Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 20.A: The Skeletal System (Axial)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
skeleton/skeletal system
gives physical support and protection for the body; provides surfaces for attachment of muscles
exoskeleton; endoskeleton
two parts of the animal skeletal system
exoskeleton
includes the hardened portion of the integument, such as cuticle in arthropods, shells in mollusks, etc.; all of which are present in invertebrates
endoskeleton
inner skeleton; may either be a cartilage or bone
axial; appendicular
two divisions of the skeletal system of vertebrates
axial
division of the skeletal system of vertebrates that include the bones and cartilages of the trunk region of the body; parts include: the skull, visceral apparatus, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
skull; visceral apparatus; vertebral column; ribs; sternum
parts of the axial skeleton
appendicular
division of the skeletal system of vertebrates includes those of the appendages; parts include: pectoral girdles, forelimbs, pelvic girdles, and hindlimbs
pectoral girdle; forelimbs; pelvic girdle; hindlimbs
parts of the appendicular skeleton
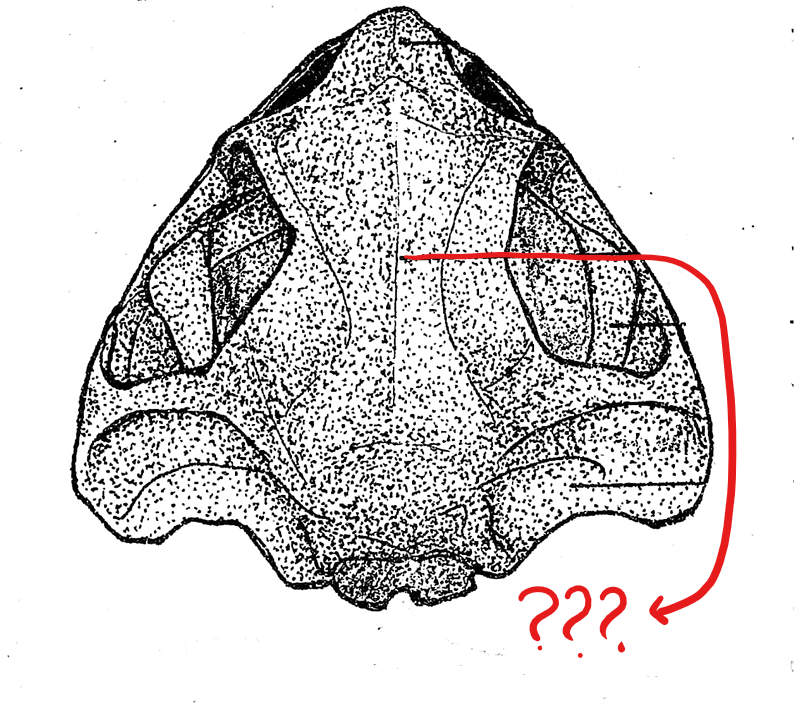
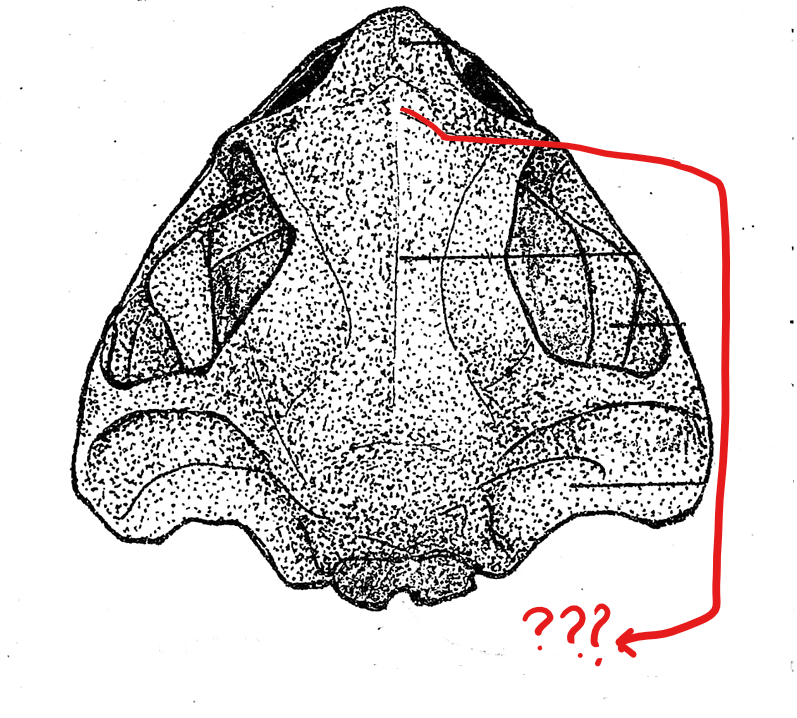
skull (dorsal view)
