Disease Detectives
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Outbreak
More cases of a particular disease than expected in a given area or among a specialized group of people over a particular period of time
Epidemic
Large numbers of people over a wide geographic range affected. The occurrence in a community or region of cases of an illness (or an outbreak) with a frequency clearly in excess of normal expectancy.
Pandemic
An epidemic occurring over a very wide area (several countries or continents) and usually affecting a large proportion of the population.
Cluster
An aggregation of cases over a particular period (especially cancer and birth defects) closely grouped in time and space, regardless of whether is more than the expected number (often the expected number of cases is not known)
Public Health Surveillance
The systematic and ongoing collection, analysis and interpretation and dissemination of health data to gain knowledge of the patterns of disease occurrence in order to control and prevent disease in the community.
Case Definition
Limits the following characteristics: time, person and place for data collection
Case Identification
Confirmed - have diagnosis with case definition plus lab verification; Probable - many factors point to diagnosis but my lack lab verification; Possible - some factors point to diagnosis;
Line Listing
Chart of specific cases including information about each case: Identifying information, Clinical information, Descriptive: time, person, place; Risk factors and possible causes
Epi-Curve
A histogram that shows the course of an outbreak by plotting the number of cases according to the time of onset.
Epi-Curve, Point Source
Occurs when people are exposed to the same exposure over a limited, well defined period of time. The shape of the curve commonly rises rapidly, contains a peak, followed by a gradual decline.
Epi-Curve, Continuous Common Source
Occurs when exposure to the source is prolonged over an extended period of time and may occur over more than one incubation period. The down slope of the curve may be very sharp if the common source is removed or gradual if outbreak exhausts itself.
Epi-Curve, Propagated (Progressive source)
Occurs when a case of disease serves later as a source of infection for subsequent cases and those subsequent cases in turn serve as sources for later cases. Shape of curve usually contains successively higher peaks. Person-Person contact.
Descriptive Studies
Study the distribution of a problem by cases or outcome, frequency in the population, exposure, time pattern or environmental factor. (Studies without a control group can be used for descriptive purposes)
Case Report - Case Series (Descriptive)
Detail report of a single patient from one or more doctors; - Characteristics of several patients.
Correlative studies (Descriptive)
correlates general characteristics of the population with health problem frequency with several groups during the same time period.
Time Series Analysis (Descriptive - Correlative)
correlate within the same population at different point in time
Ecologic relations (Descriptive - Correlative)
comparisons of geographical locations
Cross-Sectional (Descriptive)
a survey, "snapshot in time"; a survey of a population where participants are selected irrespective of exposure or disease status
Analytical Studies
Requires a Control Group
Observational Studies (Analytical)
study determinants of health problems - how and why
Cohort Study (Analytical)
Both groups have a known exposure and are checked for future outcomes or illness; retrospective - starts at exposure in past and moves forward to outcome; prospective - starts at present exposure and moves forward in time to outcome.
Attack Rate (Cohort)
The rate that a group experienced an outcome or illness; equal to the number sick divided by the total number in that group.
Relative Risk (Cohort)
A comparison of the risk of disease in the exposed group compared to the risk of disease in the unexposed group. Meaning: RR >1.0 positive association with increased risk; RR = 1.0 risk in exposed and unexposed group is equal (data does provide evidence of an association)
Case Control Study ( Analytical)
A study type that works backward from effect or illness to suspected cause; control group is a selected group with similar characteristics but is not ill; the two groups are checked for similar exposure.
Odds ratio (Case Control)
Calculated to evaluate the possible agents and vehicles of transmission. Odds for exposure cases divided by odds of for controls.
Risk Factor
Personal characteristics (age, sex, health) behavior or lifestyle including diet, an environment exposure, or a family trait (genetic) that might cause or add to a health problem.
Case Fatality Rate -1
The ratio of the number of deaths caused by a specified disease to the number of diagnosed cases of that disease. (CFR)
Case Fatality Rate -2 (CDC)
The proportion of persons with a particular condition (cases) who die from that condition. The denominator is the number of incident cases; the numerator is the number of cause-specific deaths among those cases. (Note: For longer periods of time, a more specific term may be used: e.g. 5-year survival rate)
Randomized controlled trial study design
human experiment;
Epidemic Threshold
The point where the disease in question becomes widespread (an epidemic)
Incidence Rate
The number of individuals who fall ill with a certain disease during a defined period, divided by the total population.
Prevalence
The number of all current (existing) cases in a population during a certain time period.
Morbidity
All cases fatal and nonfatal
Mortality
Measure indicating what proportion of the entire population die from each disease per year
Endemic disease
Present at a continuous level throughout a population / Geographic area; constant presence of an agent / health condition within a given geographic area / population; refers to the usual prevalence of an agent / condition.
Incubation period
Time between when a person comes into contact with a pathogen and when they show the first symptoms or signs of disease.
Agent
A causative factor, such as a biological or chemical agent that must be present (or absent) in the environment for disease occurrence in a suspectible host.
Fomite
A physical object that serves to transmit an infectious agent from person to person.
Reservoir
An ecological niche where a pathogen lives and multiplies.
Vector
An animal, most often an insect, that transmits disease.
Zoonosis
An infectious disease that is transmissible from animals to humans
Plague
A serious, potentially life threatening infectious disease that is usually transmitted by the bites of rodent fleas. Three types: bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic.
Chain of infection
Includes: infectious agent, reservoir, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portal of entry and susceptible host.
