exam end of year 2024 psychology
1/286
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
287 Terms
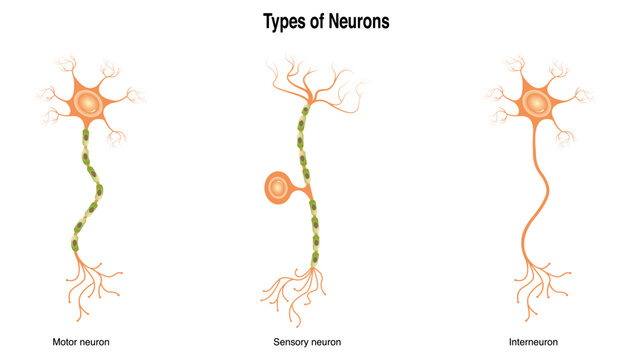
nervous system
The _______ is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body, allowing for communication and control of bodily functions.
peripheral nervous system
The ___________ consists of the skeletal muscles. connecting the central nervous system to the rest of the body for sensory and motor functions. has somatic and autonomic nervous system.
somatic nervous system
The ___________ is responsible for voluntary control of skeletal muscles and relaying sensory information to the central nervous system. has afferent and efferent nerves.
autonomic nervous system
The ___________ regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. with afferent and efferent nerves
sympathetic nervous system
The __________ nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, releasing adrenaline to prepare the body for emergencies.
somatic
controlled consciously
autonomic
The __________ nervous system controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate and digestion.
all voluntary
All voluntary _______ are actions or behaviors that are chosen willingly by an individual without external coercion or force.
afferent
Definition: _______ (approach) neurons carry sensory information from the body to the central nervous system.
efferent
Definition: _______(exit) neurons carry signals away from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands to produce a response.
central nervous system
The _______ _______ _______ consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information, coordinating actions, and transmitting signals throughout the body.
parasympathetic
Fill in the blank: ___________ nervous system is responsible for rest and digest functions, promoting relaxation and conserving energy in the body.
sensory neurons
Afferent neurons, also known as _________, carry sensory information from the body to the central nervous system for processing.
motor neurons
Fill in the blank: Motor neurons are responsible for carrying signals from the brain and spinal cord to _________.