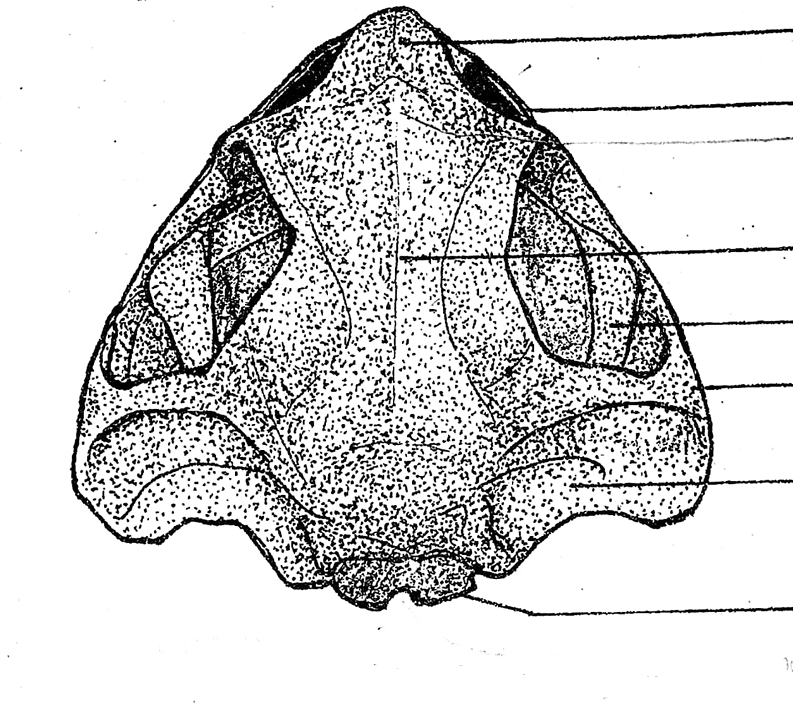
foramen magnum
located on the skull (dorsal view); a large opening at the posterior end of the skull for the passage of the spinal cord
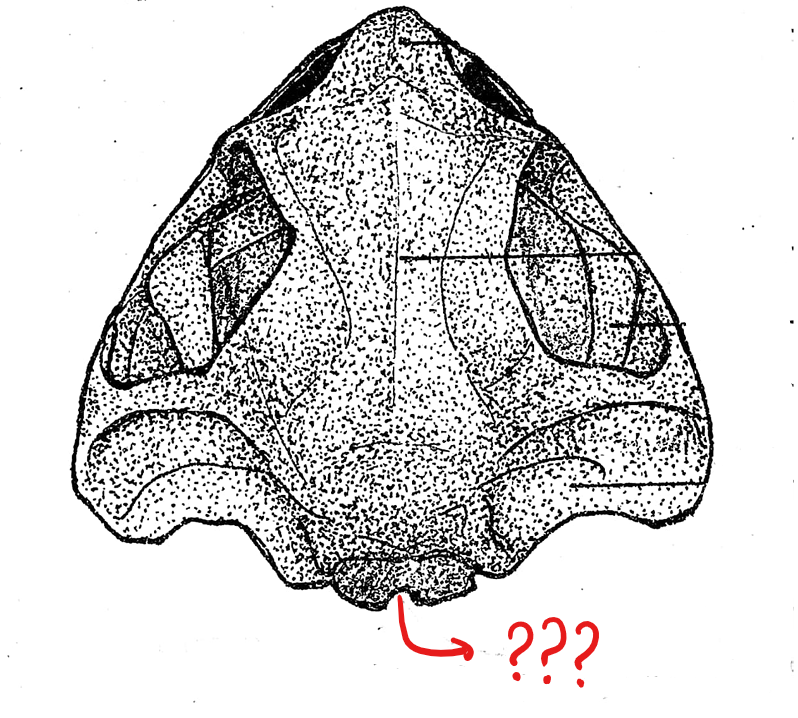
exoccipital
located on the skull (dorsal view); two flat bones bordering the two sides of the foramen magnum; articulate the skull with the atlas, the first and the only cervical vertebra of the frog
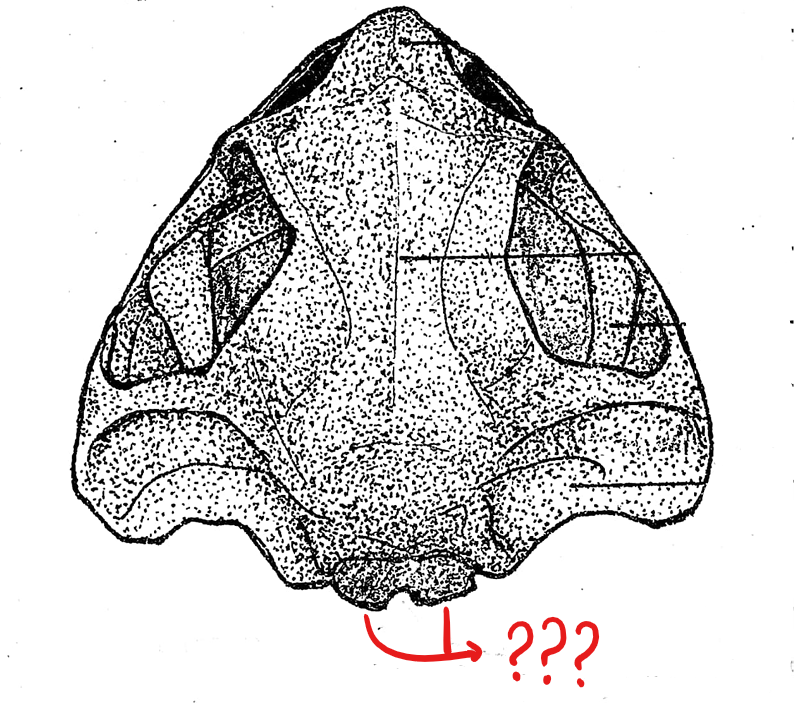
prootic
located on the skull (dorsal view); boxlike bones located in front, and a little lateral to the exoccipital bones; encircles the inner ear; each anterior end is perforated by an opening for the passage of the 5th, 6th, and 7th cranial nerves
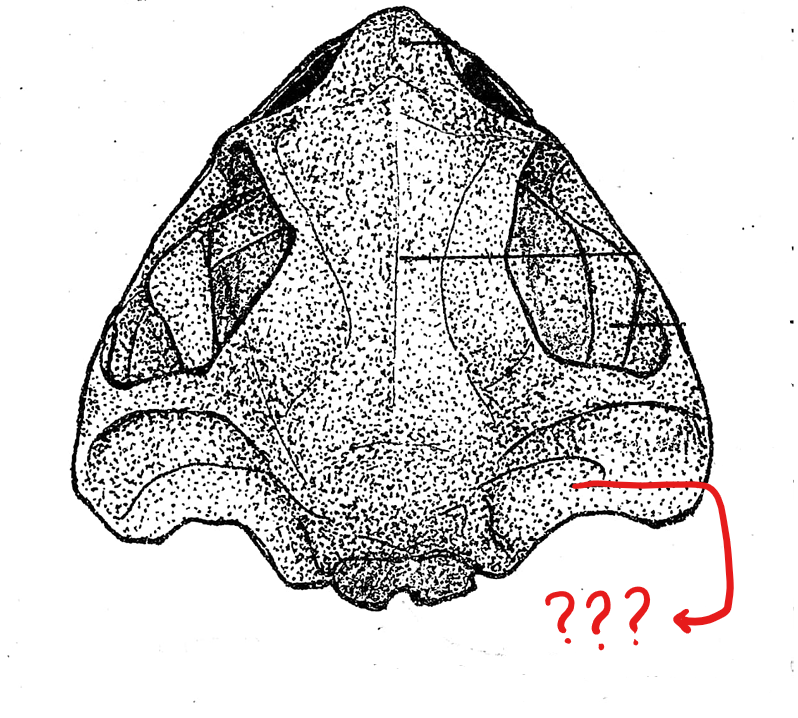
squamosal
located on the skull (dorsal view); hammer-shaped bones, lateral to the prootic; anterior piece corresponds to the structure for pulling the nails of the hammer; the middle piece is attached to the prootic as the head of the hammer; and the posterior component which corresponds to the handle of the hammer, and is attached to the posterior end of the upper jaw; this attaches the upper jaw to the cranium of the skull
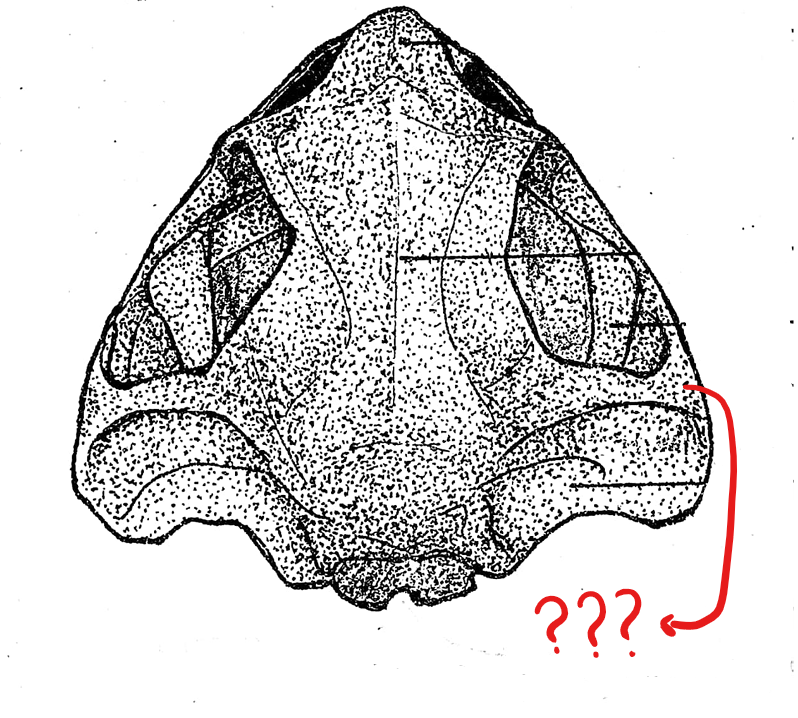
fronto-parietal
