* impacts on health
* concomitant strengths, resilience, and power arising from combinations of social locations
* mobilize to improve health/ social status
19
New cards
Ageism
* negative value of ageing process
* seeing older people as ‘others’
* frequent verbal comments, jokes
* stereotypes include:
* weak, incompetent, no contribution
* seeing older people as ‘others’
* frequent verbal comments, jokes
* stereotypes include:
* weak, incompetent, no contribution
20
New cards
Social consequences of ageism
* An unhealthy aging population
\
* Assumed burden becomes real burden
\
* Internalization: accepting that when you are old you are only receiver of services
* Can’t contribute anymore
\
* Assumed burden becomes real burden
\
* Internalization: accepting that when you are old you are only receiver of services
* Can’t contribute anymore
21
New cards
Why does ageism persist?
* Normal response to fear of death?
* Old age as a reminder for inevitable death
* Learned socialization
* ➢ During childhood
* ➢ Media
* ➢ Marketing
\
* Social discourse
* Culture(s) that value health, youth, independence
* Old age as a reminder for inevitable death
* Learned socialization
* ➢ During childhood
* ➢ Media
* ➢ Marketing
\
* Social discourse
* Culture(s) that value health, youth, independence
22
New cards
culture vs cohort
“Caring for” does not necessarily mean “caring about”
* Neglect of issues in other cultures
* Living together not necessarily equals better care, higher affectation
\
Growing up in different times means different life skills
* Misunderstanding
\
Segregation of age groups
* Stereotypes
* Conflicts
\
%%Key: age integration, age literacy%%
* Neglect of issues in other cultures
* Living together not necessarily equals better care, higher affectation
\
Growing up in different times means different life skills
* Misunderstanding
\
Segregation of age groups
* Stereotypes
* Conflicts
\
%%Key: age integration, age literacy%%
23
New cards
Is it possible to eliminate ageism?
* Fundamental changes in social structure, attitude, etc.
* Some progress
* We can learn from improvement in other ….isms
\
* A Public effort
* Example of positive ageism?
* Some progress
* We can learn from improvement in other ….isms
\
* A Public effort
* Example of positive ageism?
24
New cards
What does ageism do to the society?
* Reinforces intergenerational conflicts
* Segregates the society
* Deprives the society of potential contribution of potentially efficient older individuals who have internalized ageism
* Impacts social, mental, and physical health of older individuals
* Delays achieving the goal of health aging
* Segregates the society
* Deprives the society of potential contribution of potentially efficient older individuals who have internalized ageism
* Impacts social, mental, and physical health of older individuals
* Delays achieving the goal of health aging
25
New cards
Birth rate vs Fertility rate
__**Birth Rate:**__
* The total number of births in a year per 1,000 individuals.
\
__**Fertility Rate:**__
* The total number of births in a year per 1,000 women of reproductive age in a population
* The total number of births in a year per 1,000 individuals.
\
__**Fertility Rate:**__
* The total number of births in a year per 1,000 women of reproductive age in a population
26
New cards
Summary
* Potential detrimental impact of aging population can be modified by proper policies
\
* Strong social-related factors generate and reinforce ageism
\
* Combating ageism is a social effort, responsibility of all age groups
\
* Strong social-related factors generate and reinforce ageism
\
* Combating ageism is a social effort, responsibility of all age groups