Peri-anesthesia Monitoring and Complications II
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Resting heart rate
The most ideal heart rate is a ____?
35-100 Bpm
Large dogs have what resting HR?
50-120bpm
Medium dogs have what resting HR?
80-150bpm
Small dogs have what resting HR?
90-160bpm
Cats have what Resting HR?
25-45
Horses have what resting HR?
15sec x 4 to get beats per minute
What is the basic rule to count a normal heart?
Count over 20-30 and multiply by 3 or 2
If a patient has an arrhythmia or severe bradycardia how should we count it?
Only electrical signal
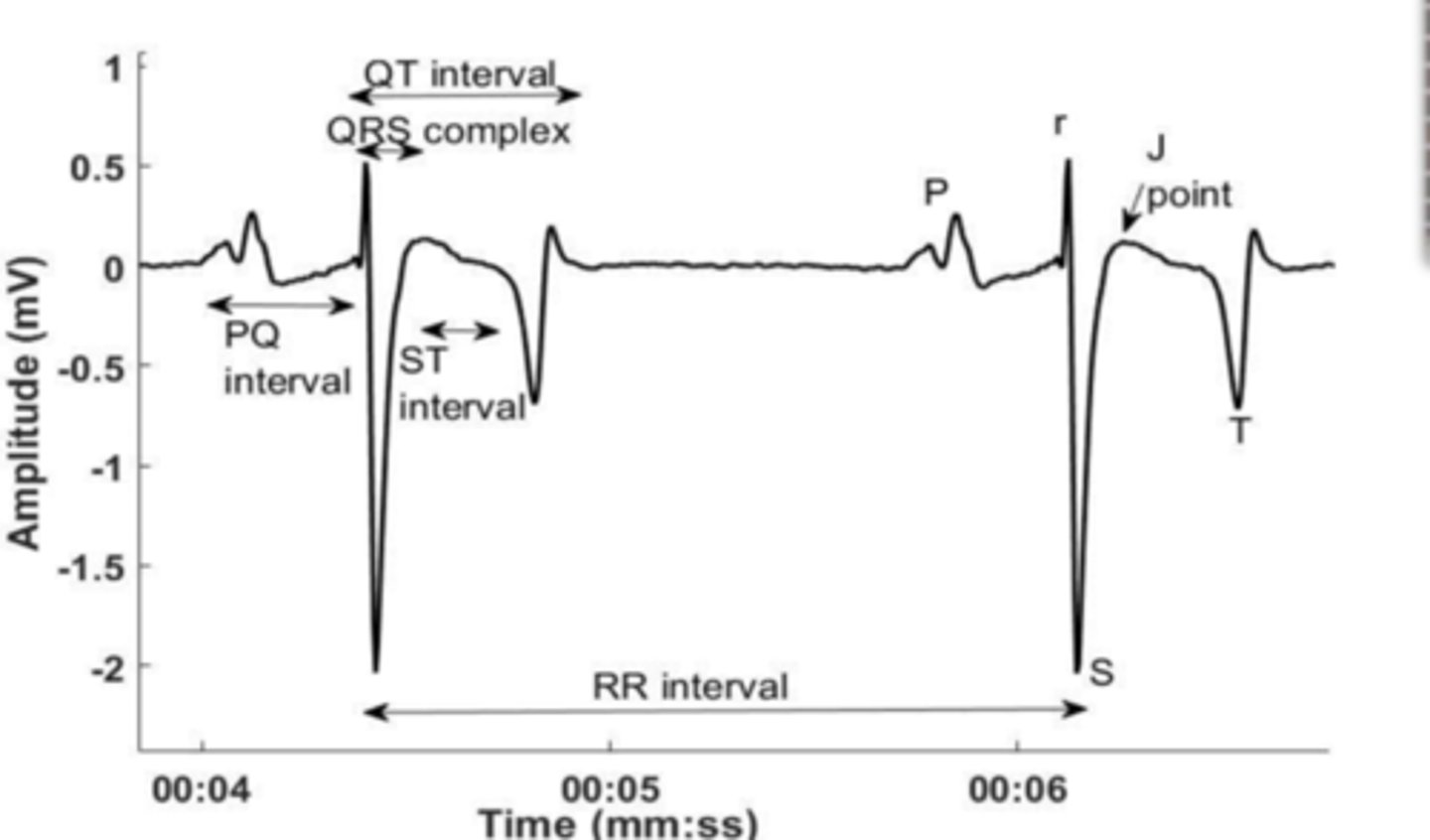
What will an ECG tell you?
