5.6- Photosynthesis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
oxidation
atom gains oxygen
atom loses electron
atom loses hydrogen
reduction
atom loses oxygen
atom gains an electron
atom gains hydrogen
relationship between photosynthesis and respiration
the products of one reaction are the raw materials for the other
autotroph
an organism that uses an external energy source and inorganic molecules to make complex organic molecules
photoautotroph- uses light energy to make complex organic molecules
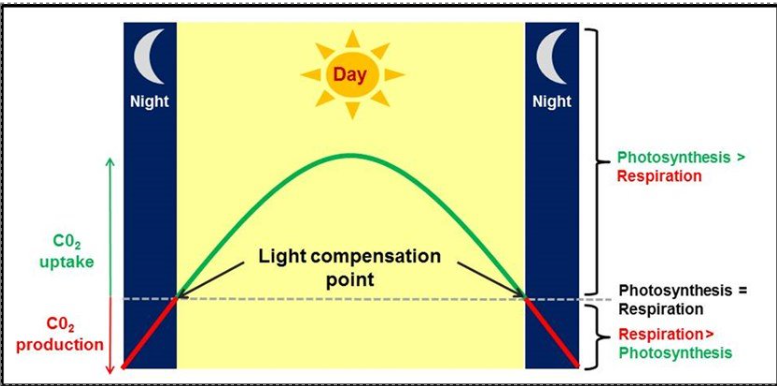
compensation point
the point when photosynthesis and respiration proceed at the same rate- no net gain or loss of carbohydrate
structure of chloroplast
2-10μm long, 1μm diameter
outer membrane is highly permeable
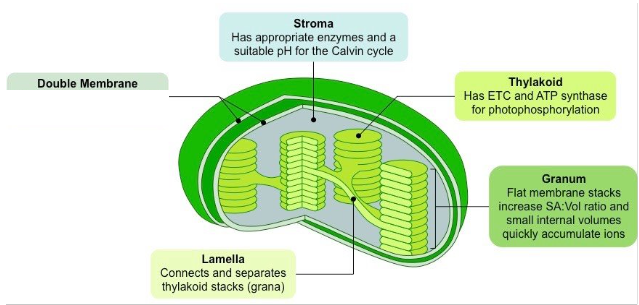
structure of thylakoid membrane
form discs that contain chlorophyll
each stack of thylakoids is called granum- can contain many thylakoids
some thylakoids have tube shape extensions- join with thylakoids in another grana→ intergranal lamellae
light dependant stage takes place in thylakoids
stroma
fluid filled matrix around grana
light independent stage takes place here
adaptations of chloroplasts to their function (6)
granal membranes provide large SA for chlorophyll electron carriers and enzymes to attach
network of proteins in grana hold chlorophyll in specific way to allow max. light absorption
fluid in stroma contains enzymes needed for Light independent stage of photosynthesis
chloroplast is membrane bound→ optimal pH for enzyme function
granal membranes have ATPase channels→ catalyse ATP production
stroma surrounds grana→ products of LDR can easily diffuse into stroma LIDR
ATP
cells cannot get energy directly from glucose→ energy released from glucose during respiration used to synthesis ATP
ATP acts as energy carrier→ transports energy around cell
ATP synthesis from ADP and inorganic phosphate→ catalysed ATP synthase
products of light dependent reaction
For Calvin Cycle:
ATP
NADPH
Oxygen
occurs in thylakoids
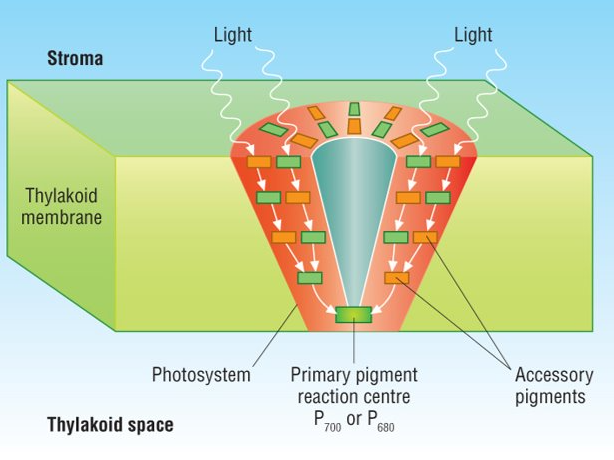
photosynthetic pigments
molecules which absorb light energy→ absorbs certain wavelengths and reflects others
arranged in photosystems in thylakoid membranes
types of chlorophyll
chlorophyll a
chlorophyll b
chlorophyll a
primary pigment
two types:
P680
P700
both found at centre of photosystems→ primary reaction centre
P680 found in photosystem II→ peak absorption is light at wavelength 680nm
P700 found in photosystem I→ peak absorption is light at wavelength 700nm
chlorophyll a also absorbs blue light wavelength 450nm
structure of chlorophyll
long hydrocarbon chain and a porphyrin head (ring structure) containing magnesium ion in the centre
when light hits magnesium 2 electrons become excited and leave chlorophyll
accessory pigments
absorb wavelength that are not well absorbed by chlorophylls→ pass energy to chlorophyll a at base of the photosystem
chlorophyll b:
absorb light at wavelengths between 500-640nm
appears blue-green
carotenoids:
absorb blue light (400-500nm)
reflect yellow and orange light
light dependant stage of photosynthesis
water is in thylakoid membrane. light hits PSII, breaking water molecule down→ photolysis
H2O→ 2H++2e-+1/2O2
H+ accumulates, e- used to restabilise chlorophyll a, O2 by product
light energy excites 2e-.
