Bio 151
1/61
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
\-Unicellular
\-No interior compartments
\-Cell membrane
\-Cell wall
\- Some are photosynthetic
\-No true organelles
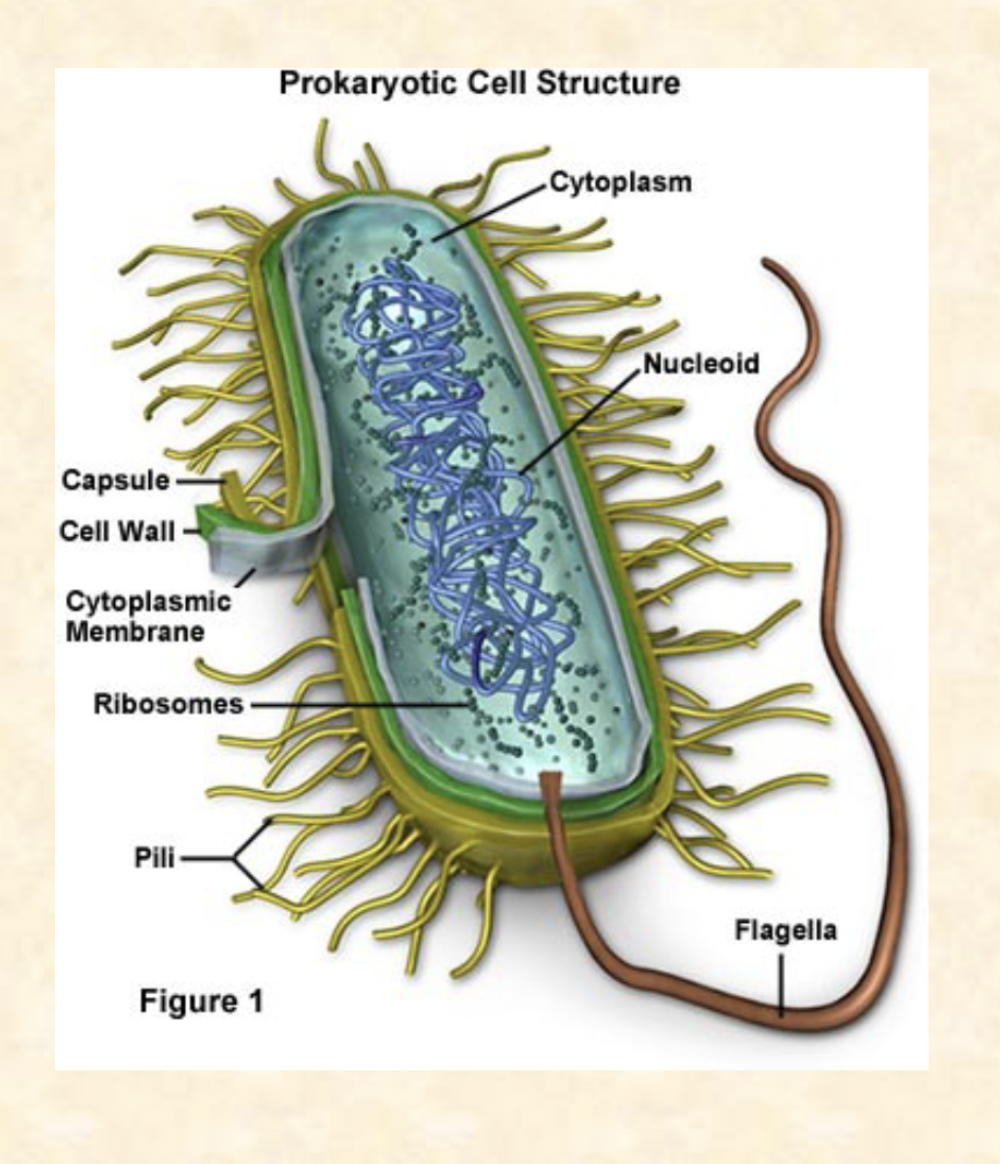
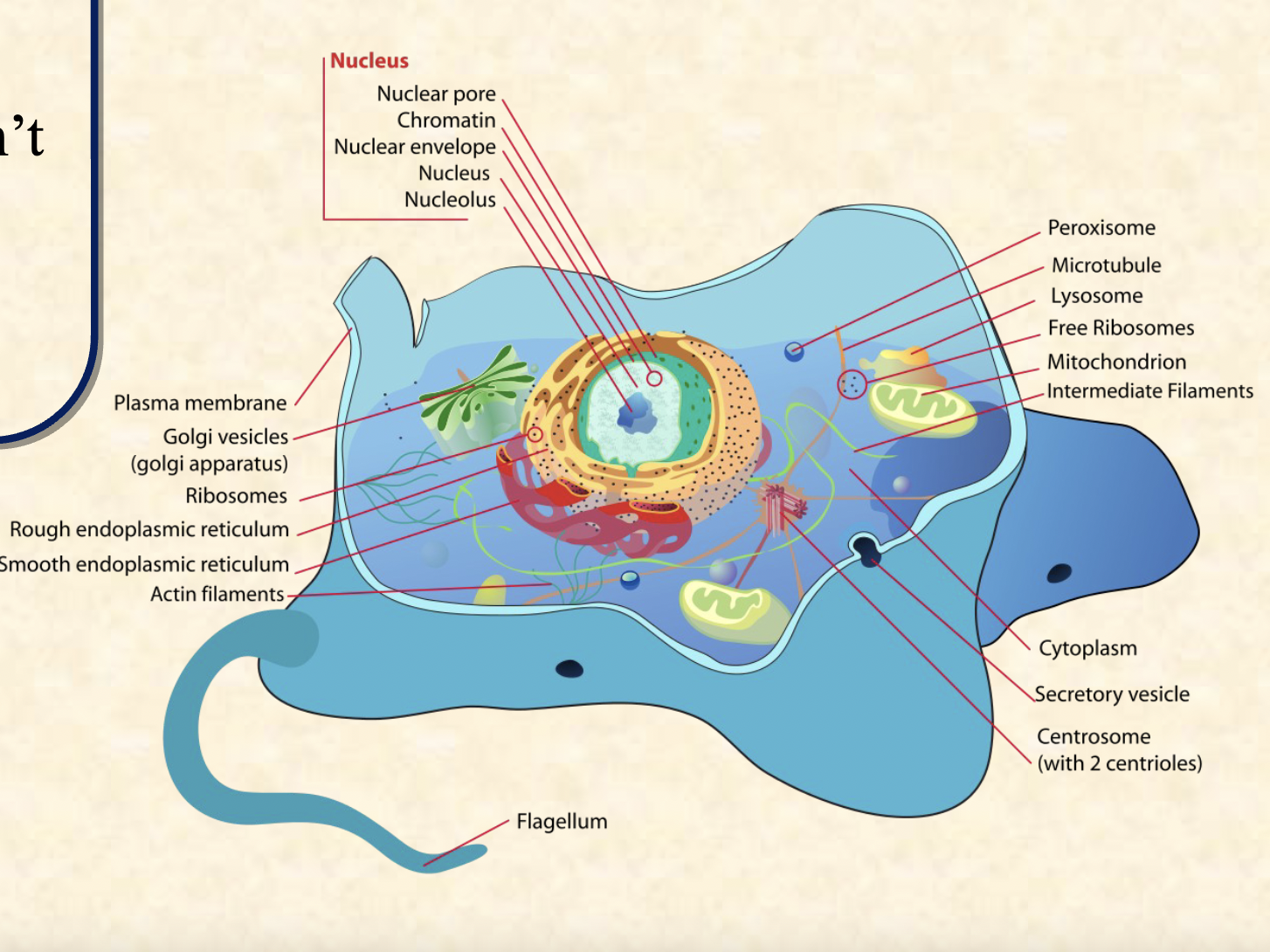
Are all organisms made of cells or have a single cell?