No - always place capnograph and pulseox first
Should you place ECG first?
Lead 2
Small animals will use what leads?
Base-apex lead (Lead 1)
Horses and cattle will use what kind of leads?
White - RF
Black - LF
Red-LH
Where do you place each lead on a small animal?
White -on neck
Red - FR
Black - FL
Where is the proper placement of the lead on large animals?
Find obvious arrhythmias and major changes
What is the purpose of ECG?
Ears
You can use the ___ if forelimbs aren't accessible?
Yes for large animals and birds
Is this a a normal ECG?
Miniature dachshunds
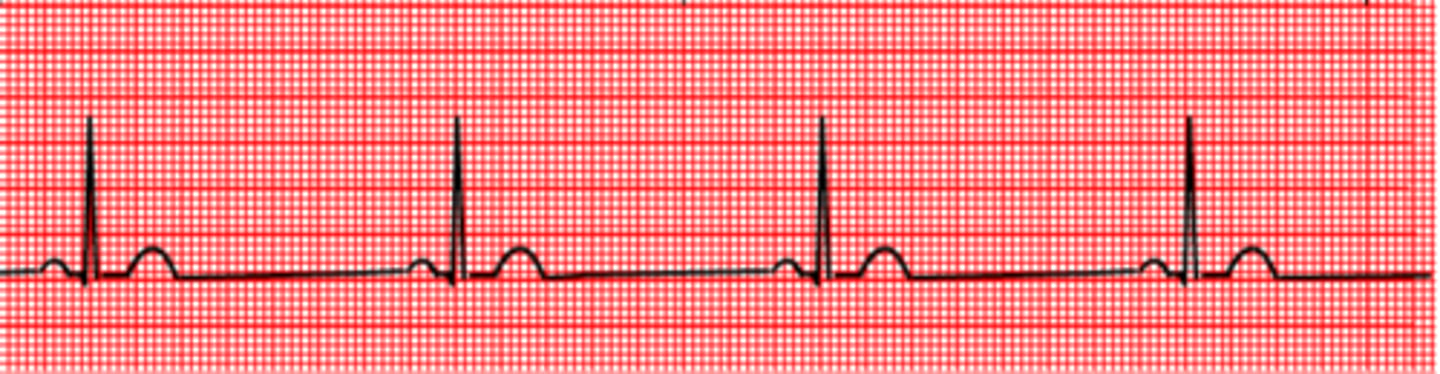
What breed naturally gets sinus bradycardia under anesthesia?
Longer R-R
What will sinus bradicardia going to look like on ECG?
-Anesthesia
-Opioids
-Sedatives
-Hypothermia
-Neck/abdomen/ manipulation
What is going to cause vagal sinus bradycardia?
Cardiac dz
Endocrine dz
Electrolyte abnormality
Beta blockers
Ca2+ channel blockers
What is going to cause non-vagal sinus bradycardia?
Hypotension
When do we tx sinus bradycardia?
Young - neonates
-fixed sv so HR dependent CO
What animals is sinus bradycardia dangerous?
Anticolenergis
- Atropine (less potent, most efficacious 60min)
- Glycopyrrolate (Less efficacious but more potent 90min)
How can tx vagal bradycardia?
Atropine,
(glycopyrrolate might not work and need multi-doses)
Which drug used to tx sinus bradycardia will be more likely to cause tachycardia and should be used in emergency situations?