located on the skull (dorsal view); pair of elongated bones anterior to the exoccipitals; formed by the union of the frontal and parietal bones, and form the dorsal covering of the skull
nasal bone
located on the skull (dorsal view); pair of triangular bones anterior to the sphenethmoid where the nostrils are located
maxilla
located on the skull (dorsal view); elongated bone located postero-lateral to the pre-maxillae; form the greater part of the upper jaw; also teeth-bearing in frogs but not in the toads
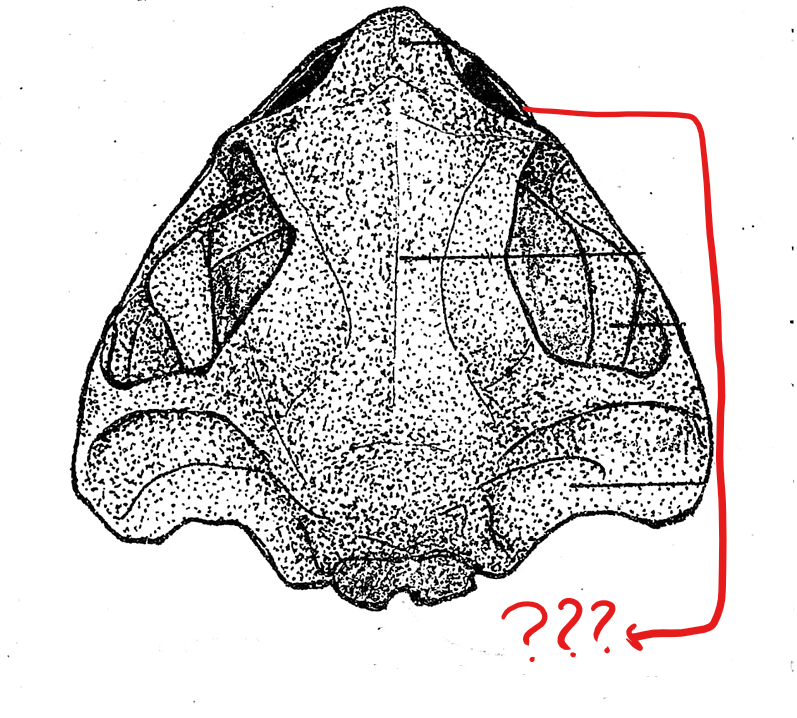
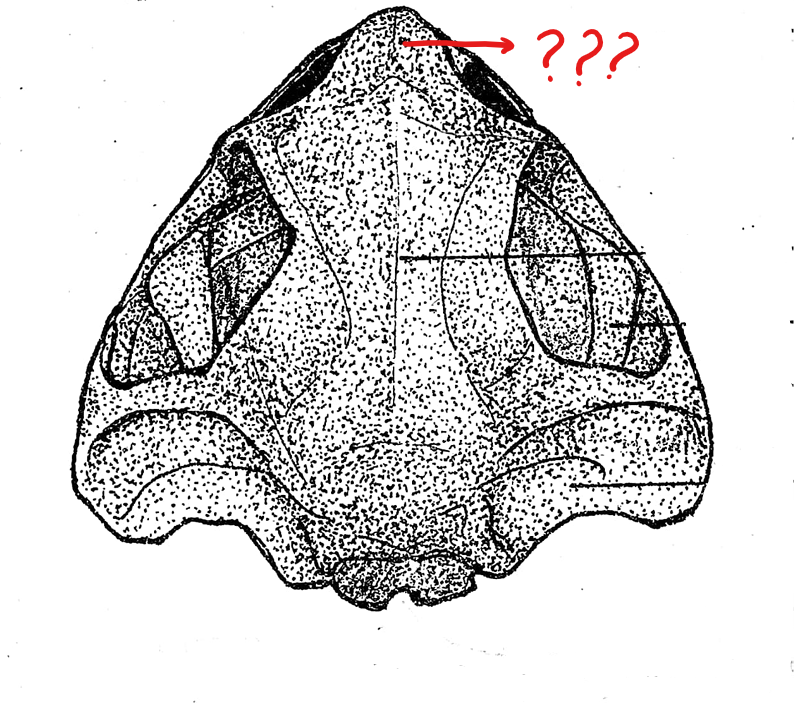
pre-maxilla
located on the skull (dorsal view); part of the upper jaw and the anterior-most bones of the skull; teeth-bearing in frogs but not in the toads
skull (ventral view)
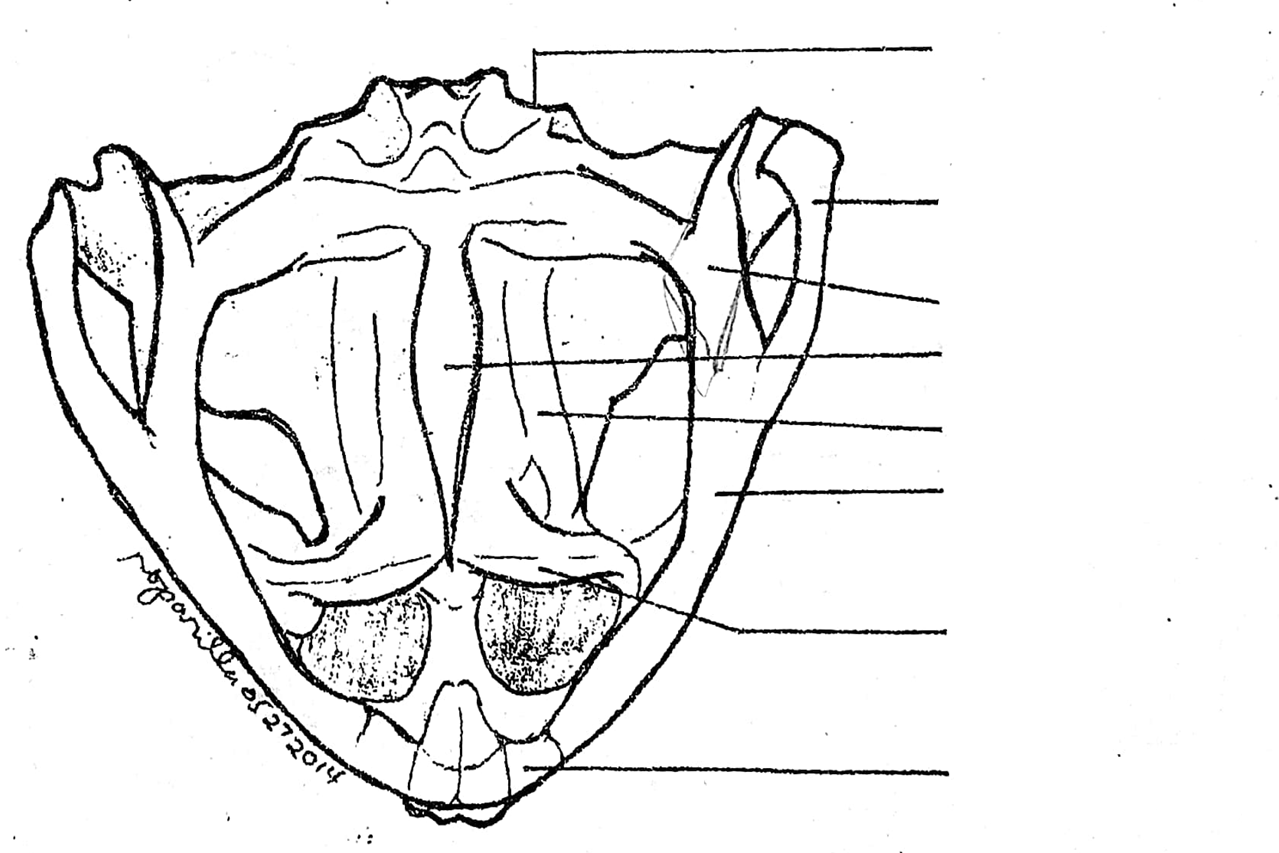
spenethmoid
diamond-shaped bone anterior to the fronto-parietals
quadratojugal
small bone forming the posterior end of the upper jaw to which the posterior piece of the squamousals is attached.; this does not bear teeth in both frogs and toads
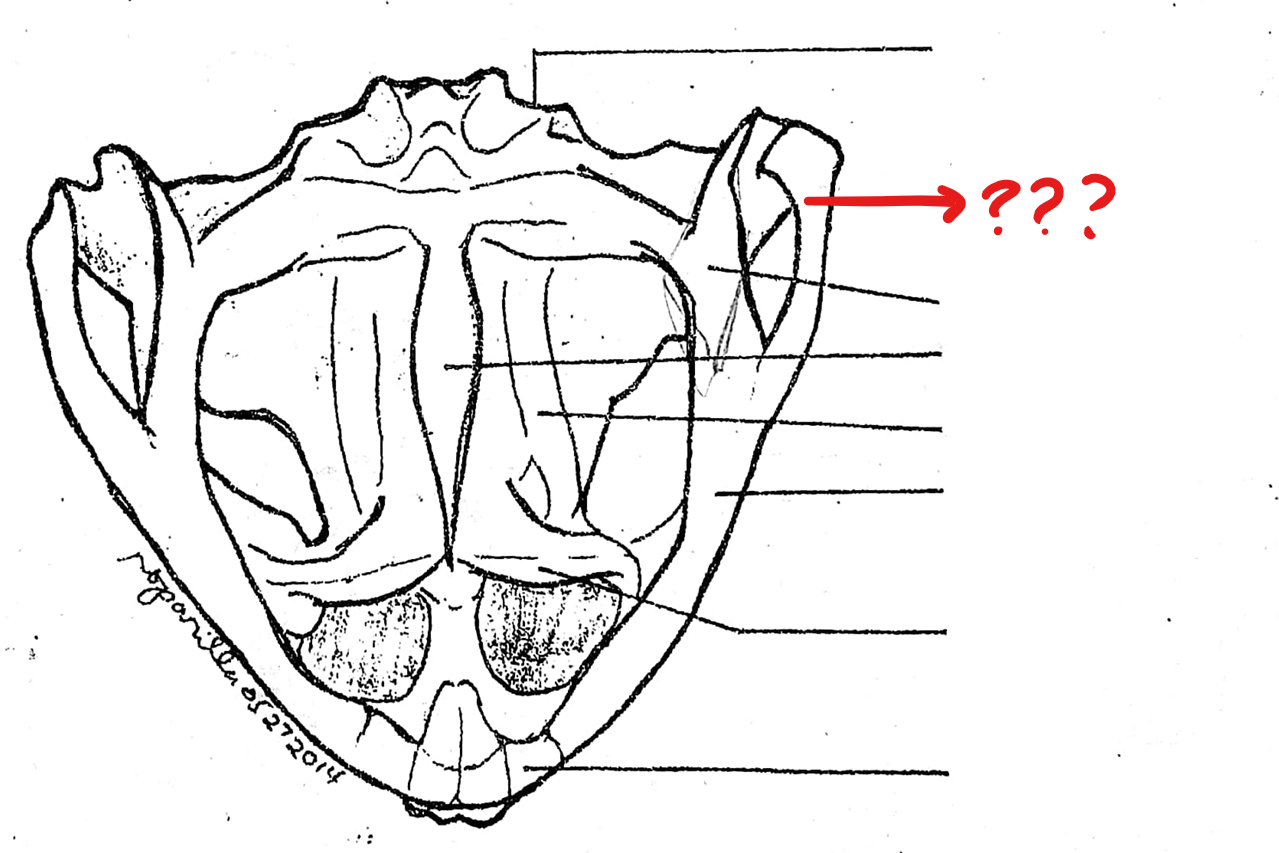
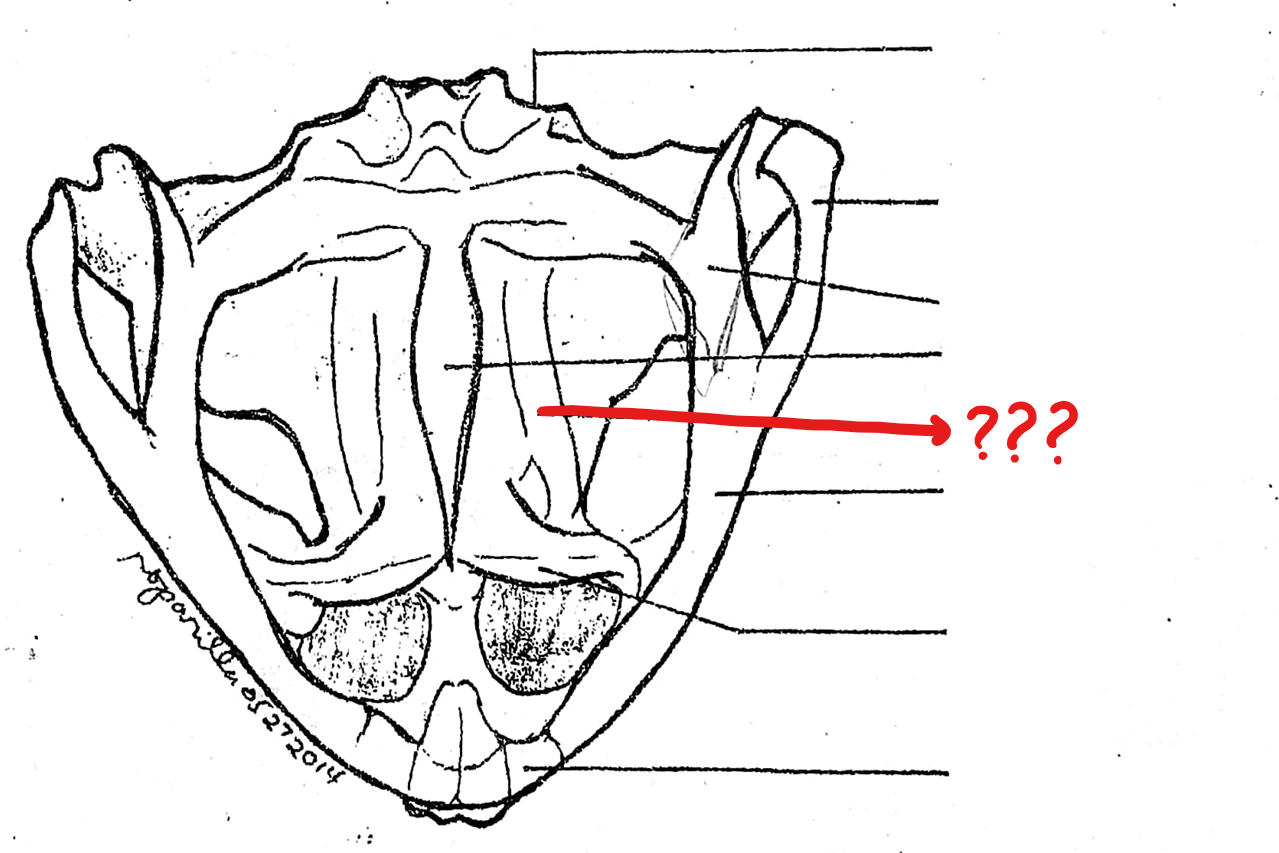
pterygoid
located on the skull (ventral view); triangular bone lateral to the base of the parasphenoid and prootic; anterior part of it articulates with the maxilla, the middle part with the prootic, and the posterior part with the quadratojugal
