Bio 1B
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Ecology
Home; study of relationships (<3) btw organisms and their environment
Biosphere
The earth basically; Organisms, pop., comm. ecosys.

Organisms
individual

Population
Multiple organisms 1 species

community
Multiple species in 1 place

ecosystem
multiple species in 1 place + environment
What is life unified by?? -_-
Reproduction; life cycle completion; highly variable across species
What are examples of different life stages?
Redwoods: reproduction of new, large life
What is life history?
Suite of traits connected to a species life cycle and timing of MAJOR events

What are some examples of life history?
Average life span; survivorship, # and timing of reproductive episodes

WHAT are MORE examples of life history bruh
size and number of offspring in each telenovela (reproductive) episodio
time and inversiones de parental care
survival: Alice in Borderland
Principle of Allocation
Organism w/ limited res. to invest in diff. actions and function
res. invested in, function x available for another (so sacrificing)* trade off
life cycle res. got to be allocated among growth, survival, and reproduction

example of principle of allocation in animals?
foraging
breeding
caring for offspring
allocation of biomass to offspring
example of principle of allocation in animals?
seeds
growth
biomass
nutrients
Does reproduction size = trade off? Why?
yee hAW
like an example would be smaller or bigger offspring
what are the costs of reproduction?
more reproduction in one year → less next year
What is the survivorship curve variationS?
Fraction of individuals surviving to a given age
What are the types of survivorship curves and their meanings
Type I: long life to old age; most reach old age
Type II: semi mid long life; some reach to old age
Type III: short life span; very few individuals reach old age
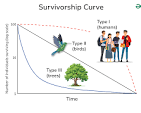
Explain and identify them curves
demography define!
How populations change over time
Types of Species interaction (3 types)
Individual of species A influences behavior or life of of species B
A influences growth, survival, or reproduction of individual species B
population of species A influences growth rate (dN/Dt) of a population of species B
What are the types of pairwise interactions and their meningin haahahahah
competition- A and B fight for resources and consumption
predation: A slays B
herbivory: A eats B (a bitchy plant), can kill B
Mutualism: A and B ❤ help each other;
Commensalism: B helps A, B not affected
Facilitation: General for mutualism and Com.
Parasitism: A lives on B rent free, can kill it
define competition
2 organisms fight for same resource and consumption of it
1 reduces the availability of resource for others → reduced growth , survival, etc.
What is the difference between intraspecif and interspecific competition
Intraspecific competition- Competition between individuals of the SAME species
behind density-dependent population growth
interspecific competition: Competition between individuals of DIFFERENT species
Do predators eat prey
yes.
often reduces abundance of prey
What are prey strategies?
Chemicals
Escape
Mimicry: imitations
dishonest: looks bad but is appetizing five star michelin
honest- taste bad is bad
Fight back
is herbivory always predation?
nah. plant many not always be unalived
does predation always have a negative impact? Explain
usually yes, but some benefit like plants like beargrass
What are examples of mutualism
spreading seeds (birds collecting pollen and got them seeds in their feathers or wtv, and they be dispersing them), pollinate flowers (bees)
Explain facilitation in more details NOW
usually positive
often the other species be impacted
sometimes mutualism for plants
what can fungal interactions do?
Can shift from mutaulism to parasitism depending on resource availibility.
elaborate on commensalism
1 benefits and the other is not affected its just sigma like that
egret and human be an example
How do species interact
In networks
represented with arrows linking species that hace a direct pairwise interaction
Food webs: complex interactions
food chains: simple interactions
do not show energy transfer
What are human interactions w/ non-human species
.. we be changing shit, changing the things we consider useful, and explit resources from the planet
e.g: agriculture of corn, harvesting animals
What does the Bide model mean
Accounts for all processes of the population
B-birth
I- immgration
d- death
e- emmigration
What is the equation of the Bide model (simplified)
N(t)+N(delta)t= Nt+B-D
population size at the time right now plus the population size at the current time plus the new number of individuals born minus the number of individuals dead
What do we assume about the population growth
every individual int he population = the amount of reproducion and death regardless of size and future
demographic rates don’t depend on conditions they experience
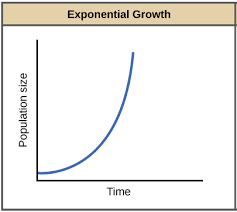
What does exponential growth mean. explain.
-J-shaped in the graph; positive slope
outcome; positive
r>1; population size in increasing
what does dN/dt=b-d= rNt
every individual in the pop has an equal chance of removing and dying no mater how big the population is, differs form density independence, but reminds me of density dependence a little bit since it relate to population size, but they differ.
What does Nr= Nsubcript 0 * e^rt mean?
… exponential groeth of population; population groeth calculation
N- population time
N0- initial number of individuals at t=0
r- intrinsic growth rate of population (units: number of time)
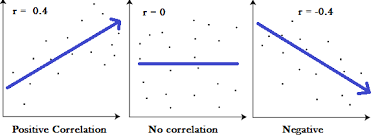
What type of graph is this? (2nd)