Increased work load due to A2 causing vasoconstriction and Anticolinergic causing increased HR
What interactions will anticholinergics have w/ A2 agonists?
60mins
You should avoid using an anticholinergic for ____ after use of dexmedetomine?
A decrease in HR or AV block that will resolve w/ time
What is paradoxical bradycardia caused by anticholinergics?
Stop the cause
Isoproterenol - Nonselective B agonist
Pacemaker
How do you tx non-vagal bradycardia?
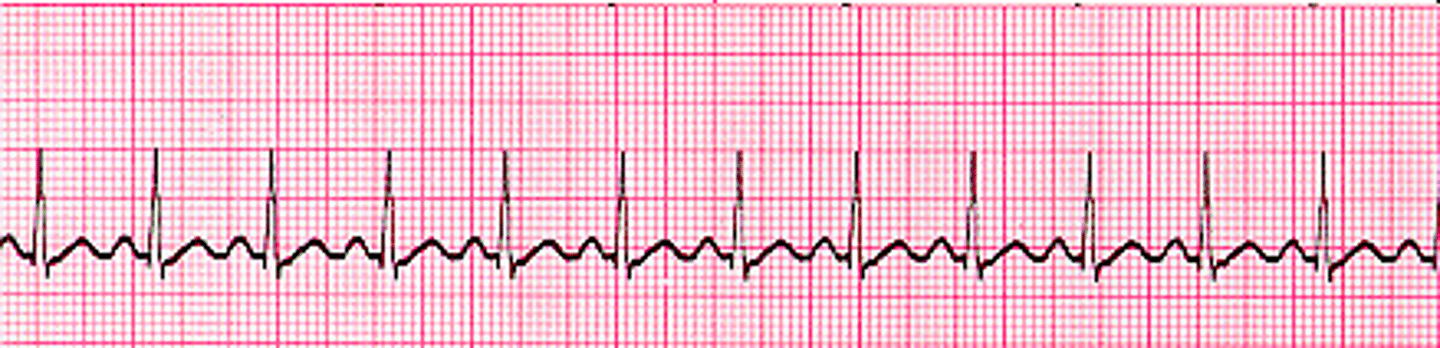
RR interval will be shorter
What will we see on the ECG if we have sinus Tachycardia?
Shorter diastolic period - less filling time
Less coronary perfusion
Decrease CO b/c smaller SV
What will happen physiologically w/ sinus tachycardia?
High Sympathetic tone - less depth, pain
Compensatory response (baro/ hypovolemia/ hypotension)
What are causes of sinus tachycardia?
Increased
Separation
High sympathetic tone will have __ in BP and HR, Compensatory response will have ____ in BP and HR?
More analgesics
Increase vaporizer
How do you tx High sympathetic tone sinus tachycardia?
Decrease vaporizer
Volume replacement (5ml/kg fluid bolus)
Colloid
Tx hypotension
How do you tx compensatory response sinus tachycardia? ?
Esmolol -Beta antagonist (give loading dose and CRI)
Diltiazem - ca2+ channel blocker (refrigerated)
If the tachycardia is persistent in Hight SNS tone sinus tachycardia what drugs can we use to tx?
Benign arrhythmia due to decrease in pleural pressure during inspiration - increase in venous return, volume in R atria and stimulating stretch receptor while increasing HR. Will stop w/ cessation
What is a respiratory sinus arrhythmia?