All living things are made up of cells, but they can have different numbers of cells. Organisms can be unicellular, like bacteria and protozoa, with just one cell that does everything. Or they can be multicellular, like plants, animals, and fungi
What are the three subtypes of carbohydrates and their definition
Monosaccharides: Simple sugars like glucose, galactose, fructose. Ratio of carbon :3-6
Disaccharides: Form of two monosaccharides. When two monosaccharides form a dehydration reaction (removal of water molecule)
Polysaccharides: Complex carbohydrates made up of multiple monosaccharides
How are disaccharides broken into monosaccharides?
Through Hydrolysis: A chemical reaction where bonds are broken by adding water. Water is split by hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) which breaks bonds between molecules. Used to break down complex molecules into smaller units like disaccharides into monosaccharides or proteins into amino acids
What are phospholipids and function?
Composed of fatty acid chains attached to glycerol or a similar backbone. Has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. The phosphate group can face outside and the fatty acids stay inside. It is a bilayer that makes up cell membranes.
Are all eukaryotic cells heterotrophic?
No, they can be heterotrophic and autotrophic
What is the function of Quaternary Structure?
Arranges multiple protein subunits such as hemoglobin which carries oxygen.
What is the function of the Lactase in E. Coli?
The lactase binds to the regulatory protein repressor by the alactose. It creates a conformational change preventing it from binding to the operator so RNA polymerase is able to bind to the promoter to initiate transcription
what is a trans fatty acid
a trans fatty acid is straight with no kink so less fluid
what is a cis fatty acid
causes a kink and changes direction which makes it more fluid
What is Lacl code for
The repressor
what’s the difference between heterochromatin vs euchromatin
Heterochromatin is highly condensed, gene-poor, and transcriptionally silent. Euchromatin is less condensed, gene-rich, and more easily transcribed
what are nucelotides
section of DNA that is wrapped around core of protein
What does the lac repressor do when there is no lactose present?
Binds to the operator preventing RNA polymerase from attaching to the promoter
what happens when there is lactose present?
Lactose binds to the lacl repressor which creates an confrontational change to the shape which causes rna polymerase to then bind to promoter and transcription occuring
When is transcription at its highest?
When there is low glucose and high lactose.
Describe the Central Dogma of Biology
DNA-MRNA-PROTIEN
What is transcription?
Where genetic information stored in DNA is used to synthesize RNA
What is translation
going from mRNA to protein
what are protiens made of
amino acids
what are sterols
class of lipids(fats)
what are polypeptides?
consist of a chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds and are building blocks of protiens
what are the building blocks of protien
polypeptides
what does cholesterol do in terms of membrane fluidity
acts as a buffer by preventing fatty acid chains of phospholipids from packing too closely together which helps regulate the membrane at different temperatures
What increases membrane fluidity
shorter chains or unsaturated fats with double bonds increase membrane fluidity. The double bonds introduces kinks to the membrane which prevents from packing closer.
What decreases membrane fluidity
Saturated fatty acids since they have straight chains that can pack tightly, making the membrane less fluid
What is passive diffusion
From high to low, carbon and water molecules and need to be nonpolar molecules
What is facilitated diffusion
From high to low and needs protein to go through a protein gradient, selective since it needs specific protein gradients.
What is active transport
Low to high and need energy to go through transport as it goes against the gradient. Uses atp to go through gradient
What is secondary active transport
Uses pumps and energy from both charged molecules to go move against gradient. Such as using Na+ and K to move against gradient to form energy
Are Transcription factors (activators and repressors) and RNA polymerase (enzyme) proteins?
Yes
Can Epigenetic changes alter the base pairs? Why or why not?
No, they are chemical alternations to the DNA
What is DNA methylation
Addition of methyl groups in the cytosine residue, involved in gene splicing
What is RNA splicing?
removal of introns(non-coding sequence) and join exons(coding sequence) in pre mRNA to create mature mRNA. Splicesomes remove the introns
What is histone methylation
Tightens DNA structure and decreases transcription
what is histone Acetylation
This weakening of the interaction allows the DNA to unwind or loosen from the histones and increases transcription
How are nucleotides held together?
phosphodiester bonds
How are amino acids held together to become a polypeptide chain?
peptide bonds
What are peptide and phosphodiester bonds classified as?
covalent bonds