2. covalent bonding + charge cloud
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
bond enthalpy
energy needed to break a bond
mean bond enthalpy
average energy needed to break a certain type of covalent bond over a range of compounds
solubility
ionic compounds tend to dissolve in water. water molecules are polar- meaning part of the molecule has a small negative charge and the other part in positive. water molecules pull the ions away from the lattice and cause it to dissolve
molecules
form when 2 or more atoms bond together via covalent bonds
covalent bonds can be…
single bonds
double bonds
triple bonds
single bonds
a single covalent bond contains a shared pairs of electrons to gain a full outer shell
both positive nuclei are attracted electrostatically to the shared electrons
simple covalent compounds
compounds that are made up of lots of individual molecules held by strong covalent bonds,
but the molecules within the simple covalent compounds are held by weak intermolecular forces
intermolecular forces in simple covalent compounds
its the intermolecular forces that determines the properties of simple covalent compounds
so in general they have low melting and boiling points and are electrical insulators
giant covalent structures
a type of crystal structure that has huge networks of covalently bonded atoms AKA macromolecular structures
graphite
the carbon atoms in graphite are arranged in sheets of flat hexagons covalently bonded with 3 bonds each so the 4th outer electron of each carbon atom is delocalised.
the sheets of hexagons are bonded together by weak van der waals forces
property of graphite, weak VDWs between layers:
bonds can be easily broken so the sheets can slide over each other. graphite feels slippery and is used as a dry lubricant and in pencils
property of graphite, delocalised electrons:
free to move along the sheets so an electric current can flow
property of graphite, here is a large distance between the layers of graphite:
so it has a low density and is used to make strong lightweight sports equipment
property of graphite, very high melting and boiling point:
due to strong covalent bonds in hexagon sheets
property of graphite, insoluble in any solvent
because covalent bonds are too strong to break
carbons in diamonds
are arranged in a tetrahedral crystal lattice structure
property of diamond, very high melting points
due to covalent bonds
property of diamond, extremely hard:
due to covalent bonds
property of diamonds, a good thermal conductor:
vibrations travel easily throughout the stiff lattice due to covalent bonds
property of diamond can’t conduct electricity
because all outer electrons are held in localised bonds
property of diamonds, cant dissolve in any solvent
due to covalent bonds
coordinate dative covalent bonds
1 atom provides both shared electrons in a covalent bond
ammonium ion NH4+
nitrogen atom donates a pair of electrons to a proton H+
coordinate bonds form when…
… one of the atoms in a bond has a lone pair of electrons and the other doesn’t have any electrons available to share
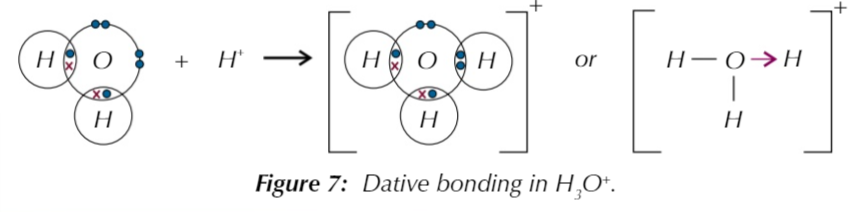
the hydroxonium ion H3O+
formed when H2O reacts with H+, H+ has no electrons so can only receive electrons and oxygen in H2O has 2 lone pair electrons so 1 lone pair is used to form a dative bond with H+
WHY DOES CHLORINE HAVE A LOWER BOILING POINT THAN BROMINE?
Chlorine has a lower boiling point than bromine due to its smaller molecular size and weaker van der Waals forces. As a result, it requires less energy to overcome these intermolecular forces.
halogen bond strength
strongest Cl2>Br2>F2>I2 weakest