AP Psychology Unit 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Biological perspective
Body, brain chemistry and structures, neurons and neurotransmitters, drugs all influence behavior
Evolutionary perspective
Behaviors are influenced by two basic principles, the need for survival and the need to reproduce to ensure species survival
Psychodynamic perspective
Behavior is largely influenced by the unconscious, uncontrollable defense mechanisms, and repressed from childhood
Behavioral perspective
Behavior determined by how a person has been conditioned, rewarded, or punished in past struggles
Cognitive perspective
Behaviors of how a person thinks about their situation or develops expectations about a situation
Social-cultural perspective
Behaviors are explained by looking at societal norms, expectations, and family beliefs in a particular society
Hindsight bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it (I knew it all along)
Confirmation bias
A tendency to search for information that supports OUR preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Overconfidence bias
The more confident someone is the less accurate their answer is (I'm 90% sure that's right)
Hypothesis
-A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
-IT MUST BE FALSIFIABLE
-Example: People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress values
Operational Defintion
-A statement of the procedures used to define research variables
-Precise parameters or qualifications
-Necessary for replication
Reliability
Consistency
Validity
Accuracy
Survey Method (PROS)
-Faster
-Wider scope of people
Survey Method (CONS)
1. Self-report bias
2. Self-desirability bias
Quantitative
-Numerical data
Qualitative
-Categorical data
Peer Review
-Evaluation by other members in the field
-This is then replicated
-Studies that are deemed unethical will NOT be replicated
Non-Experimental Research
-No cause and effect
-Lacks manipulation and control
-Measures variables as they occur