r=0
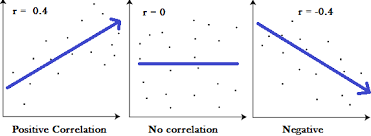
What type of graph is this? (third on the right)
logistic
r<1
can exponential growth be forever???
no
slow down if some probability: low resources, size/space
pop. does tend to stop growing
Mega… population - exhibit changes in per capita pop. change…
What is the percapita/individual growth rate?
rate if a population growth /pop. size
metric of average rate of population change ..individual in populations
growth rate decreases when pop. is larger; necessary condition for pop. to stop growing
What does density dependance mean?
changes in per capita population growth rate with population size
slope positive
What is the equation for equilibrium and what does it mean?
1/n, dN/dt=0; per capita birth rate = per capita death rate
Why are birth rate negative density dependence
life be challenging in denser populations. Think about hella herds of taejus.Thye would lowkey if they were to get like a pathogen, they would die faster because of like limited space and easier contact that they have with each other cuz they be so big.
Why are death rate positive density dependet?
They be having less people….
Why is negative density dependance common?
life and challenges be hella hard in denser conditions.
if the total resources pool is limited, then the birth rates decrease, and the death rates increase
few resources per each individual
few available suitors/mates
more competition for survivors
more disease and parasites that can develop and be transmitted
Does exponential growth have density dependen?
hell nah
What does r refer to when taking about the logistic model
constant number parameter
not a var.
pop. at which n comes to an equilibrium
what does the logistic model look like
s shaped
has the carrying capacity; imit of the max. in the population in an area
r<1
what is density independent refer to?
-factors that do not relate to the population size that influence the population
N limited by something unrelated to the size of the population
population fluctuations cuz these factors change over time (like climate, fires, etc)
ex: changes in tmeperature, water availibiility, land area
population fluctuations are common
when species coexist, populations can fluctuate (correlates to mainly to the community aspect though ahh)
eLABORATE ON the definition of a community
multiple species co-occuring in a place at a time
maybe interacting with each other
does not include abiotic environment
mostly restricted to a single type of organism
such as plants community or microbial community, just that they be different species
spatial extent (overall area)
sometimes it is clear (like a pond for fish)
defnine coexistence
when several species interact with each other in the area
what did home boy g.e hutchinson discover
homeboy discovered hella plankton intercting with each other in aquatic environments when one might imaging 1 species would be fittest
paradox of plankton
define scarcity and negative species interactions and explain
Scarcity- no resource is unlimited; shit be finite
allocated by any individuals within species and across
negative species interactions-
define funamental niche and realized niche and give example
fundamental niche:
FULL RANGE of conditions/resources used in which a species could maintina a stable population.
No existance of other species.
niche limits are based on physiological TOLERANCE
also resources and needs
realized niche: REAL/current conditions used → species can mantain a stable population in the presence of other co-occurring species
limits usually set by community/predation or other negative interactions
define spatial partitioning
homeboy robert mcarthur studied this in warbles
same fundamental niche
each different realized niche
competition reduced through each species Dominating different realized niche
basically its when species that live in a given area, do not compete with each other for the same resources, rather the species have a section of food to themselves, that no other species like gets cu they can’t eat it I imagine.
what are disadvantages of niche overlap?
…. less niche overlap
more niche partioning→ decrease in community → a possible possibility of increased coexistance
How would a high niche overlap look like
mainspaning, ovaries wide
high community
potential competition excluded
How would a low niche overlap look like
low mainspaling; not as dominating; meek
low competition
potential indicator of coexistence so no one is like dominating
Explain predatory /prey systems
species do not hare a resource,
one is a resource for the other!
Example: predators eat all prey→ prey gone→ predatory dead (an example of no predator/ prey existence)
OOOOOORRRRRRRRR
PREDATOR finds little prey→ death of predator→ prey increase → 1 species exists; predator and prey coexist with each other
does predaotor increase if prey increase
yes
negative density dependance
1 species population has low desinity since it bounced back like atees
does better when rare than common
negative density dependance is REQUIRED for species to coexist
each has to be able to bounce back like ateez form low density
wHat did homebofy Carl Hufferskins do
-studied predator and prey relationships
borke habitat in 2 patches → coesixtence
spatial refugges enable existance
what doe simple environment refer to?
when predaotr kills prey → no prey = no predator because big back ate it all
explain the concept of a complex environment in the context of the carl huffertchers shit
with refugees for prey, tge prey are killed by any given chance, but can colonize new oranges fast enough to escapr the predator and persist in the overall experiment
what is the loktova model and how does it relate to negatice density dependance
