ARCC HOA REVIEWER PART 2
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Scope: Ma'am E's Lecture video day 2 - Asian and Philippine Traditional Architecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Mehrgarh
Also known as harappa, it is a planned layout that uses brick, mud-brick and wood, and characterized by grid patterned streets
Hinduism
A religious sect that combines Vedism and Brahmaism
Ashoka
Initiated the first rock-cut technique during the Mauryan period
It is easier to excavate a rocky mountain than pile up stone
This is the reason why caves, rock-cut sanctuaries, and cave temples are primarily used during the Mauryan period
Stupa
A rock-cut chamber was planned to facilitate the religious services around this principal symbol of worship in the Mauryan period
Chaitya hall
The Mauryan place of worship/temples/assembly hall with an ornamental facade, central vaulted hall, and a rock-cut stupa at the rear
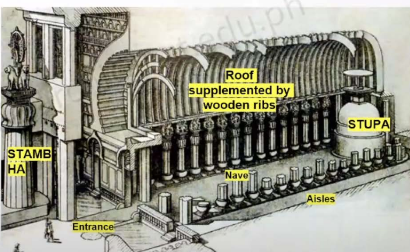
Vihara
Refers to a monastery for Buddhist renunciates in the Mauryan period
Barabar hill caves
The oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India that were hewn from granite
Ajanta caves
A UNESCO World Heritage Site in Maharashtra, India that contains 29 rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments
Ellora caves
A multi-religious rock-cut cave complex in the Charanandri Hills, India
Buddhist architecture
This is characterized by monumental, monolithic, and rock-cut design for congregational use, with examples being stupas, stambhas, chaityas, and viharas
Wheel of Law
Symbolizes the 3rd great even in Buddha’s life, who turned the wheel of dharma by preaching his first sermon
Lotus
The Indian symbol for spiritual growth, divinity, purity, and enlightenment.M
Mandala
A diagram or geometric pattern that represents the cosmos
Sanchi Stupa
The Great Stupa commissioned by Mauryan emperor Ashoka, located in the birthplace of his wife
Torana
The stupa’s ceremonial gateways positioned in each cardinal direction
Lion
A Buddhist symbol associated with regality, strength, and power, and the sons of Buddha who are spiritually developed
Stambhas
Also known as Lats, it is a monumental, free-standing pillar that symbolizes the world axis in Indian architecture; can be of Persepolitan or Graeco-Roman type.
Ashoka pillar
A pillar consisting of a shaft and crown of four lions that stand back-to-back in Mauryan architecture
Garbhagriha
The “house of God” and the basic form of a Hindu temple along with a mandapa
Nagara
A Hinduist style that consists of a fluted stone disk (amalaka), a tower (shikhara), surrounded by an ambulatory (garbha griha), an open/closed vestibule (antarala), and an assembly hall (mandapa)
Dravidian
A Hinduist style that consists of a pyramidal tower, square-chambered sanctuary, exterior pilasters, wall of tower in graduating levels, capped with a dome-shape cupola, pot, and finial
Gopurams
These are tall gateways that lead to a Dravidian-style temple
Vimana tower
Nagara style : Sikhara tower
Dravidian Style : ___________
Pagoda
It contains holy relics or collections related to Buddhism, comes from the Sanskrit word “bhagavat”
Vesara
A Hinduist style that is also known as Karnataka Dravida, a combination of Nagara and Dravidian styles
Jainism
A religion found by Mahavira or the Jina, that advocated non-violence
Jainism architecture
This is characterized by a profusely ornamented and military character in the architecture
Four-faced open form
The basic form of a Jain temple
Mughal architecture
A style developed by the Mughals in the 16th-18th centuries, which is an amalgam of Islamic, Persian, Turkic, and South Asian architecture
Jalis
Pierced screens used in Indian architecture as windows, room dividers, and railings around thrones, platforms, terraces, and balconies; ideal for cutting down glare while permitting air to circulate
Chorten
Term referring to the Tibetan stupa
Gong
Chinese palace and later referred to imperial and religious buildings
Liangting
Chinese kiosk where travelers rest
Ting
Chinese gazebo with columns supporting a roof
Curved roof
This architectural feature is used in Buddhist belief to ward off evil spirits
Tai
Chinese terrace or belvedere with a flat top
Lou
A Chinese building of one or more storeys used as a tower
Ge
Storeyed pavilion similar to a lou but with windows, doors, and walls
Dougong
Bracket system used in Chinese architecture
Feng Shui
Chinese geomancy used to harmonize individuals with the environment
Chinese architecture
A style of architecture characterized by the unity of architectural components, seismic responsiveness, standardization of parts, bright colors, and systematic grouping of buildings
Hanok
Traditional Korean house dating to the Joseon period
Hanji
Traditional paper made from the mulberry tree used for partitions, walls, and ceilings in Korean architecture
Ondol
Also known as gudeul, this is a system of heating utilized in Korean architecture
Daechong
A wooden-floored, openable hall that lays on posts to allow airflow in Korean architecture
Minka
Traditional Japanese house characterized by wooden frame and modular plan
Tatami
A Japanese mat used as a modular system in space arrangement
Fusuma
A Japanese partition using cloth or heavier opaque paperW
Washi
A Japanese paper used for making room partitions
Tokonoma
A raised alcove for hanging a picture, scroll, or ikebana in Japanese houses
Shoji
A lighter partition in Japanese architecture using translucent sheer paper affixed to a wooden lattice frame
Ikebana
Japanese term for a flower arrangement
Nature
Traditional Japanese buildings reflect a strong emphasis on humans’ relationship with _________.
Himeji Castle
The first declared World Heritage Site, located in Japan and also known as the White Heron castle
Horyuji Temple
The oldest wooden building in the world, built in 607.
Todaiji Temple
A Japanese temple that houses the largest bronze image of Buddha Vaicosana (Daibutsu)
Zen garden
A Japanese garden featured with raked gravel and rock islands
Torii
Refers to a Japanese gate to a Shinto shrine
Angkor Wat
A 12th century Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu and built by Suryavarman II; based on a mandala layout
Angkor Thom
Last and most enduring capital city of the Khmer empire, established in the 12th century by King Jayavarman VII
Sukothai
Foundation of Thai civilization where its institutions and culture first developed
Ayutthaya
A society of builders, preoccupied with building monuments to impress outsiders through their sheer immensity
Lamyong
A feature in Thai architecture that represents the beak of the mythical bird garuda
Bagan
Ancient Burmese city dating to the 9th to the 13th centuries with Buddhist structures in the landscape
Hue
An ancient imperial city located in Vietnam
Hoi An
A Vietnamese World Heritage Site
Batak
Also known as Toba, it is a boat-shaped house with carved gables and a dramatic oversized roof
Gadang House
A structure in West Sumatra famous for its saddle back roofs
Toraja
Houses in the Sulawesi highlands that are built on piles and dwarfed by massive pitch-saddle roofs
Long House
A Dayak traditional house made of ironwood and tree bark, decorated with water snakes and rhinoceros birds
Borobudur temple
9th century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Central Java, designed with a mandala plan
Rumah
Traditional term for a house in Malaysia
Rumah Kutai
Preferred by influential people, it is a house distinguished by carvings on the door, porch, awnings, windows, and walls.
George Town and Malacca
These two are Malaysia’s two World Heritage Sites
Marina Bay Sands
World’s largest cantilevered platform structure located in Singapore, designed by Moshe Safdie Architects
Colonization
This caused the incursion of western styles and technology in indigenous Asian settings resulting in a fusion of styles and a unique colonial character to Asian architecture
Callao Man
Also known as Homo Luzonesis, discovered in Penablanca, Cagayan (2007) in a fossilized state; less than 4 feet tall
Tabon Man
A homo sapiens fossil found in a cave at the coast of Palawan in 1962
Angono Petroglyphs
Oldest known work of art in the Philippines, declared a National Cultural Treasure in 1973
Datag
Sleeping platform made of tree branches
Windbreak
Lean-to’s that were set up by the Aetas during hunting and food-gathering periods
Hawong
Pinatubo Aetas’ lean-to that has two sloping sides
Dait-dait
Lean-to of the Mamabua, made up of banana fronds or leaves
Idjang
A precolonial citadel in Batanes
Out of Taiwan/Austronesian Migration Theory
A theory by Peter Bellwood that highlights Austronesians are originated from Taiwan and moved south to migrate to other lands
Nusantao Theory
A theory by Wilhelm Solheim that highlights Southeast Asia being peopled by groups who shared the same cultural traits
Austronesian house
A basic unit of a village that is commonly adaptive to the environment through stilts, dominant roofs with ridge poles and gables, and informally built.
Balai/bahay
Filipino traditional architecture emanates from the _________.
Cave dwellings
The earliest human shelter in the Philippines
Datag
Basic sleeping bunk or platform made of tree branches, twigs, and dried leaves built inside the cave by the Tau’t Bato
Tinguian
A Cordilleran arboreal shelter/tree dwelling
Fayo
A Bontoc house
Abong
Poor man’s dwelling among the Ifugao with non-uniform dimensions and built of poorer materials
Bale
Wealthy man’s dwelling among the Ifugao with carved posts in the interiors and flutings on the exterior underneath the roof eaves
Isneg
Boatmen native to Apayao, with their house suggesting an inverted hull
Binayon (finaryon)
The Kalinga octagonal house found in Upper Kalinga along the Chico River
Sagada house
The house that is completely enclosed and yet has living quarters on a ground level
Ifugao house
A three-level structure located amid rice terraces, usually found in clusters in Banaue, or scattered in Mayoyao
Mayoyao house
Igorot house characterized by purity of line, classic simplicity, and stone pavement and wall