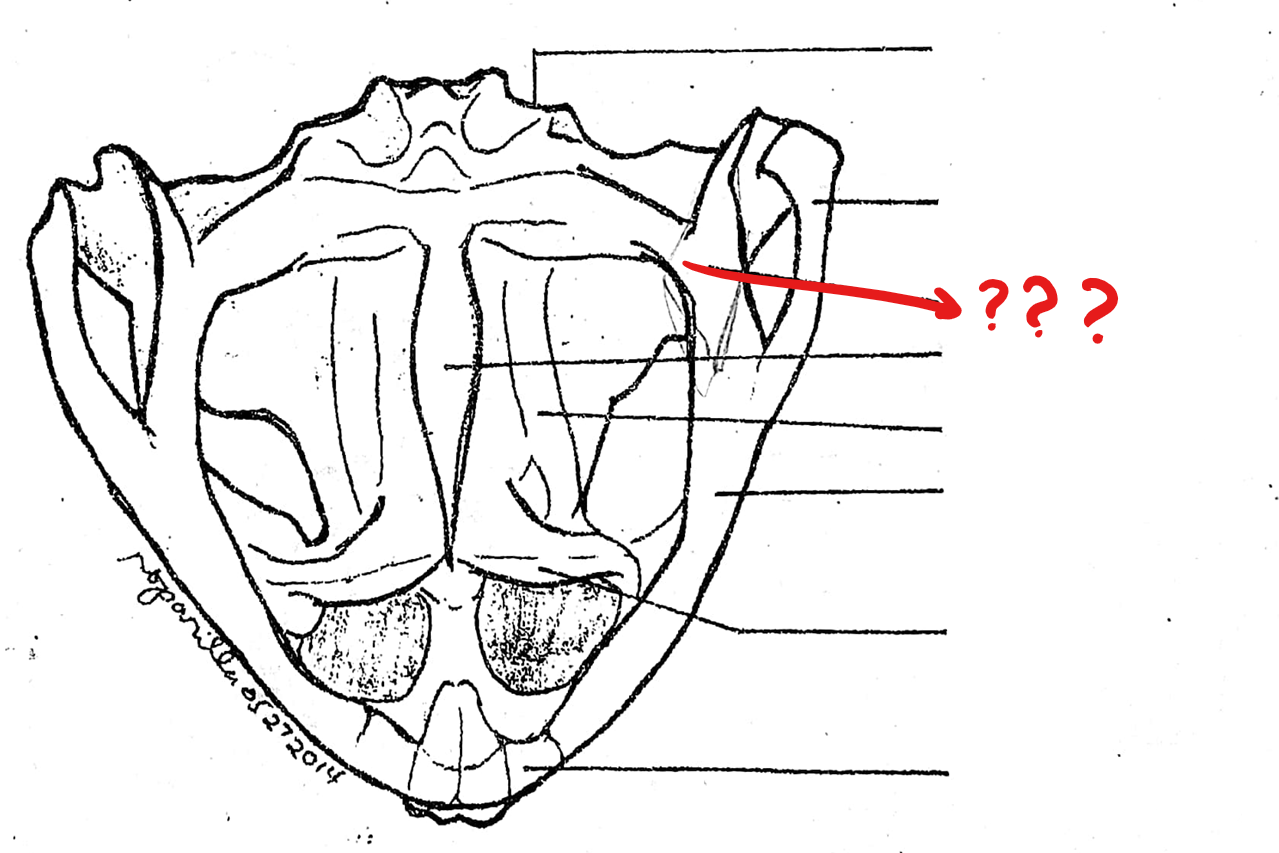
parasphenoid
located on the skull (ventral view); unpaired dagger-shaped bone at the base of the cranium, ventral to the fronto-parietals; forms the floor of the cranium
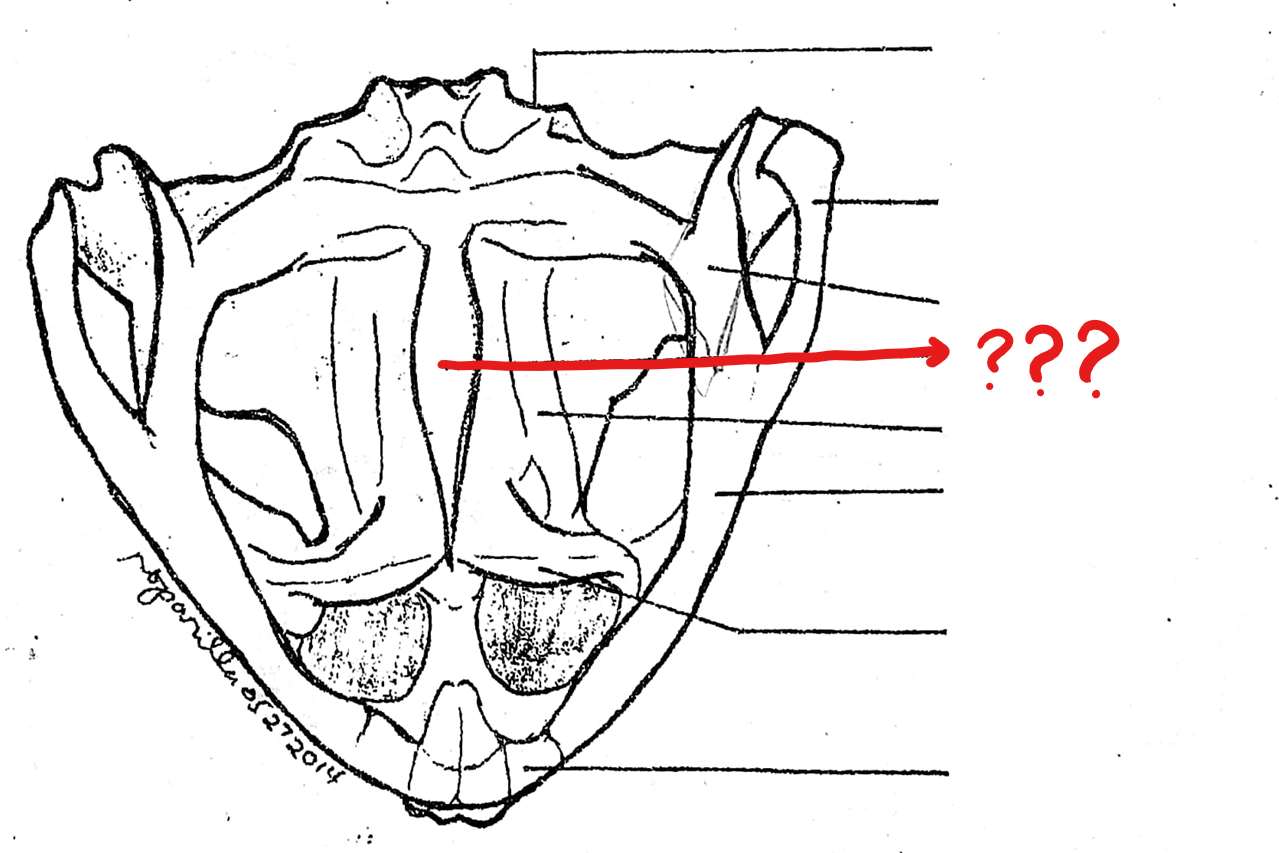
palatine
slender, rod-like bone extending laterally from the anterior part of the parasphenoid to the maxilla; connects the upper jaw to the cranium
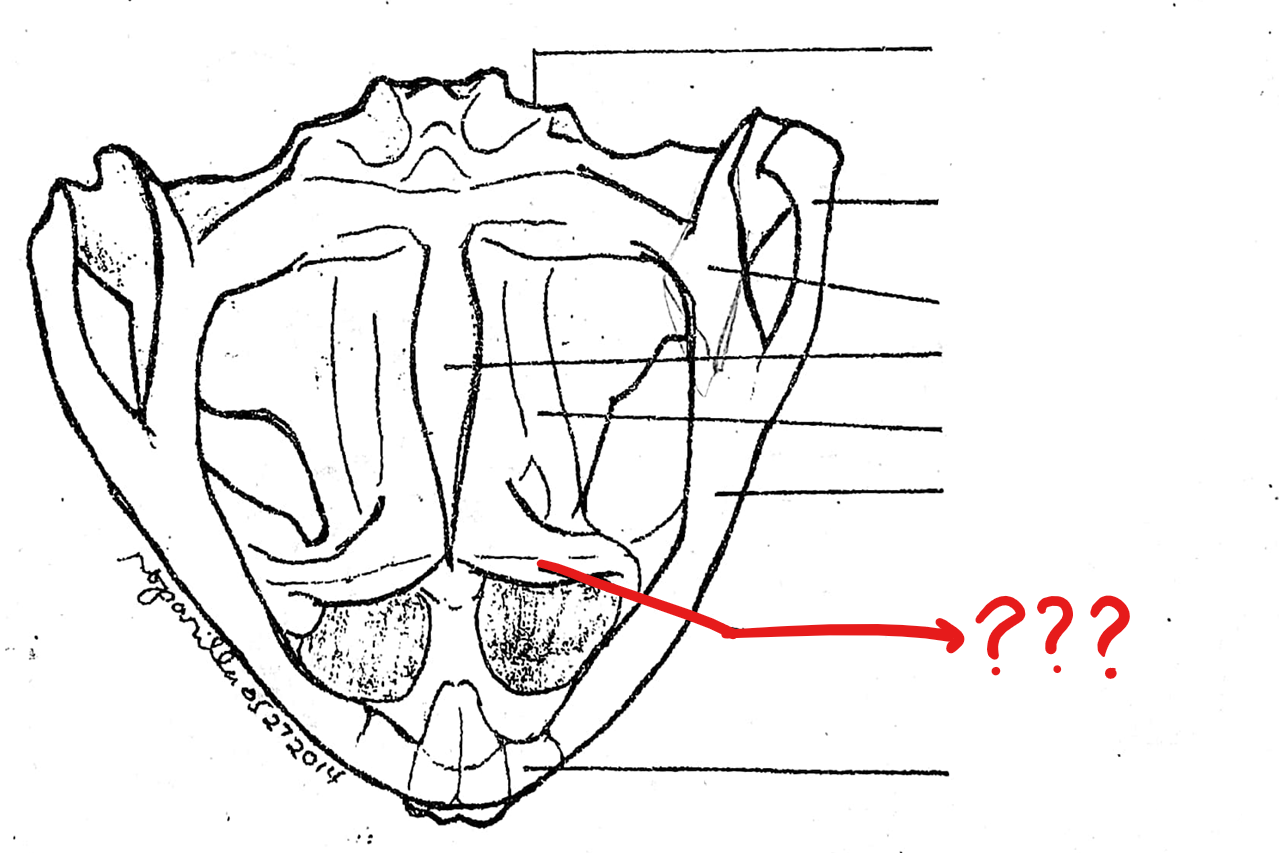
vomer
irregularly-shaped bone anterior to the parasphenoid, bearing fine teeth-like structures, the vomerine teeth; the teeth are absent in toads
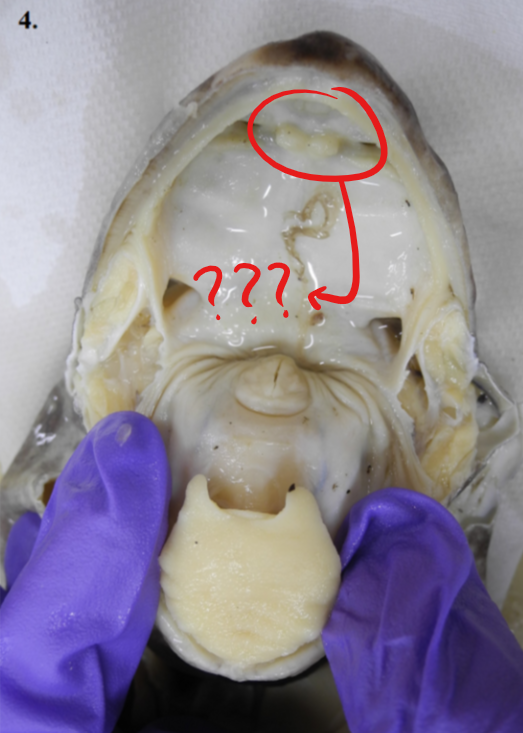
visceral apparatus
function to support the anterior portion of the digestive tract; consists of the lower jaw/mandible and hyoid cartilage
lower jaw/mandible; hyoid cartilage
two parts of the visceral apparatus
lower jaw/mandible
one of the component parts of the visceral apparatus; composed of right and left halves; each half is divided into three parts
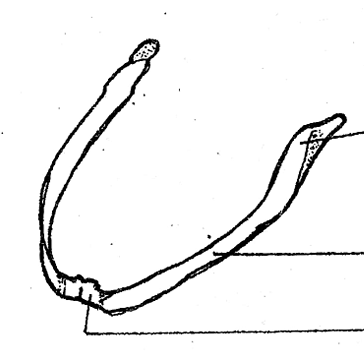
mento-meckelian
located on the lower jaw/mandible of the visceral apparatus; a small bone at the tip of the lower jaw which is an ossified part of the Meckel’s cartilage
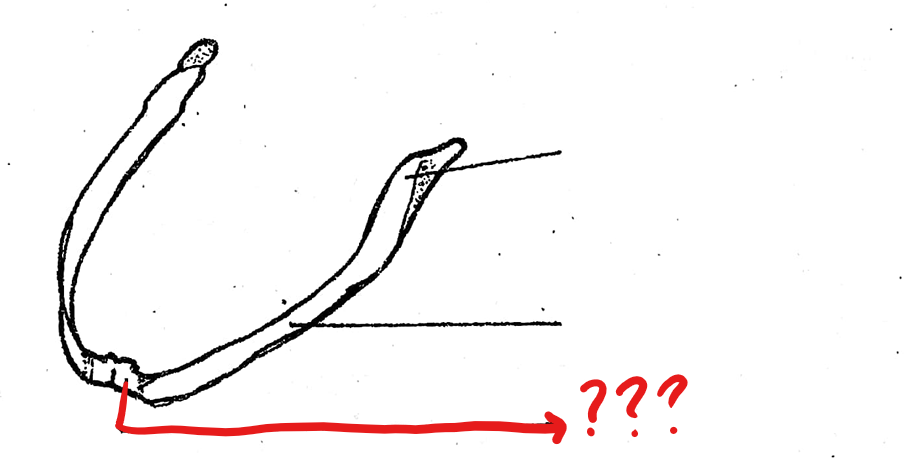
dentary