Case study
-In depth investigation of an individual or small group who may have a highlight usual trait
Case study (PROS)
-Details of subjects
-Unique quality or situation
-Unethical treatment
Case study (CONS)
-NO correlational data
-NO generalizability
-Time consuming
How can wording effects influence survey results?
The question can propose a bias upon research
Positive Correlation
Exercise and healthy eating has a strong association with excellent overall longevity
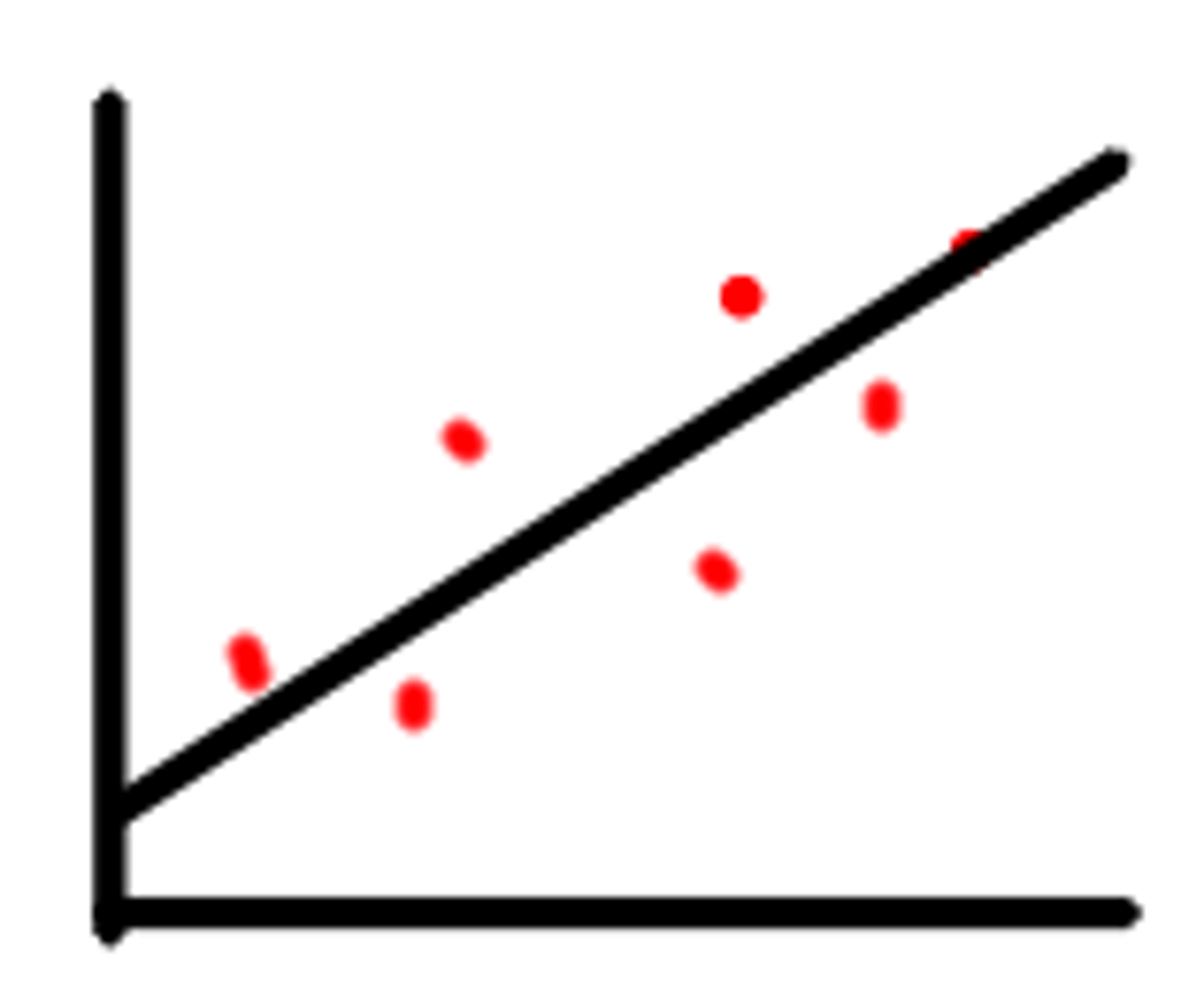
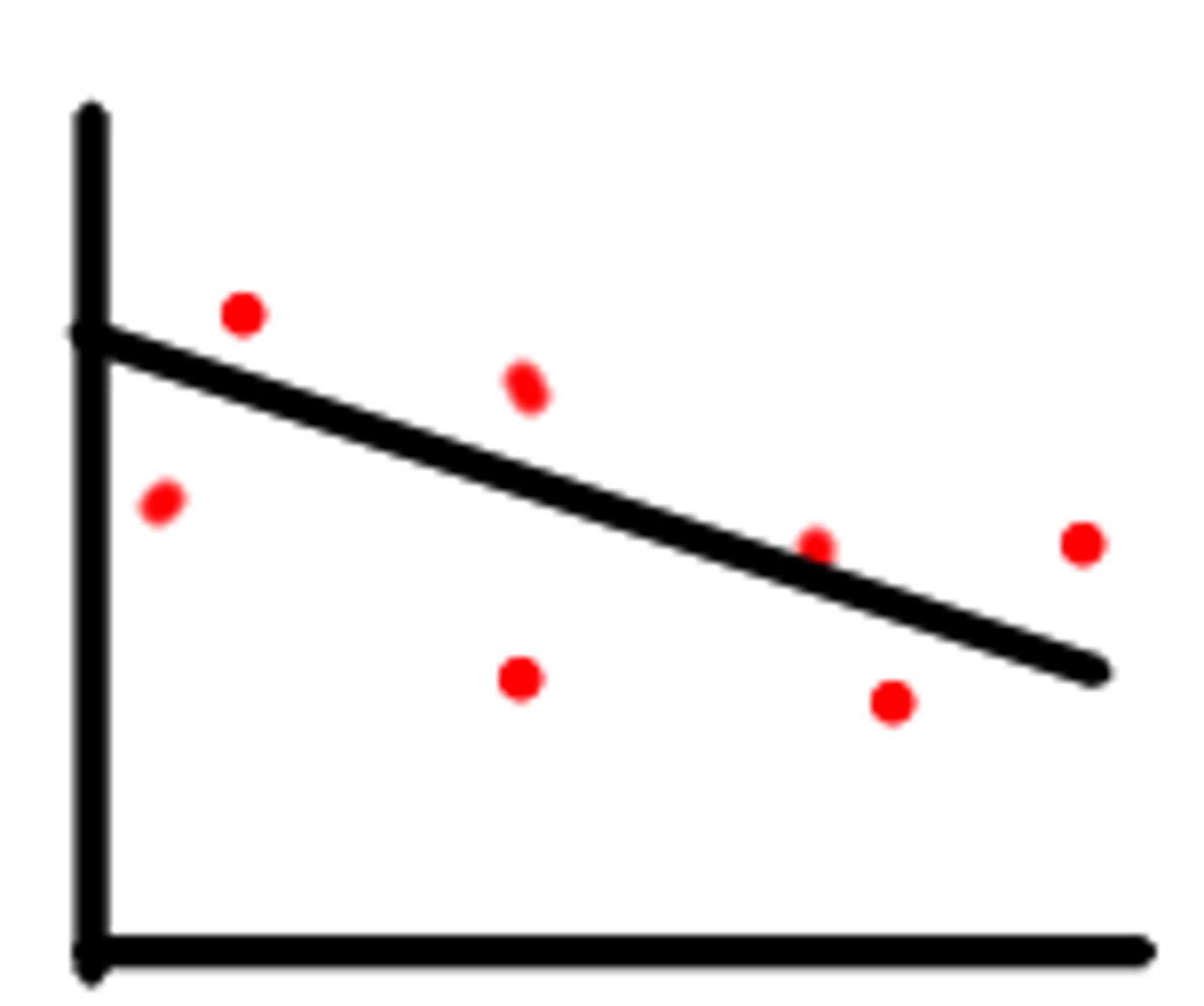
Negative Correlation
When alcohol consumption rises, mental and physical decreases sharply
No Correlation
The bigger someone's shoe size is the higher pay salary they receive
Meta-Analysis
The statistical combination of results for two or more separate studies
Meta-Analysis (PROS)
-Accuracy
-Pose and answer questions
Meta-Analysis (CONS)
-Applicability
Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording natural behavior
Naturalistic Observation (PROS)
Ecological validity
Naturalistic Observation (CONS)
-NO manipulation
Correlation
The extent to which two variables are related
Correlation (PROS)
-Predict behavior
Correlation (CONS)
-Directionality problem
-Third variable problem
Correlation Coefficient
A numerical index of the degree of relationship between two variables.

Describe the relationship between correlations and causations?
Correlation will never equal causation. Correlation is simply the extent to which two variables are related
Third variable/Third variable problem
An undiscovered causative variable
Illusory correlation
Perceiving a relationship where none exists or perceiving a stronger than the actual relationship
Regression to the Mean
The tendency of activities to be followed by data points that are closer to the mean
How can placebo effect influence the results of an experiments?
It makes participants who receive a placebo, report or show improvements because they believe they are being treated