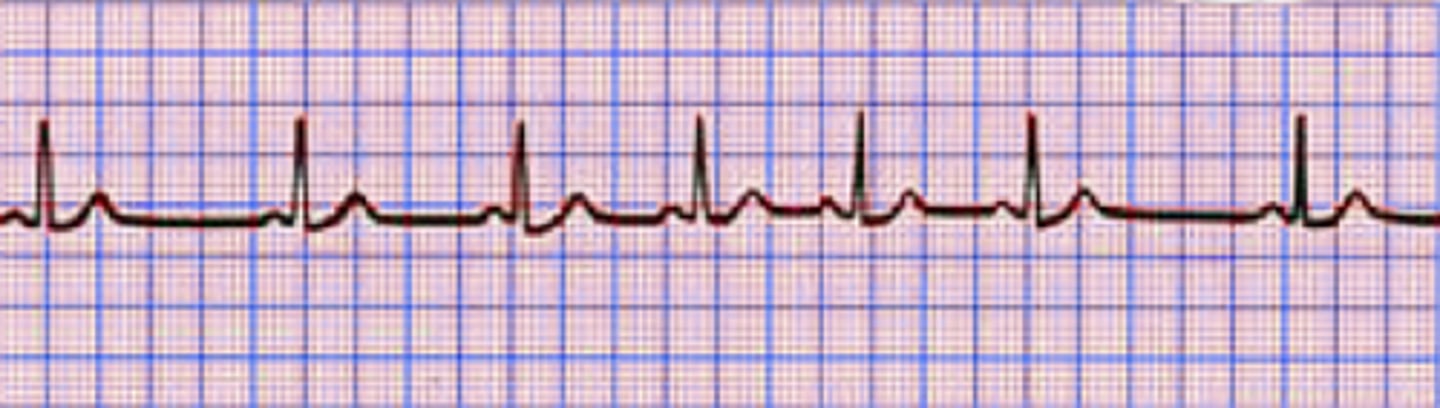
No tx necessary
How do you tx respiratory sinus arrhythmia?
Delay in transmission, PR interval is prolonged but every P wave has a QRS complex
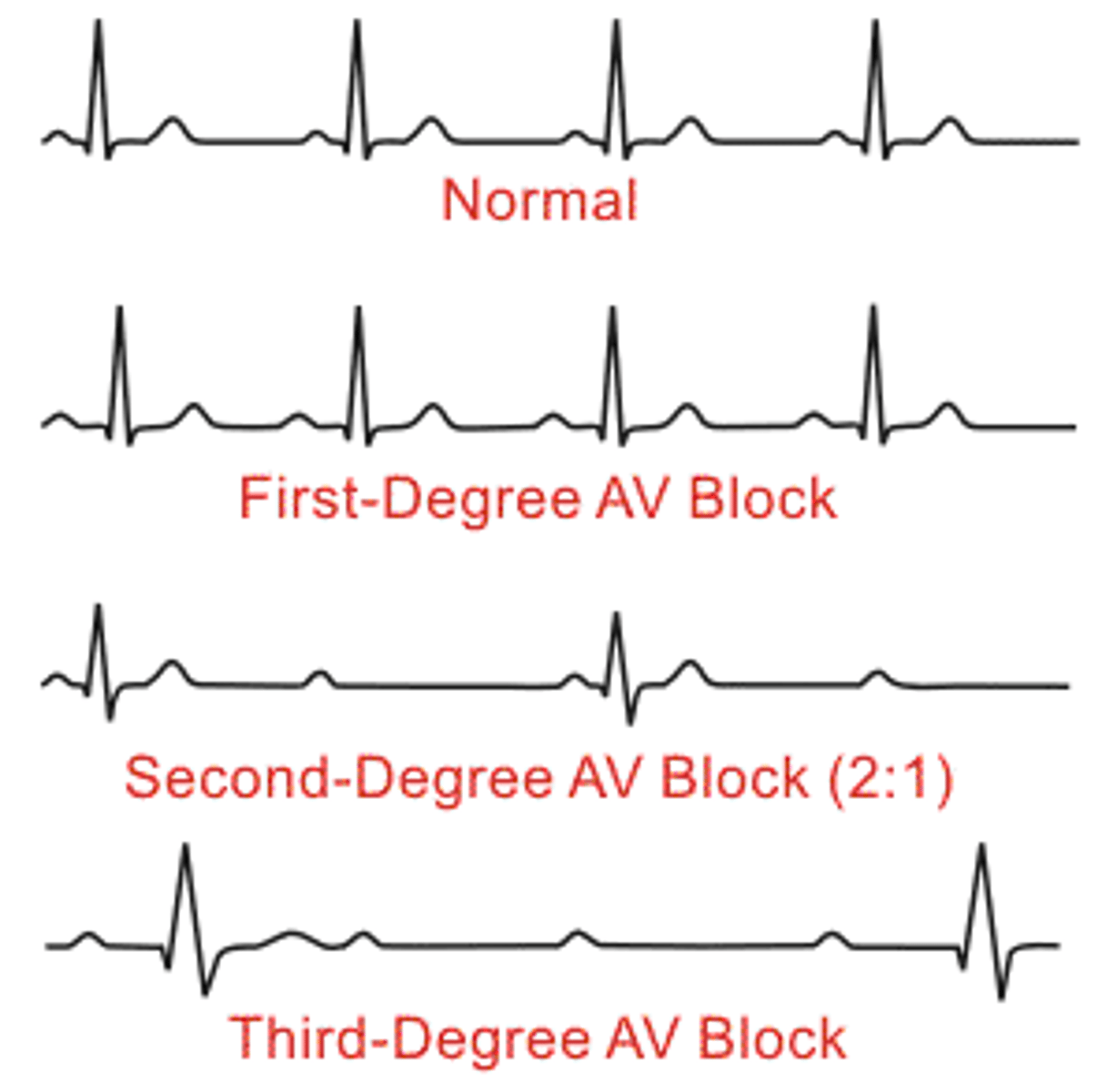
What an AV block 1ST degree?
Vagal tone
Drugs - beta blockers, Ca2+ channel blockers
Electrolyte abnormalities
Heart dz
What causes AV block 1ST degree?
No tx needed - very minor
Should you tx AV block 1ST degree?
Intermediate failure of AV conduction - not all P waves have a QRS complex - occasional drops
What is a AV 2nd degree block?
Vagal - prolonged P-R intervals before beat drops
What is mobitz type 1 AV 2nd degree block?
A pathological condition in which there is no prolongation of P-R interval before dropped beat - sudden drops
What is Morbitz type 2 AV 2nd degree block?
If hypotensive or progressing severely w/ time
When do you tx AV 2nd degree block?