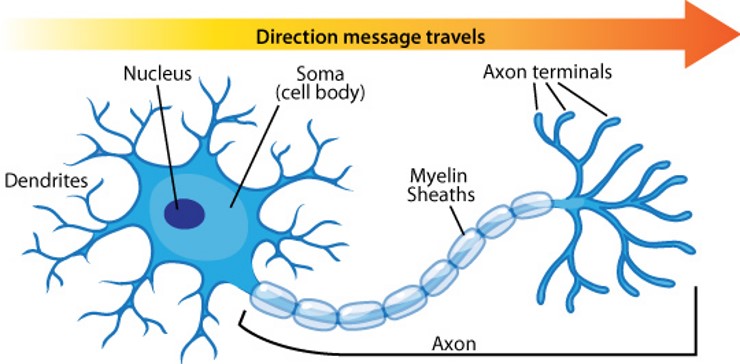
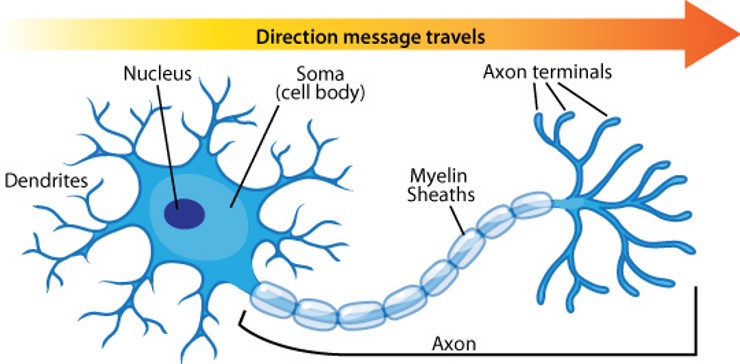
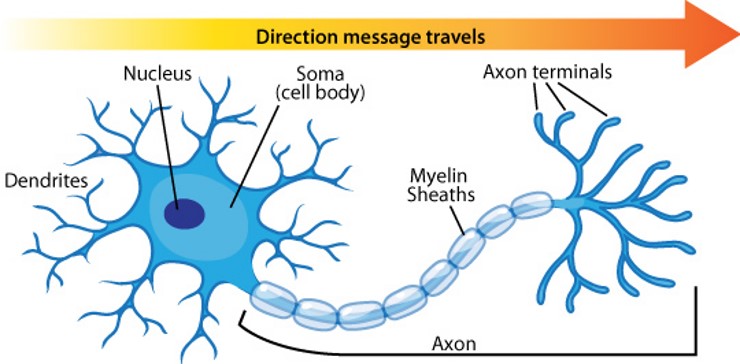
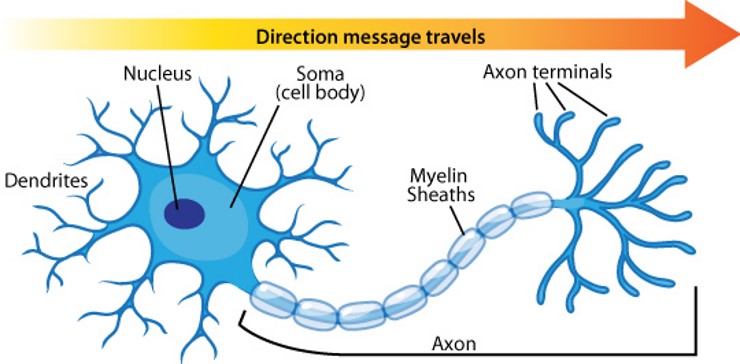
cell body
Flashcard: The ___ is the main part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles, responsible for maintaining the cell's function and metabolism.
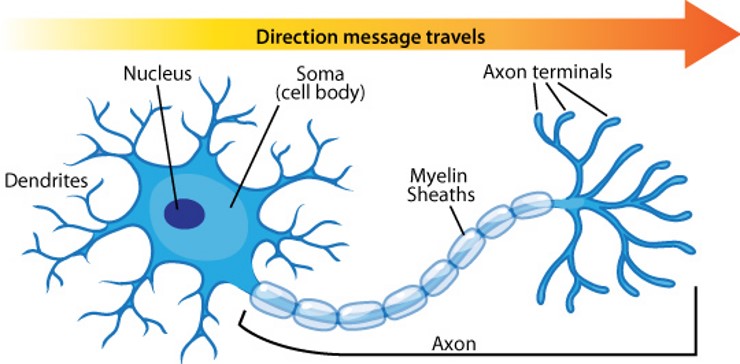
axon
A(n) _______ is the long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body to other cells.
interneurons
Interneurons are neurons that act as a bridge between sensory and motor neurons, helping to process information within the __________ system.
axon terminals
The _______ are the endings of an axon that release neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons or muscles.
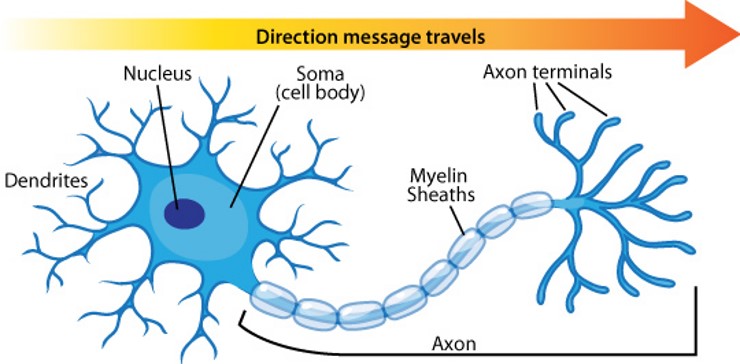
myelin sheath
The _______ is a fatty substance that surrounds and insulates nerve fibers, allowing for faster transmission of electrical impulses along the neuron.
sympathetic nervous systems
The __________ nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, releasing adrenaline to prepare the body for stressful situations.aut
autonomic nervous system
The ___________ regulates involuntary bodily functions like heart rate and digestion, consisting of sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
nerve
A _______ is a bundle of fibers that transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
neuron
A _______ is a specialized cell that transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system.
depolarized
Definition: State of a cell where the inside becomes less negative compared to the outside, making it more likely to generate an action potential.
reploarized
After an action potential, the cell membrane returns to its resting state during the process called ____________.
cation potential
Cation potential is the ability of a _______ to attract and hold onto positively charged ions.
the synapse
A synapse is a junction between two neurons where communication occurs through the release and reception of neurotransmitters.