Why do psychologists use random assignment in experiments?
It helps to reduce bias and increases internal validity
Double Blind Procedure
An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo. Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies.
Independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
Dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
What are the main ethical consideration in psychological research?
1. Confidentiality
2. Debriefing
3. Informed consent
4. Protection from harm and discomfort
Confounding variable
A factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment
If the data is skewed which one would you use mean or median?
Median
If there is a cluster of data, remember that your graph....
would have a less range
If the data is more spread out, remember that the graph....
has a more wider range
When analyzing data would you rather use standard deviation or range?
Standard deviation because it helps to analyze how far or close each data point is from the mean
Mean
Average
Median
Middle number
Mode
Most frequent variable/number
Range
Highest number minus lowest number
Standard Deviation
A measure of how broadly or narrowly a set of scores or values deviate from the mean
Statistical significance
The degree to which a research outcome CANNOT be reasonably attributed the operation of chance or random factors
Effect Size
Any of various measures of the magnitude or meaningfulness of a relationship between two variables
In a double-blind study investigating the efficacy of a new medication for treating insomnia, participants are randomly assigned to receive either the medication or a placebo. Neither the participants nor the researchers administering the treatment know who is receiving the actual medication and who is receiving the placebo. Sleep quality is measured using standardized scales before and after the treatment period. What is the primary purpose of implementing a double-blind design in this study?
