Benign Ovarian Cysts
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Ovarian torsion
Mass + Symptoms of unilateral, intermittent, and then acutely worsening pelvic pain may indicate an
Infectious Etiology (tubo-ovarian abscess)
Mass + A indolent, progressive pelvic pain associated with fevers, chills, vomiting, and vaginal discharge may indicated
Endometrioma
Mass + Acute and chronic dysmenorrhea or pain with intercourse may have an
malignancy
Mass + Persistent bloating, generalized abdominal pain, and early satiety may be signs of
estrogen produced by sex cord-stromal tumors
Mass + Abnormal uterine bleeding or postmenopausal bleeding may be caused by
Vitals (stable/unstable), Lymph nodes, pulmonary, abdominal, and pelvic (visual inspection, bimanual palpation, with rectovaginal examination as indicated)
The physical exam for an adnexal mass should include:
TVUS (most common - assess the size, composition, laterality, presence of septations, mural nodules or free fluid); abdominal is a good back up plan
Imaging for an adnexal mass should include:
CT, MRI, PET
What imaging are we NOT doing for an adnexal mass?
readily available, less expensive 🤑, findings may be discussed immediately
Why is TVUS the go-to?
CA-125 (tumor marker - glycoprotein antigen, elevated in 50% of early disease)
What can be used to help distinguish between benign and malignant masses - especially in post-menopausal patients?
pregnancy, fibroids, ovarian cancer (used to monitor treatment response and 1000s), endometriosis (100s), liver disease, PID
CA-125 can be elevated in conditions such as
follicle has a diameter of at least 3 (presumptive diagnosis is made when a 5-8 cm mass is noted on bimanual)
How do you classify a functional cyst?
pelvic pain, dull sensation, heaviness in the pelvis
Symptoms of a functional cyst
mobile, unilateral, and not associated with ascites
In general a functional cyst is…
Low dose OCPs (suppress gonadotropin levels)
What can be given to prevent the development of an another cyst?
persist for longer than 6 weeks, symptomatic, large cyst 10 or more, you cannot r/o ovarian torsion
When should a cyst be referred to OB/GYN?
Ovarian Torsion
The complete or partial rotation of the ovary on its ligamentous support, that results in the impedance of the blood supply - gyn emergency
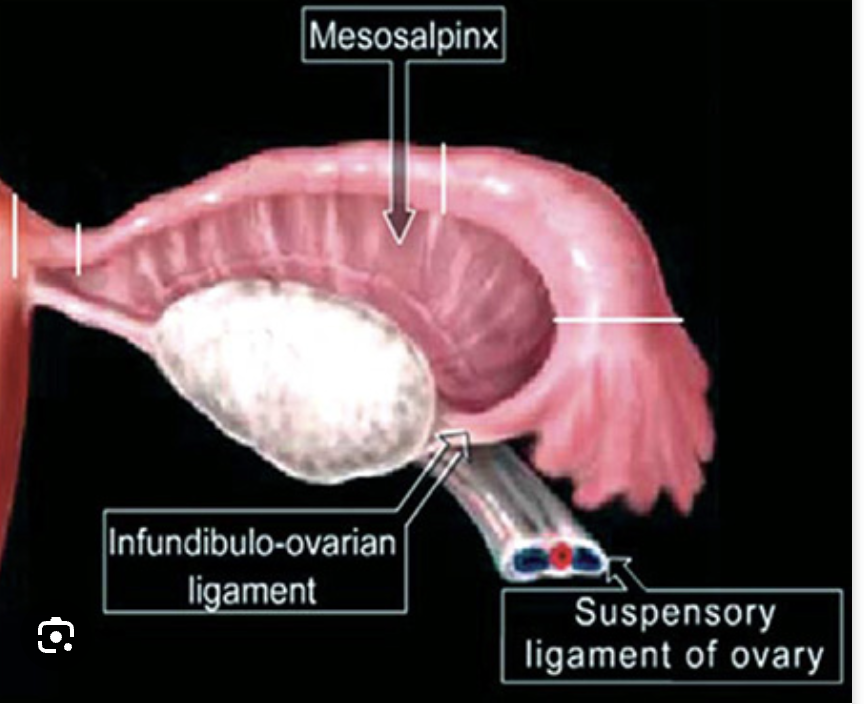
ovary rotates around the infundibulopelvic ligament and the utero-ovarian ligament
Mechanism of Torsion
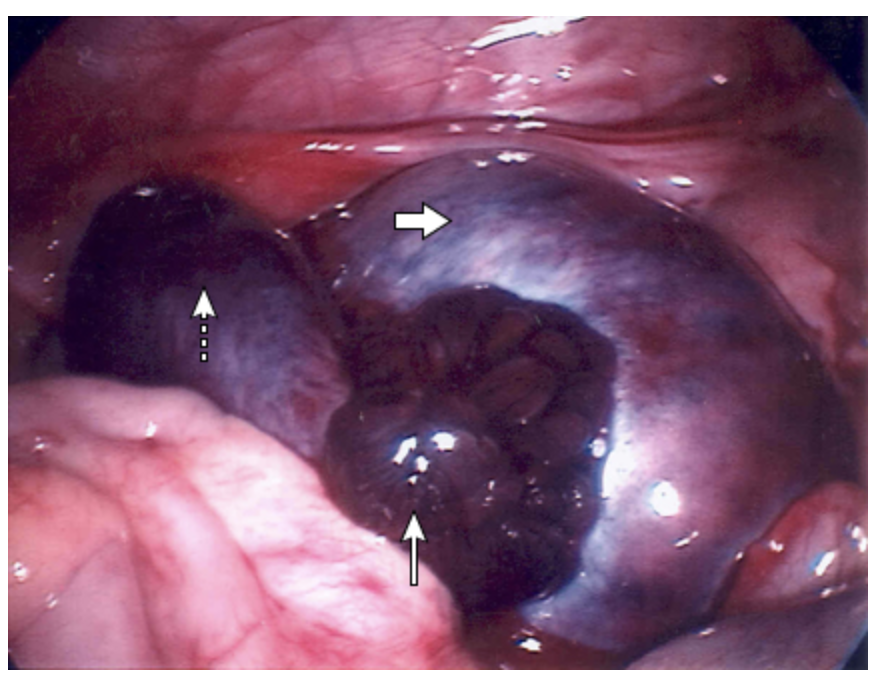
ovarian functional cyst (more likely when 5+ cm)
What is the most likely factor to predispose someone to torsion?
loss of ovarian function, necrosis, hemorrhage, peritonitis
Complications of ovarian torsion