Anticholinergics - type 1
Pacemaker - type 2
Type 1 AV 2nd degree block is treated w/ _____ and type 2 is treated w/ ___?
Complete AV dissociation - no relation between P and QRS complex - PP and RR are constant
What is a 3rd degree AV block?
Pathological
-heart dz
-hyperkalemia
-digoxin tox
What are most common cause of 3rd degree AV block?
Ectopic pacemaker location (junctional better. ventricle can have problems)
What is the severity of a 3rd degree AV block dependent on?
Cats - adequate ectopic pacemaker rates
What animals will have asymptomatic 3rd degree AV block?
Pacemaker
Stop procedure if possible
What is tx of 3rd degree AV block?
Depolarization of ectopic area in ventricle that is more rapid and premature than signal at SA node
-missing P wave,
-shorter RR interval,
-wide bizarre QRS complex
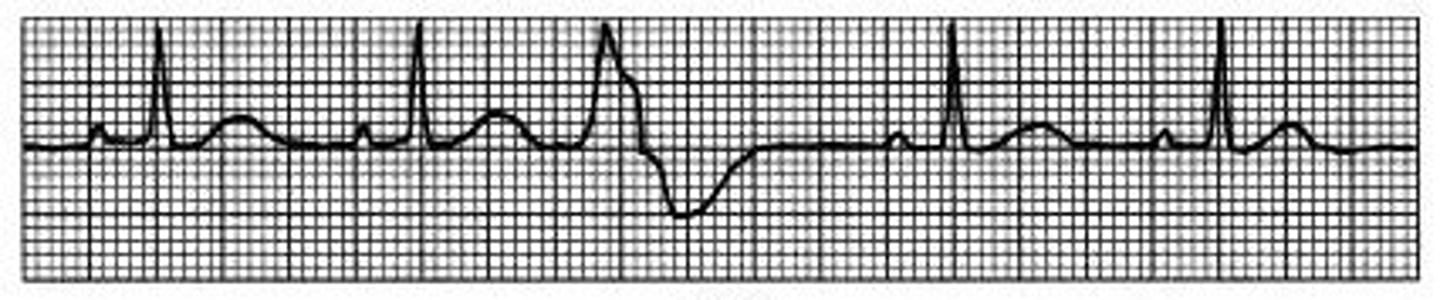
What is a ventricular premature complex (VPC)?