Transferred into electron carriers→ take electrons through electron transport chain:
each carrier has higher affinity for e- than the previous.
e- move in series of redox reactions
ATP produced→ releases energy
energy released along ETC used to actively transport protons into thylakoid space. H+ move through channel coupled to ATP synthase. Movement drives production of ATP from ADP and Pi.
arrive at PSI. Light energy excited 2e-. Electrons can either undergo cyclic phosphorylation OR passed to ferredoxin.
2H+ from photolysis, 2e- and NADP form reduced NADP→ catalysed by NADP reductase
phosphorylation
making of ATP using light energy
2 types:
cyclic
non-cyclic
non-cyclic phosphorylation
light energy absorbed by PSII
light energy excites electrons in chlorophyll
high energy electrons move along ETC to PSI→ energy released used to synthesise ATP
Light energy also absorbed in PSI→ excites electrons to higher energy level
electrons transferred to NADP along with H+ to form NADPH
cyclic phosphorylation
only uses PSI
electrons used aren’t passed to NADP, but passed back to PSI via electron carriers
electrons recycled and used repeatedly to flow through PSI
produces small amounts of ATP
no photolysis of water or generation of NADPH
the light independent stage
produce organic compounds needed by the plant including glucose
requires ATP and NADPH
reactions happen without light but will eventually stop in its absence as NADPH and ATP is not being replaced
The calvin cycle
carbon fixation/ carboxylation: RuBP (5 carbon compound) and CO2 react to make unstable 6C compound→ catalysed by RuBISCO
6C compound breaks down into 2 GP (3 carbon)
NADPH from LDR reduces GP into 2 TP molecules (3 carbon)
1 carbon used to produce organic molecule e.g. glucose→ remainder regenerated into RuBP
law of limiting factors
at any given moment, the rate of photosynthesis is limited by the factor that is least favourable
limiting factors of photosynthesis
light intensity
carbon dioxide concentration
temperature
light intensity
higher LI= higher rate of e- excitation= higher rate of LDS
after certain point, no change as other factor is limiting
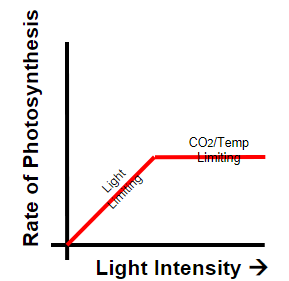
CO2 concentration
more CO2= more carboxylation=higher rate
after certain point, no change as another factor becomes limiting
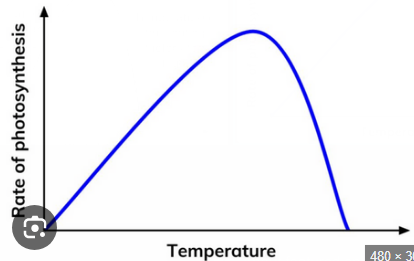
temperature
higher temp= more collisions= more ESCs made= higher rate
after optimum temp, enzymes denature= less products made
how light affects levels of GP, TP and RuBP
as light levels fall:
RuBP levels fall due to less TP
TP levels fall
GP levels rise due to accumulation as a result of low TP
how CO2 levels affect levels of GP, TP and RuBP
as CO2 levels fall:
RUBP levels increase as they cannot accept CO2
GP and TP levels fall as GP cannot be made
affect of water on photosynthesis
cells become plasmolysed as insufficient water taken up by roots
plant roots produce abscissic acid→ causes stomata to close, reducing gas exchange
tissue becomes flaccid
rate of photosynthesis falls