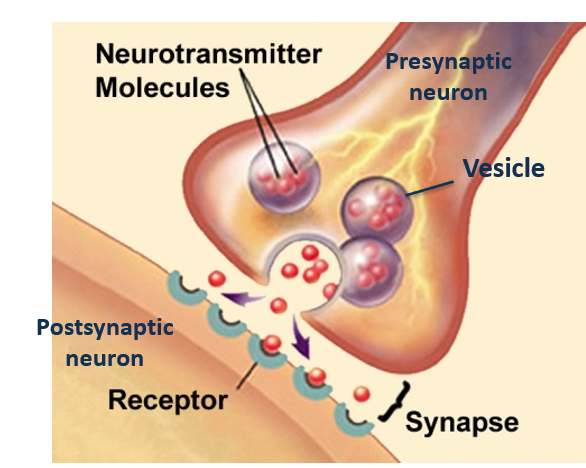
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that transmit signals across the synapse
between neurons.
serotonin
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating mood, ____, and sleep.
dopamine
A neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the brain's reward system, __________, and motor control.
medulla oblongta
autonomic functions
. breathing,
heart rate,
blood pressure.
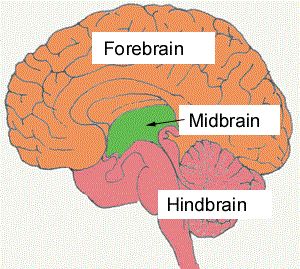
hindbrain
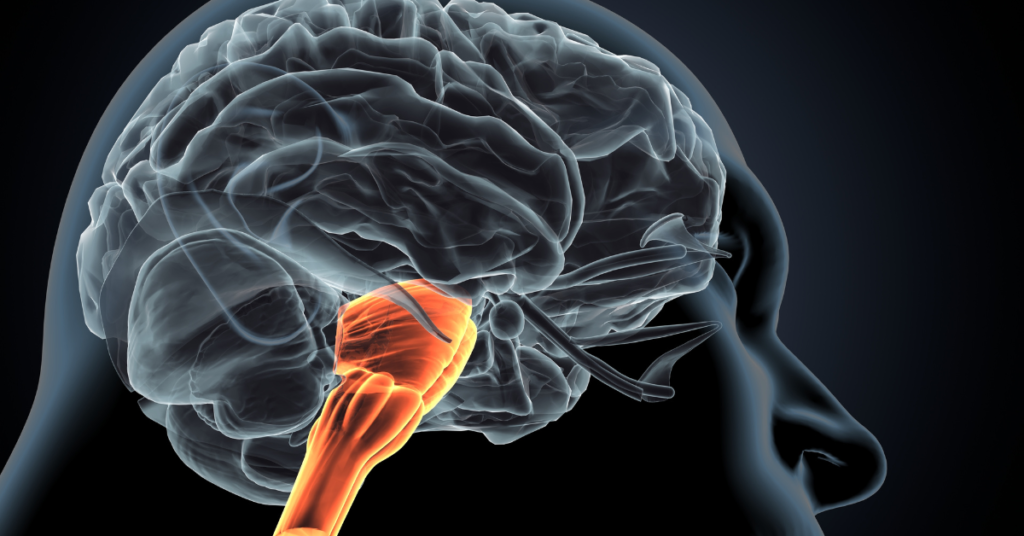
cerebellum
The cerebellum is a part of the hind brain that plays a key role in coordinating __________ and is essential for balance and motor control.
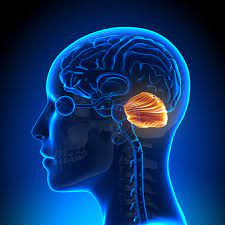
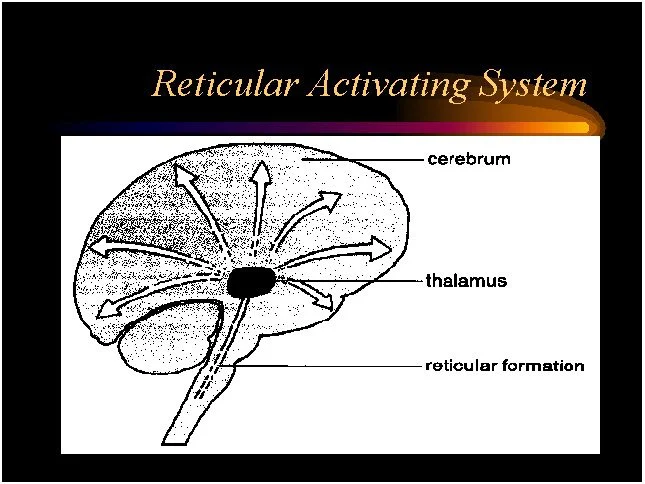
reticular formation
network of nuclei in the brainstem
regulating arousal,
sleep-wake cycle,
filtering sensory information.