Reentery - (something wrong with the heart)
High SNS tone - GDV, pain, high stress
What are common causes of ventricular premature complex (VPC)?
Pay attention to pulseox wave and if AUC of each triangle is large enough you still have an adequate stroke volume
How can you tell if ventricular premature complex (VPC) is clinical needing tx?
4 or more VPC in succession at more than 160 BPM
When do you have V-tach?
Check for pulse
-no pulse - CPR - Cardiac arrest
-Pulse - correct hypotension
What do you do if the pet is in V-tach?
Lidocaine -Na+ channel blocker B1 antiarrythmics
Procainamide - class A1
What is tx for VPC/ V-tach?
slow V-tach - alternating between 2 sites - no tx nessasary
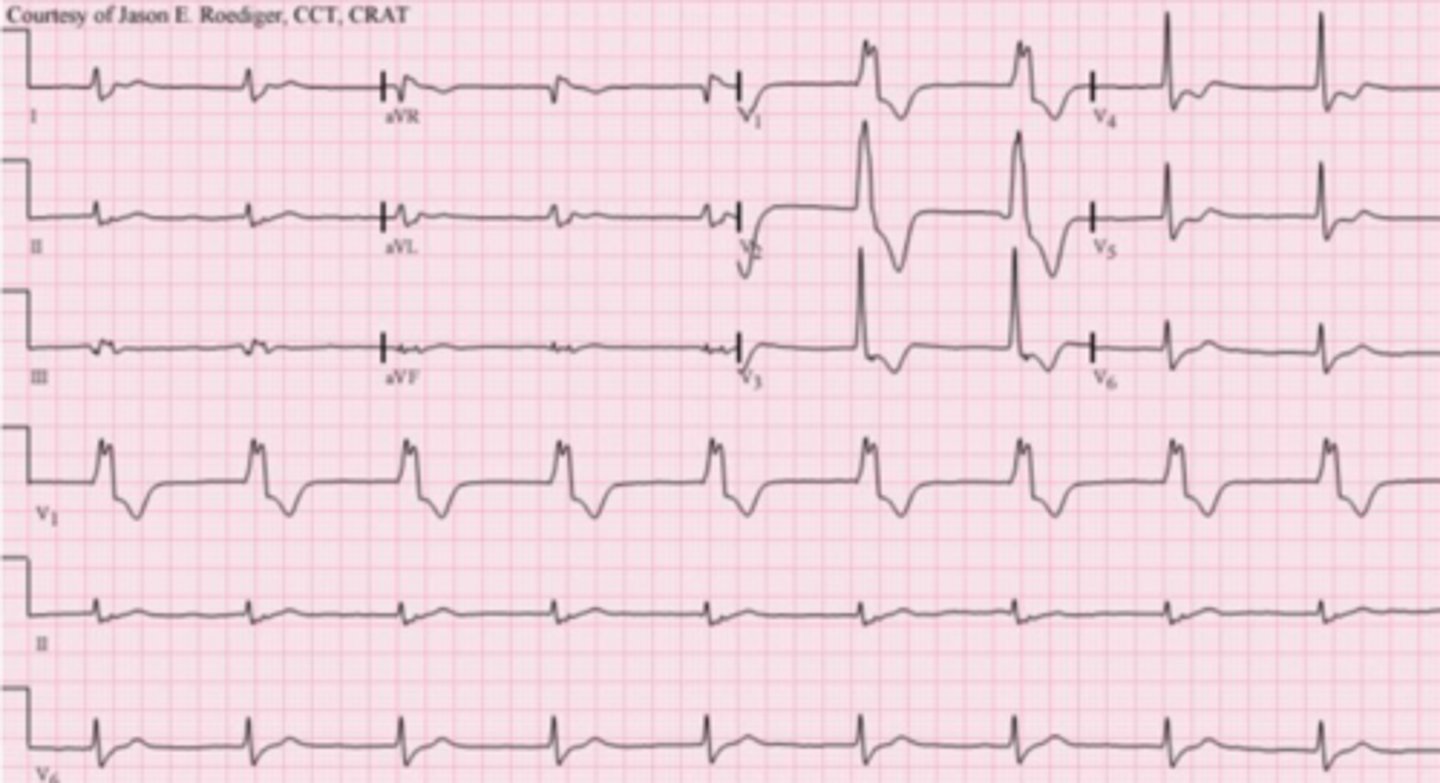
What is an accelerated idioventricular rhythm
GDV,
splenic dz
When are accelerated idioventricular rhythm most common?
Normal spontaneous depolarization of junctional or ventricular pacemakers - safety system in cases of conduction failure
What is an escape beat?
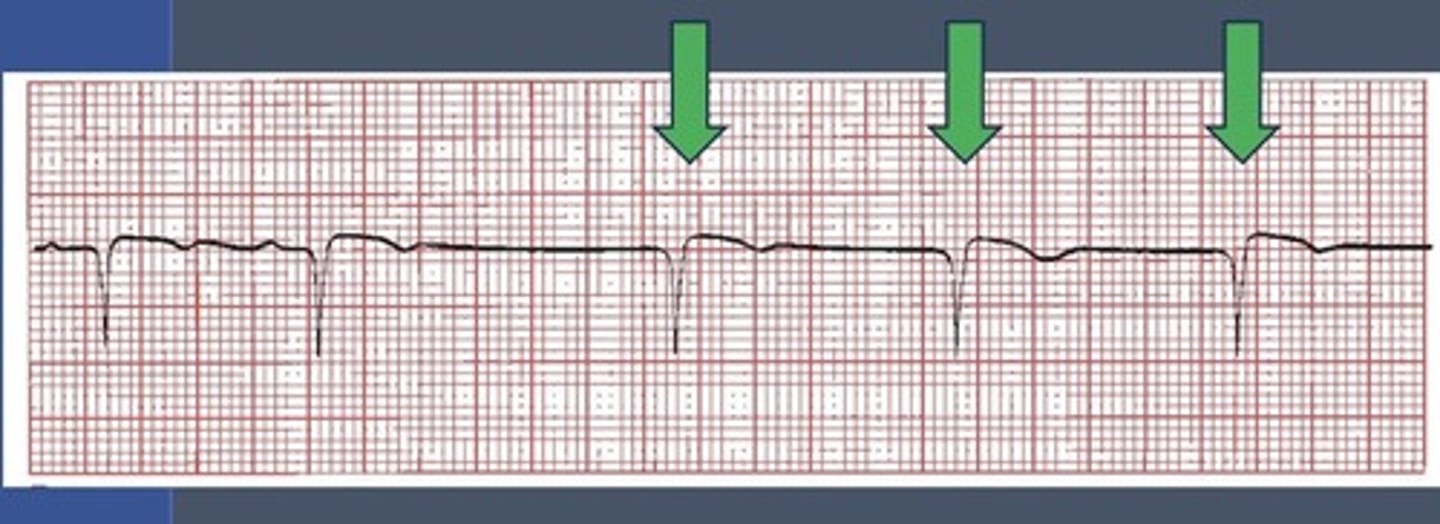
Pause
Not be treated as VPC (can use anticholinergics
Escape beats will alway follow a ___ and should ___ be treated?