located on the lower jaw/mandible of the visceral apparatus; the thin portion which lies on the lateral surface of the middle part of the lower jaw
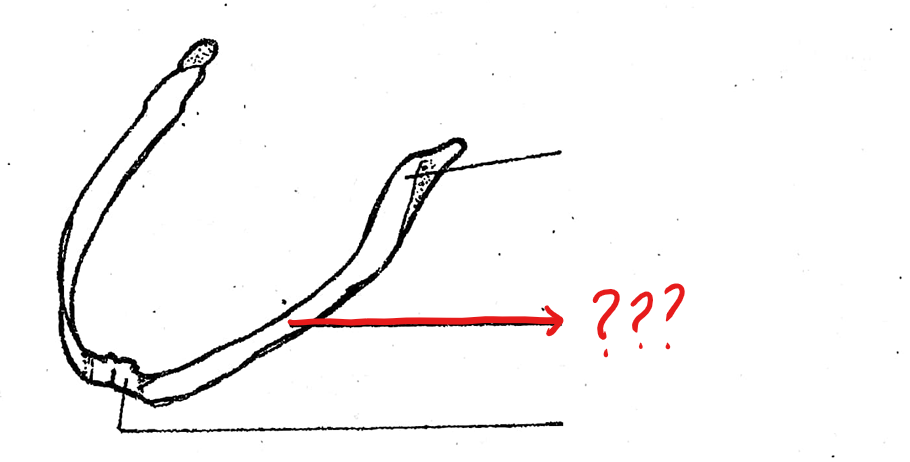
angulo-splenial
located on the lower jaw/mandible of the visceral apparatus; posterior to the dentary which is a stout and largest component of the lower jaw; articulates with the upper jaw of the skull
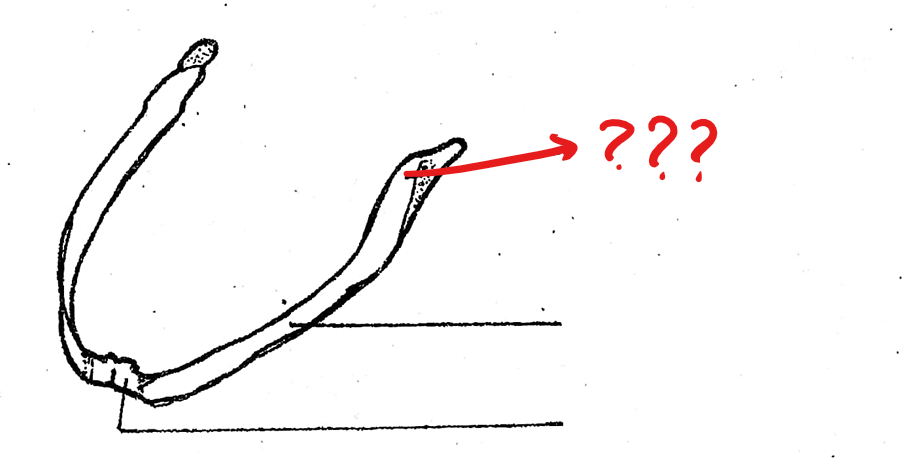
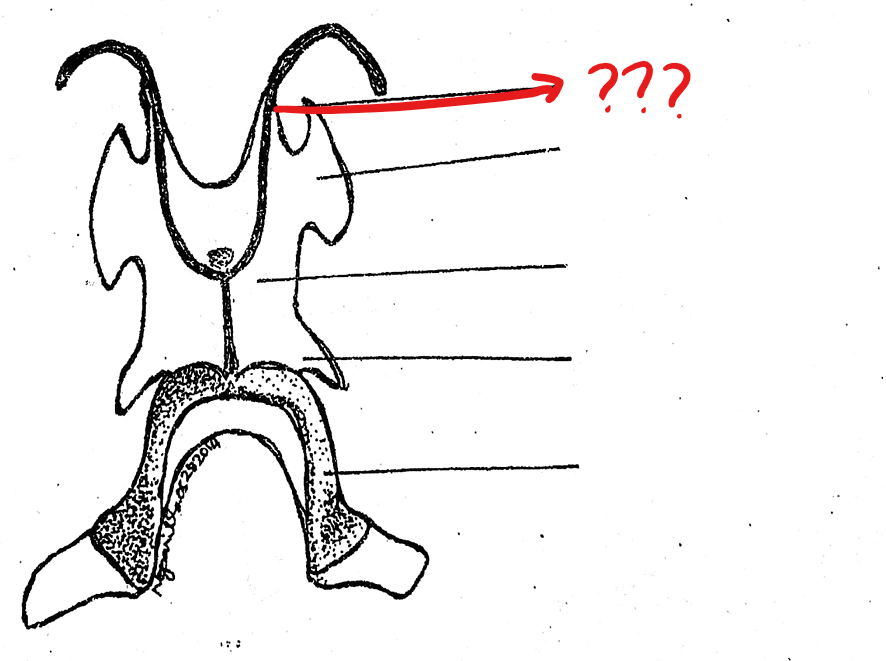
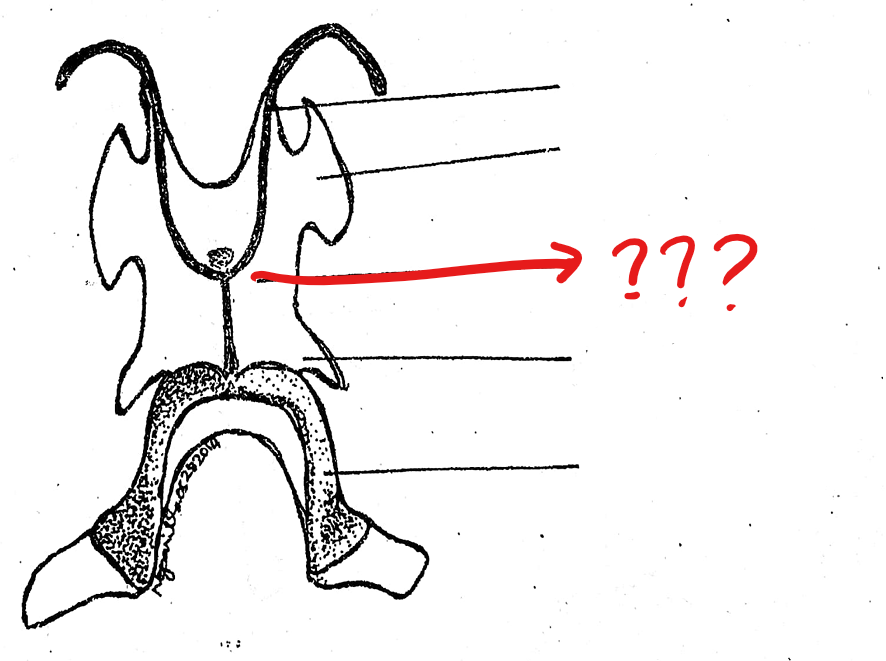
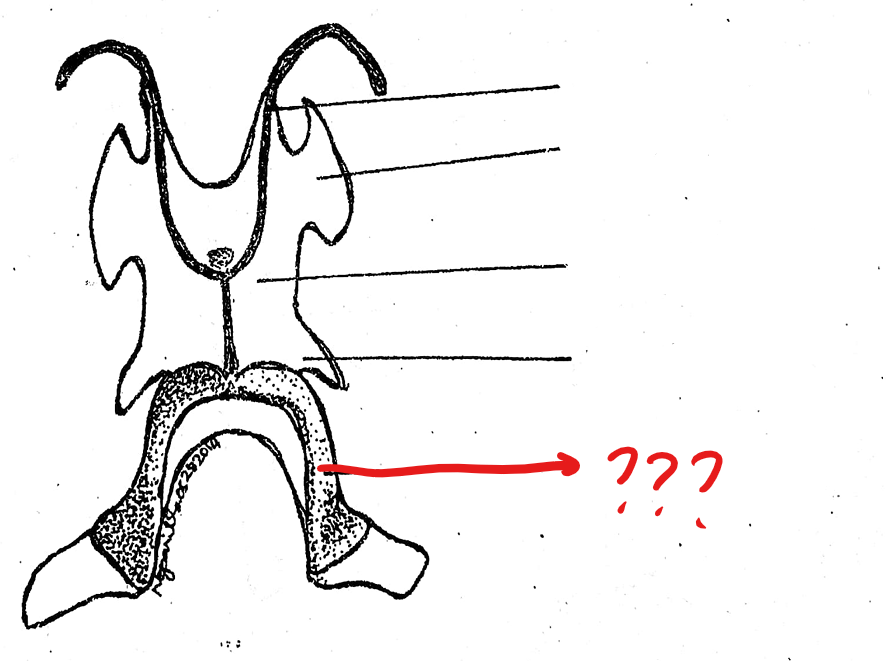
hyoid cartilage
another component of the visceral apparatus; a thin cartilaginous plate supporting the floor of the mouth
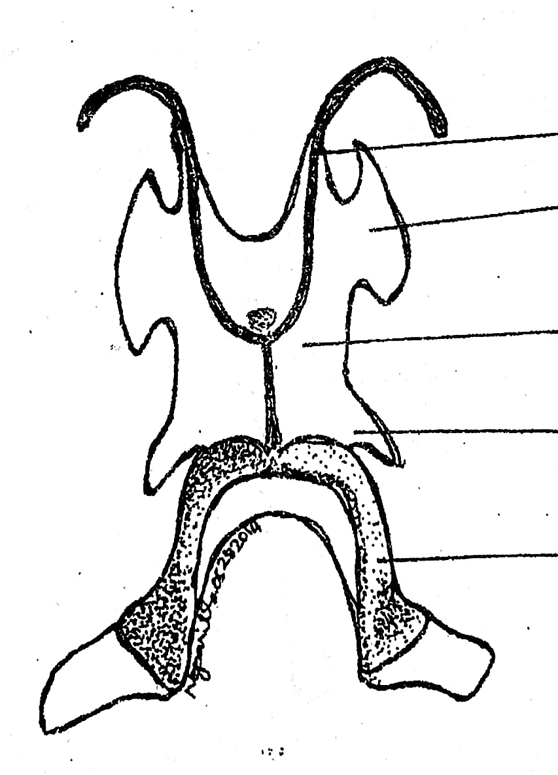
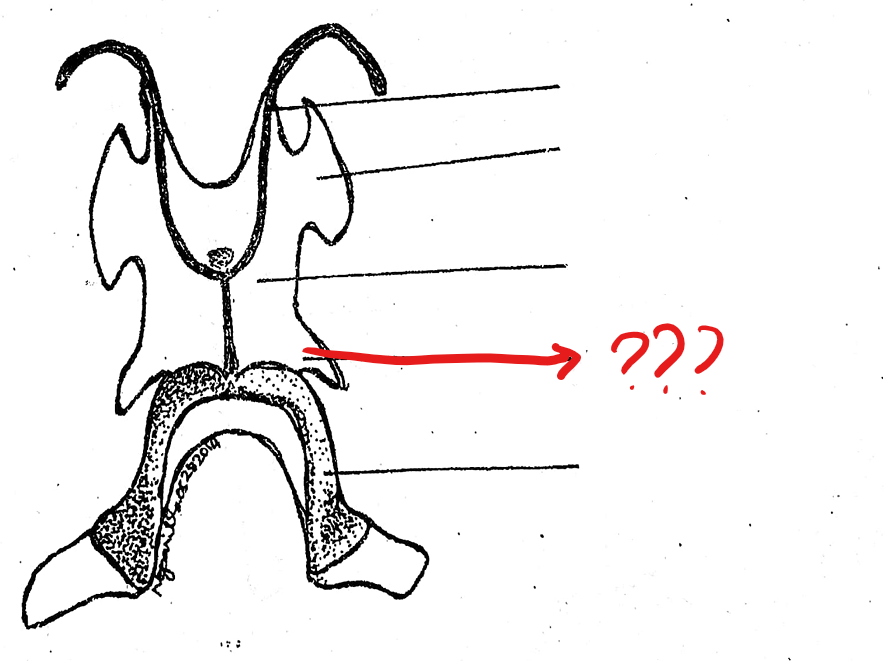
anterior cornua/horns
located on the hyoid cartilage of the visceral apparatus; a pair of long, slender, cartilaginous processes arising from the antero-lateral borders of the hyoid; often destroyed during the preparation; tips articulate with the prootic bones of the skull
body of the hyoid
located on the hyoid cartilage of the visceral apparatus; large, flat, four-angled, ventral cartilage
alary process
located on the hyoid cartilage of the visceral apparatus; a pair of small lateral expansion from the antero-lateral borders of the hyoid, posterior and lateral to the anterior cornua