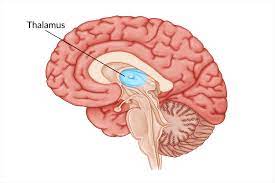
midbrain
thalamas
acts as a relay station for sensory information, directing it to the appropriate areas
hypothalamus
hunger,
thirst
, body temperature,
forebrain
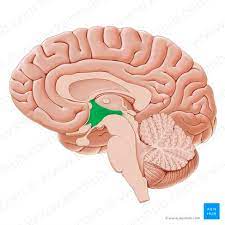
cerebrum
The __________ is the largest part of the brain responsible for higher brain functions such as thinking, perceiving, planning, and understanding language. forebrain
forebrain
higher brain functions
decision-making,
processing sensory information.
cerebrum
thalamus
hypothalamus
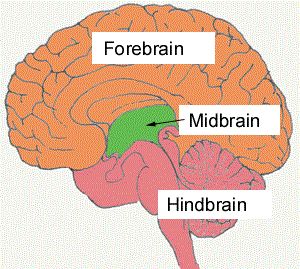
hindbrain
basic life functions
breathing
heart rate.
medulla oblongta
cerebellum
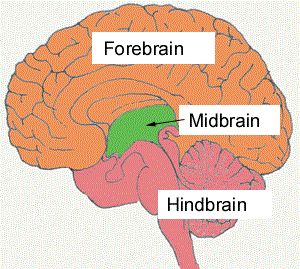
midbrain
relaying sensory and motor information vision,
hearing,
eye movement.
reticular formation
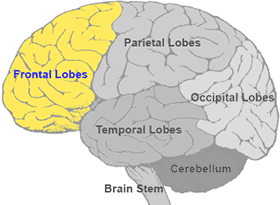
frontal lobe
decision-making,
problem-solving,
voluntary movement.
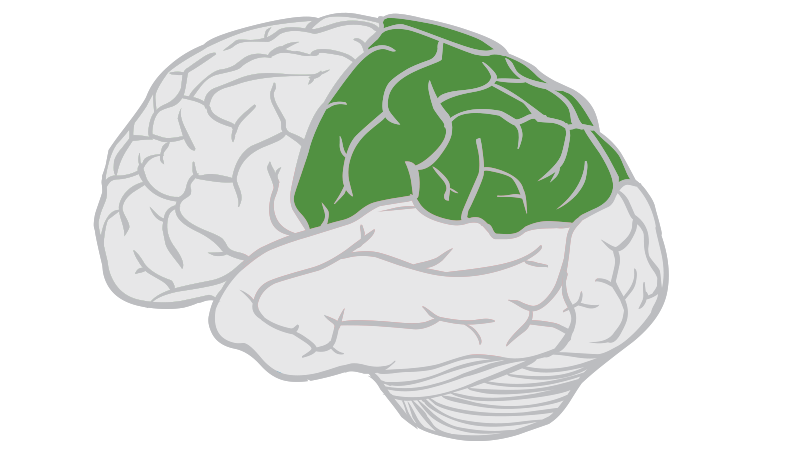
parietal lobe
processing sensory information
touch,
temperature,
spatial awareness.
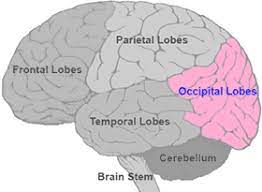
occipital lobe
processing visual information.
temporal lobe
processing auditory information
, language comprehension,
memory.
dendrite
A _______ is a branch-like extension of a neuron that receives signals from other neurons and conducts them towards the cell body.