A) To provide researchers with the flexibility to alter the study's parameters as needed.
B) To minimize bias in the results by preventing expectations from influencing outcomes.
C) To increase the likelihood of statistical significance in the findings by manipulating data.
D) To ensure that participants are unaware of the study's objectives.
B) To minimize bias in the results by preventing expectations from influencing outcomes.
A psychologist is conducting a study to investigate the effect of mindfulness meditation on anger management. Participants are randomly assigned to one of two groups: a mindfulness meditation group and a control group. Both groups complete a standardized anger questionnaire before and after the intervention period. In this study, what is the independent variable?
A) The type of questionnaire used to measure anger
B) The duration of the intervention period for each participant
C) The mindfulness meditation used in the study
D) The participants' anger levels before and after the intervention
C) The mindfulness meditation used in the study
A psychologist conducts a study to examine the effectiveness of a new therapy for reducing symptoms of anxiety in adolescents. The study involves a large sample size and rigorous methodology. After analyzing the data, the psychologist finds a statistically significant difference between the treatment group and the control group. However, she is cautious and decides to calculate the effect size to further evaluate the practical significance of the finding. Which of the following statements accurately describes the concept of effect size in this study?
A) Effect size measures the strength of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables
B) Effect size indicates the probability of obtaining the observed results by chance alone
C) Effect size quantifies the magnitude of the difference between groups, independent of the sample size
C) Effect size quantifies the magnitude of the difference between groups, independent of the sample size
Peter, an avid beachgoer, spends his weekends at the seaside, enjoying the sun, sand, and surf. He decides to conduct a personal experiment to explore the relationship between beach time and happiness. Over several weekends, Peter records the number of hours he spends at the beach and his self-reported level of happiness on a scale from 1 to 10. Based on Peter's observations, which of the following statements best reflects a positive correlation between beach time and happiness?
A) Peter's happiness levels fluctuate randomly, regardless of the amount of time he spends at the beach.
B) Peter notices that as he increases the number of hours spent at the beach, his reported happiness levels also increase.
C) On weekends when Peter spends more time at the beach, he tends to report lower levels of happiness.
D) There is no discernible pattern between the time Peter spends at the beach and his reported happiness levels
B) Peter notices that as he increases the number of hours spent at the beach, his reported happiness levels also increase.
A psychologist conducts a study to investigate the effects of a new medication on reducing alcohol cravings in individuals with alcohol use disorder. Participants are randomly assigned to one of two groups: a treatment group receiving the medication and a control group receiving a placebo. Neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the actual medication and who is receiving the placebo. After the study period, participants' self-reported alcohol cravings are assessed. In this study, which of the following best describes the placebo effect?
A) Researchers observe a direct physiological response to the active medication in the treatment group.
B) Participants in the treatment group report a significant decrease in alcohol cravings compared to the control group.
C) Participants in both groups show a reduction in alcohol cravings, despite only the treatment group receiving the active medication
A) Researchers observe a direct physiological response to the active medication in the treatment group.
In a study investigating the effects of a new medication on reducing anxiety levels, researchers measure anxiety using a standardized questionnaire that assesses symptoms such as worry, nervousness, and tension. Which component of this study represents the operational definition of the dependent variable?
A) The number of participants recruited for the study
B) The amount of the new medication being tested
C) Symptoms such as worry, nervousness, and tension
D) The standardized questionnaire used to measure anxiety
You are analyzing a dataset containing the salaries of employees in a company. Most salaries fall within the range of $30,000 to $80,000 per year, but there is one extreme outlier of $1,000,000 per year. Based on this, why is the median a more appropriate measure of central tendency to summarize the typical salary in the dataset?
A) The median accounts for the distribution's skewness, making it more suitable for asymmetrical datasets.
B) The median is calculated by summing all values and dividing by the total number of observations, ensuring a balanced representation of the dataset.
C) The median reflects the arithmetic mean of the dataset, allowing for a more precise estimate of the central tendency.
D) The median is less affected by extreme values, providing a better representation of the typical salary when outliers are present.
