Money and the Federal Reserve
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Econ103 Final Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Monetary Policy
the actions the Federal Reserve takes to influence the level of real GDP and the rate of inflation in the economy
M1
narrowest definition of the money supply, includes only the most liquid assests
The Three Functions of Money
medium of exchange
unit of account
3.store of value
Jerome Powell
Current chairman of the Federal Reserve System..
M2
broader definition of M1, a measure of the money supply that includes certificates of deposits and other less-liquid assets
Liquidity
the ease with which an asset can be converted into the economy's medium of exchange
Bond
a debt or obligation to pay issued by a government or corporation in order to raise a large amount of capital; can be traded in the stock market
Commodities
raw materials (like soybeans, cotton, oil and coal) traded on a mercantile exchange
Medium of exchange
Anything that is traded broadly for goods and services in an economy
Unit of Account/Standard of Value
Measure in which prices are quoted (or the unit by which the prices of all other items are quoted)
Stuff has a price
Store of Value
A means for holding wealth
Money holds its value
Fiat Money
No value except as the medium of exchange
No intrinsic value; just green paper
Value comes from government decree, or fiat
Commodity Money
Actual physical commodity (e.g., gold, silver, or tobacco)
It has value in and of itself, so it has intrinsic value
Commodity-backed money
Can be exchanged for a commodity at a fixed rate
Ex: Silver certificate (serial and crest are blue on dollar bill)
Characteristics of Money
durability, portability, divisibility, uniformity, limited supply, acceptability
Durability
ability of an item to last a long time
Portability
Can be carried around easily
Could apples be a unit of account?
No. It is not standard or uniform like money — also many different types of apples
Uniformity
Money is the same across the country
Limited Amount
Money is limited to prevent inflation
Acceptability
Money is accepted
FOMC
Part of the FED
Made up of 7 board members and 5 district banks
NY is always a part of it
Set interest rates
Number of Districts in Federal Reserve
12
Our district number in Federal Reserve
11
Location of our Federal Reserve Bank
Dallas
FDIC
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation: A federal guarantee that insured savings deposits
Federal Reserve Act of 1913
This act created a central banking system, consisting of twelve regional banks governed by the Federal Reserve Board. It was an attempt to provide the United States with a sound yet flexible currency. The Board it created still plays a vital role in the American economy today.
Are apples a good store of value?
No. They will eventually rot and are not consistent long-term
Money
Anything that is a widely accepted form of payment for goods and services / repayment of debt
Money and currency
All currency is money, but not all money is currency
Examples of currency are cigarettes or mackerel, tobacco, etc
Barter
Trade goods and services (both people have to want to trade and want what is being traded)
Money supply
The U.S. Money Supply comprises currency and various kinds of deposits held by the public at banks and other depository institutions (e.g. thrifts and credit unions)
Money supply is important because
Growth in the money supply is the cause of inflation
Value of the money supply
~$21.6B
The money supply includes…
Both currency and bank deposits
Credit cards
Not money and not part of the money supply
Involve a loan make at the cash register
Bank deposits from elsewhere pay for the purchase
Debit cards
Not money themselves, just a means of accessing your money
The physical card is NOT part of the money supply, but the balances (checking and/or savings account) they are tied to are
Fractional Reserve Banking
How we make money in the US
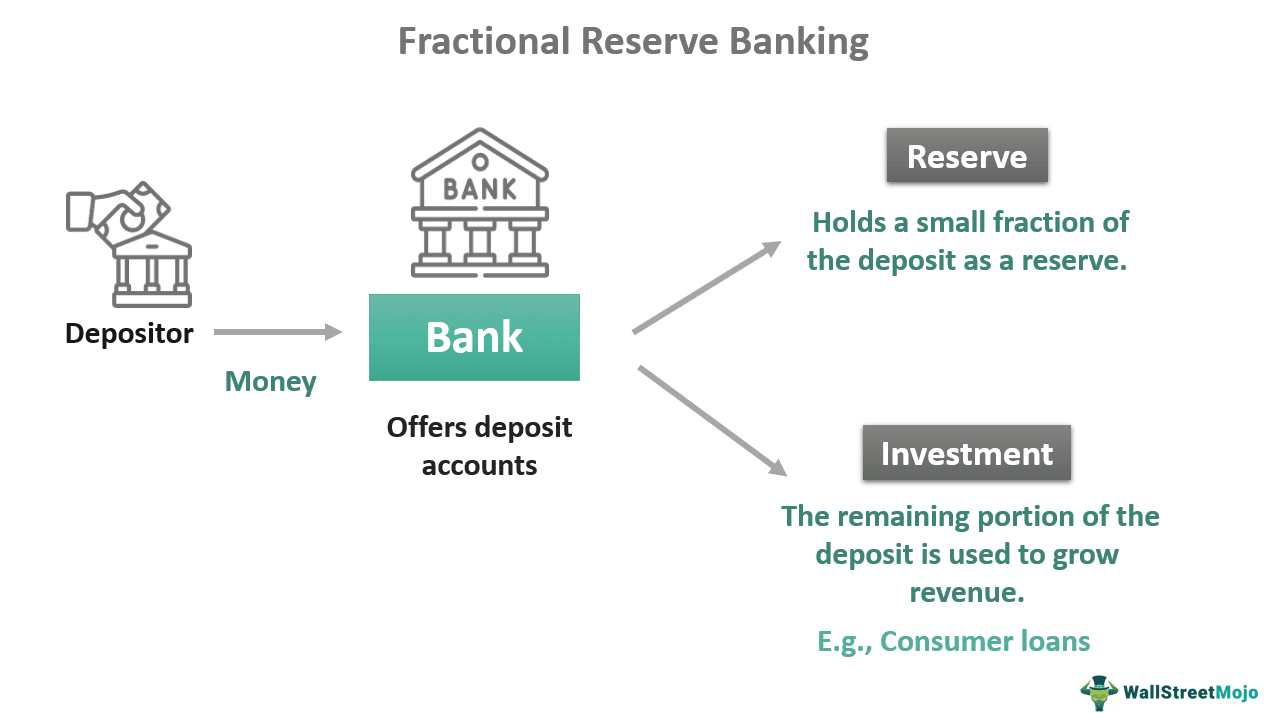
Banks two important roles in the economy
They are critical participants in the loanable funds market (willing to provide loans)
They play a role determining the money supply
Their function is to serve as a financial intermediary
Deposits
Primary source of funds
Loans
Primary use of funds
Interest Rates on Bank Deposits and Loans
Banks charge more interest for loans than they pay for deposits. The difference pays the banks’ expenses and produces profits