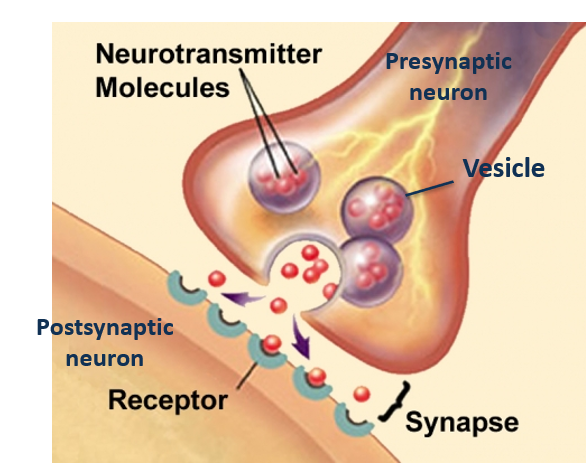
synapse vesicle
A synapse vesicle is a small sac that stores and releases neurotransmitters at the __________.
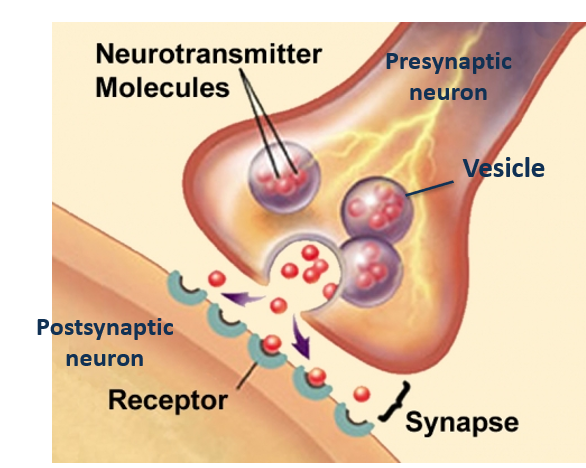
synapse receptors
Synapse receptors are specialized proteins located on the postsynaptic membrane that bind neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron, allowing for the transmission of signals across the ________.
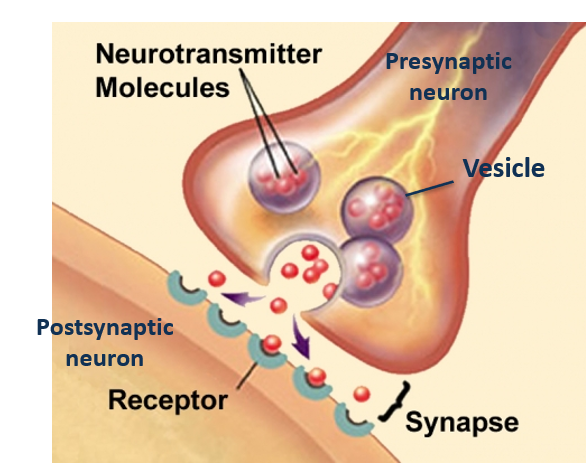
synapse neurotransmitter
A synapse is a junction between two neurons where communication occurs through the release of ____________.
left hemisphere brain
language processing,
logic,
analytical thinking.
right hemisphere brain
for creativity,
spatial awareness,
facial recognition,
emotional processing.
independent variable
is manipulated or changed by the researcher to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
dependent variable
t is measured and affected by the independent variable. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable.
extraneous variables
: Extraneous variables are additional factors that may affect the outcome of an experiment, leading to inaccurate results if not controlled for.
extraneous researcher variables
Variables related to the experimenter that may impact how each participant responds. Age, gender, accent, manner etc of the experiment can affect the behaviour of the participants.
confounding variable
An unmeasured variable that may influence both the independent variable and dependent variable, altering the relation between them.
confounding variable example
Annually murder rates and ice cream sales are highly positively correlated. As murder rates rise, so does the sale of ice cream. A confounding variable—which causes the increase in BOTH ice cream sales AND murder rates
demand characteristics
refer to cues in a study that lead participants to infer the researcher's expectations, influencing their behavior or responses."
the faithful participant
Follows all the instructions that are given by the experimenter, word-to-word.
the apprehensive participant
Is concerned about the ‘evaluation’ they receive from the experimenter; they end up behaving in a socially desirable way so that the experimenter has a favourable opinion about them.
the good participant
Tries to understand the aim of the research and then alters their behaviour according to what the experiment demands. They do not have the intention of ruining the experiment in any way
the negative participant
Tries to understand the aim of the subject and then alter their behaviour in a negative manner so that the credibility of the experiment is compromised.