TVUS (shows lack of blood flow, but absence does not exclude), CT scan (1st choice in the ED), MRI
24 y/o female with a PMHx of ovarian cysts presents to the ED for the acute onset of 10/10 lower abdominal pain that comes in waves. She also notes N/V. On physical exam you note tenderness to palpation during the abdominal exam with guarding. As well as unilateral adnexal tenderness on bimanual examination, and presence of a latero-uterine mass. What do you want to order?
Surgery
Treatment plan for ovarian torsion
Dermoid Cyst (benign cystic teratoma)
What is the most common, slow growing ovarian neoplasm and is a type of germ cell tumor composed of sweat and sebaceous glands, hair follicles, and teeth.
Cystectomy or Oophorectomy if symptomatic (check the contralateral side 10-15% are bilateral)
Treatment for Dermoid Cyst
5 cm or less, asymptomatic
When is it okay to observe a dermoid cyst?
hydrosalpinx and pyosalpinx
The most common benign tumors of the fallopian tubes that are infectious or inflammatory
operative exporation
How do you confirm a hydrosalpinx and pyosalpinx?
Salpingectomy
Treatment plan for hydrosalpinx and pyosalpinx
Theca-Lutein Cyst
What type of cyst may develop in with an associated with high levels of hCG in patient with a hydatidiform mole or choriocarcinoma - may be due to gonadotropins or clomiphene (OHSS)
IV fluids, correct electrolytes, Stop medications
Treatment for Theca-Lutein Cyst due to Ovarian Hyperstimulation syndrome (confirmed on TVUS)
Usually bilateral, large (30 cm+), regress slowly after the gonadotropin level falls
What are the characteristics of Theca-Lutein Cyst?
evacuate the uterine content (dilation and curettage), afterwards HCG should regress
If a patient has a molar pregnancy, what is the treatment
NAH FAM
Is the pregnancy test is negative is it a Theca-Lutein Cyst?
Rupture Ovarian Cyst (look for fluid on U/S)
A common occurrence in women of reproductive age that is associated with mild mid-cycle pain (mittelschmerz) pain tends to start AFTER sexual intercourse
Vaginal intercourse, likelihood for ovulation
Risk factors for rupture ovarian cyst
observation, analgesics, rest, Surgery (maybe - but not for prevention)
Management plan for rupture ovarian cyst
Existing ovarian cysts, suspicion of malignancy, hypotension, tachycardia, NOT prevention of cyst rupture
What are the indications for surgery on an adnexal mass?
Urine hCG, CBC with diff, type and cross (peritoneal signs, unstable), STI panel (fever), Pelvic U/S 🥇 (fluid in the pelvis and an adnexal mass)
23 y/o female with a hx of ovarian cyst presents to the ER with sharp RUL pain that occurred suddenly after vaginal intercourse. On physical exam you note RUL tenderness on light palpation. What do you want to order?