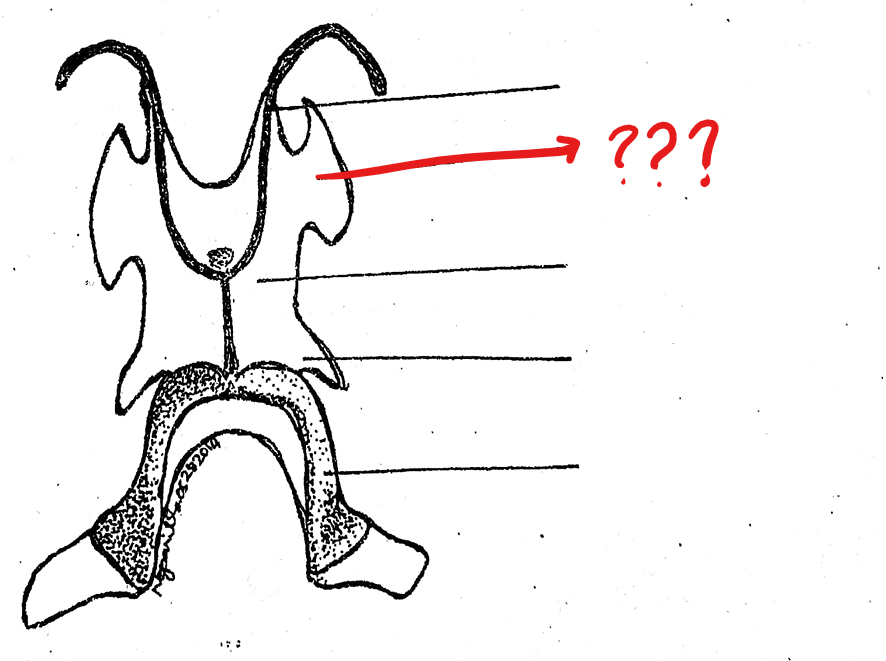
posterior cornua
located on the hyoid cartilage of the visceral apparatus; a pair of short cartilaginous processes which project from the postero-lateral borders of the hyoid
thyroid processes
located on the hyoid cartilage of the visceral apparatus; a pair of bony processes posterior and medial to the preceding and arising from the middle part of the posterior margin of the hyoid body; ossified parts of the apparatus and they support the larynx
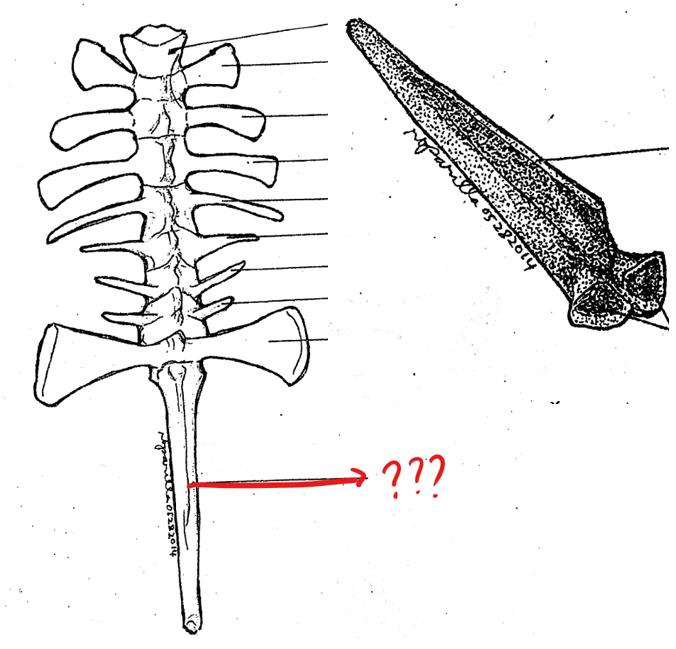
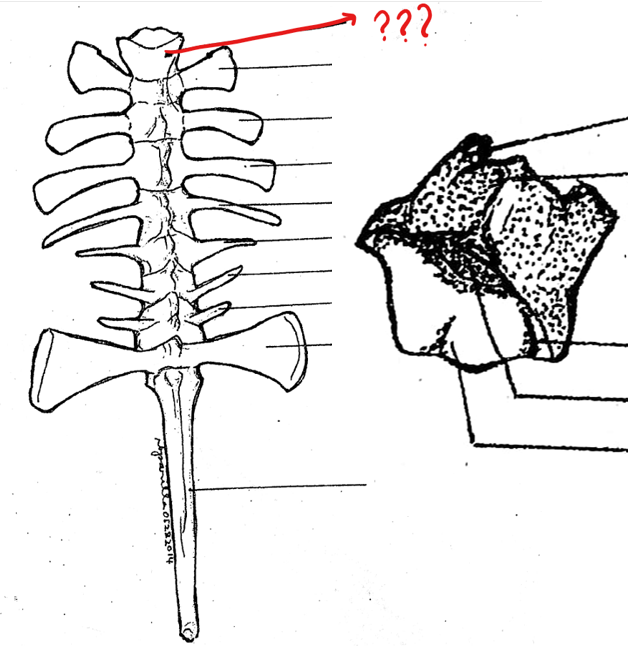
vertebral column
made up of ten vertebrae; passage way of spinal nerves out from the spinal cord
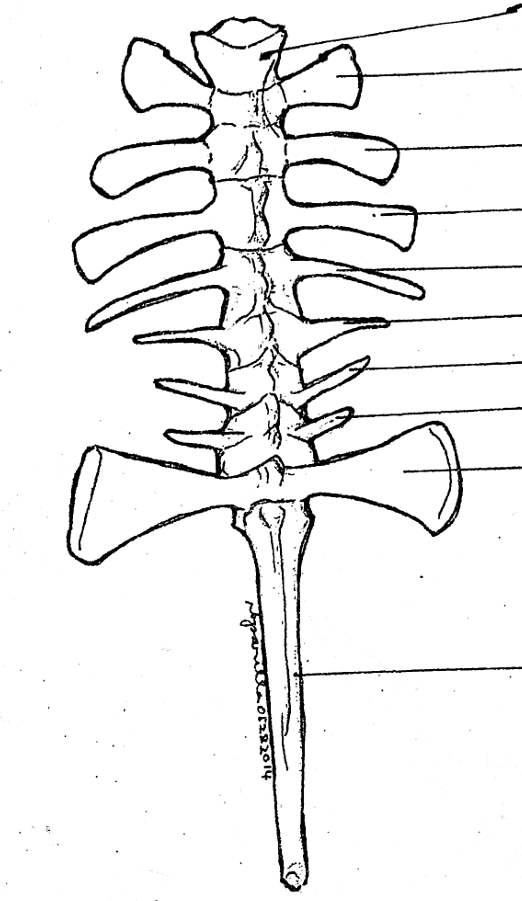
atlas; typical vertebrae; sacral vertebra; urostyle
parts of the vertebral column
zygapophyses
articulating processes; from where the neighboring vertebrae are joined with each other together with the centra
atlas
part of the vertebral column; the first vertebra and the only cervical vertebra of the toad and frog; does not possess any processes; has a pair of depressions on its anterior surface for the articulation with the exoccipital condyles of the skull
processes
a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body
typical vertebrae