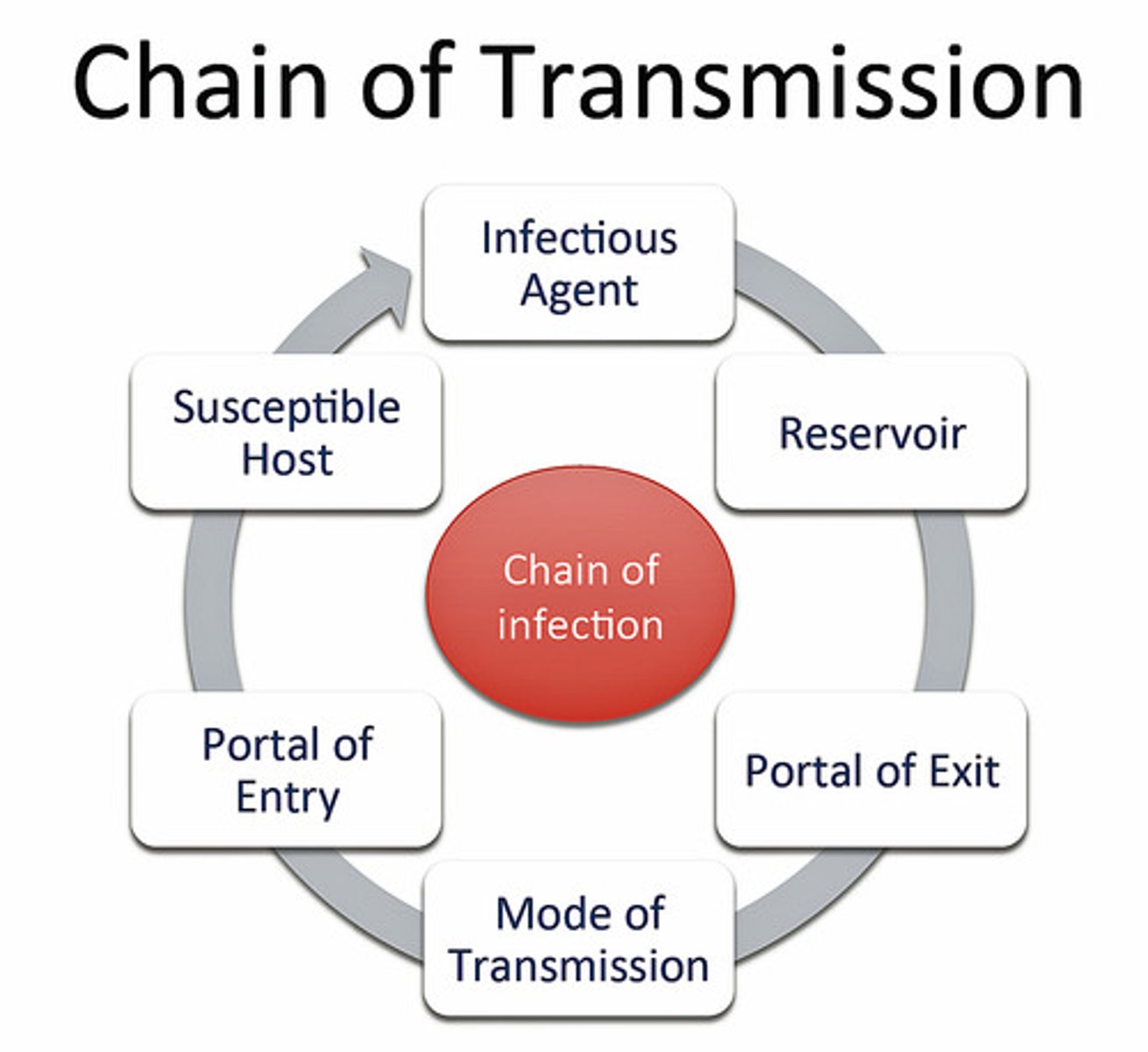
Portal of entry
Respiratory (breathing or through the air); Ingestion (food, eating or water, drinking); Dermal contact (skin or absorption); Blood (insect bite or needle stick);
Modes of Transmission
Direct or Indirect contact; Direct can be skin to skin or soil to skin and also droplet spread by sneezing, coughing or talking; Indirect can be by vector (insect), vehicle (water, biologic product, fomites) or airborne.
Triad of Analysis
Person, place and time; Agent, host, environment
Sensitivity
1. In disease epidemiology, the ability of a system to detect epidemics and other changes in disease occurrence. 2. In screening for a disease, the proportion of persons with the disease who are correctly identified by a screening test. 3. In the definition of a disease, the proportion of persons with the disease who are correctly identified by defined criteria.
Specificity
The proportion of persons without a disease who are correctly identified by a test. The specificity is the number of true negative results divided by the sum of the numbers of true negative plus false positive results.
R-0
Susceptible population divided by the Threshold Population; average number of additional infections per infected person.
infectivity
the ability of an infectious agent to cause infection, measured as the proportion of persons exposed to an infectious agent who become infected.
pathogenicity
ability to cause disease; the ability of an organism to cause disease (ie, harm the host). This ability represents a genetic component of the pathogen and the overt damage done to the host is a property of the host-pathogen interactions
virulence
degree of pathogenicity; The ability of any agent of infection to produce disease. The virulence of a microorganism (such as a bacterium or virus) is a measure of the severity of the disease it is capable of causing.
temporality
cause / exposure must precede the effect / outcome
natality
the ratio of births to the general population, birth rate.
etiology
the study of all factors that may be involved in the development of a disease, including the susceptibility of the patient, the nature of the disease agent, and the way in which the patient's body is invaded by the agent; the cause of a disease.
risk
the probability that an event will occur. In epidemiology, it is most often used to express the probability that a particular outcome will occur following a particular exposure.