Econ 200 Final
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Autarky
an economy that is self-contained and doesn’t engage in trade with outsiders. the economy neither exports nor imports goods
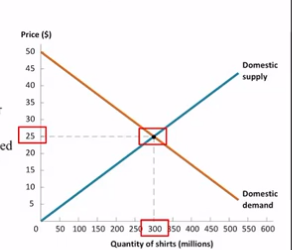
Imports
Goods or services produced elsewhere, consumed domestically
Exports
Goods or services consumed elsewhere, produced domestically
Tariff
tax targeted at certain imports, the purpose is to reduce the quantity of imports to protect domestic producers
Quota
a limit on the amount of a particular good that can be imported
Quota rents
the additional revenue earned by those who are allowed to import goods
Externality
a cost or benefit to a third party that results from the production of consumption of a product or service. (unintended effects upon others, spillover effects)
Market failure
a situation in which the market fails to produce the efficient level of output
Private benefit
the benefit received by the consumer of a good or service
Social benefit
the total benefit from consuming a good or service
The Coase Theorem
the idea that private parties can solve the externality problem and reach the socially efficient output through private bargaining requires (1) enforceable assigned property rights, (2) low transaction costs, (3) full information about costs and benefits
Transaction costs
the costs in time and other resources parties incur in the process of agreeing to and carrying out an exchange of goods or services (the time spent gathering information, cost of negotiation, legal fees to close a transaction, cost of enforcing an agreement).
Pigouvian taxes
Increase efficiency while bringing in tax revenue, allowing for inefficiency-causing taxes in other markets to be reduced. Known as the double-dividend of taxation
Opportunity cost (review)
the true cost of a choice is the value you could have gained by choosing the next best alternative instead. Always a #
Trade off (review)
What I have to give up in order to gain something else.
a technology in economics
the process by which a firm transforms inputs into outputs
positive technological change
When a firm improves its ability to turn inputs into outputs
Firm Production
The firm takes inputs and produces the goods and/or services it sells. Y = f(K, L). Y = amount of input, f(.) = production function, K = capital input, L = Labor input
Profit
a firms goal in producing output is to maxmimize profit. Profit - Total revenue - Total cost
Total Revenue
the amount a firm receives from the sale of its output. Total revenue = Quantity x price
Total cost
the amount that a firm pays for input used to produce outputs
the short run
a period of time during which at least one of a firms input is fixed
the long run
no inputs are fixed, the firm can adopt a new technology or scale up or down any inputs
variable cost
costs that vary depending on how much is produced
fixed costs
costs that don’t change according to how much is produced
Explicit costs
costs that involve spending money. ex. wages, replacement of depricated capital, materials, rent, etc.
Implicit costs
Opportunity costs for firms. ex. salary as entrepreneur has to give up his current job in order to open his new business
Accounting profit
When companies report profits, they provide accounting profits and they may be misleading indicators of how businesses are doing
Economic profit
used to account for implicit costs
Production function
the relationship between the inputs employed and the maximum output of the firm
marginal product
the increase in output that is generated by an additional input.
MP = change total output / change input
The average product
the total production divided by the amount of input
AP = total output / total input
minimum efficient scale
the lowest level of output at which all economies of scale are exhausted
Market Structures
models of how the firms in a market interact with buyers to sell their output
Perfectly competitive market
a market with many buyers and sellers, identical products sold by each firm, and no barriers to new firms entering the market.
average revenue
total revenue divided by the quantity of the product sold
marginal revenue
the change in total revenue from selling one or more unit of a product
What is profit maximization?
The main goal of a firm, firms choose the output quantity that maximizes profit
What is productive efficiency?
Producing a good at the lowest possible cost
What is allocative efficiency?
Producing where marginal benefit to consumers equals marginal cost of production
Monopoly
a market structure consisting of a firm that is the only seller of a good or service that does not have a close substitute
Natural Monopoly
a market where a single firm can produce the entire market’s quantity demand at a lower cost than multiple firms
Price discrimination
The practice of charging customers different prices for the same good
first degree price discrimination
when a seller charges each individual consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay for each unit of a good or service
second degree price discrimination
offering different prices for different quantities
third degree price discrimination
offering different prices to different groups of consumers
monopolistic competition
describes a market with many firms that sell similar but differentiated goods and services
product differentiation
firms that have an interest in persuading that their products are a unique practice
Exiting
if a firm is losing money in monopolistic
duopoly
if there are two firms in the market and both make identical (or nearly identical) products