part of the vertebral column; consists of the centrum, neural canal, neural spine, transverse process, prezygapophyses, and postzygapophyses
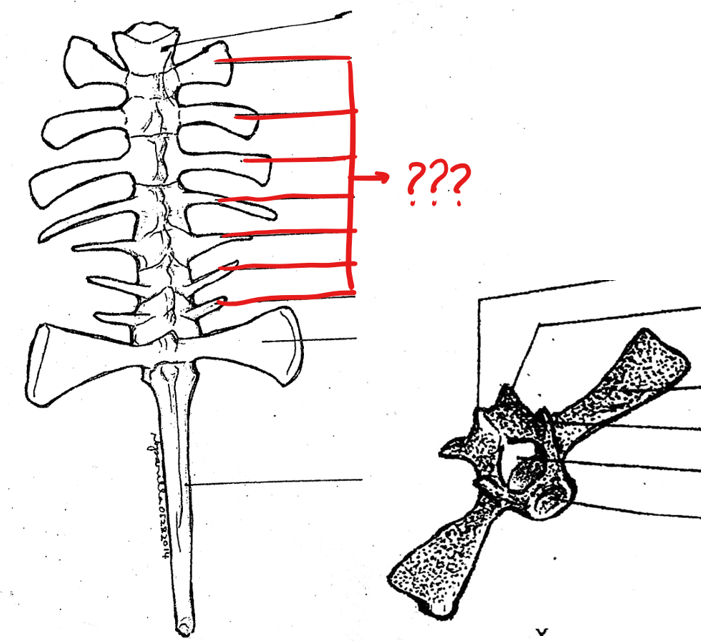
centrum
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; a solid mass of bone at the base of the vertebra; concave anteriorly and convex posteriorly (procoelous); 8th vertebra is biconcave (amphicoelus type)
procoelous
concave at the anterior end of the centrum and usually convex at the posterior end of the centrum
biconcavities of the centrum (amphicoelous type)
both the surfaces are concave and it permits some motion across a wide range of directions
neural canal
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; opening above the centrum through which the spinal cord passes; around it is the neural arch
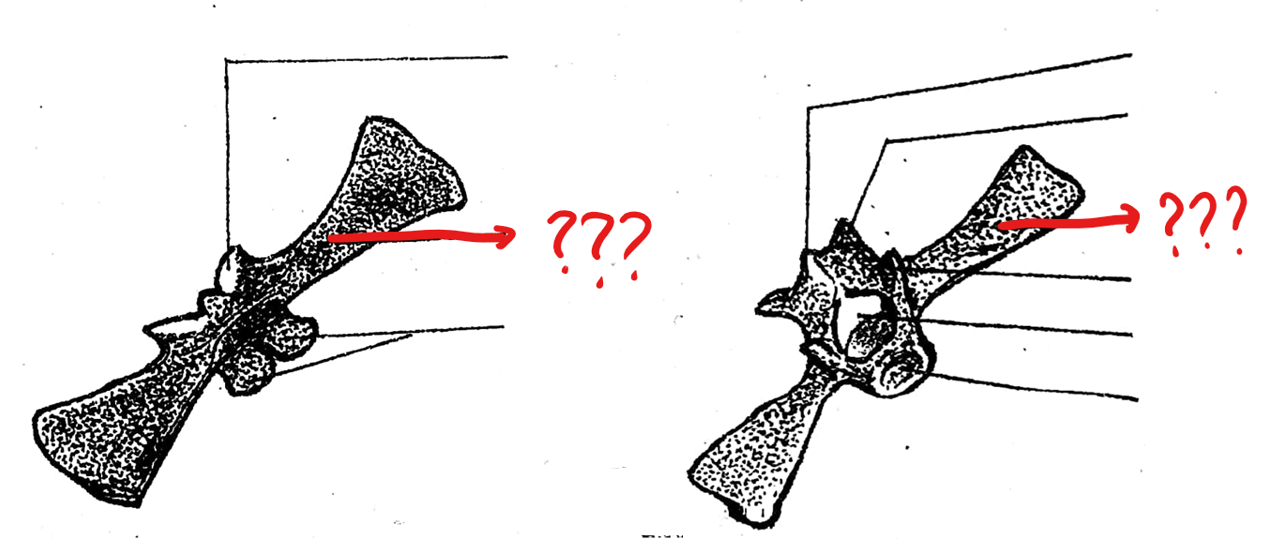
neural spine
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; a projection arising from the mid-dorsal portion of the neural arch
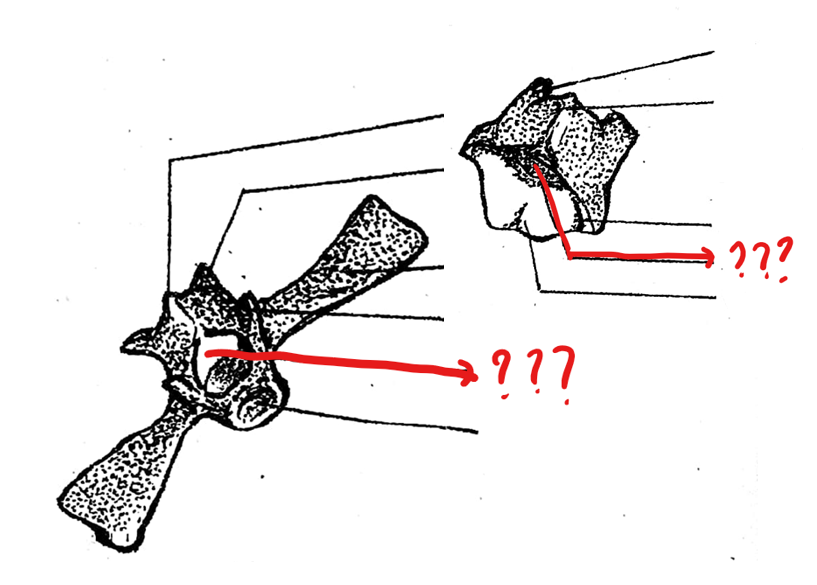
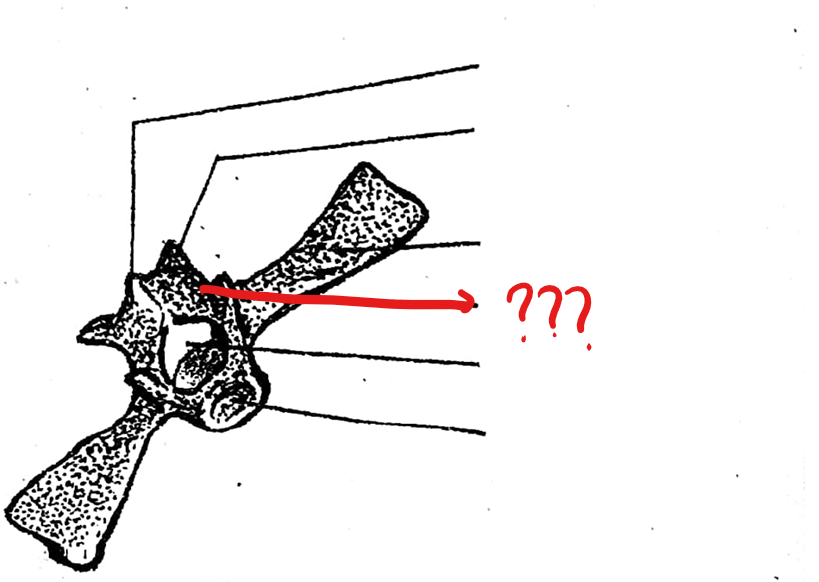
transverse process
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; an elongated bone arising from the lateral portion of the vertebra at the junction of the centrum and neural arch
prezygapophyses