D) The median is less affected by extreme values, providing a better representation of the typical salary when outliers are present.
A group of psychologists conducts a study to investigate the effectiveness of a new therapy in reducing symptoms of social anxiety disorder. They recruit 100 participants diagnosed with social anxiety disorder and randomly assign them to either the treatment group receiving the new therapy or the control group receiving standard care. After the treatment period, participants complete a standardized questionnaire to assess their anxiety symptoms. What concept is the most appropriate to determine whether the observed differences in anxiety symptoms between the treatment and control groups are meaningful and not due to chance?
A) Statistical significance
B) Effect size
C) Research methodology
D) Random sampling
A) Statistical significance
In a psychological study investigating the effects of music on mood regulation, researchers randomly assign participants to two groups: Group A listens to classical music, while Group B listens to heavy metal music. What is the primary purpose of using random assignment in this study?
A) To ensure that all participants have an equal chance of being exposed to the different types of music.
B) To eliminate the need for informed consent from participants, ensuring unbiased results.
C) To increase the likelihood of detecting significant differences in mood between the two music conditions.
D)To guarantee that participants in both groups have identical personality traits and preferences.
A) To ensure that all participants have an equal chance of being exposed to the different types of music.
In a comprehensive psychological study investigating the effectiveness of a new happiness intervention, participants are randomly assigned to one of two groups: Group A receives weekly mindfulness training sessions aimed at enhancing positive affect and well-being, while Group B, comprising individuals with similar demographics, continues with their regular activities, including work, school, and leisure pursuits, without any intervention. Which group in this study serves as the control group?
A) The researchers of the training program.
B) Group A: Participants receiving mindfulness training sessions
C) Group B: Participants continuing with their regular activities
D) Participants who receive extra mindfulness training
C) Group B: Participants continuing with their regular activities
In a study examining the relationship between hours spent studying and intelligence scores among college students, researchers find a strong positive correlation between the two variables. Which of the following statements best explains why correlations cannot prove causation in this study?
A) Correlation does not provide information about the direction or causality of the relationship.
B) There is insufficient evidence to support a relationship between studying and intelligence scores.
C) The study lacks statistical power to detect meaningful associations between the variables.
D) In this type of study, there is no way to control for extraneous variables that may influence both studying habits and intelligence scores.
A) Correlation does not provide information about the direction or causality of the relationship.
Steve, a psychology researcher, is interested in understanding how individuals process and remember information in real-world settings. In his study, Steve investigates how people recall the details of their daily routines, such as commuting routes, work tasks, and meal preparation. Which psychological perspective is most likely guiding Steve's research?
A) Behavioral perspective
B) Humanistic perspective
C) Psychoanalytic perspective
D) Cognitive perspective
D) Cognitive perspective
In a psychological study investigating the effects of social media usage on self-esteem, a researcher recruits participants from a local community group without fully informing them about the purpose of the study. Which ethical consideration has the researcher violated in this scenario?
A) Deception
B) Debriefing
C) Confidentiality
D) Informed consent
D) Informed consent
In a comprehensive psychological study investigating the association between anger and aggressive behavior, researchers meticulously control for various factors. However, they discover that despite their efforts, there is still a strong positive correlation between the two variables. Upon closer examination, they find that participants who reported higher levels of anger also tended to engage in more physical exercise on a daily basis. In this study, what is the example of a confounding variable that challenges the interpretation of the relationship between anger and aggressive behavior?
A) Socioeconomic status of participants
B) Gender differences in anger expression
C) The time of day when the study was conducted
D) Amount of physical exercise engaged in daily
D) Amount of physical exercise engaged in daily
A team of researchers is conducting a study to explore the experiences of individuals living with chronic pain. They use interviews to gather in-depth narratives about the participants' daily struggles, coping mechanisms, and interactions with healthcare providers. Which research approach best describes the method employed by the researchers?
A) Qualitative research
B) Observational research
C) Experimental research
D) Quantitative research
A) Qualitative research
Placebo effect
When a person experiences a real improvement in their symptoms after receiving a treatment that has no active therapeutic effect, simply because they believe they are receiving a real treatment.