ways to reduce effect of extraneous and confounding variables
random allocation of participants
single blind procedures
standardization of procedures and instructions
experiment groups
groups in an experiment that receive a specific treatment or intervention, allowing researchers to compare outcomes with other groups.
control groups
Control groups are a crucial part of experiments used to compare results with the group that does not receive the treatment.
random allocation of participants
A technique that chooses individuals for experimental groups and control groups entirely by chance.
single blind procedure
A methodology where participants are unaware if they have been allocated to the experimental group or the control group.
standardization of procedures and instructions
ensure each participant experiences the experiment in the same environment, e.g., with the same lighting conditions, same noise levels
population
A population is the total group of individuals that an experimenter is interested in and from which a sample group might be drawn.
sample
the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
sample bias
• Sample bias is when a sample is collected in such a way that some members of the intended population are included in too high or too low numbers. This means the sample is not representative of the population.
generalizability
The sample, should be as representative of the target population as possible. The more representative the sample, the more confident the researcher can be that the results can be generalised to the target population.
convenience sampling
Selection of participants is based on the researcher’s accessibility to the participants or the participants’ availability
positives; quicker, easy
negative'; doesnt represent population
random sampling
Uses a carefully planned method that ensures every member of the population has a chance of being selected.
positives, no sample bias
negative, might not be representative of the population due to chance.
stratified sampling
1.Population is broken into groups based on characteristics relevant to research that they share - may require pre-testing.
2.Participants are randomly selected from each group in the same proportion as they appear in the whole population.
3.Sample should be highly representative of the population.
negative information required by individuals
snowballing
1.Population is broken into groups based on characteristics relevant to research that they share - may require pre-testing.
2.Participants are randomly selected from each group in the same proportion as they appear in the whole population.
3.Sample should be highly representative of the population.
negatives difficult to identify sampling errors
decreased personal accountability
people feel their actions are less noticeable in a group leading to reduced moral inhibitions.
influence informative
when individuals look to others for guidance in uncertain situations beleiving that the group has more accurate information
diffusion of responsibility
the tendency for individuals to feel diminished responsibility for their actions when they are surrounded by others who are acting the same way The diffusion of responsibility relates to people spreading the shared responsibility amongst those around them (1), therefore the more people around the less likely they will take shared responsibility/their share of responsibility will decrease
bystander effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
anti social behavior
behavior that either damages interpersonal relationships or is culturally undesirable
pro social behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior. The opposite of antisocial behavior
social responsibility
the obligation of a person to contribute to society
reciporcity
a mutual exchange b/t what we give and receive----for example, liking those who like us
personality characteristics
factors that help explain differences in how individuals respond differently to stressors
social influence kelman 1958
a framework for social influence explaining how individuals conform to social norms or adopt the behaviors beliefs or attitudes of others.
compliance
agrees with others outwardly not privately. a temporary influence done by a presence of social pressure or authority
identification
adopting behaviours or beleifs of a group or individual beacuase they want to establish or maintain a relationship with them they may genuinely beleive in these ideas but the beleif is tied to their connections with the influence. is longer lasting but susceptable to change if the relationship shifts.
Internalisation
A deep type of conformity where we take on the majority view because we accept it as correct. It leads to a far-reaching and permanent change in behaviour, even when the group is absent.
Obedience (Milgram)
Looks at environmental factors; how to explain specific instances of inhumane and immoral behavior; ordinary people without AP do inhumane things to other people in particular environments-when authority figure tells them to;
aim milgram expeirment
to see how far individuals would go in obeying an authority figure even when asked to perform actions that conflict with their conscience.
milgram experiment set up
participants who believed they where apart of a memory excercise where instructed to administer increasinlgy intense electric shocks to another person whenever they made an error.
Milgrim sample
40 males aged 20-50
recuited through ads in newspaper
milgrims findings
65% of particapants went to highest voltage
ethical concerns milgrim
deception psychological harm
conformity
Adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.
normative influence
conformity based on a person's desire to fulfill others' expectations, often to gain acceptance privately may disagree
Cultural Factors
collectivist cultures may encourage conformity more than individualist cultures
group size
larger groups increase conformity to a point. anonymity can reduce conformity in larger groups
deindivation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity
social loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable