Lewis Diagrams, Resonance, Hybridization, and Formal Charge
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
How do you find formal charge?
Core charge - lone pairs - bonding pairs/2
What number is the core charge the same as (on the periodic table, but they’re technically very different concepts)?
Valence electrons (Group number, but if you get into the 10s, then -10)
What is bond order?
single, double, triple bonds
How do you find resonance?
Number of electrons bonding divided by areas of bonding
What does a resonance of 1.5 mean?
It means that the central atom in a molecule with resonance has a bond order of 1.5
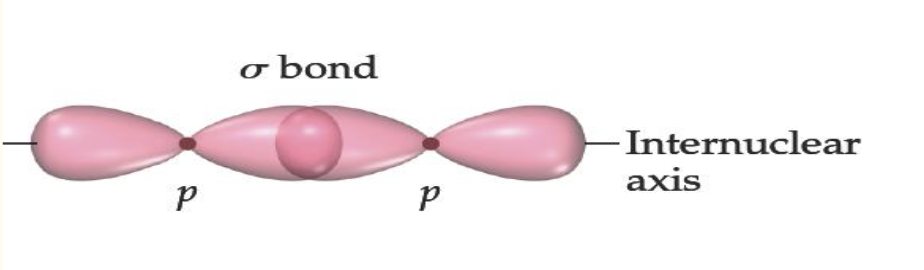
Sigma bonds are characterized by:
head-to-head overlap
cylindrical symmetry of electron density along the nuclear axis
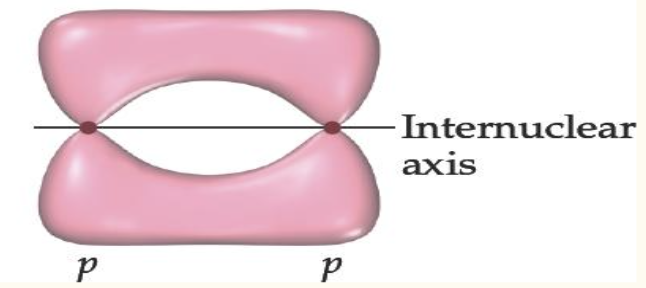
Pi bonds are characterized by
sideways overlap
electron density above and below the internuclear axis
Single bonds are always ___ bonds
sigma
Multiple bonds are have one ___ bond; all others are ___ bonds
sigma; pi
Localized electrons are…
bonding electrons (sigma or pi) specifically shared between two atoms
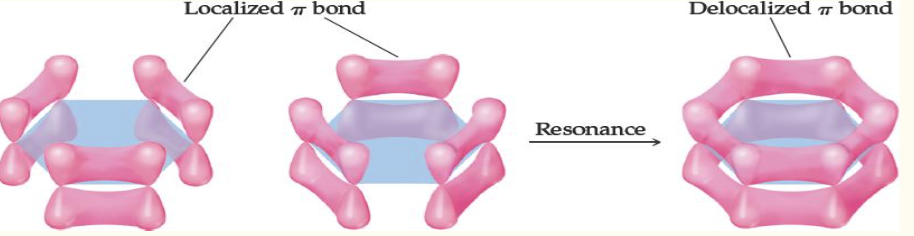
In molecules where electrons are shared by multiple atoms, like in Lewis resonance structures, the electrons are (localized/delocalized)
delocalized
What is the difference between atomic orbitals and hybrid orbitals?
Atomic orbitals describe the probability of finding an electron near the nucleus of a single atom, while hybrid orbitals are combinations of atomic orbitals that explain the geometry and bonding properties of molecules
What is hybridization?
the process of combining two atomic orbitals to create a new type of hybridised orbitals
What is the hybridization if a molecule has 2 electron domains? (like a linear molecular geometry)
sp
What is the hybridization if a molecule has 3 electron domains? (like a trigonal planar)
sp2
What is the hybridization if a molecule has 4 electron domains? (like tetrahedral)
sp3
What is the hybridization for 5 electron domains? (like trigonal bipyramidal)
sp3d
What is the hybridization for 6 electron domains? (like octahedral)
sp3d2
What do you do when a molecule is hypervalent?
Because of the expanded octet (hypervalent), the valence-bond model would use d orbitals to make more than four bonds.
This view works for period 3 and below.
In valence-bond theory, electrons of two atoms occupy ___ ____ _____
the same space (orbital overlap)
The sharing of space between two electrons of ____ ___ results in a covalent bond.
opposite spin
In valence-bond theory, increased overlap brings the atoms together until a ____ is reached between the like-charge repulsions and the electron-nucleus attraction.
Atoms can’t get too close because the internuclear ______ get too great.
balance; repulsions
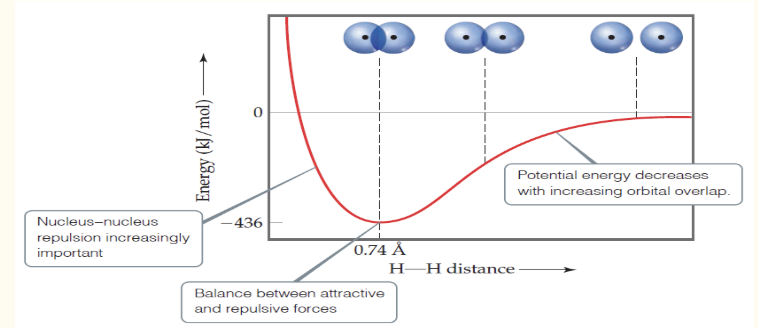
In this graph, the minimum energy is the bond ____
strength
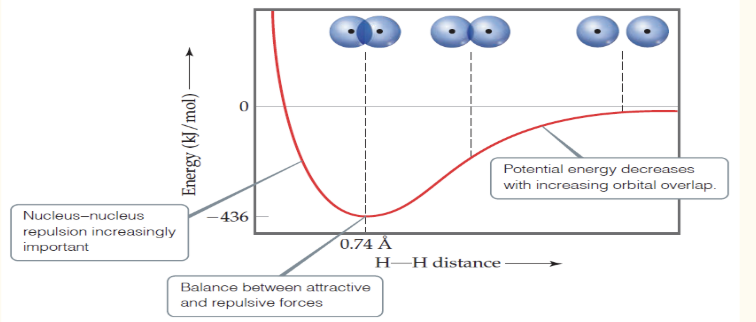
In this graph, the minimum distance is the bond _____
length