Chapter 13: Microbe Human Interactions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Normal biota
harmless &beneficial microbes (difficult to remove from skin)
Normal Resident Microbiota
Microbes that engage in mutual or commensal associations with humans
Transient Organisms
found on the skin for short periods of time but DO NOT grow there, could be a pathogen
easily removed (washing)
destroyed by the host’s defenses
cannot compete with the resident normal flora
may be flushed away by bodily secretions like sweat, oil, and urine
True Pathogen
causes disease in a healthy person
Opportunistic pathogen
causes disease when the host’s defenses are compromised
Example: C. Diff
Pathogenicity
an organism’s potential to cause infection or disease
Epidemiology
Study of the frequency and distribution of disease and other health-related factors in a defined human population
Example would be effects of disease on communitiesD
Direct Contact
transferring microbes from person to person
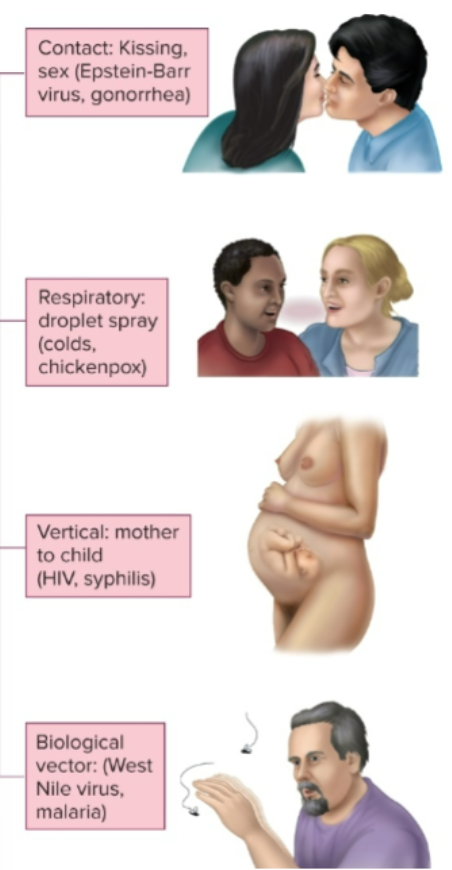
Indirect Contact
microbes pass from the infected host to the intermediate conveyor (non-living) and then to another host
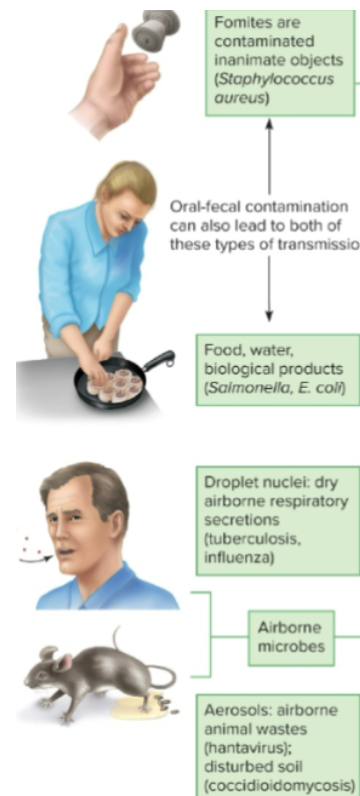
Fomite
an inanimate object capable of allowing microbe to survive but not reproduce (dry, has no food or water)
Oral - fecal
contamination through contact with fecal matter
A reservoir of infection
any inanimate object that allows a microbe to grow and reproduceA
Airborne Transmission
respiratory secretions & air itself
Droplet Nuclei - microscopic mucus & saliva create dried pellets in the air
Aerosols - fine dust or moist particles that contain live pathogens, like dust from soil and animal quarters
Chain of Infection
Portal of Entry - characteristic route a microbe follows to enter the tissues of the body
Exogenous agent - originates from a source outside the body
Endogenous agent - already exists on or in the body (normal flora); they typically enter through the respiratory tract or the digestive system
Attaching to the host
Adhesion - when a microbe establishes a stable association with the host’s cells
invading & becoming established - microbes have mechanisms for disabling and evading a host’s defenses
Toxins - can damage target cells
Inhibition - microbe capsules
Destruction - destruction of WBC
Causes of damage & disease - pathogens weaken host tissues
Necrosis - tissue death
Direct damage to cells through toxins or enzymes
Portals of Exit - pathogens depart by a specific avenue, which greatly influences the dissemination of infection
respiratory & salivary portals - mucus, nasal drainage, Etc.
Epithelial cells - skin & scalp
Fecal exit
Urogenital tract
Removal of blood or bleeding
Stages of Clinical Infection: Incubation period
time from initial contact to appearance of the first symptom
Stages of Clinical Infection: Prodromal stage
short period (2 days), earliest notable symptoms, small discomfort
Stages of Clinical Infection: Period of invasion
infective agent multiples at its highest levels
Stages of Clinical Infection: Convalescent Period
Recovery symptoms decline, gradually return to normal
Carrier
An individual who inconspicuously shelters a pathogen & spread it to others
Asymptomatic Carrier
shows no symptoms
Incubation carrier - spreads with infection
Convalescent carrier - recuperating without symptoms
Chronic carrier - an individual who shelters the infection for a long period of time
Passive Carrier
Contaminated healthcare provider transfers them to other patients