Dark Adaptation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Dark adaptation
The term Dark Adaptation (DA) describes the eye’s ability to adjust its sensitivity in scotopic conditions after previously being exposed to bright light (photopic bleach).
Photoreceptors spatial distribution
Cones mainly at fovea. Rods more numerous from the fovea towards the periphery, highest density at 18deg. Cones=rods at 1.8 deg. Ratio 9:1 (macula) 20:1 (entire retina). Human retina is rod dominated
Scotopic Vision Characteristics
Luminous sensitivity increases. VA decreases. 2.5° scotoma in foveola (only cones). No colour discrimination. Purkinje shift (≠ Vl). Night myopia can appear. 15% of the population. <1.5Dp. Spherical aberration (mydriasis). Lense shape changes (young people)
Retinoid Cycle Rods and Cones
Step I Absorption of photon by rhodopsin molecule (chromophore + opsin)
Step II Cleavage of chromophore (11 cis retinal) and opsin
Step III 11cis retinal converted to All-trans retinal
Step IV All-trans retinal reduced to all-trans retinol and transferred to RPE
Step V All trans retinol converted to 11-cis retinol in RPE
Step VI 11-cis retinol converted to 11-cis retinal and transferred to rod outer segment
Step VII 11-cis retinal combined with free opsin in rod outer segment to form rhodopsin molecule
Muller cell pathway - cone specific
Dark adaptation curve
Three phases - The first is relatively rapid and dominated by cones and, as the rods become more sensitive than cones, a steady further bi-phasic improvement in sensitivity occurs which is mediated by rods. The transition between the cone and rod sections is called the α point. The time course of sensitivity recovery in the rod section can be attributed directly to the ability of the eye to regenerate activated rhodopsin, the rod visual pigment. S2 and S3.
Dark adaptation Curve Parameters
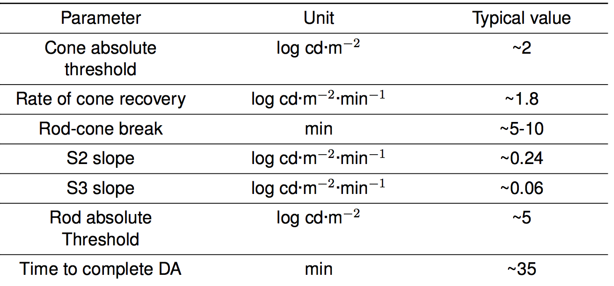
Factors affecting DA
Physical - Stimuli size, stimuli location, bleaching exposure, target wavelength. Physiological - Aging, retinal diseases.
Stimuli size and location
Due to the convergence of the photoreceptor, in the peripheral retina, a great amount of rods converge in just one ganglion cell. Due to this fact, the scotopic system has a highest sensibility and, it is less resolute than the photopic.
Ageing
Rod-cone break increased. The rate of sensitivity recovery during the second component of the rod-mediated phase decreased. The time during the second component of dark adaptation increased. The rate of recovery during the third component decreased. The time needed to complete the DA process increased. Bruch’s membrane thickens with age, and its hydraulic conductivity decreases. S2 decreased by 0.011 log units/min per decade .
Clinical applications
DA abnormal in following conditions: Systemic Vitamin A Deficiency, Macular Degeneration, Stargardt’s Macular Dystrophy, Diabetes, Retinitis Pigmentosa, Alcoholism, Crohn’s Disease.
Age Related Macular Degeneration
Debilitating loss of central vision. Main cause of blindness in EU/US. two types: common (85%) dry form, and wet form. dry AMD affects 30% of > 65 year olds. Initially no visual effects. Gradual loss of central vision. 40% develop wet AMD identified by the appearance of lipoidal deposits in outer retinal layers, called drusen.
AMD and dark adaptation
Measurement of the slowing of dark adaptation is likely to provide a valuable and non-invasive bioassay, both as a diagnostic tool for predicting the likelihood of onset of macular degeneration and as a means of assessing the efficacy of treatments of the disease.” now well known that DA abnormal in early stage AMD. functionally the only sign of the disease (early stages)
DA in early AMD
α-point delayed. S2 shallower. β-point delayed. Rod sensitivity decreased. Prolonged testing time
Grades of AMD
Grade 1 - Px have normal daytime vision. Grades 2 and 3 - Px have almost normal daytime vision.
Methods
Most of this require complicated apparatus. A mathematical model is required to fit the dark adaptation parameters. McGwing et al (1999) based on the one-exponencial two linear model, introduced nonlinear regresion analysis. Goldmann Weekers dark adaptometer - Poor repeatability. The GWA would not be a useful instrument for documenting visual changes in clinical trials. CRT- based dark adaptometry: Their temporal and spatial characteristics are well documented and they are easily controlled by a computer. Produce results that agree with previous studies. Automated and inexpensive method.
Procedure
eye exposed to short duration bright flash of light. target presented at 8 degrees eccentricity. observer presses button when target detected. as sensitivity improves target detected at lower and lower intensity. sensitivity recovery (log units) plotted against time after bleach.
Detecting early AMD
Clinical Trial: 20 normals 20 AMD patients. Outcome: measure S2 Results: Normals S2 = -0.17 (0.05), Patients S2 = -0.07 (0.08).
Clinical Trial: 20 normals 20 AMD patients. Outcome: measure S2. Diagnostic accuracy: extremely high. 95% Sensitivity, 90% Specificity.