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; pair of articulating processes anterior to the neural arch on the concave side of the centrum; smooth articulating surfaces which are facing upward
postzygapophyses
part of the typical vertebrae of the vertebral column; pair of posterior articulating processes on the convex side of the centrum; absent on the sacral vertebra; smooth articulating surfaces are facing downward
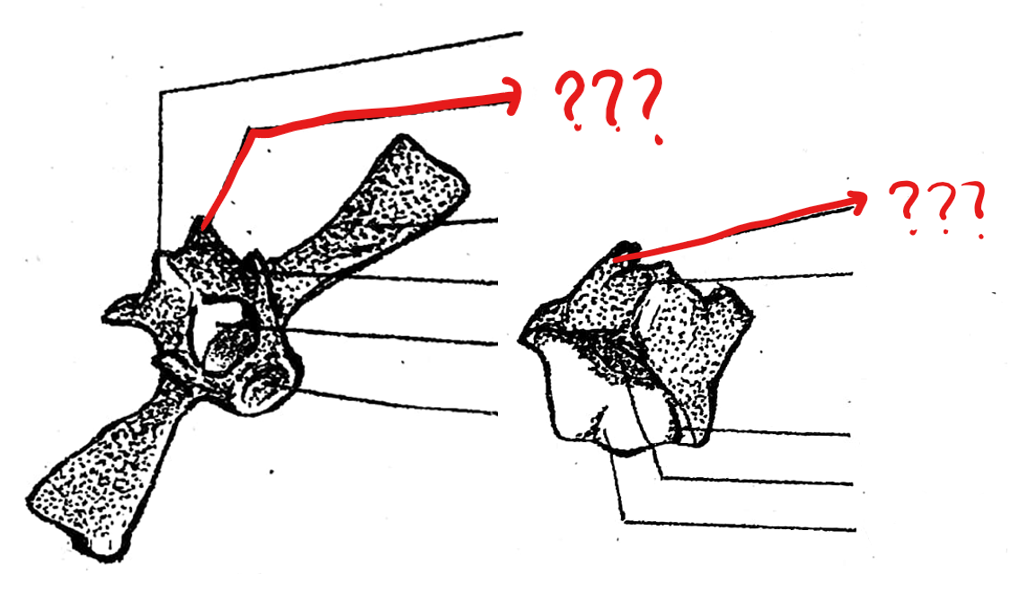
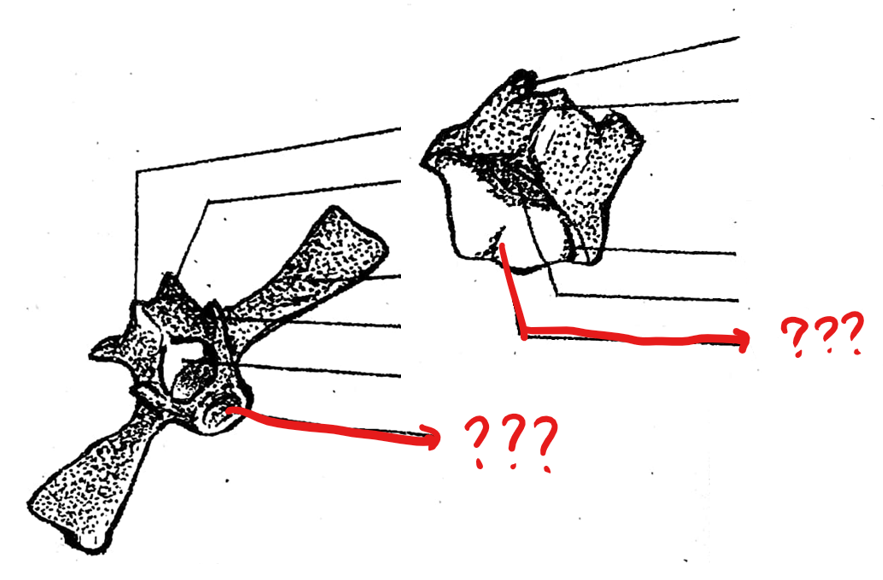
sacral vertebra
part of the vertebral column; 9th vertebra characterized by having flat expanded ends of the transverse processes with which the ilia of the pelvic girdles articulate; postzygapophyses are absent/only prezygapophyses are present; its centrum in frogs are biconvex
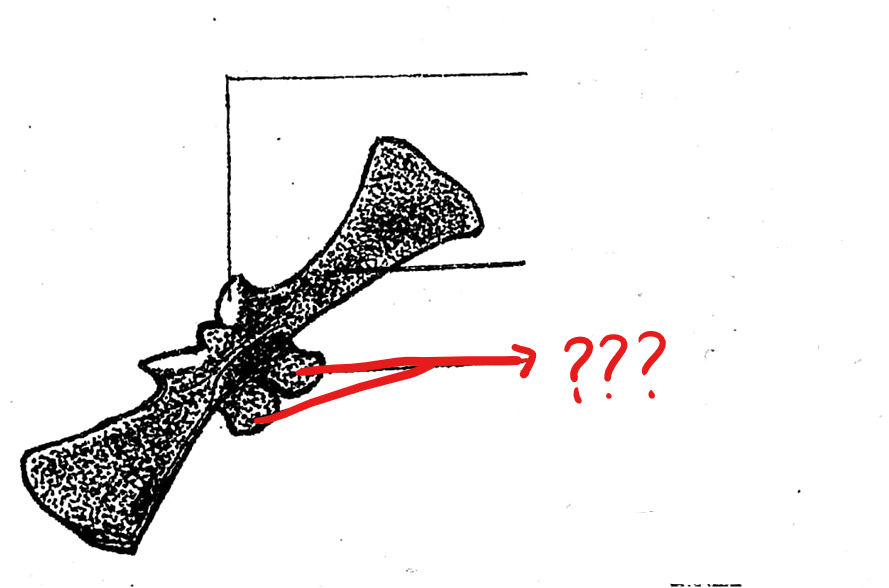
biconvexities of the centrum (acoelous type)
both the surfaces are convex
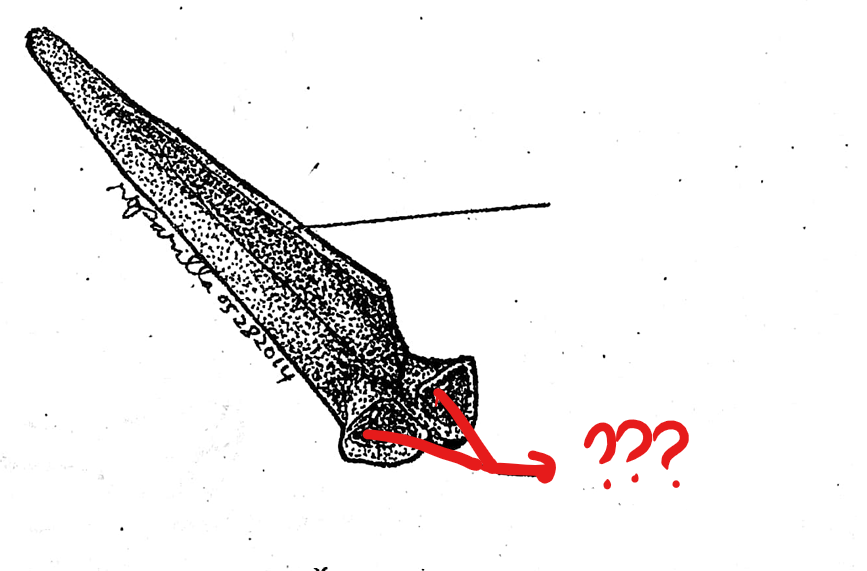
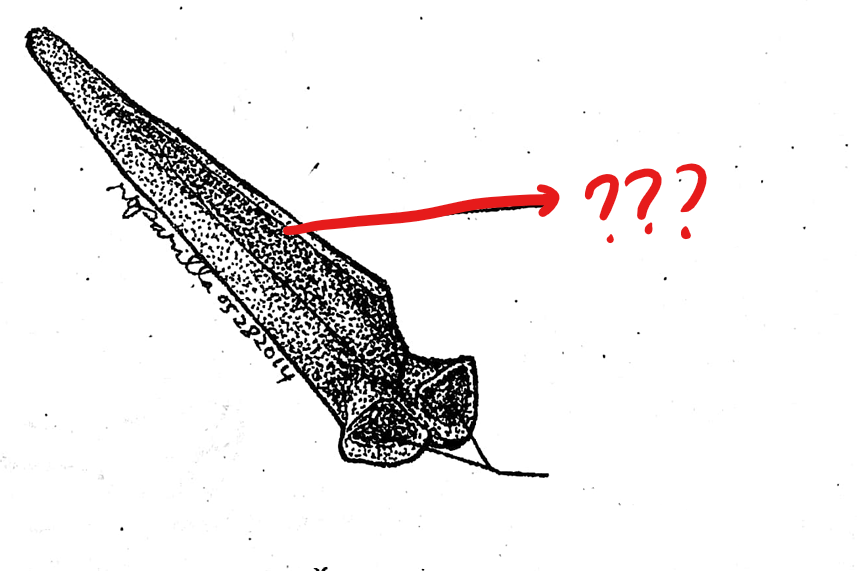
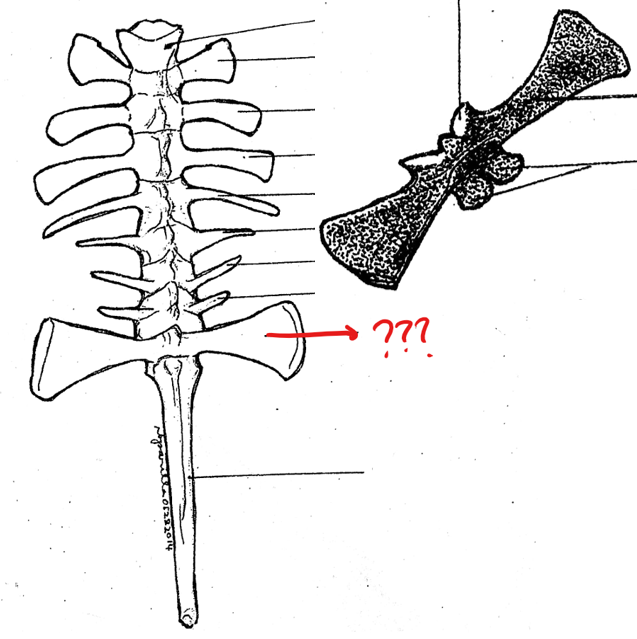
urostyle
part of the vertebral column; 10th vertebra; elongated bone between the anterior portions of the pelvic girdle; corresponds to the caudal vertebrae of other vertebrates; has a pair of small openings on the sides near it anterior portion for the passage of the 10th pair of spinal nerves