an exmaple of the predator and prey with coexistence
prey population decreases →predator decrease
predator decrease → prey increase
prey increase → predator increase
predator increase, prey decrease
predator is rare, preyare decreasing → predator ? bouncing BACK LIKE ATEEZ
what are factors of density independance
factors that do not relate to the size of the population, but rather influence the population.
effects: n limited by somrthing unrelated to the size of population
- pop. show fluctuations bc these density independant factors change over time
changes in temperature, eater availibity, land area
fluctuations are common
what does spatial refuggee refer to
enable prey to BOUNCE BACK TO ateez from rarity and increase population size
can negatice species interaction imapct on pop
yes can be slow
what happens to communities and to coexistence when environment changes
disturbace perturbs community
change in biotic and abiotic conditions in a community
happnes all of the time
doctors prescribing drugs, species introductions from humans, change in weather
community experience succession
exaplain the different types of succesion
primary succession: full on disturbance; shit wreaked its like ao3 type shit season 4
community becomes empty
any species that enters the community must 1st immgrate from another community its giving founders effect
ex: surtze island
ps influenced by dispersal and facilitations
secondary succession: full on distubrance to existing community but they are some survivors/ population decreases or anu individual of some life stages survive
species that become resident in community represents either population growth from these individuals or immgration form another community
explain early succesion and later succ. species
early: (barely arriving species) are outcompeted by the later 9already resident) species
early species can facilitate lare species by increasinfg their xp'/ nutrients or wtv
does disturbace increase richnesswhat are like exceptions
yes if its hella however if theres like more agricultural intensification, then there is a decrease in anthropod richness
more land clearance decreases abundance and richness like oil palm
what do agroforests do
maintain natural landscape fragments; intermixing species may be cultivated
maintins high biodiveristy than intense plantion agriculture
preseves indegenous knowledge
what does the luxury effect refer to?
rich people having more access to biodiversity because historical practices of redlining communities and not making them accisible to those woth low income and or non-white.
what are the limts of species distributions
happen at the same time and is not sequential
manu facots lowkey be seeing where species huzz be present
what is dispersal
movement of individual gametes/eggs away from and maybe back to their home town / og evolution
does behavior influnece dispersal
yes;
what does environment mean?
everything in organisms surroundings
what are species limit environments
temperature gradient
elevation gradient
storm risk gradient
predation risk gradient
some are physical continuous and some are patchy in the natural world and they span a range of environmetal conditions
what is biome
depend on climate
region experiences similar environments conditions→ similar core set of species
defined at different geographuc scales by humans
what does hadley cell refer to
circulation of the air depending on the side of the earth
why does temp. increase at high elevations?
air expands (low density, low pressured) and cools
falling air compresses
high density, high pressure and warms
precipitation inceases at high elevation on windward side of mountains
explain the rain shadow effect
rainfall goes up windward side of mountain rage
air cools, water vapor condenses→ falls as rainfall
decreased air and reduced moisture left in the atmosphere → rainshadow on leeward side
oceans buffer climate, so climate extremes are stringer than inferior
What does maritime climate refer to?
low ampliture of seasonal temperature functuations
What does continental climate mean?
high amplitude of seasonal temperature fluctuations
what does ecosystem mean
all organisms in a place and the environment
what does eco. ecology mean
inputs/outputs of a system
abstract complexity of a system
decrease focus on pop. and communities
what does respiration explain
metabolic reactions release chemical energy
return carbon to the environment
re-raudience thermal energy
all energy receied from the sun even re transferred away from the planet
organisms can use safe of this good energy before it goes back to space
explain gross primary production
all energy from the sun by autotrophic organism
what about npp
all energy available to other organisms
show energy flow
primary producers→ herbivores→ primary carnivores→ 2nd carnivore → detrivores (all lead to them)
what does ecological effieciency mean?
fraction of later on to other organisms as growth (eff= growth/energy av.)
what does assimulation fraction
fraction of energy used by organism for growth and respiration
trophic pyrimid rule
10% rule
what does inverted pyramids mean?
can be complex
can happen but rath not much info.
explain trophic casccade and provide 2 examples
Effect in energy flow bc of a charge in biomass of 1 trophic level
Bottom up control: Amount of limiting resources determine energy available to producrs→ limit others
Top down control: amount of top predators/consumers determine energy flows of prey→ limit others
what does sociometabolism refer to?
metabolism of human accounting for bodily energy use and also inderict consumption through appropriation of ecosystem as well as other resources